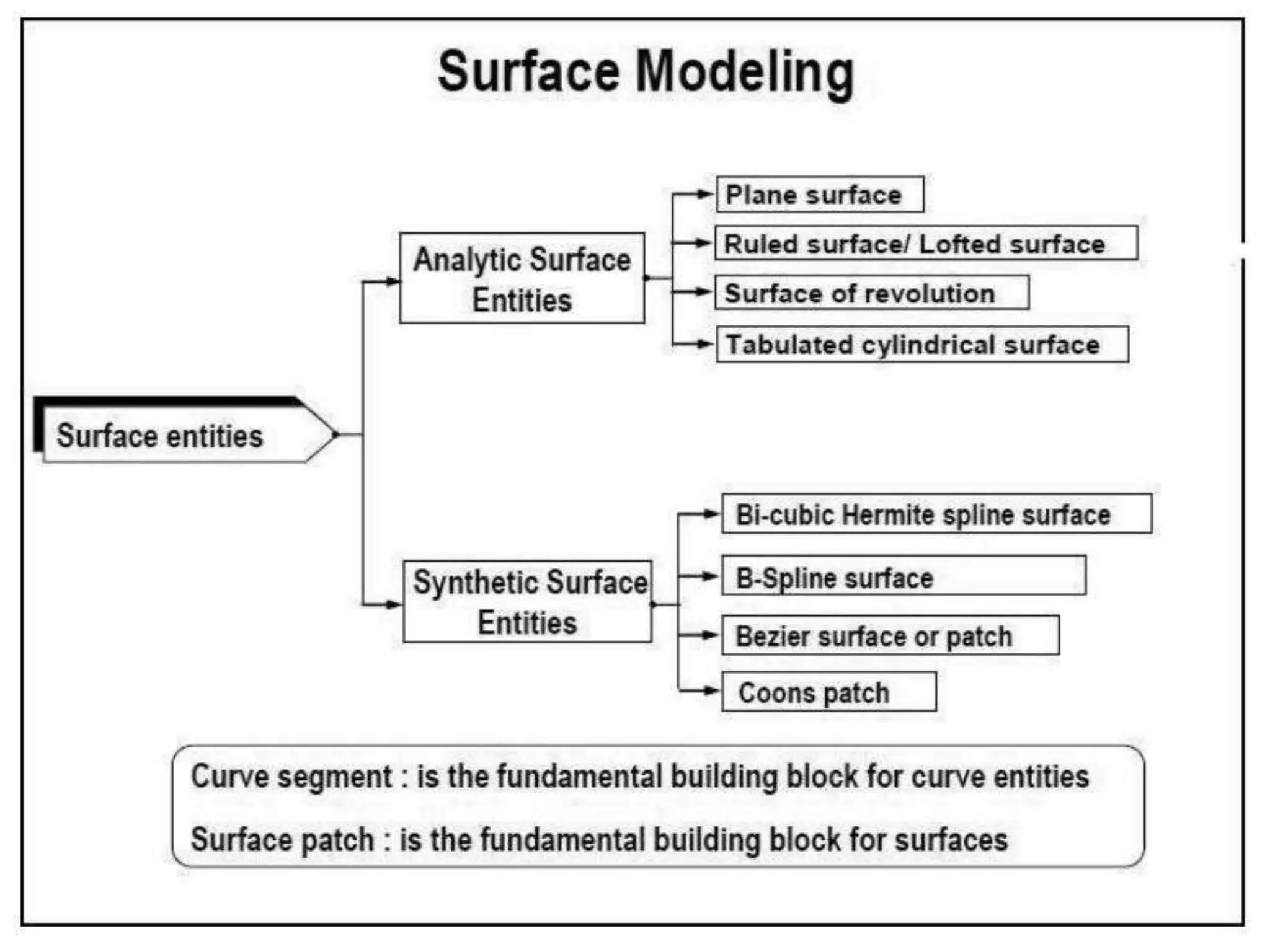
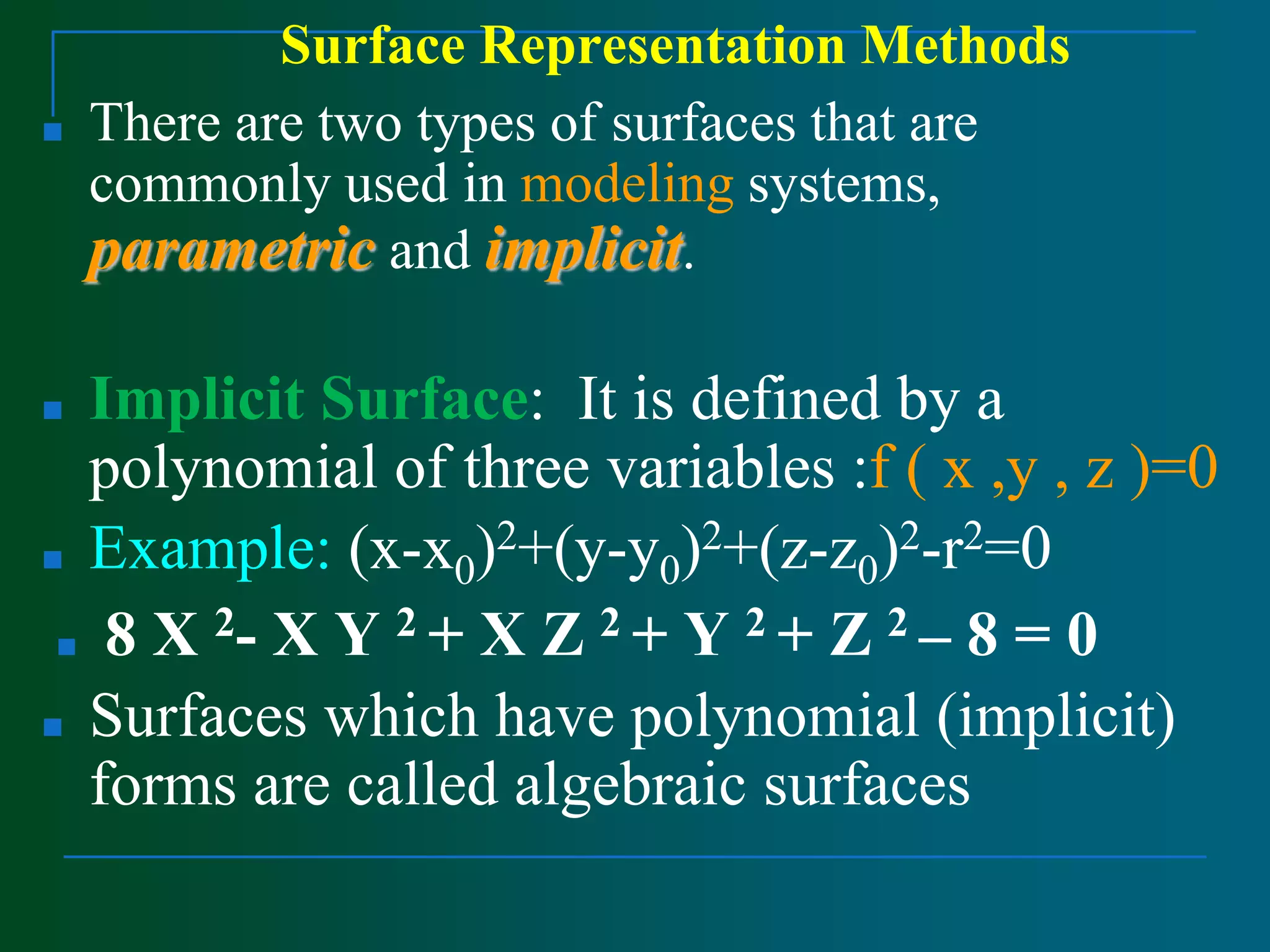
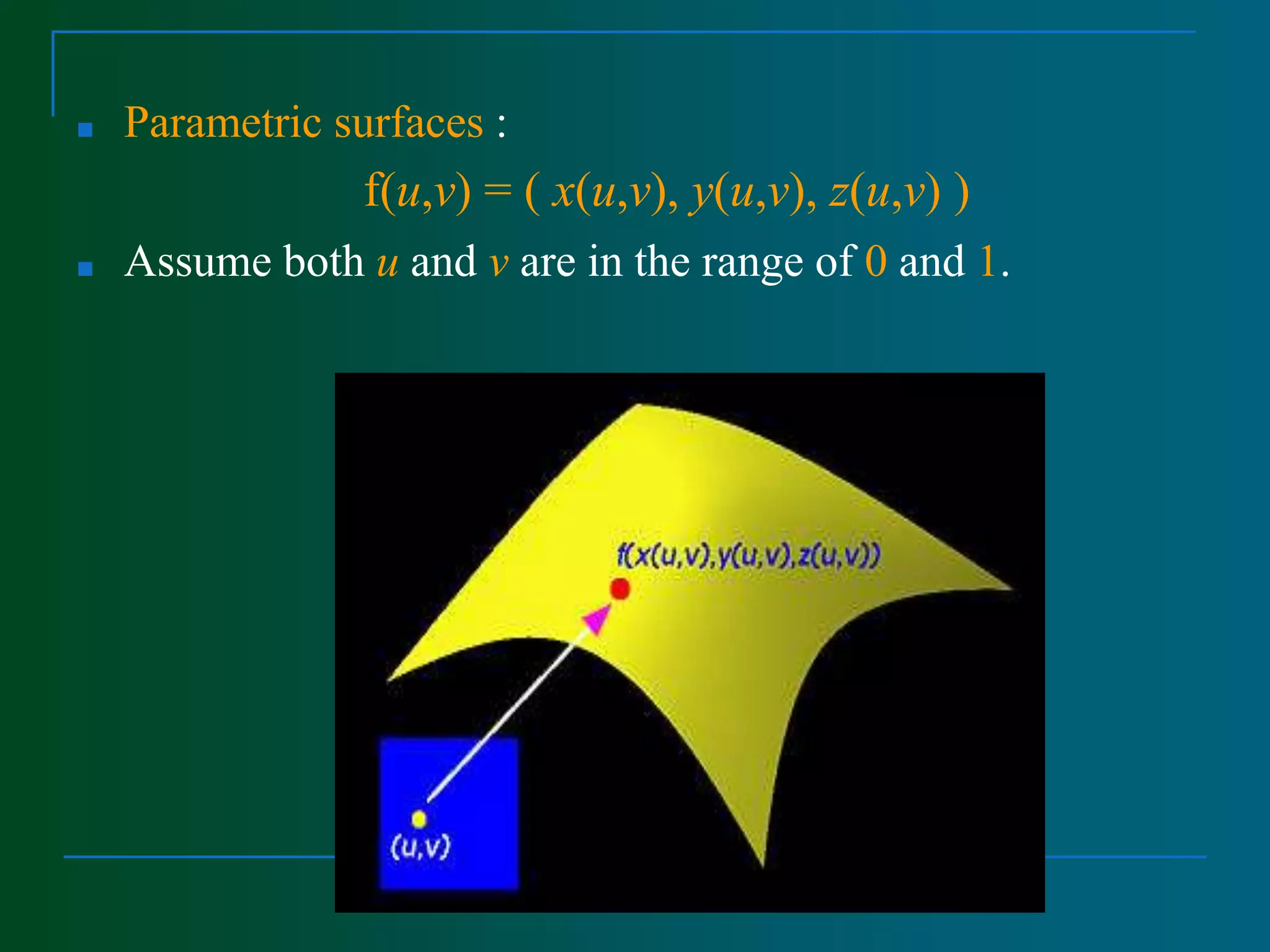
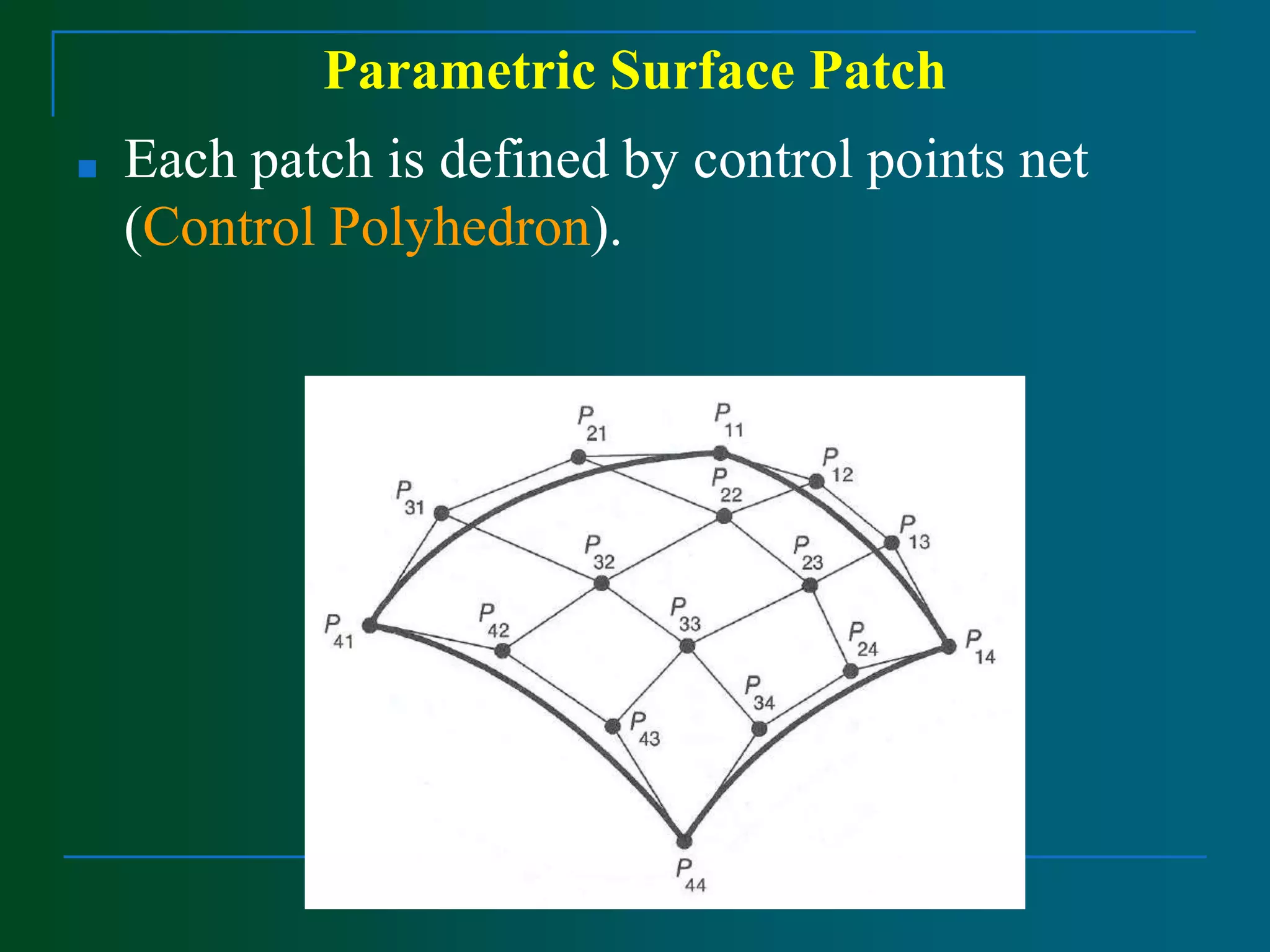
