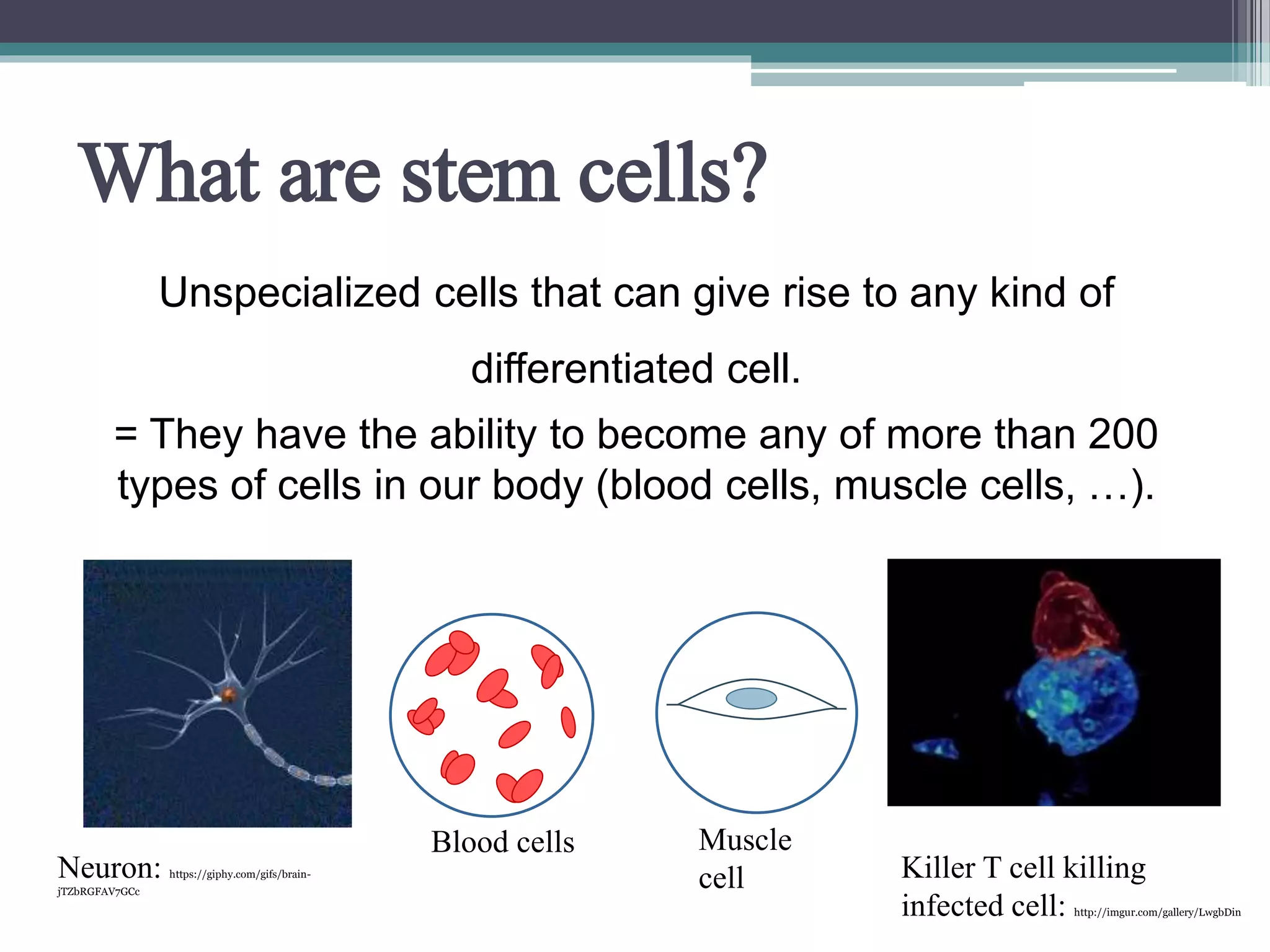
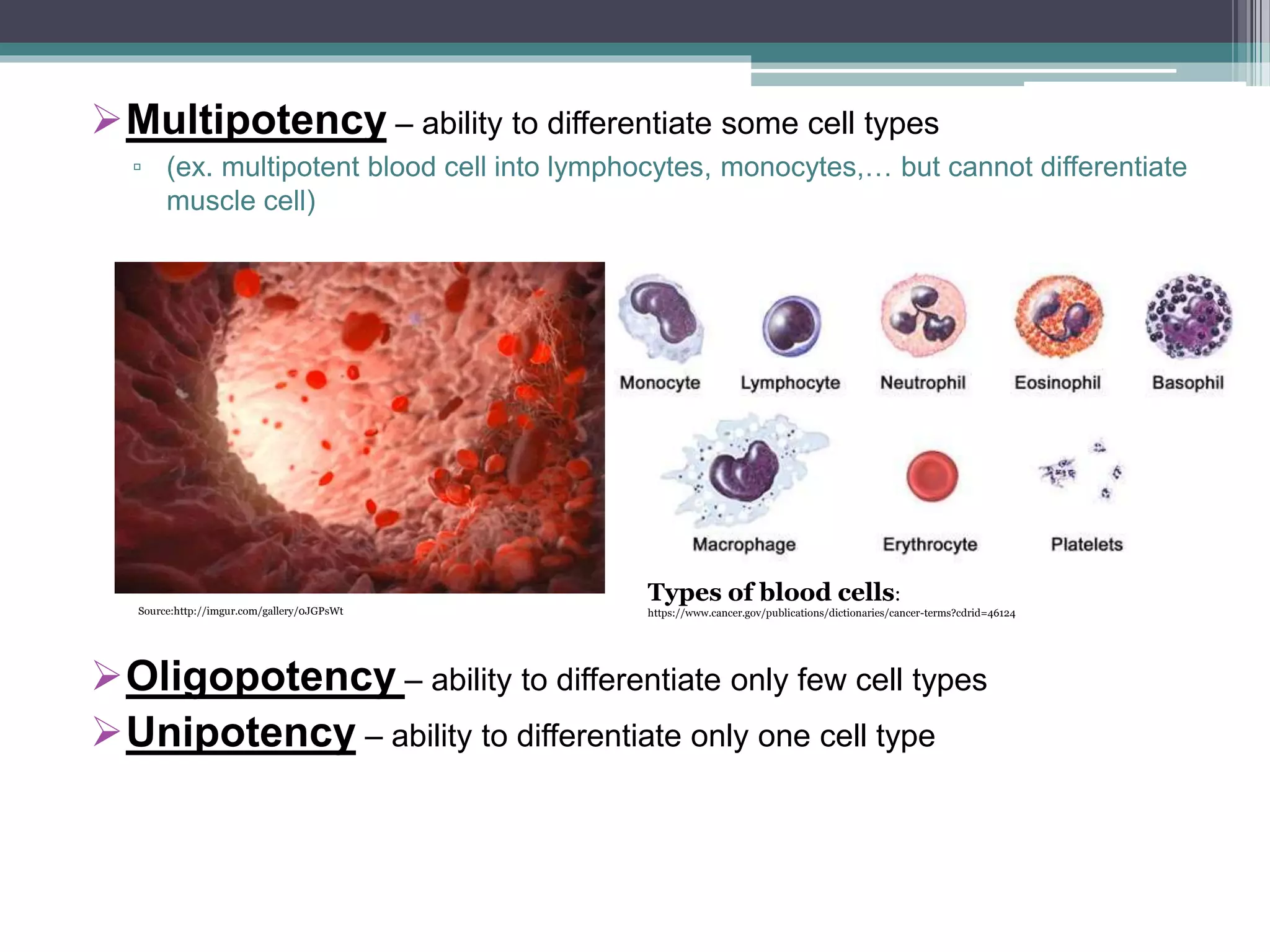
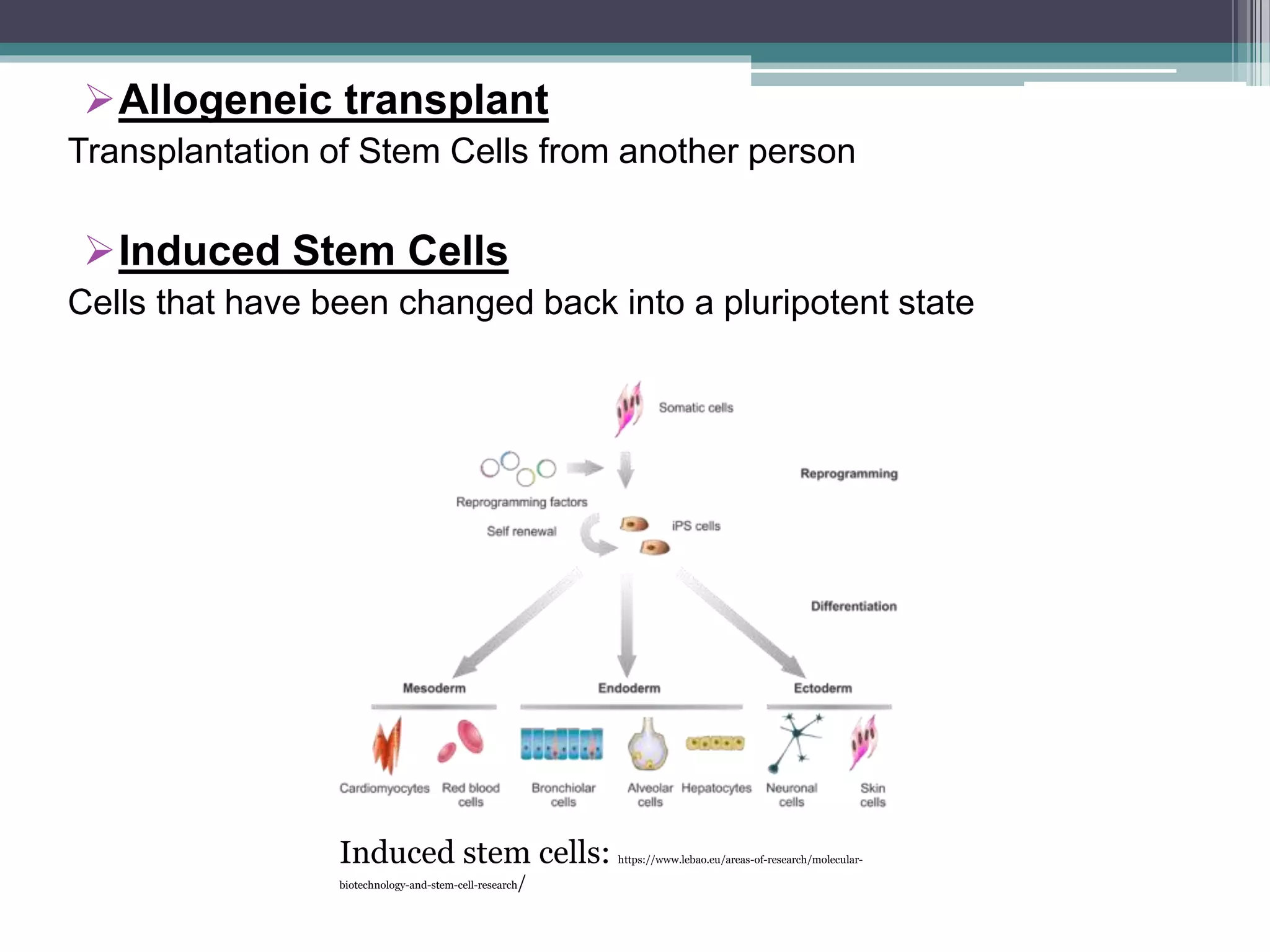
