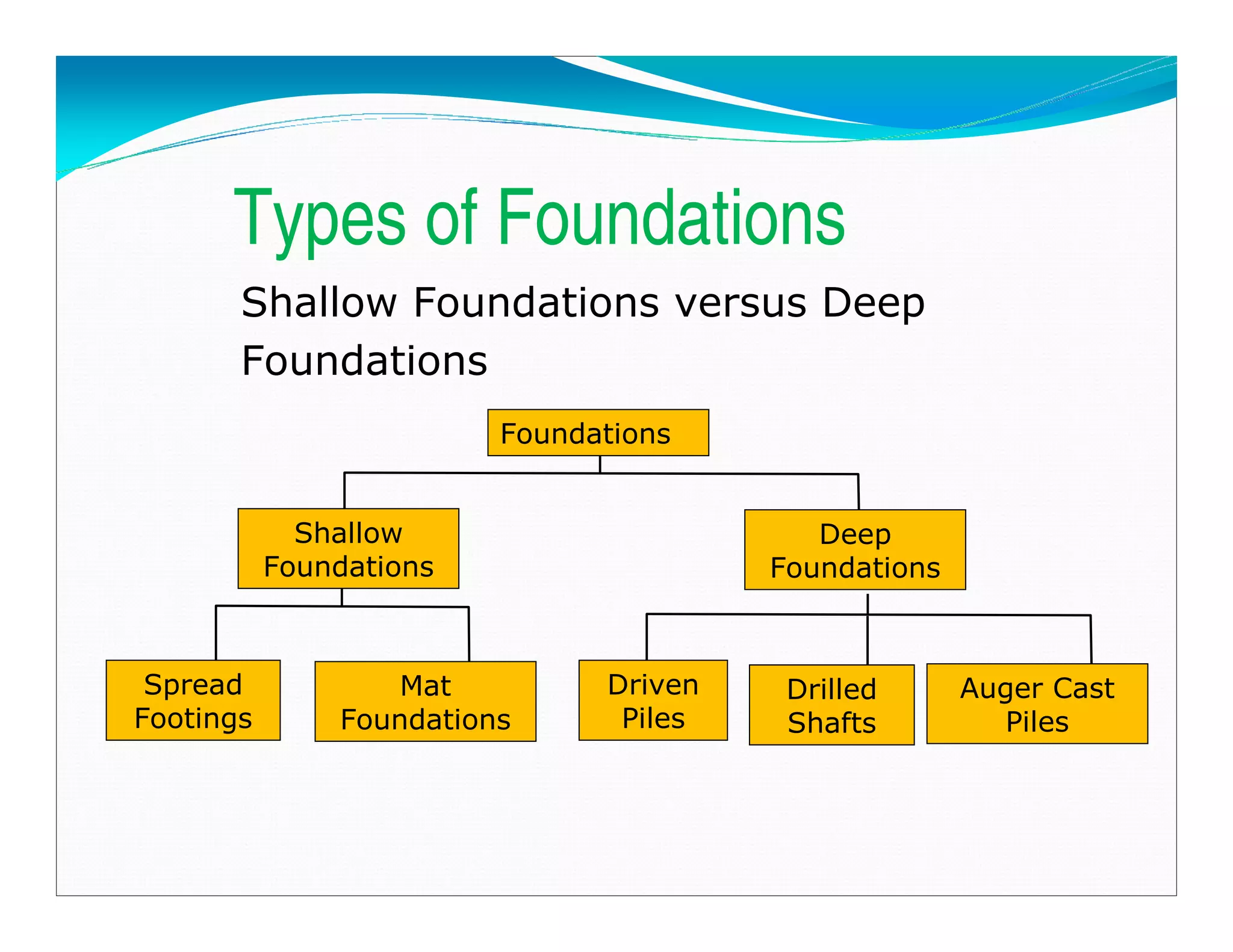