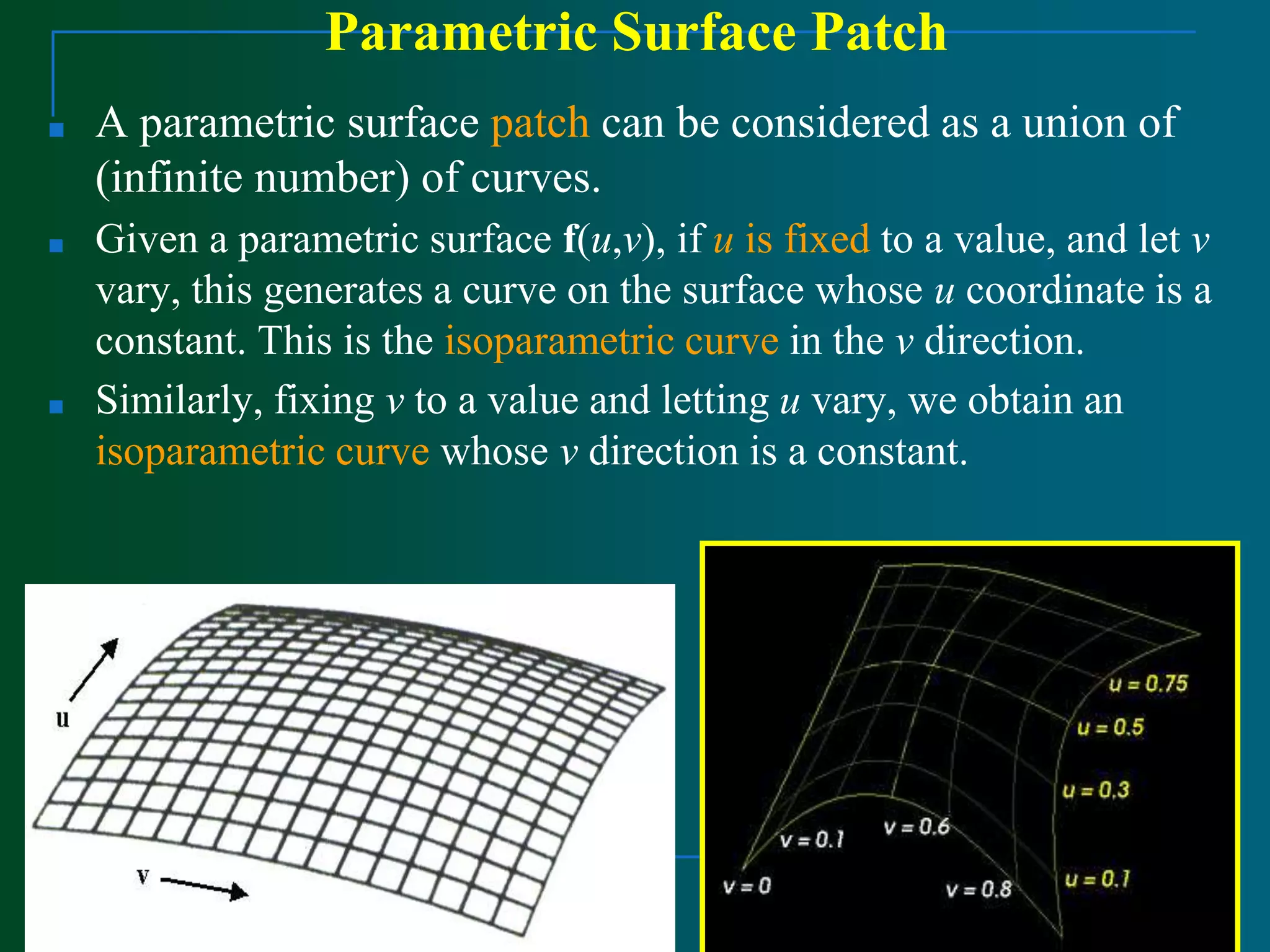
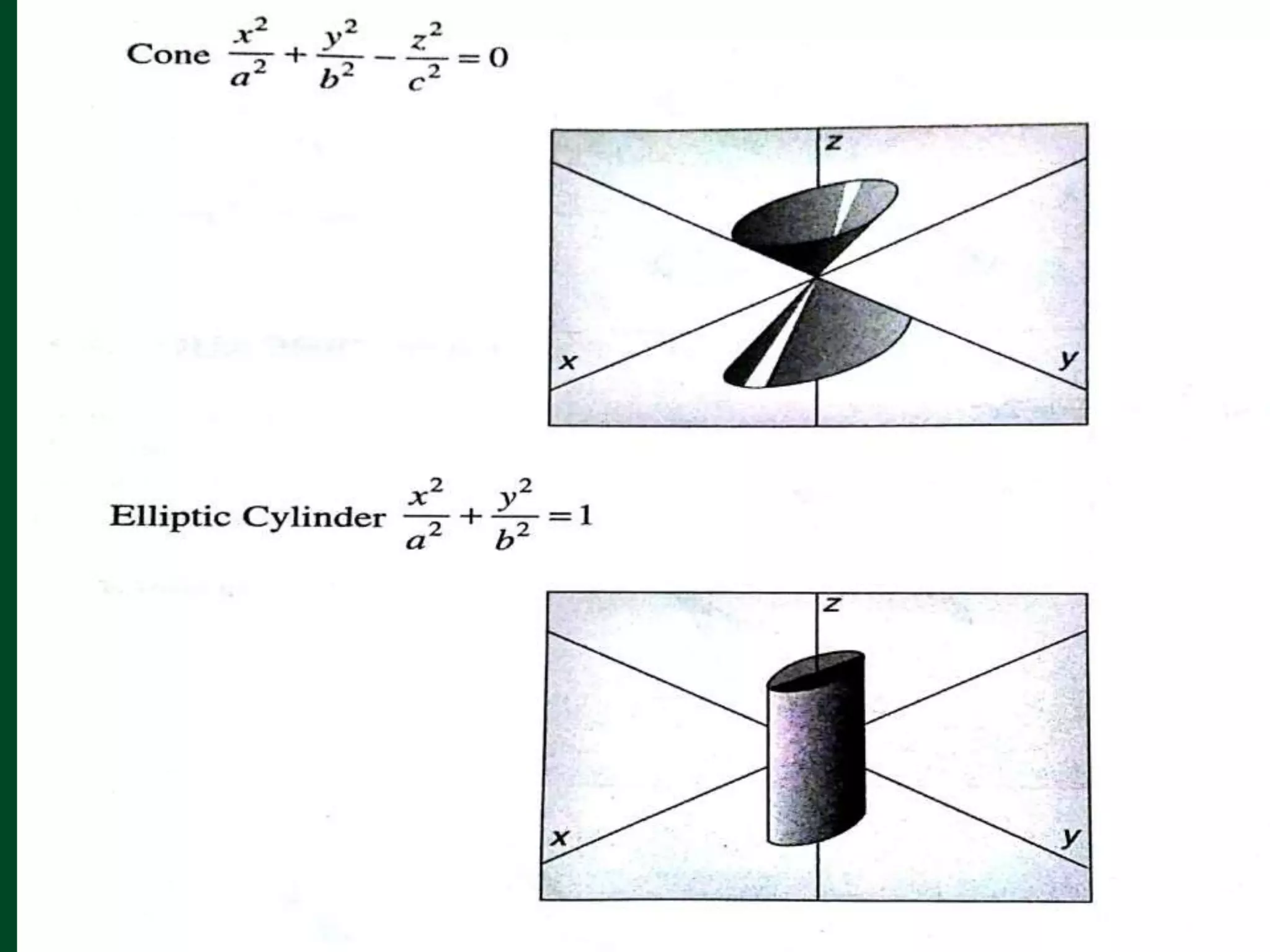
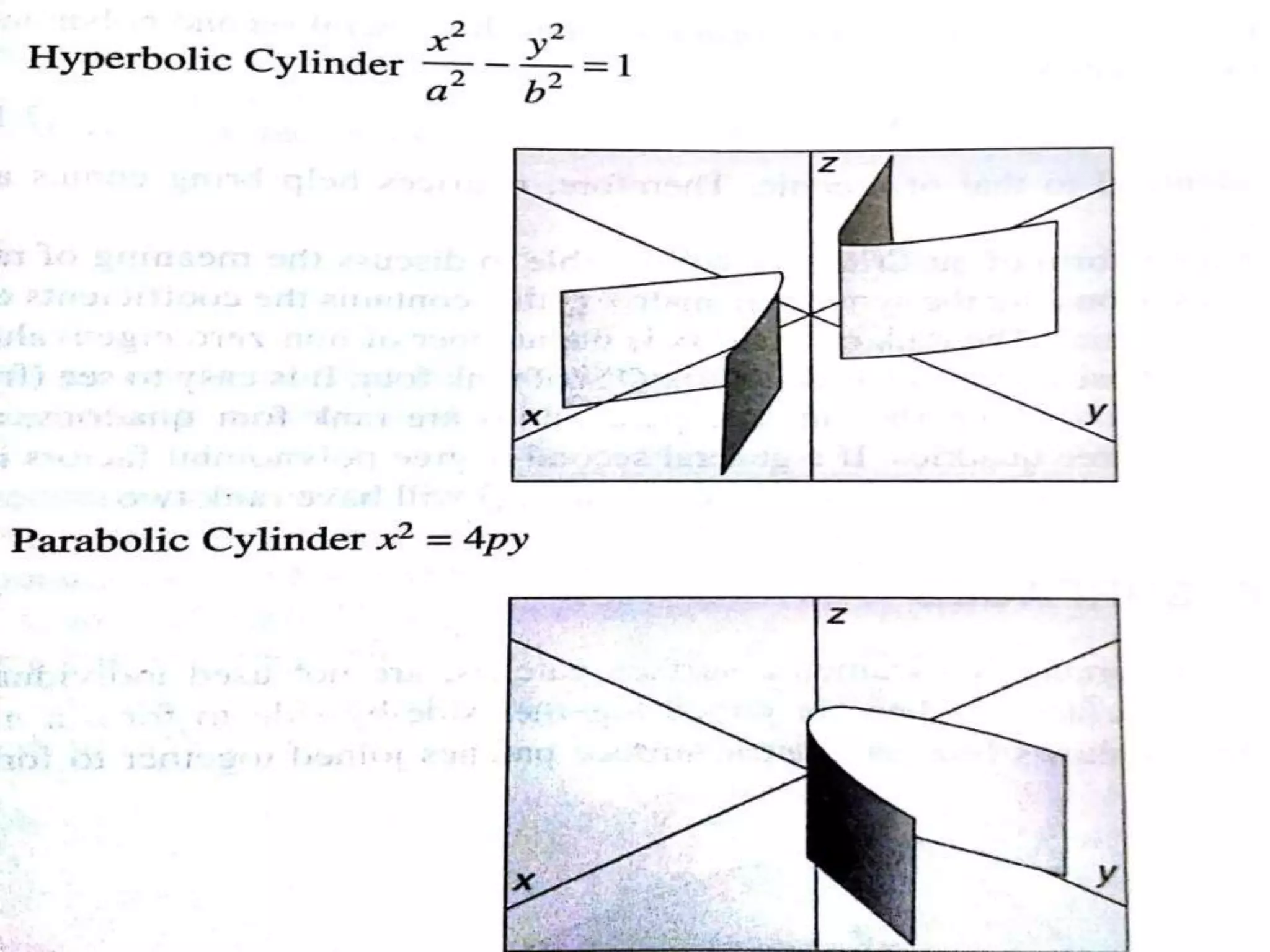
