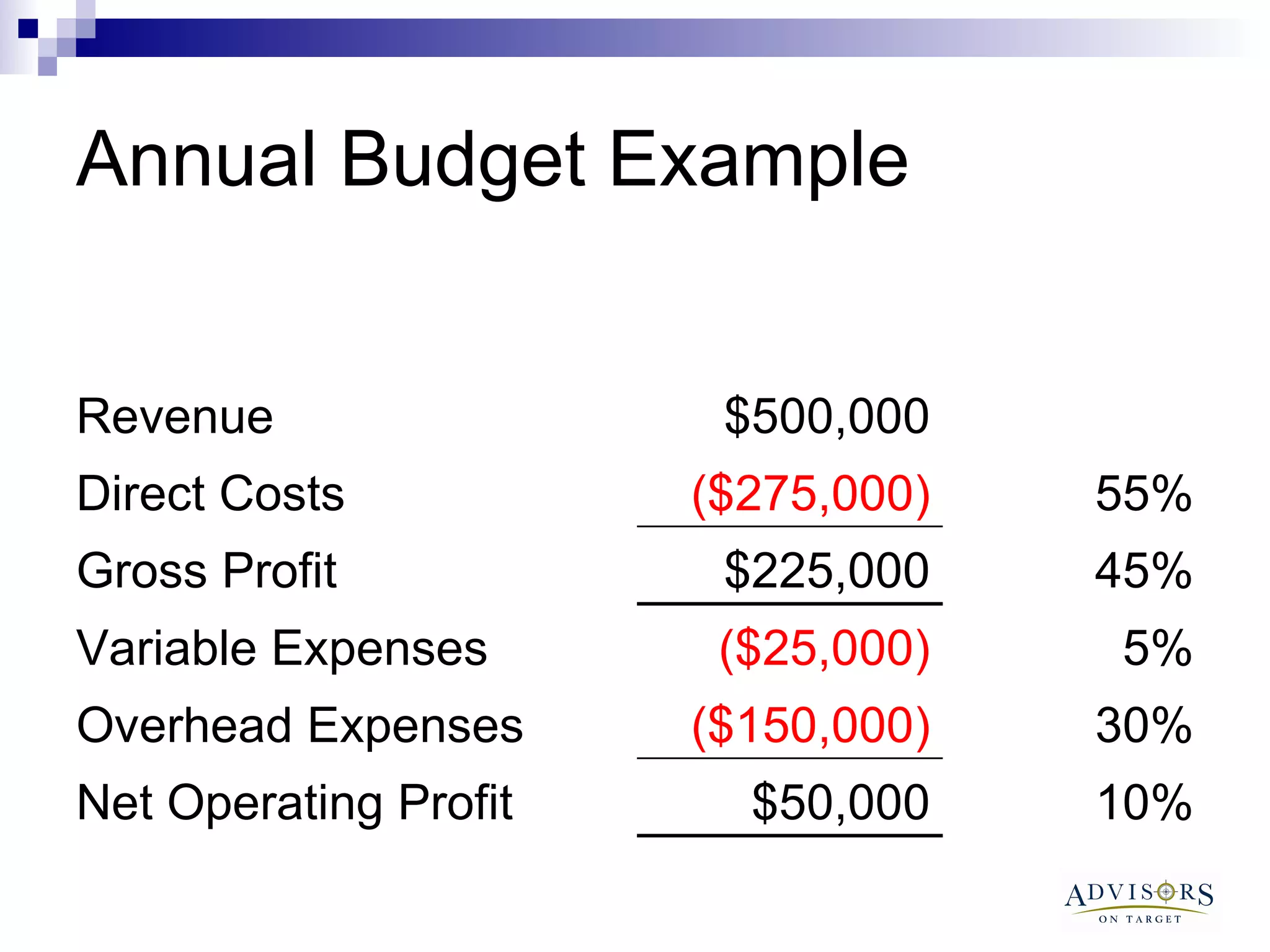
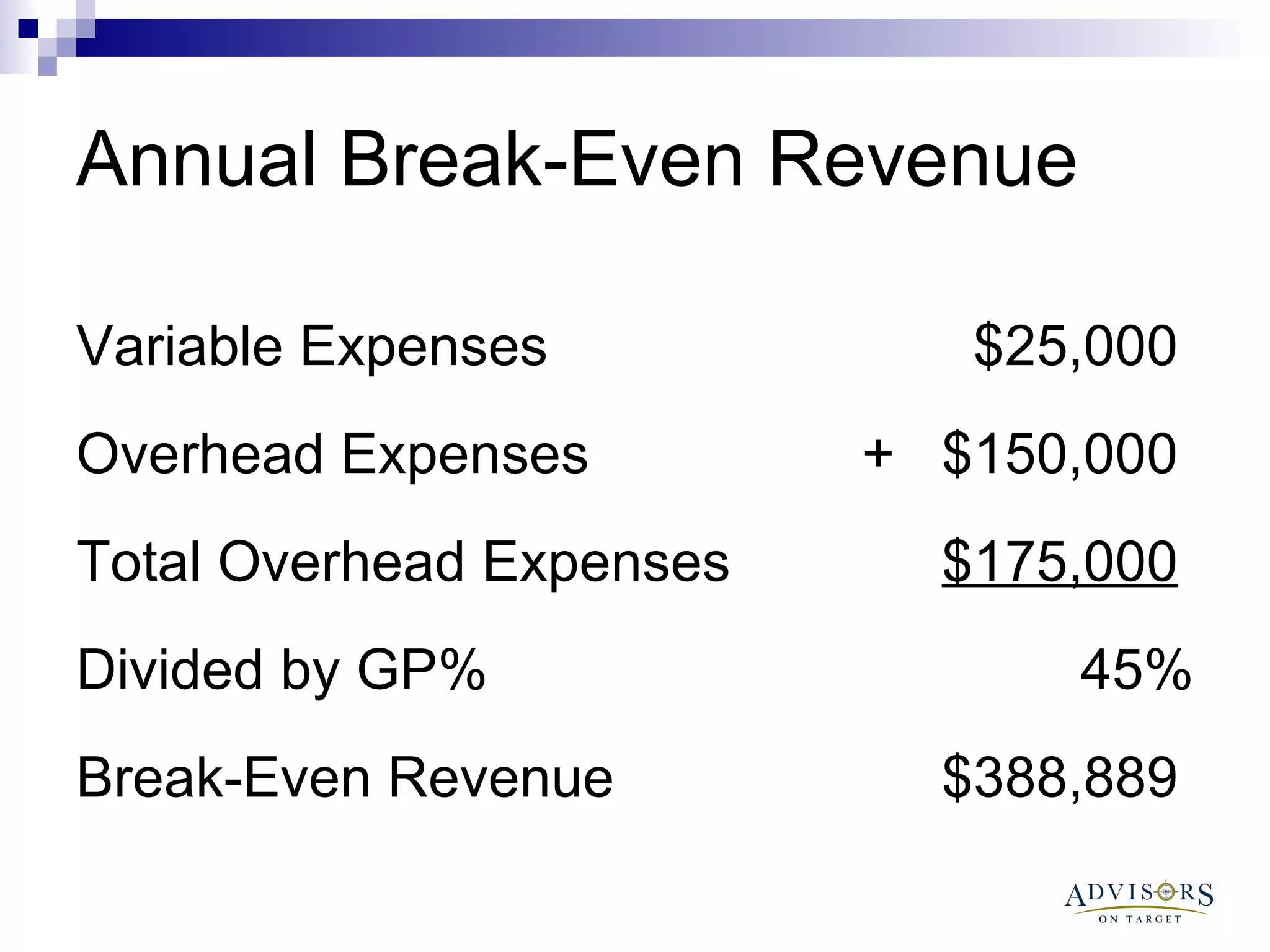
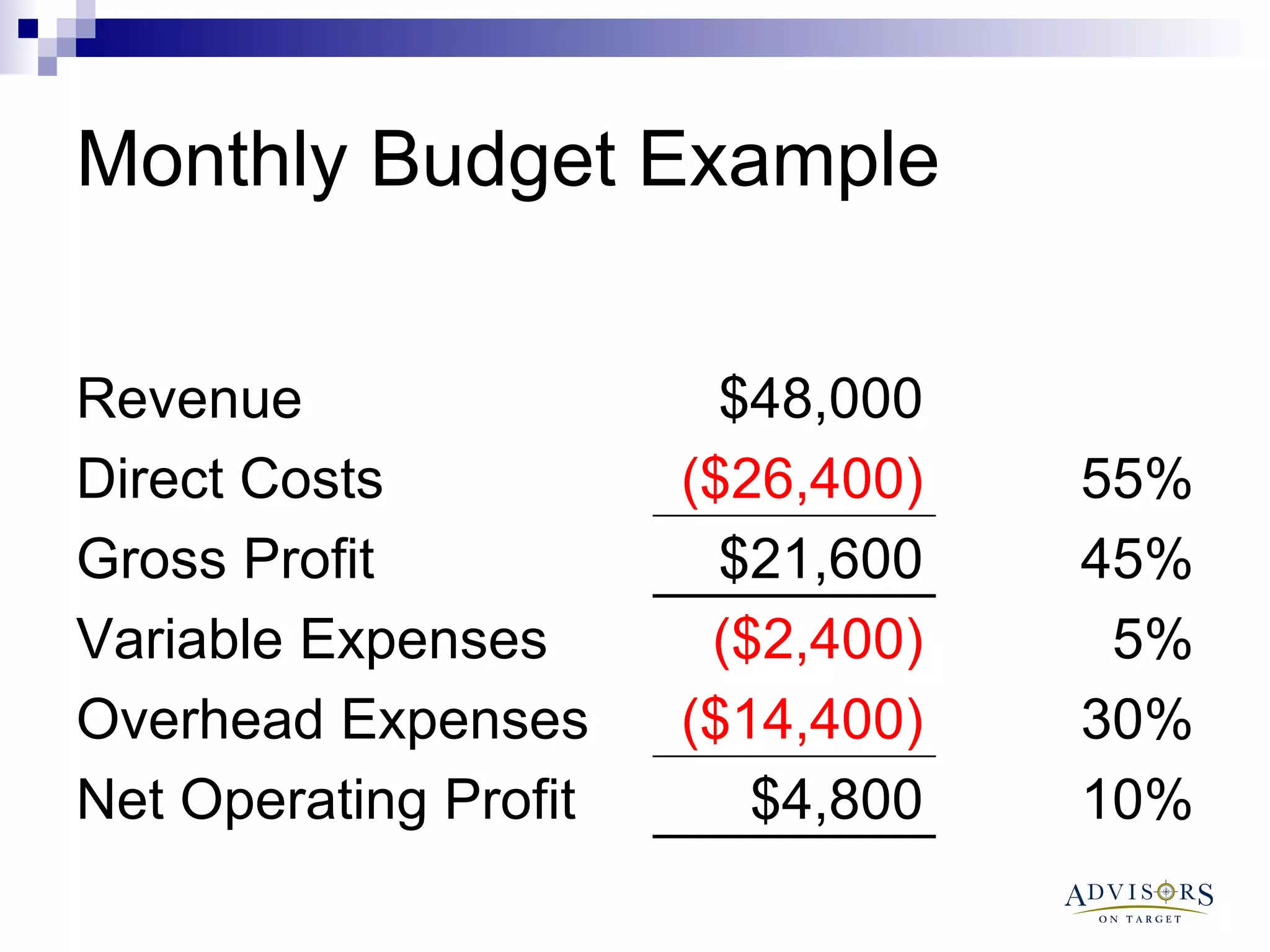
The document discusses the importance of contractors understanding their break-even point and how to calculate it. It provides examples of annual and monthly budgets, showing how to determine break-even revenue, sales, and hours. It also discusses how changing variables like overhead costs, gross profit margins, or adding new expenses can impact break-even levels. The document recommends contractors regularly monitor their break-even and take action if they are not hitting monthly targets.























![Contact us to help get your business On Target for success in 2010! Advisors On Target Linnea Blair Office: 619.291.3700 Email: [email_address] Web: AdvisorsOnTarget.com Twitter: AdvisorOnTarget Facebook:facebook.com/AdvisorsOnTarget LinkedIn:linkedin.com/in/linneablair](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/breakeven-100726141821-phpapp02/75/Break-Even-27-2048.jpg)