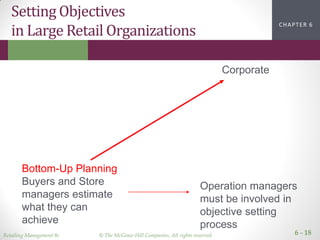
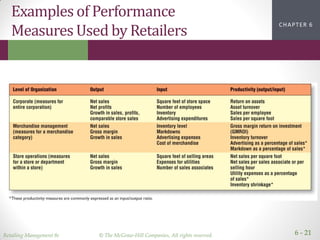
This document discusses financial strategy and performance measurement for retailers. It introduces the strategic profit model, which assesses net profit margin and asset turnover to measure return on assets. The document then examines approaches to measure and improve profit margins through cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and inventory management. It also explores using objectives, productivity and financial metrics to evaluate performance over time, compared to competitors, and through stock price and return on assets. The overall goal is for retailers to effectively measure and enhance their financial returns and operations.