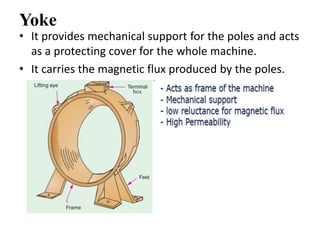
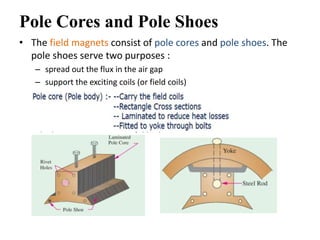
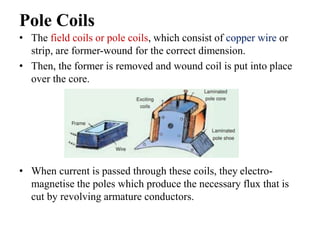
The document summarizes the key components of a DC machine, including the yoke, pole cores and shoes, pole coils, armature core, armature windings, commutator, brushes, bearings, and shaft. The yoke provides mechanical support and carries magnetic flux. Pole coils electromagnetize the poles when current flows through them. The armature core houses windings and rotates to cut magnetic flux. The commutator rectifies alternating current from the windings into direct current for the load. Brushes housed in holders collect current from the commutator.