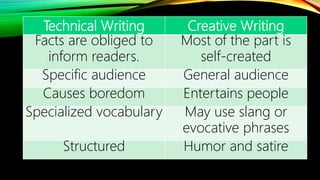
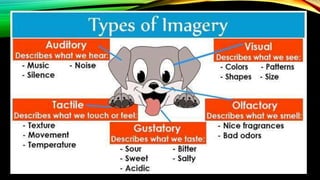
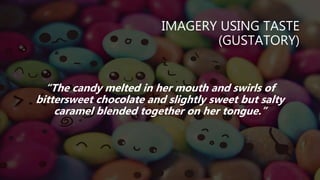This document discusses different types of creative writing such as poetry, plays, fiction, and memoirs. It describes the purpose of creative writing as entertaining and sharing the human experience. Sensory details like imagery are explained as an important part of creative writing to engage readers through their senses of sight, sound, touch, smell and taste. The document also covers language techniques in creative writing including figures of speech, imagery, and diction.