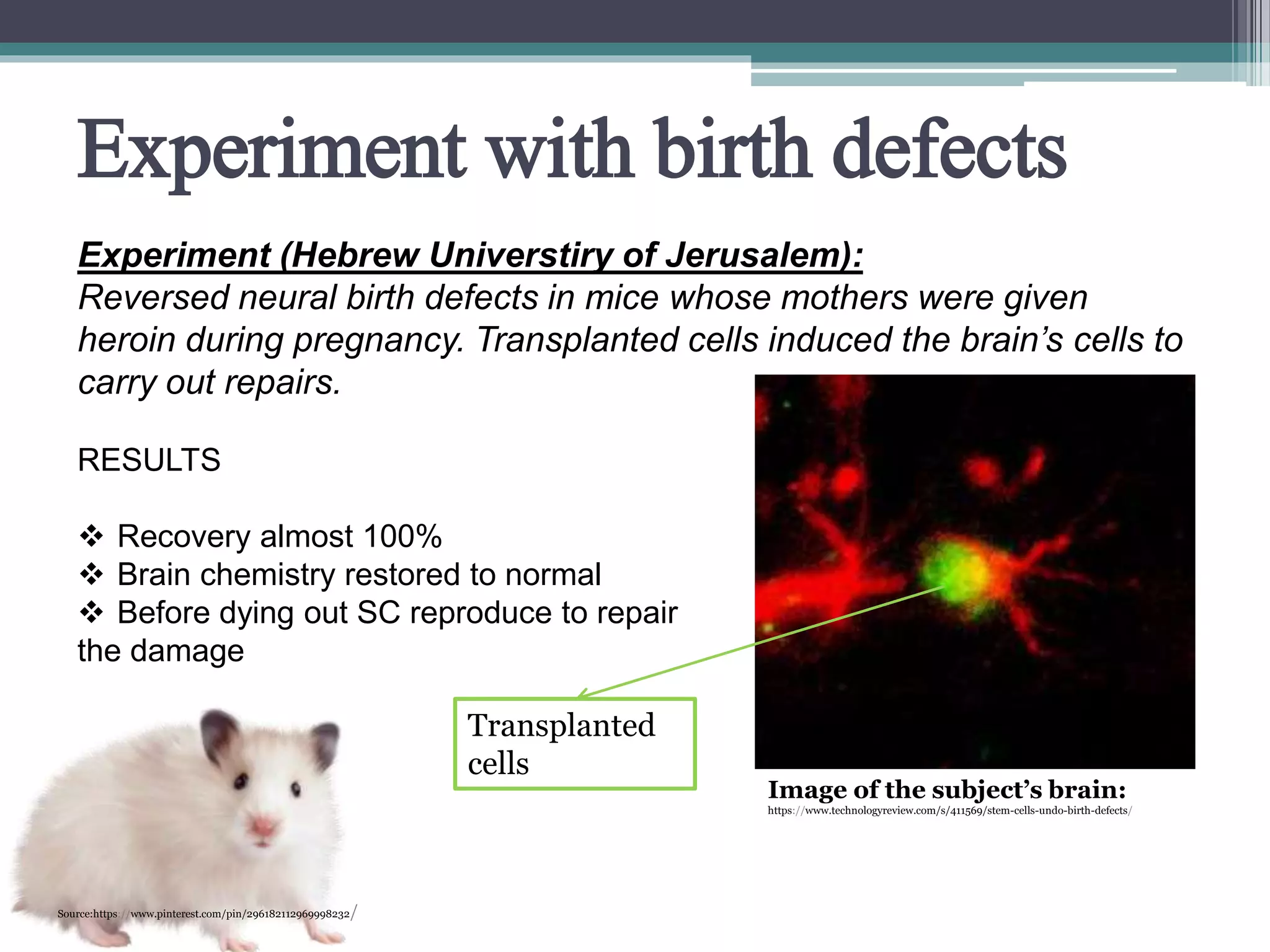
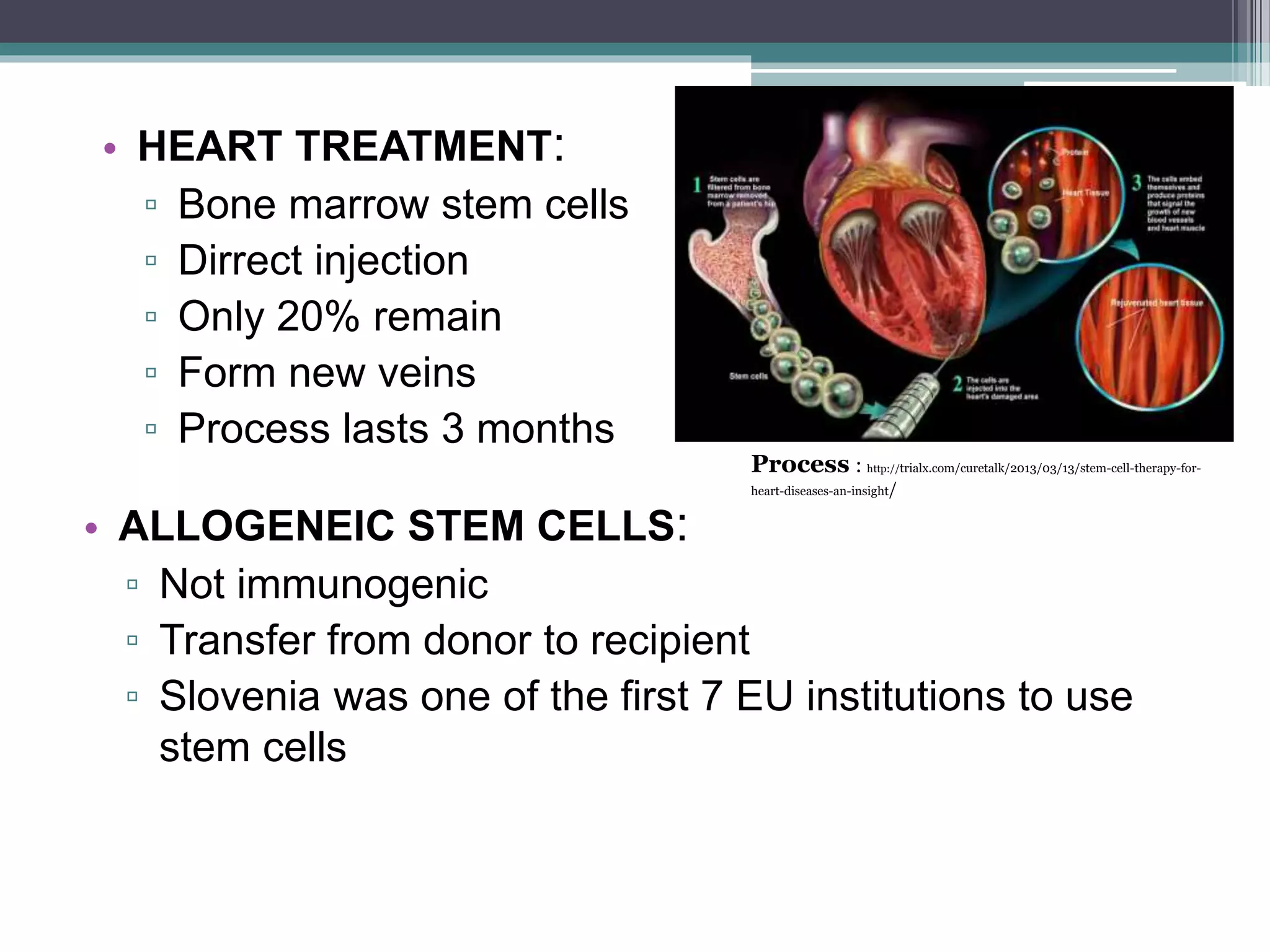
The document discusses stem cells, their types, and their potential therapeutic applications, including treating cardiovascular disease and birth defects. It outlines the history of stem cell research, the ethical considerations surrounding it, and the progress made in Slovenia's stem cell treatments. Future prospects for stem cell therapies are highlighted, addressing conditions like macular degeneration, spinal cord injuries, and diabetes.