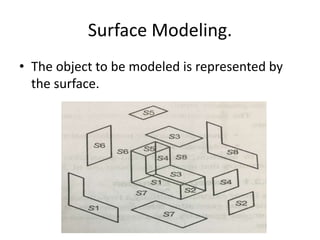
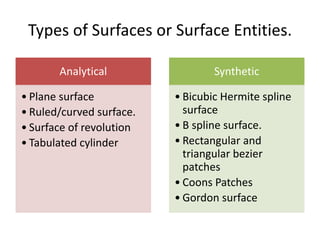
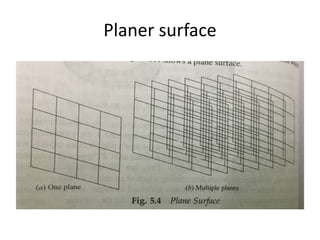
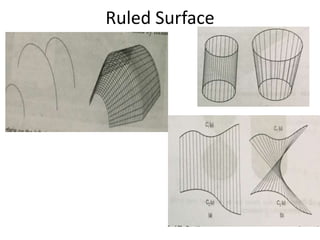
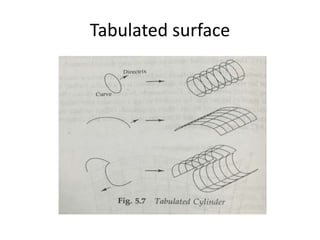
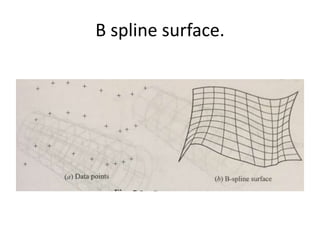
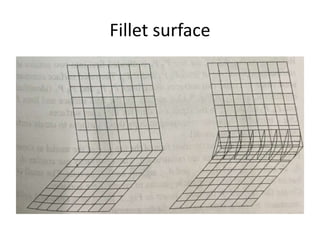
Surface modeling represents objects using surfaces rather than just lines and edges as in wireframe modeling. It uses wireframe entities to create surface entities that can represent sculpted surfaces like car bodies. Surface modeling provides more realistic representations for engineering tasks and allows for hidden line removal, shading, and calculations like interference checking and volume. However, it requires more computational resources and a trained user with mathematical skills. Common surface types include analytical surfaces like planes, ruled surfaces, and surfaces of revolution, as well as synthetic surfaces using splines, Bezier patches, and Coons patches.