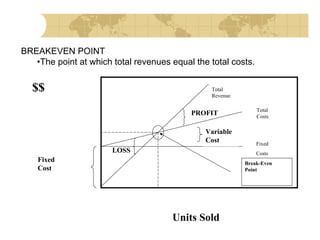
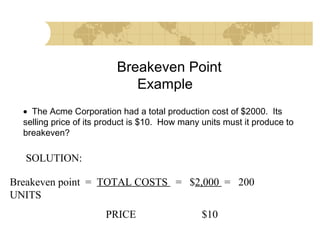
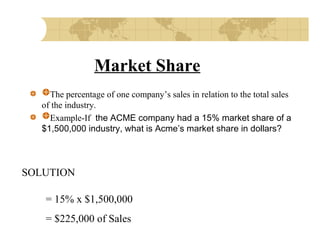
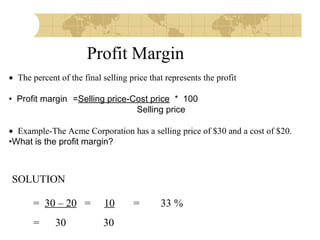
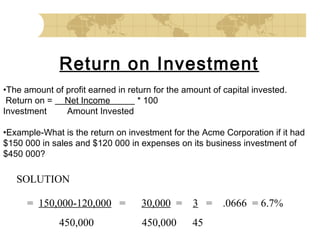
This document discusses financial strategy and objectives for a new business venture. It explains that a financial strategy should answer questions about startup costs, ongoing operating costs, capital needs, and sources of funding. The key components of a financial strategy are identified as sales forecasts, expenses, profits, balance sheets, cash flow projections, and repayment plans. The document also outlines the financial planning process and defines important financial terms like breakeven point, market share, profit margin, return on investment, and the difference between startup costs and operating expenses.