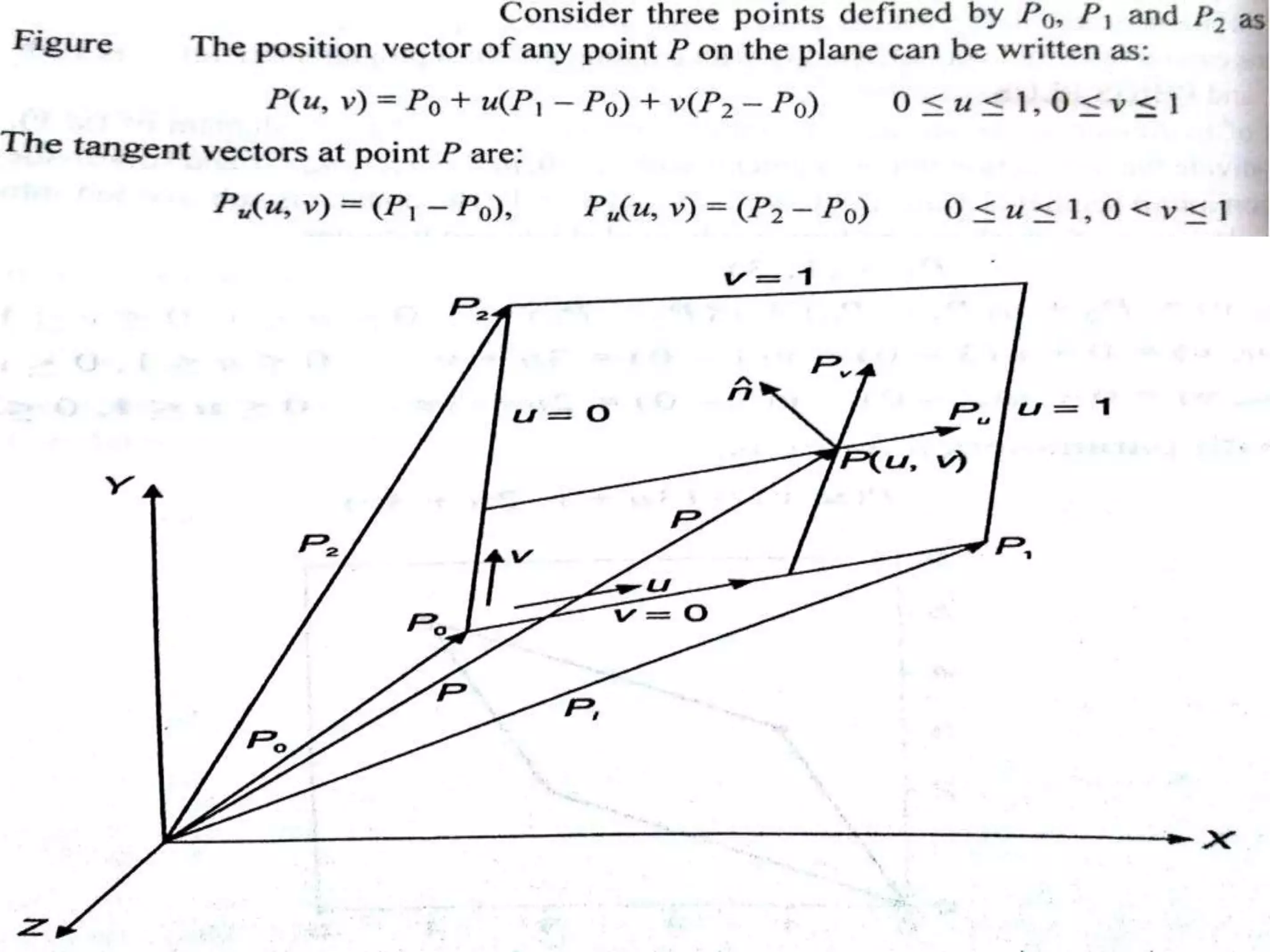
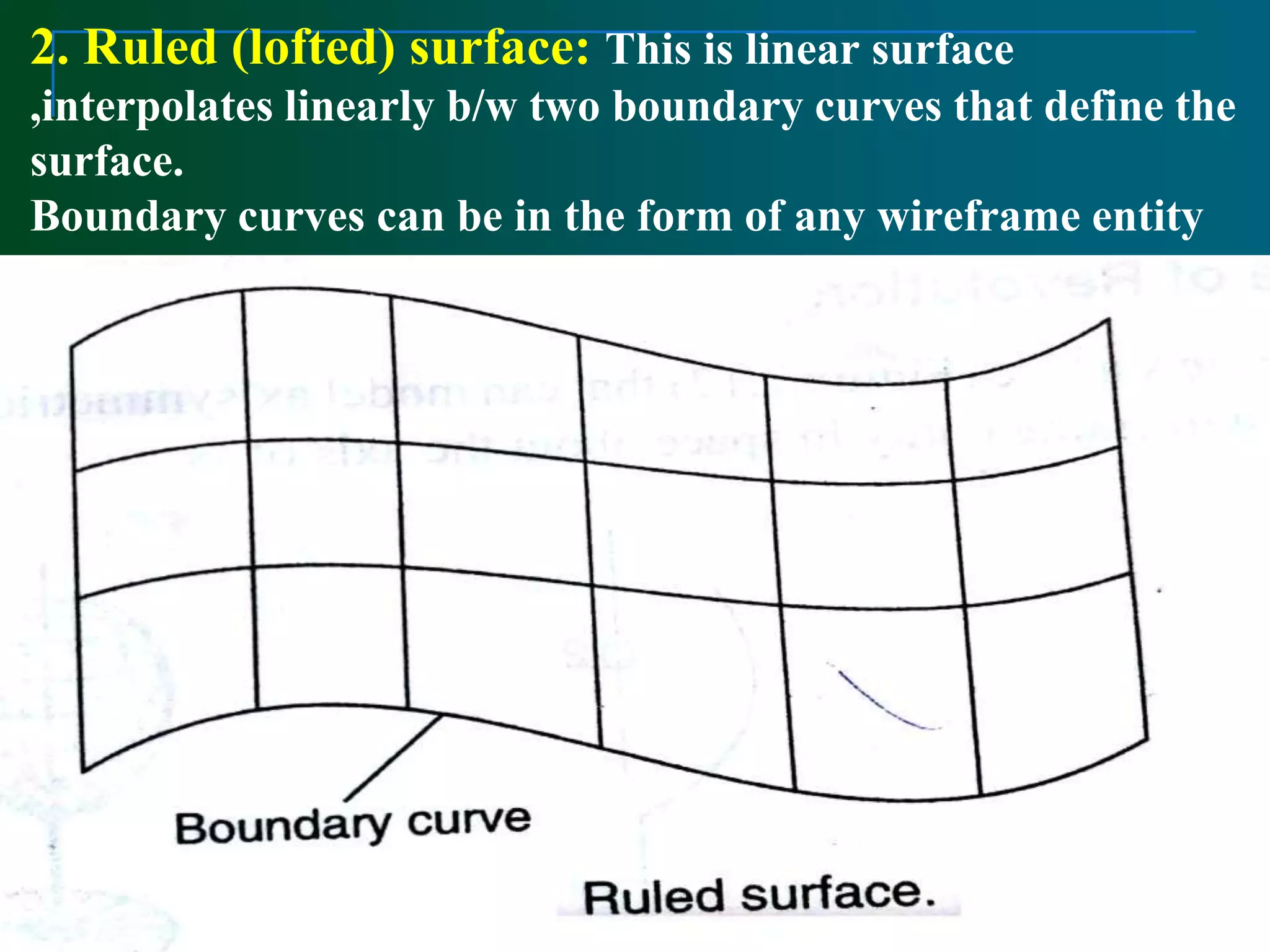
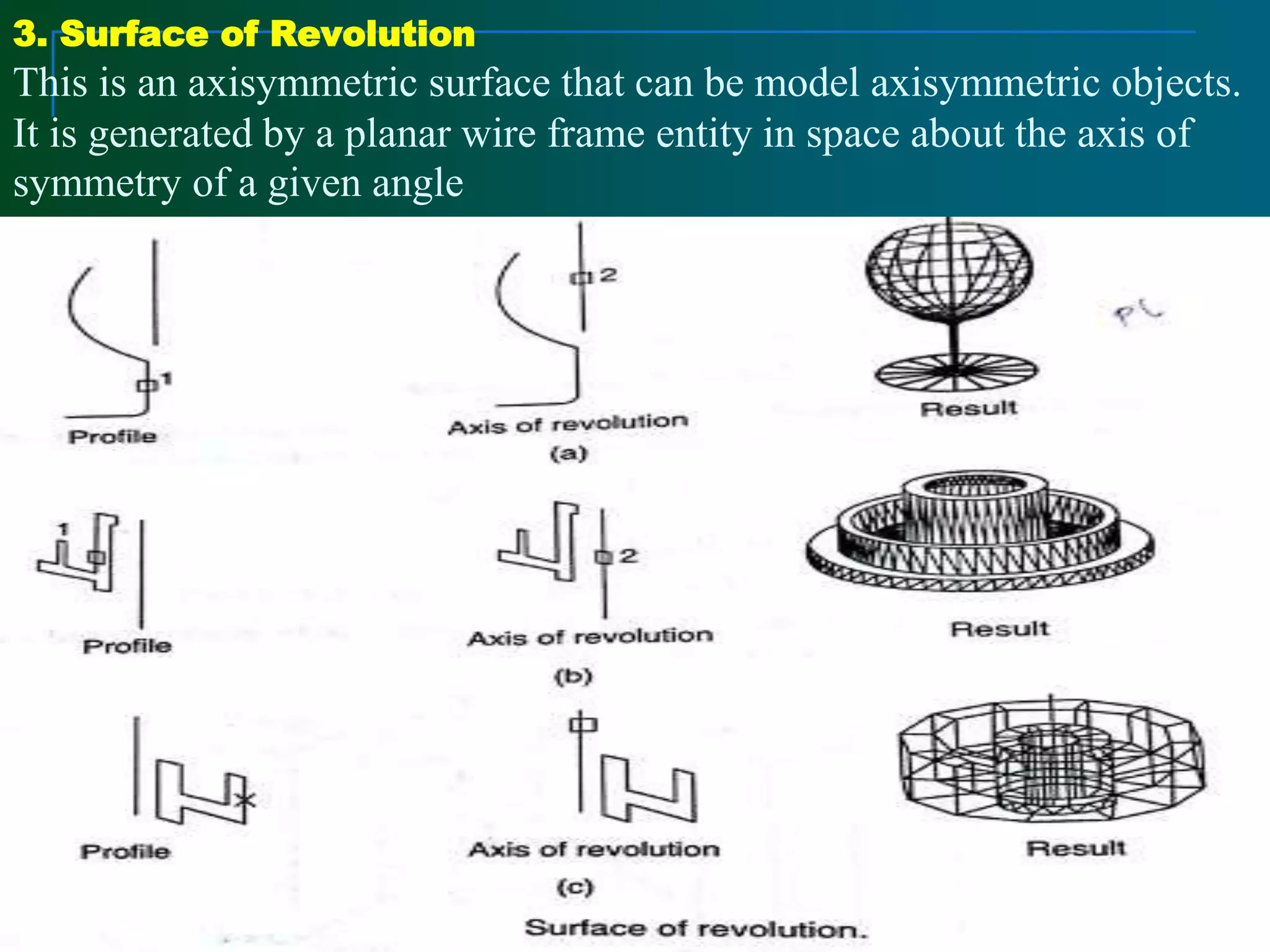
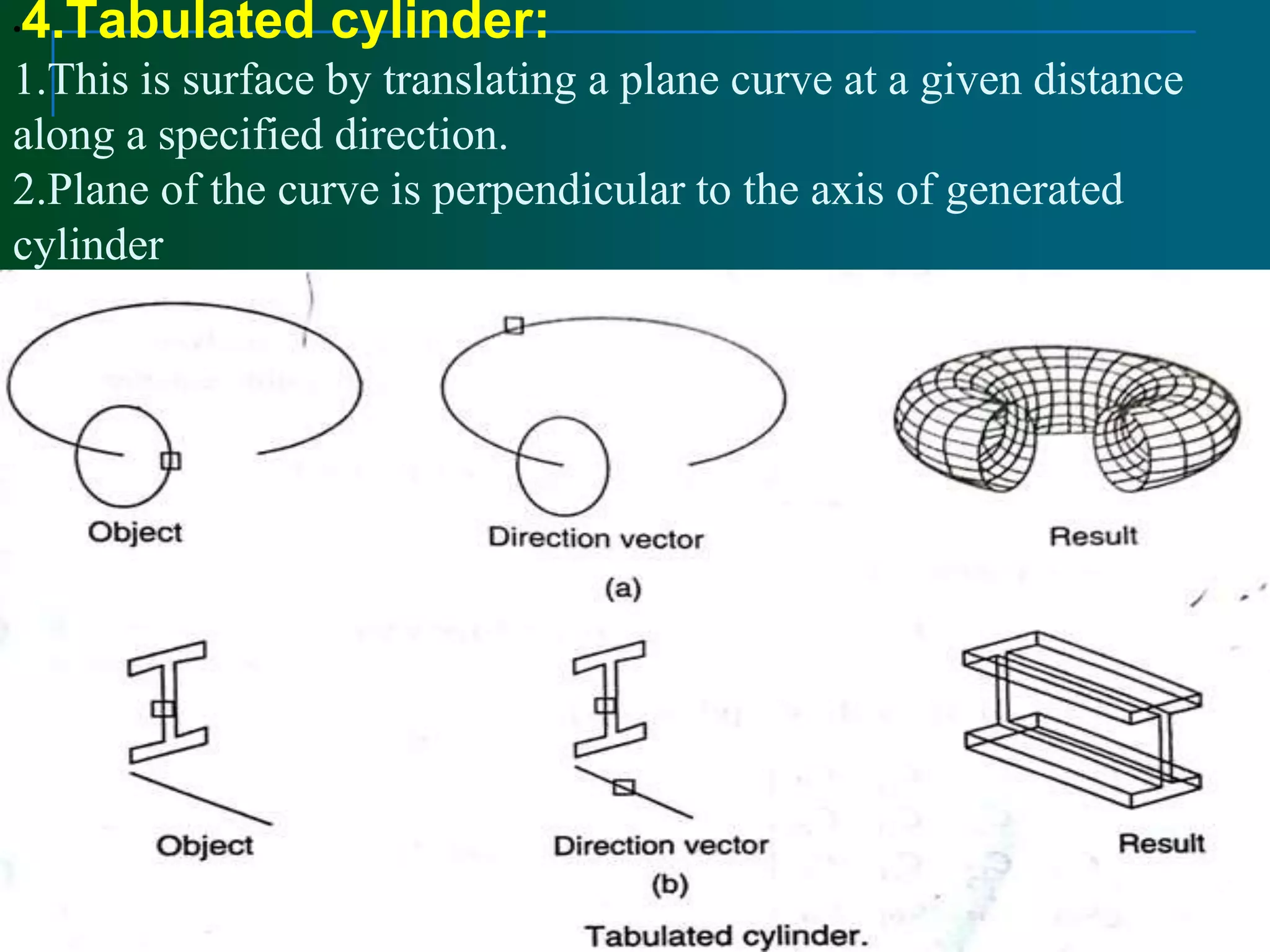
