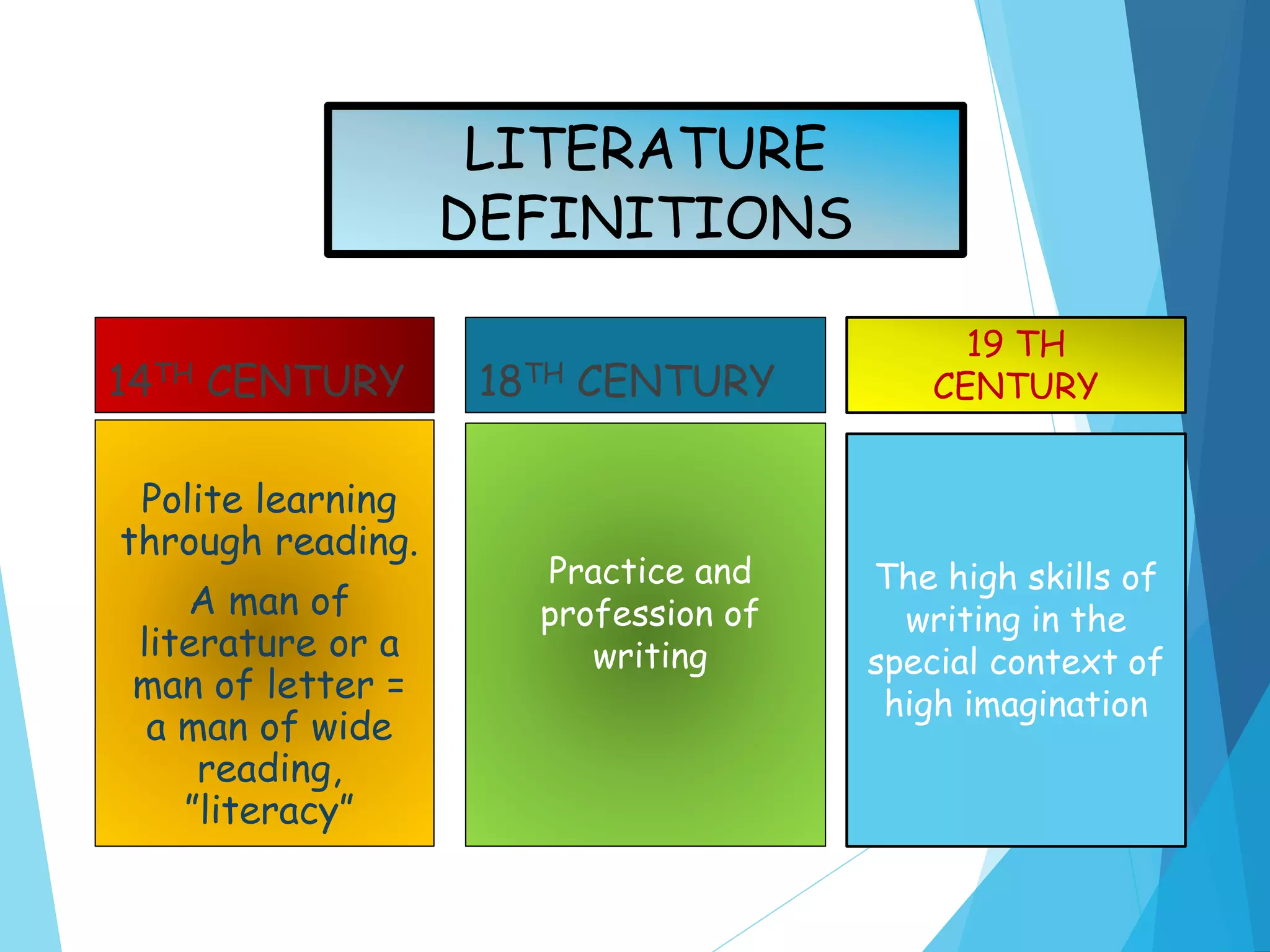
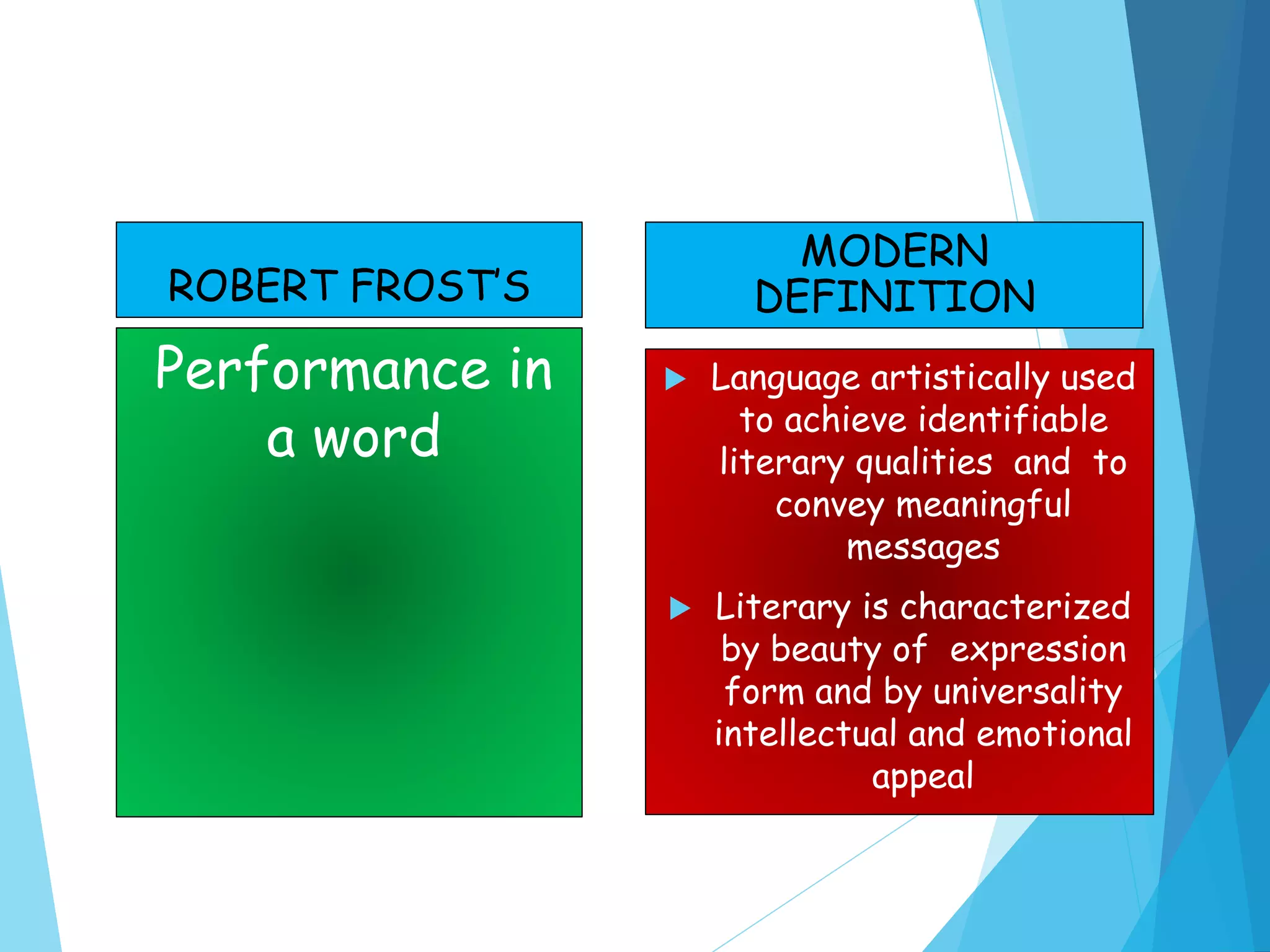
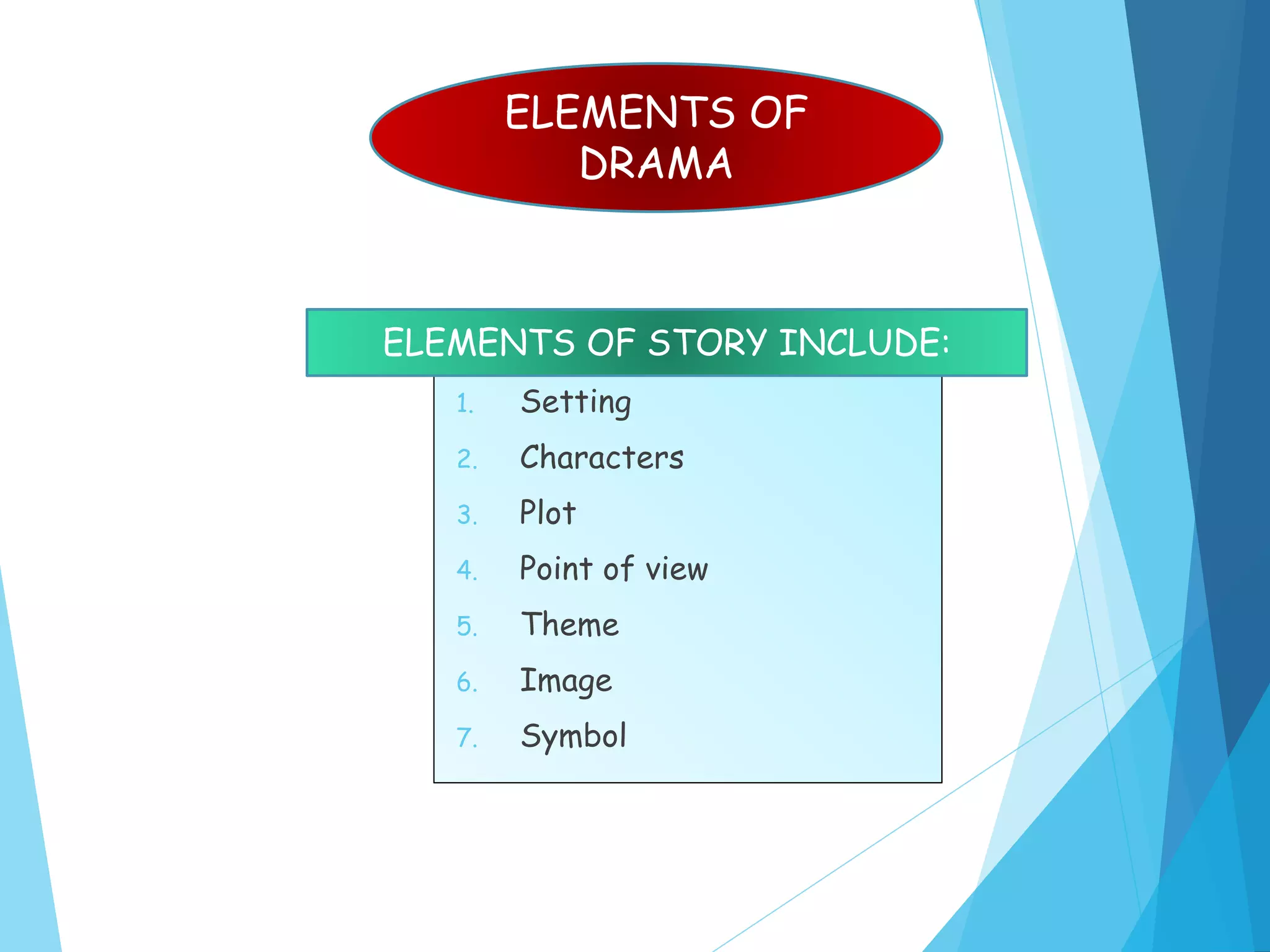
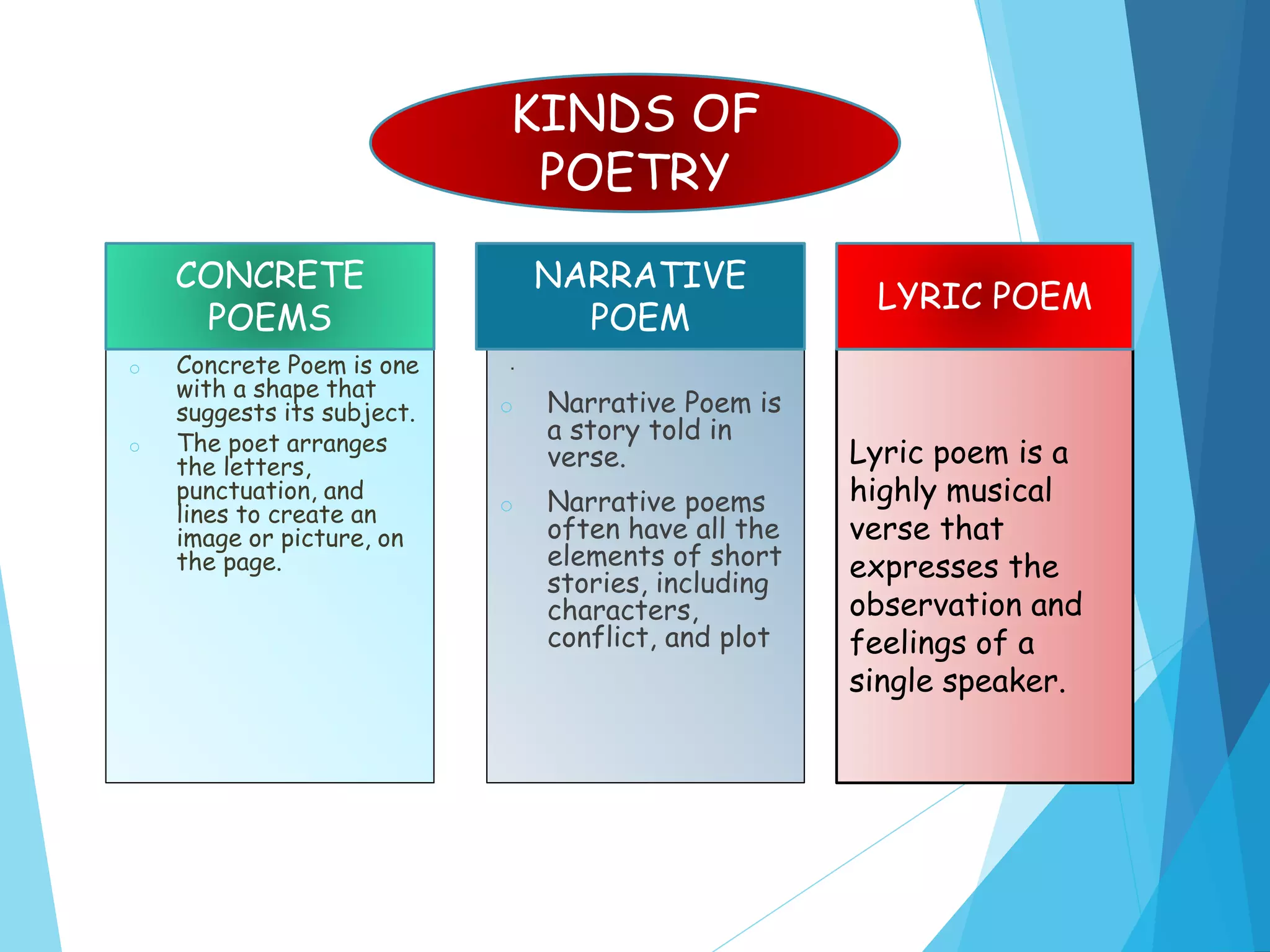
The document discusses the history and definitions of literature from the 14th to 19th centuries. It provides definitions of modern literature as language used artistically to convey meaning and messages with beauty of expression. The importance of learning literature is described as improving language skills, enhancing cultural understanding, and helping people grow intellectually. Literature genres discussed include poetry, drama, and prose. Poetry is defined as language using rhythm, imagery and figurative language. Drama is intended to be performed while prose mimics spoken language. Examples of fiction and non-fiction genres are also provided.