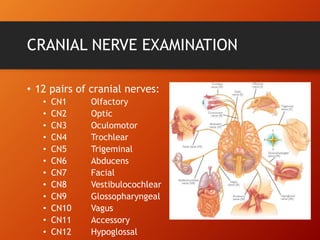
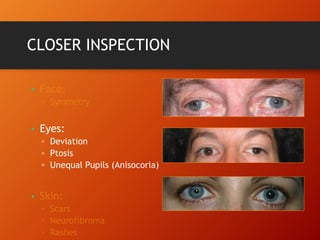
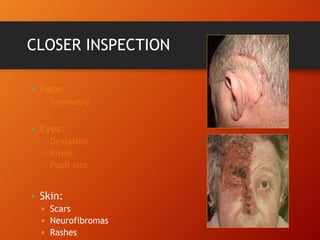
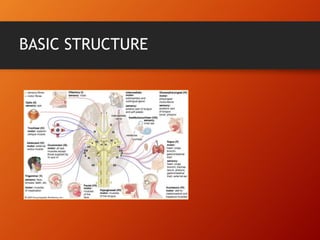
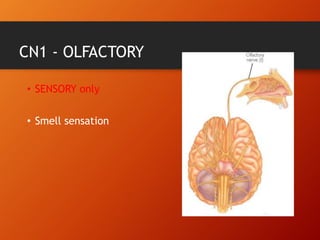
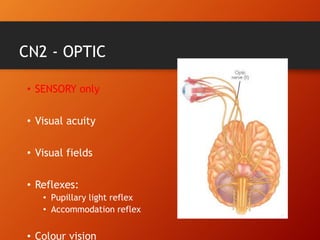
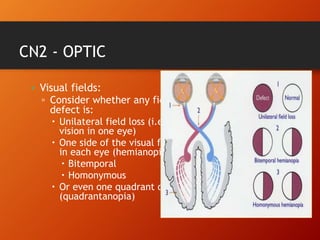
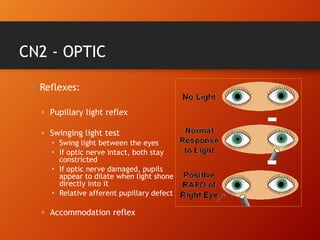
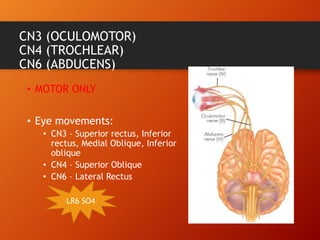
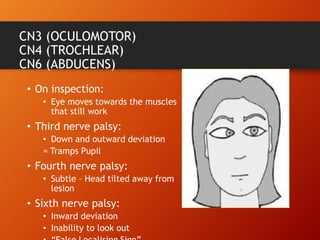
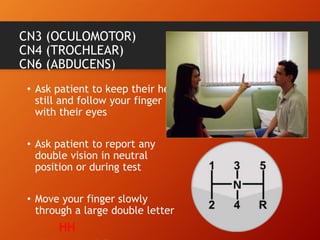
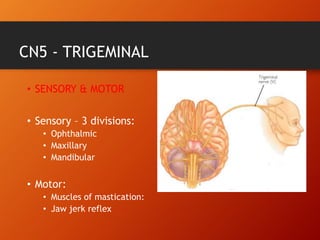
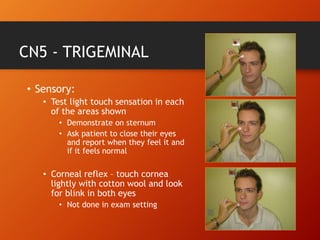
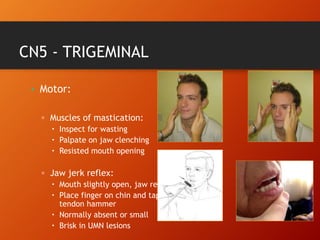
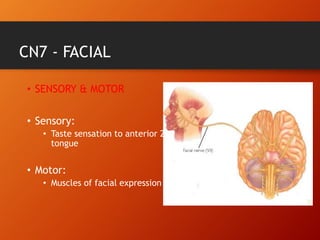
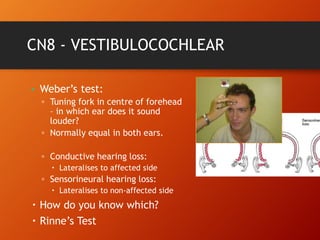
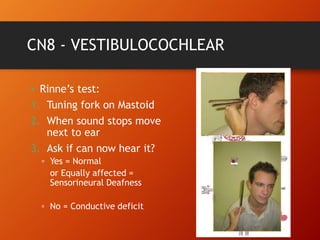
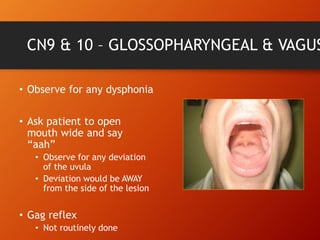
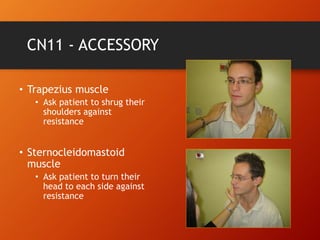
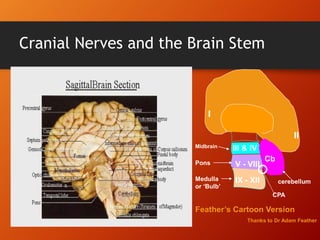
This document provides information on examining the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. It describes the motor and sensory functions of each nerve as well as how to test them. The examination involves inspecting the face and eyes, testing visual acuity, visual fields and reflexes, sensory functions like smell and touch, and motor functions like eye and facial movements. Performing a thorough cranial nerve exam requires patient cooperation and good communication skills to properly assess any neurological deficits.