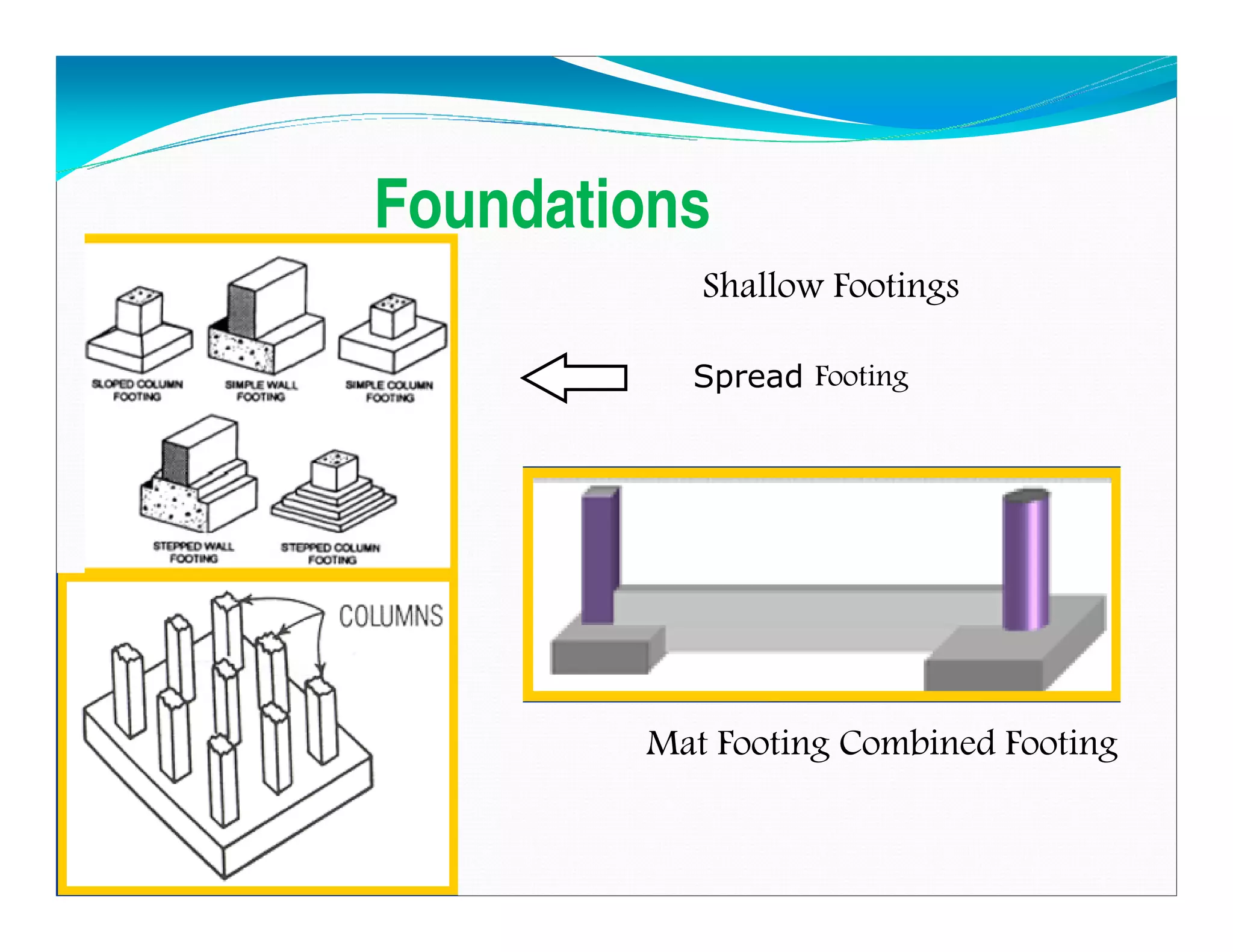
