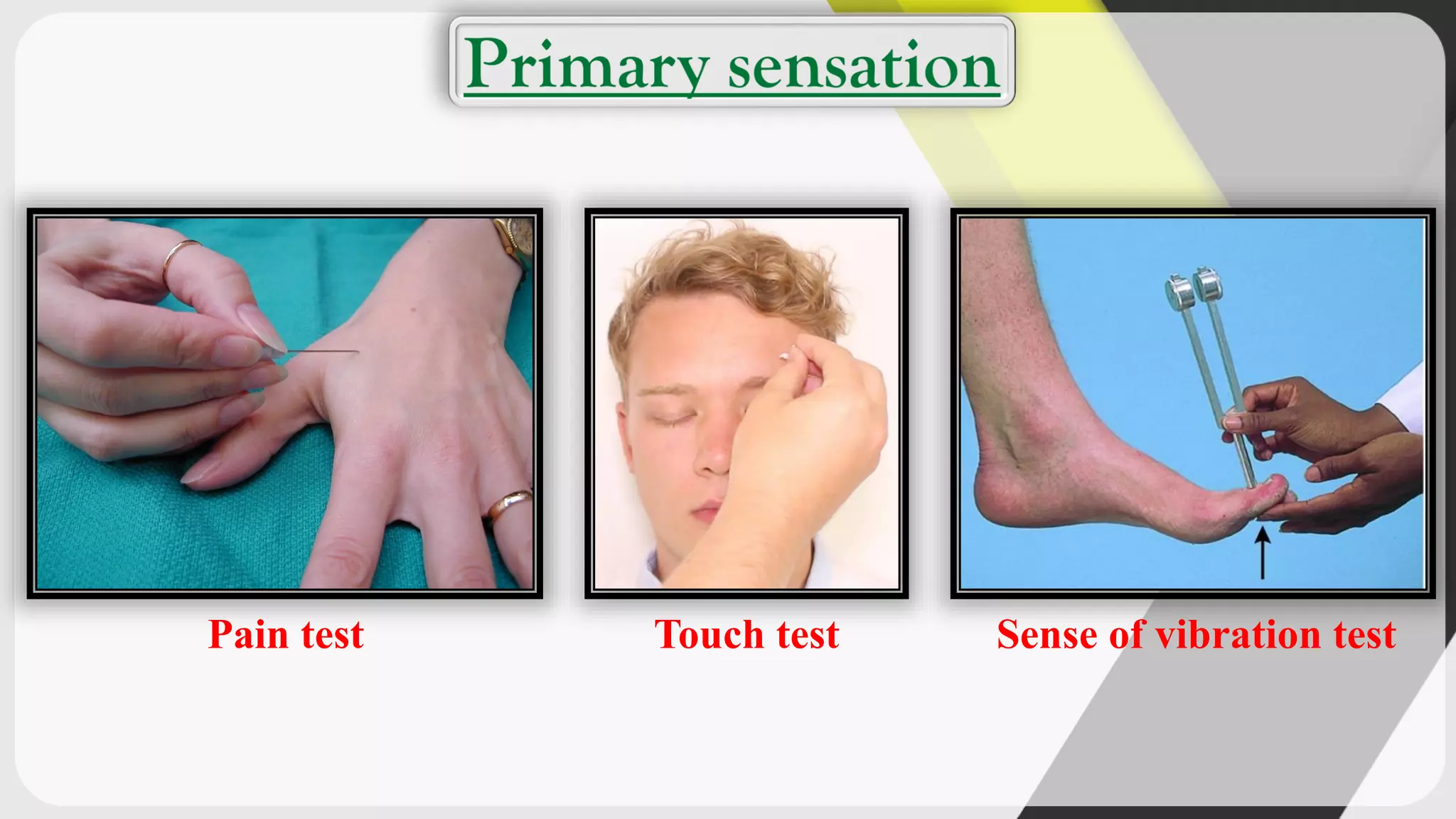
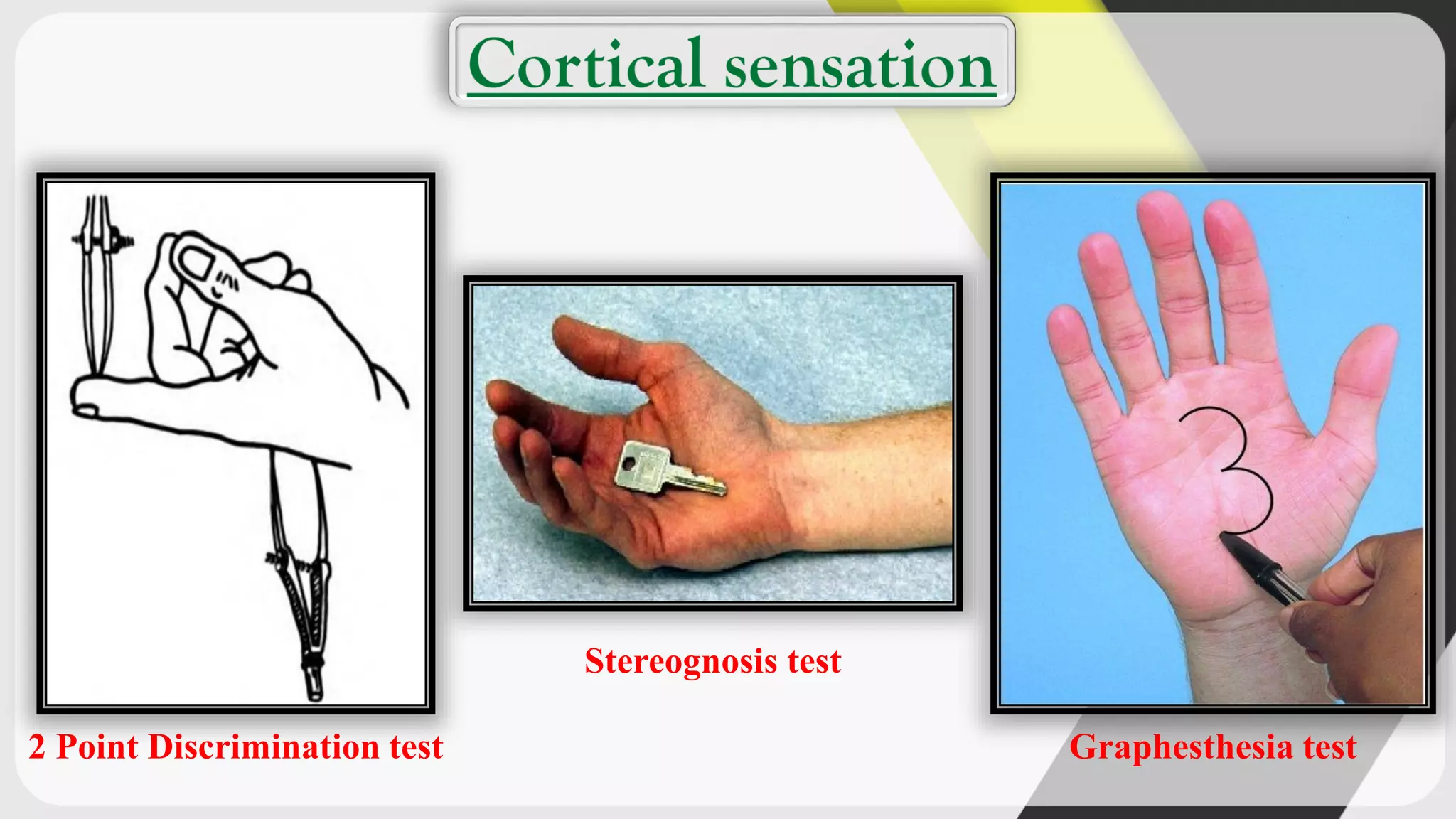
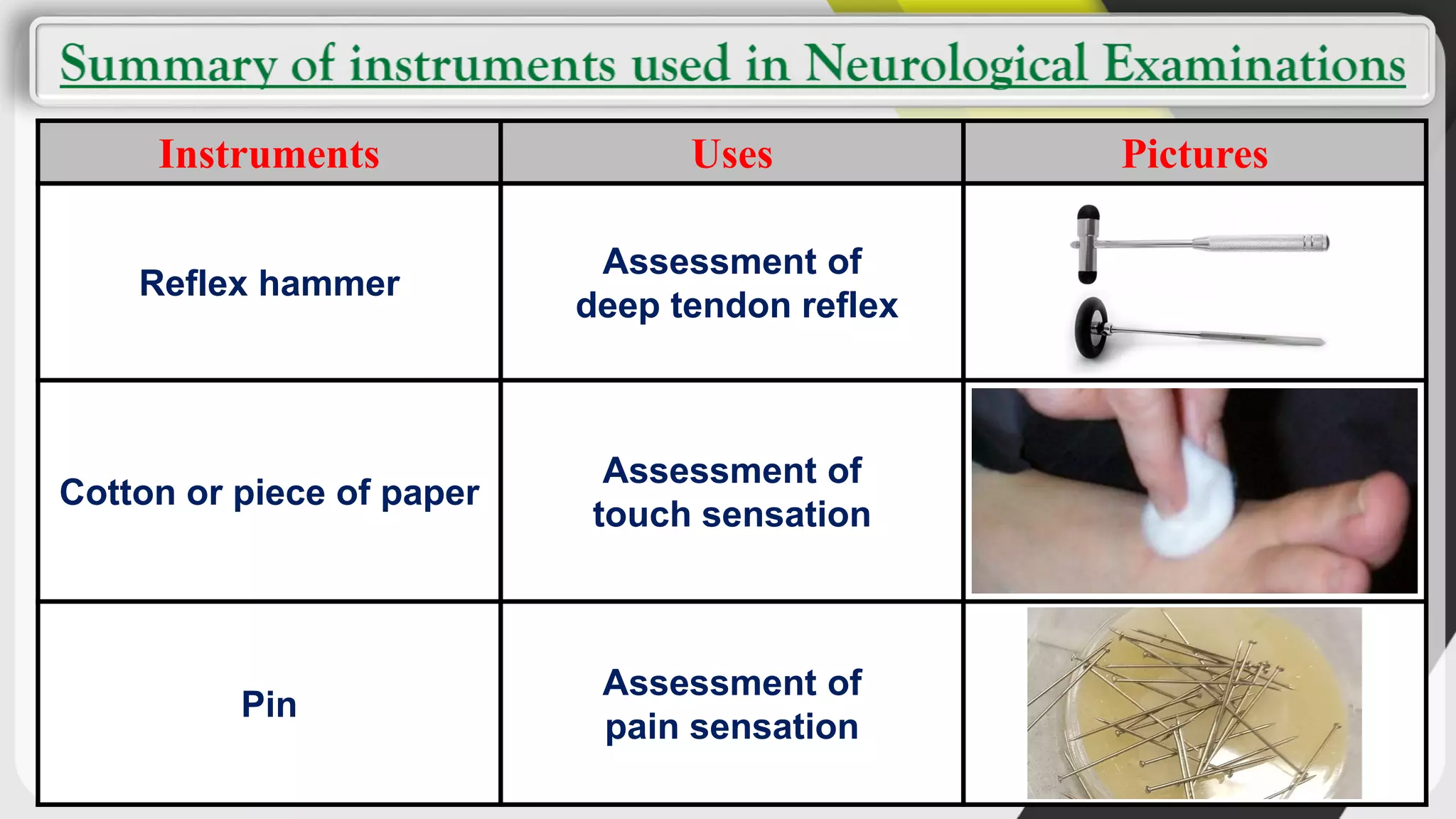
1. The document outlines various tests used in sensory examination including tests for touch, pain, temperature, vibration, hearing, vision, and cortical sensations.
2. It describes the instruments used and procedures for tests like the two point discrimination test, Rinne's test, and Weber's test.
3. The tests assess primary sensations, cortical sensations, hearing, vision, and help identify lesions in the sensory cortex.