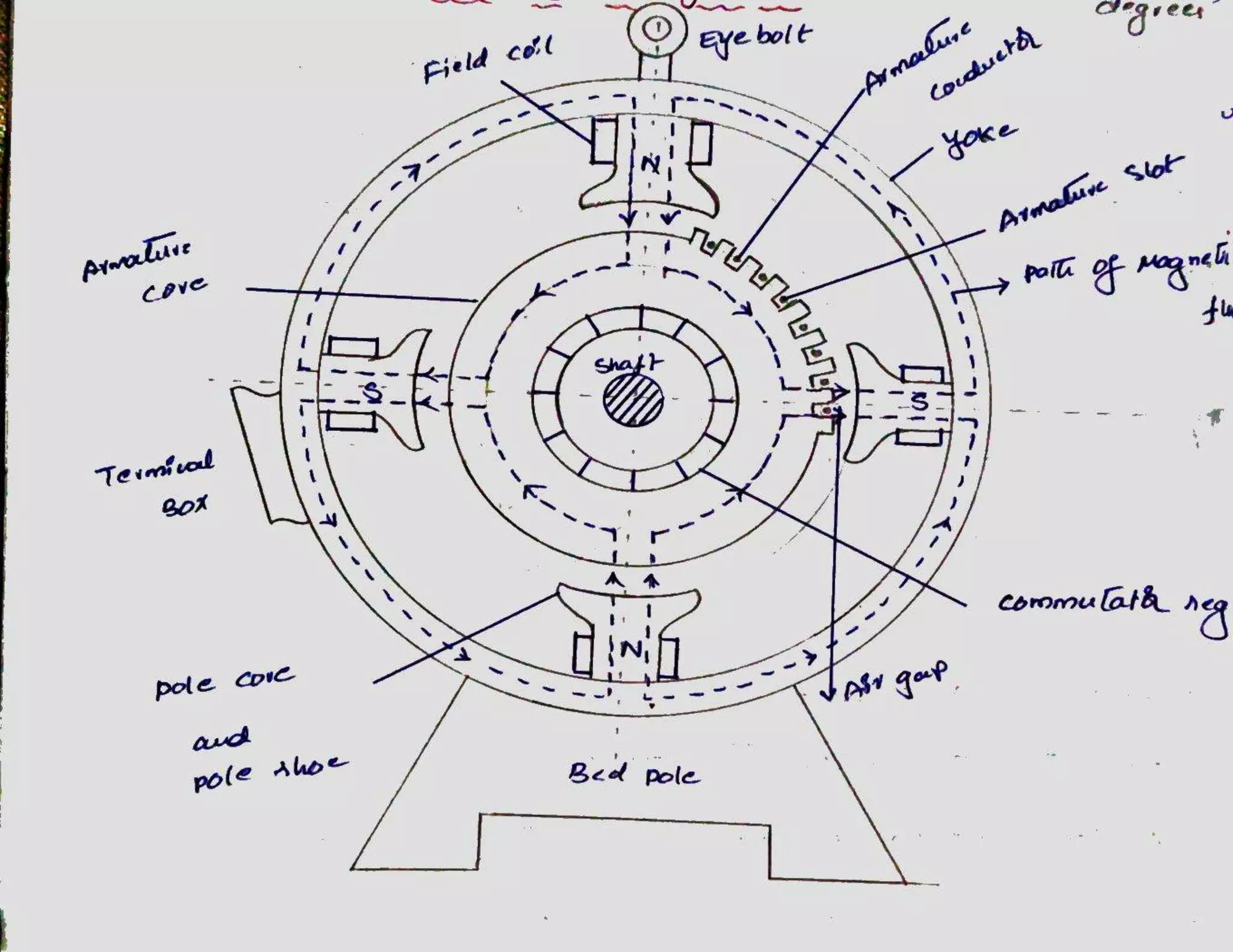
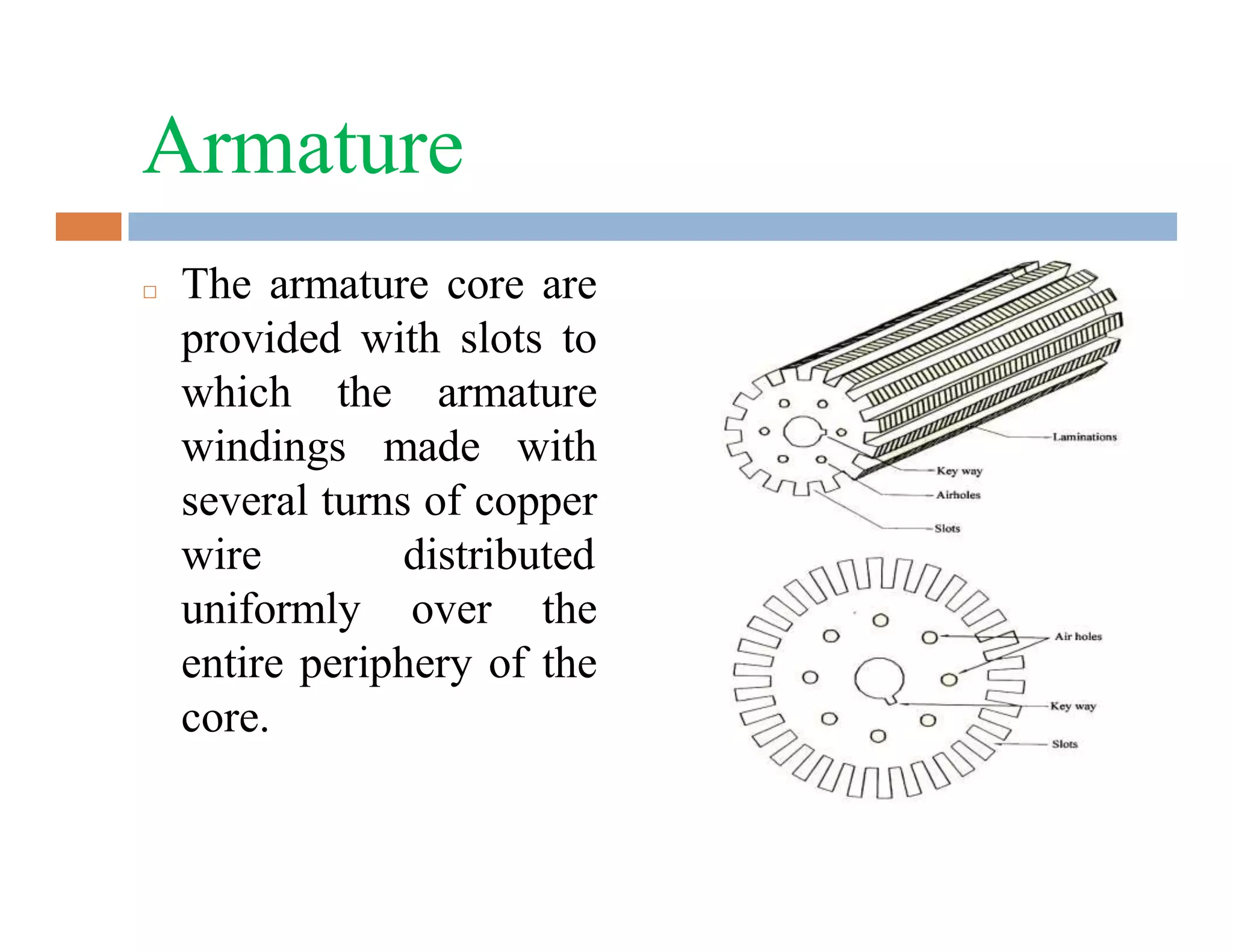
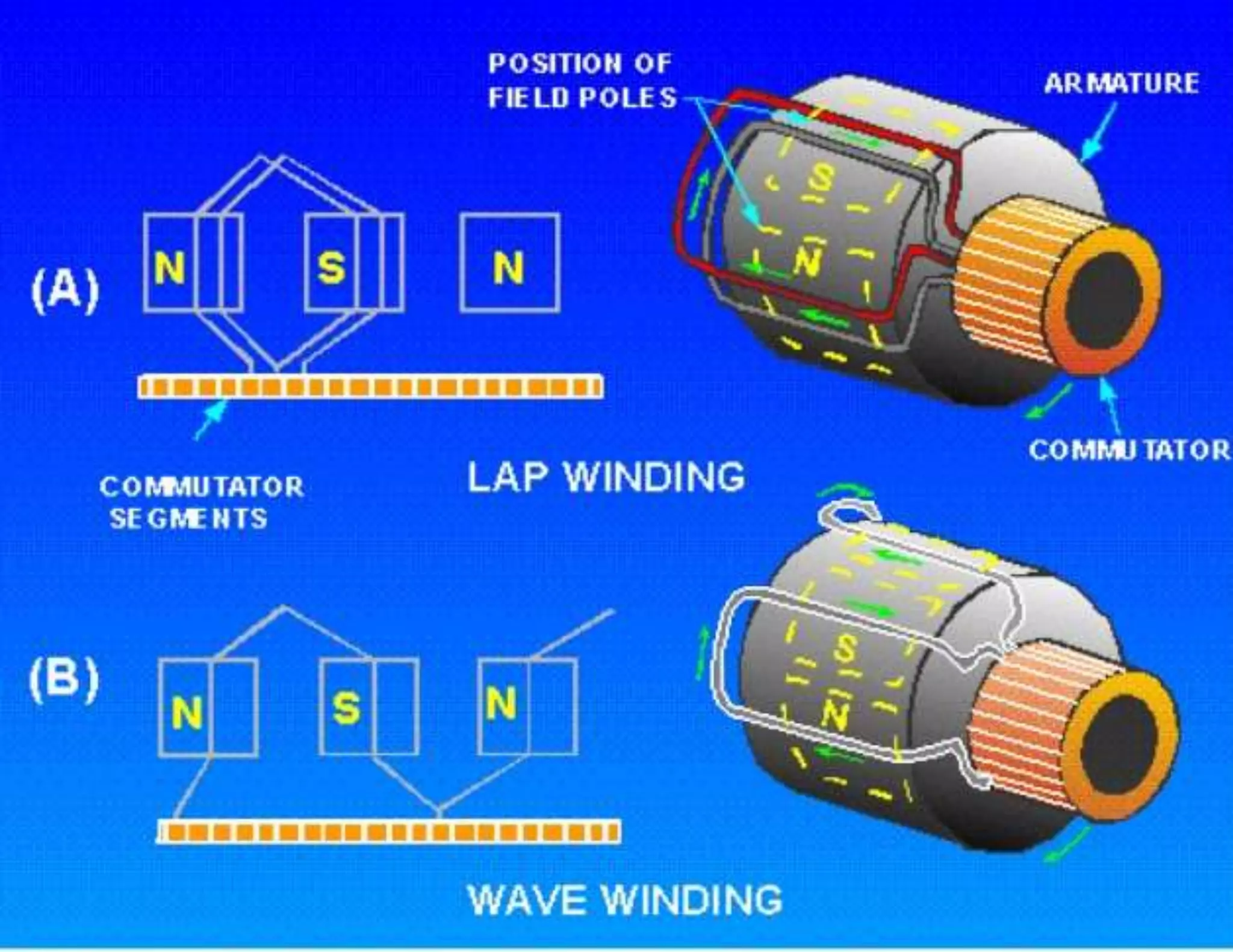
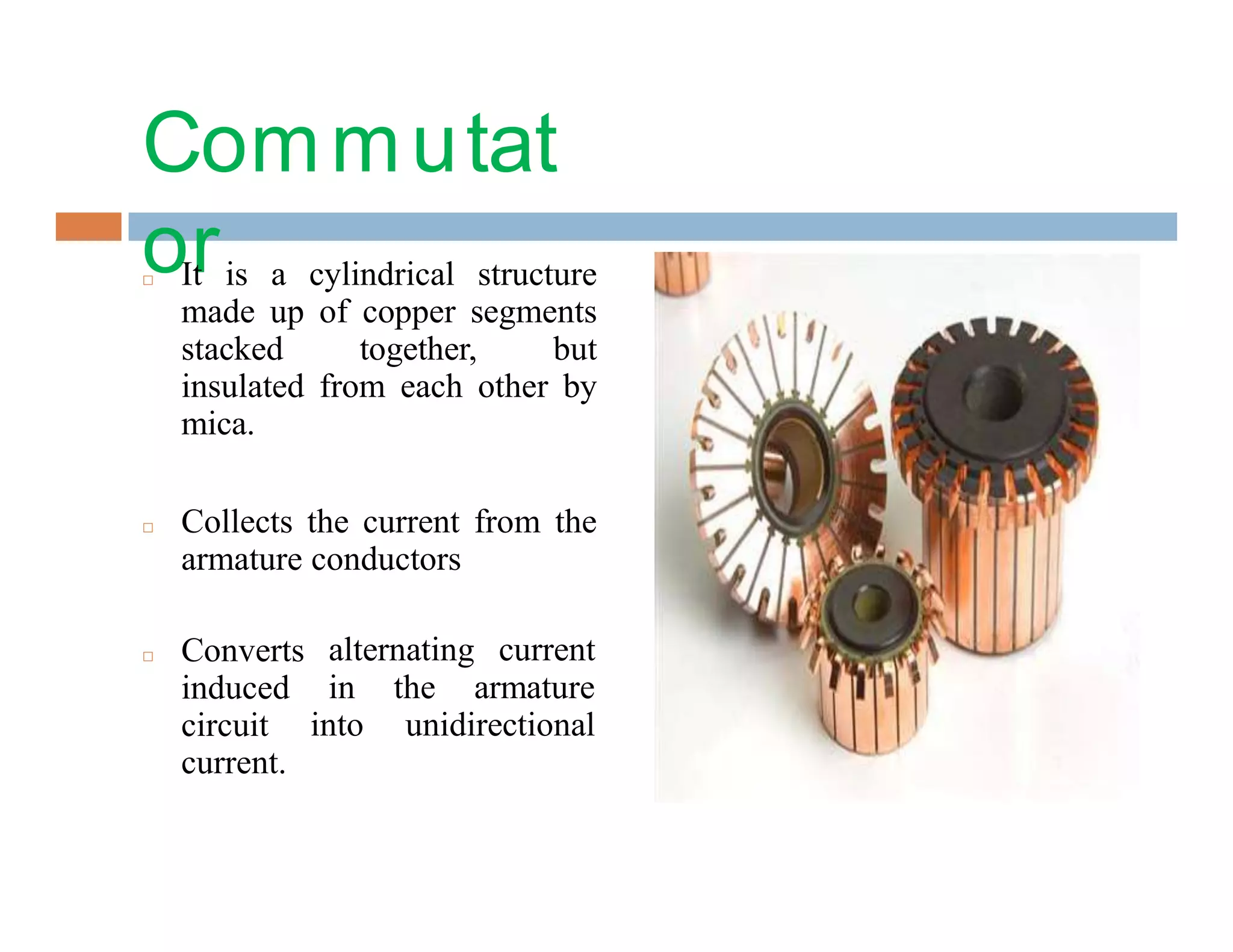
