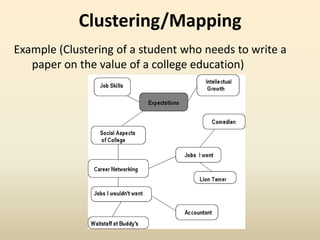
The document outlines pre-writing strategies that facilitate the discovery of initial ideas before drafting. Common strategies include freewriting, brainstorming/listing, clustering/mapping, and posing journalistic questions. Each method is exemplified to illustrate how it helps writers organize thoughts for a writing task.