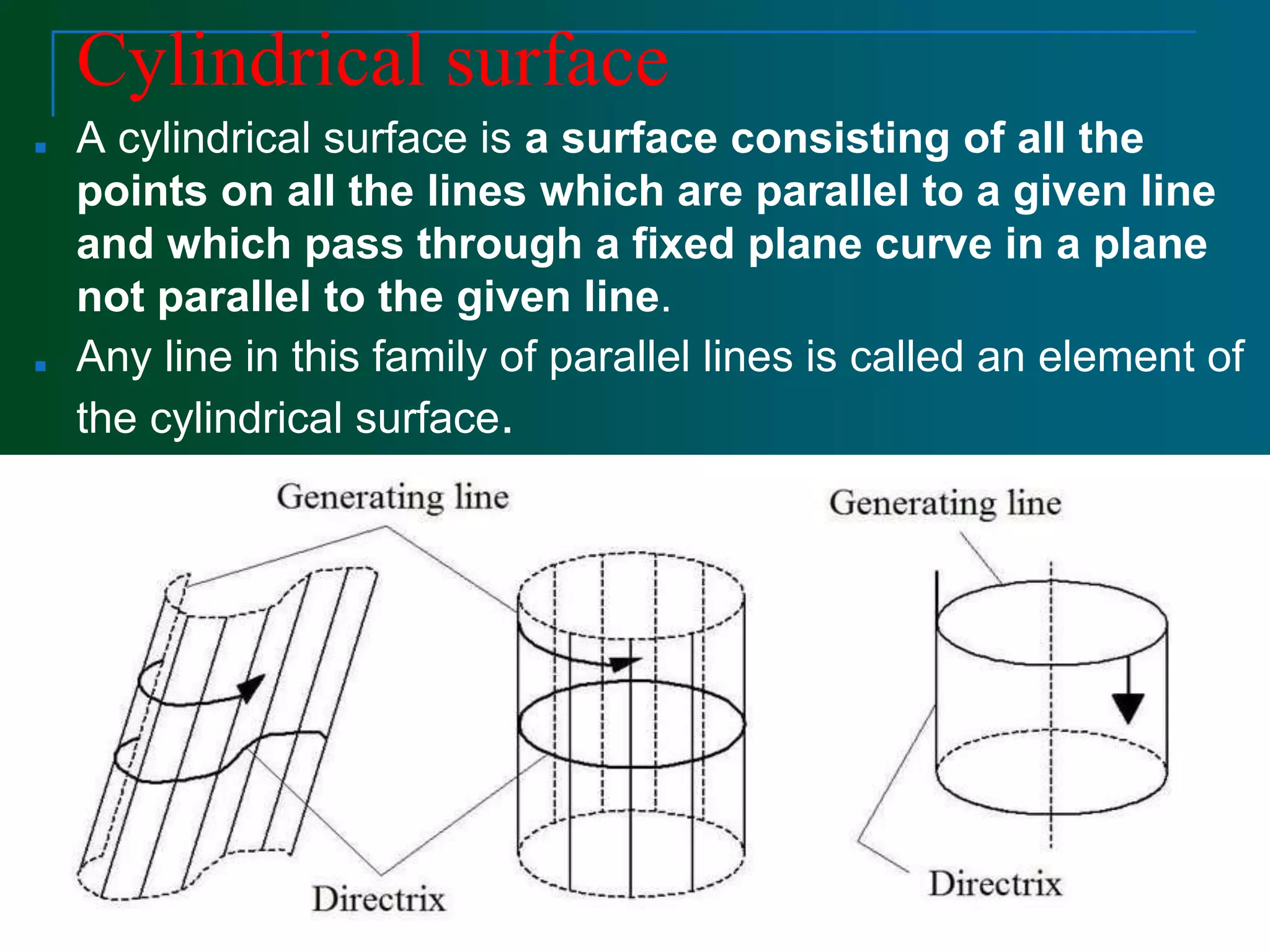
Surface modeling represents the surfaces of 3D objects and can be used to model complex shapes like vehicles, ships, and aircraft wings. There are two main types of surface modeling: parametric surfaces and implicit surfaces. Parametric surfaces use a set of equations to define the x, y, and z coordinates as functions of parameters u and v. Common parametric surface types include planes, ruled surfaces, surfaces of revolution, and tabulated cylinders. Implicit surfaces use a single polynomial equation to define the surface. Surface modeling provides more realistic representations than wireframe models and can be used for applications like finite element analysis, machining tool paths, and rendering models.