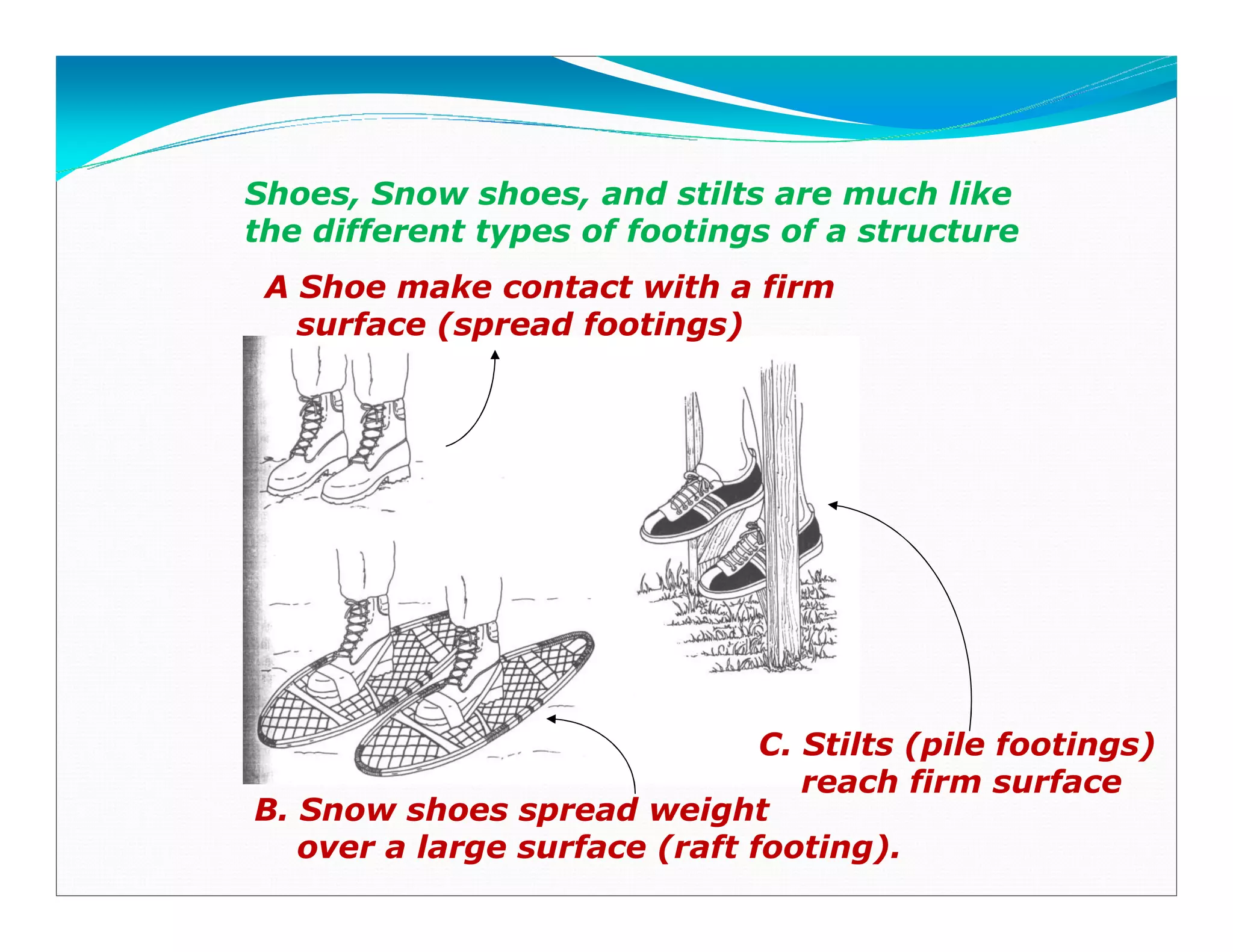
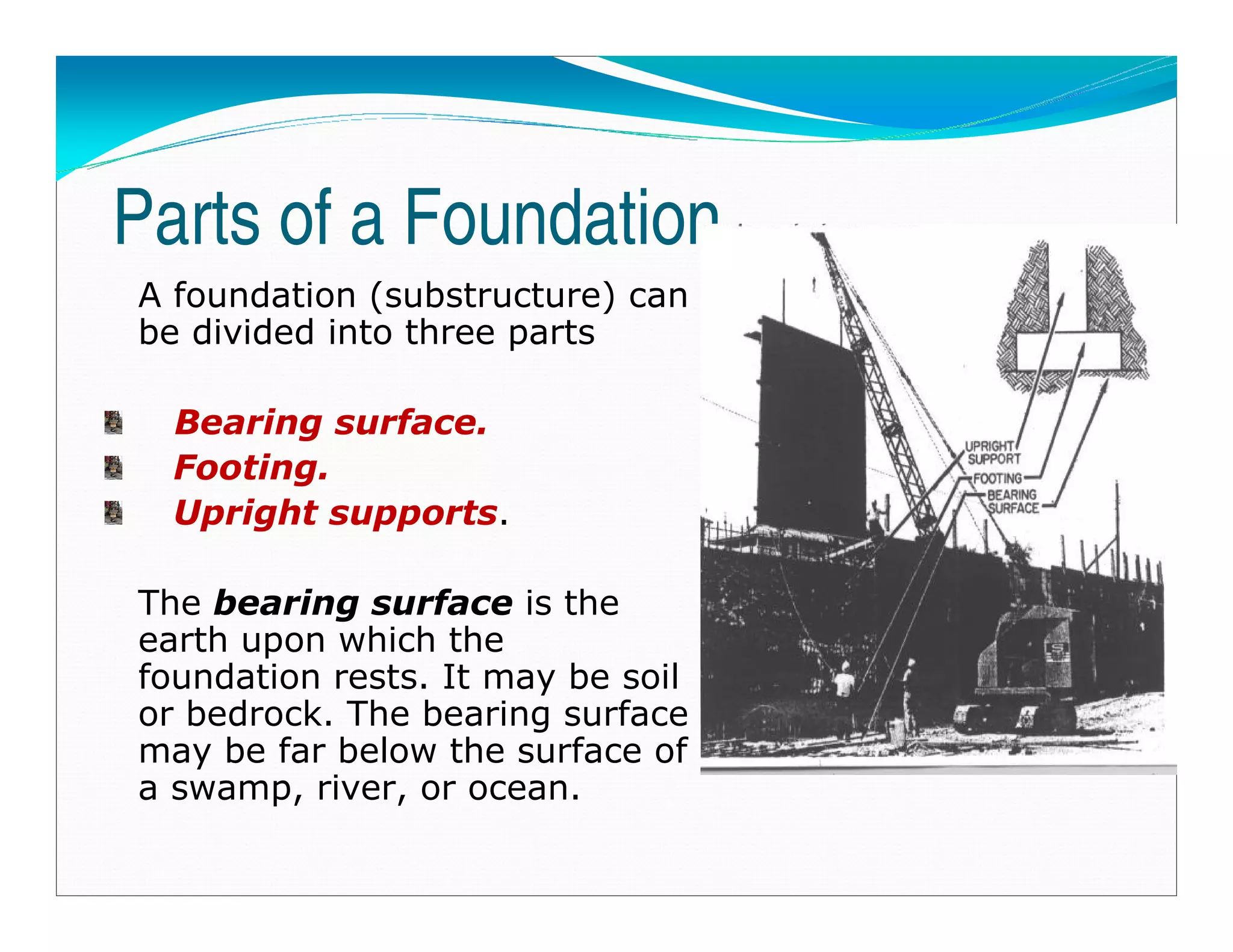