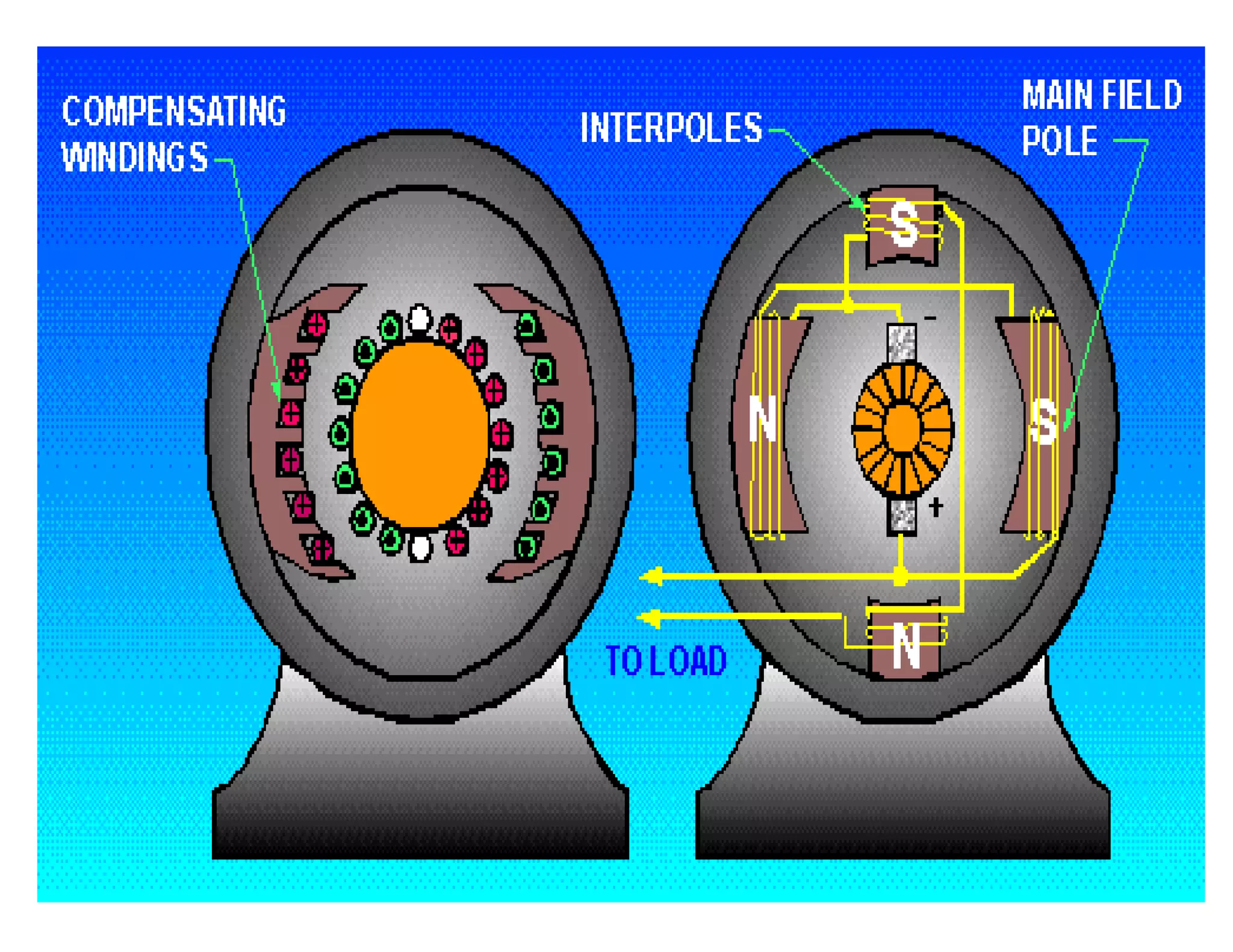
The document summarizes the main parts of an electric motor construction. The two major parts are the stator, which houses the field winding, and the rotor, which is the rotating part. Other key parts include the yoke, which forms a protective covering; poles made of core and pole shoes that produce magnetic flux; field windings wound on pole shoes to form an electromagnet; an armature core with windings to induce current; a commutator that collects alternating current and converts it to direct current; and brushes that make contact with the commutator to deliver current to the stationary circuit.