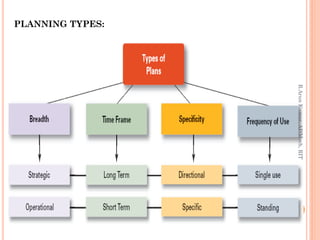
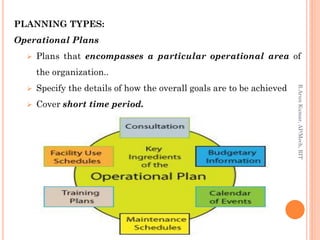
The document discusses different types of planning based on breadth, time frame, specificity, and frequency of use. Strategic plans apply to the entire organization and establish long term goals, while operational plans cover shorter time periods and specific operational areas. Plans can also be categorized as long term versus short term based on duration, and as specific versus directional based on the level of definition. Additionally, single-use plans are designed for unique situations while standing plans provide ongoing guidance for repeated activities.