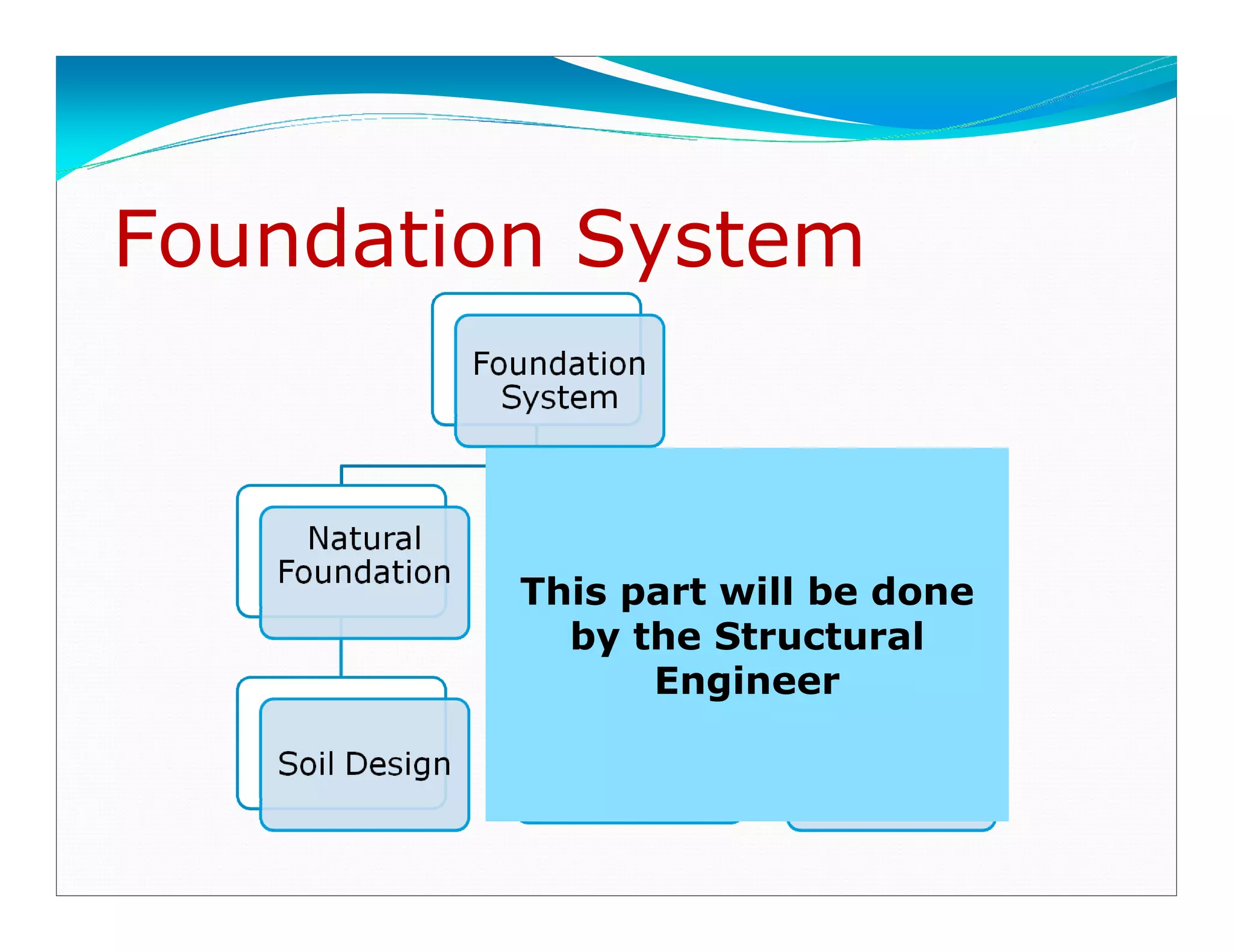
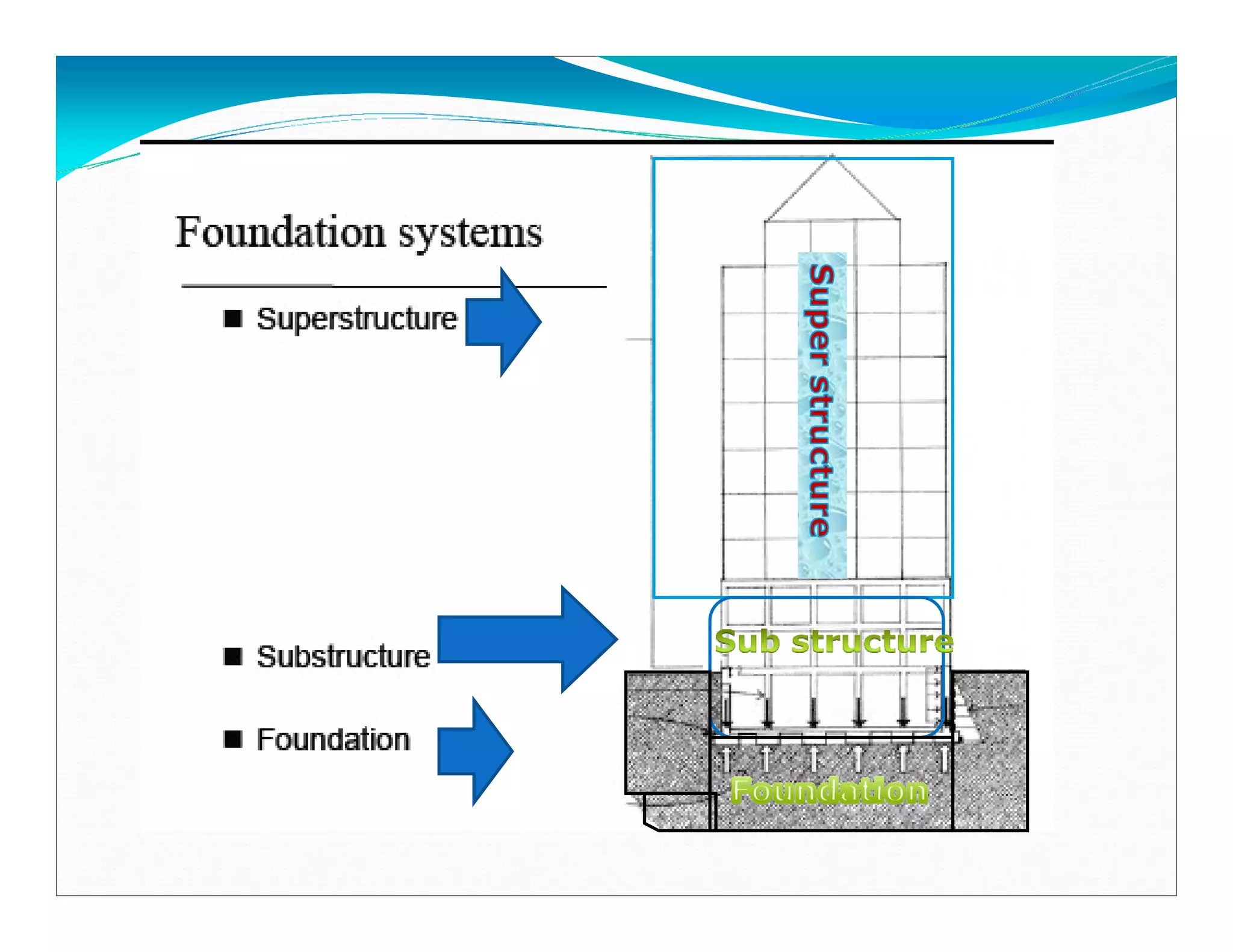
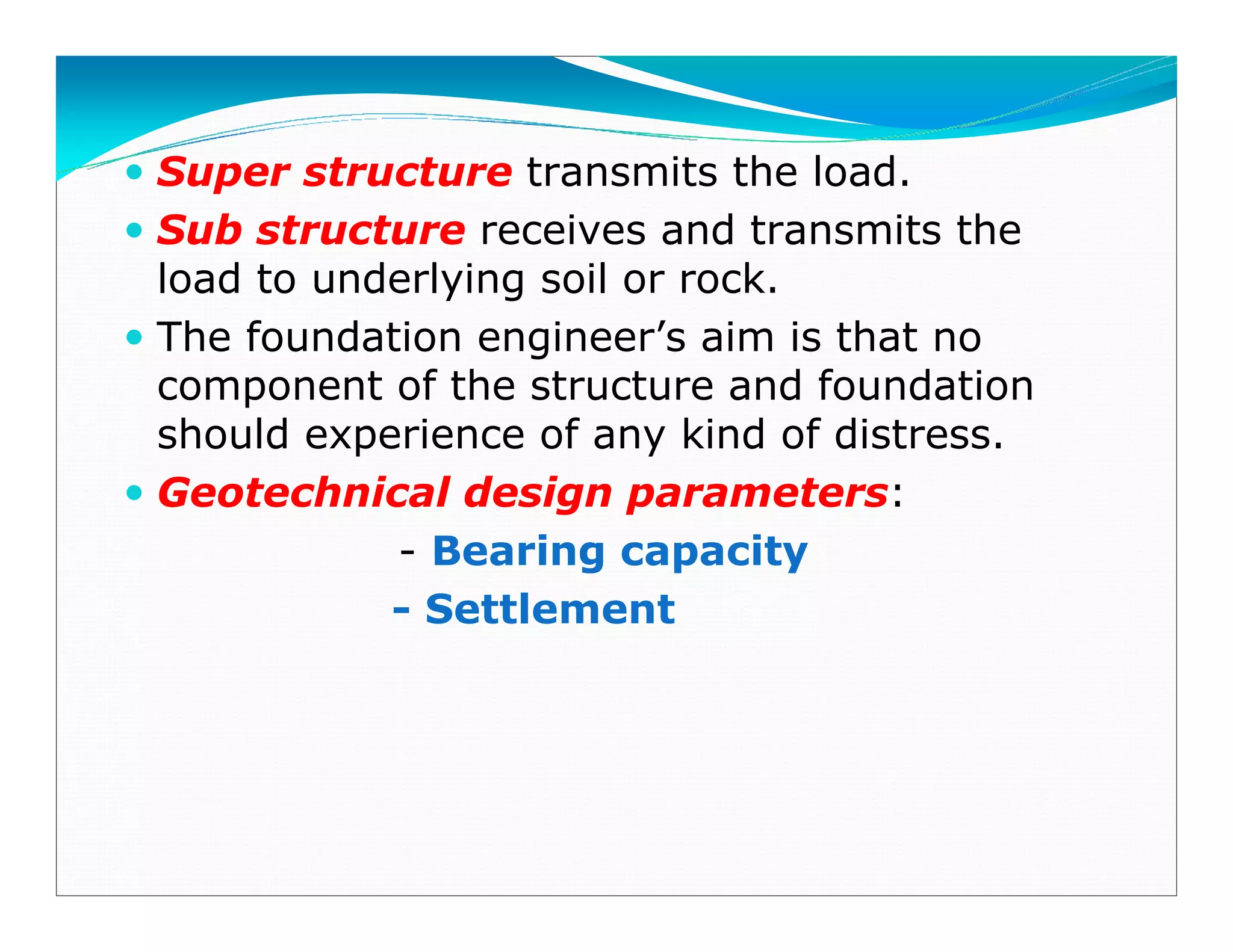
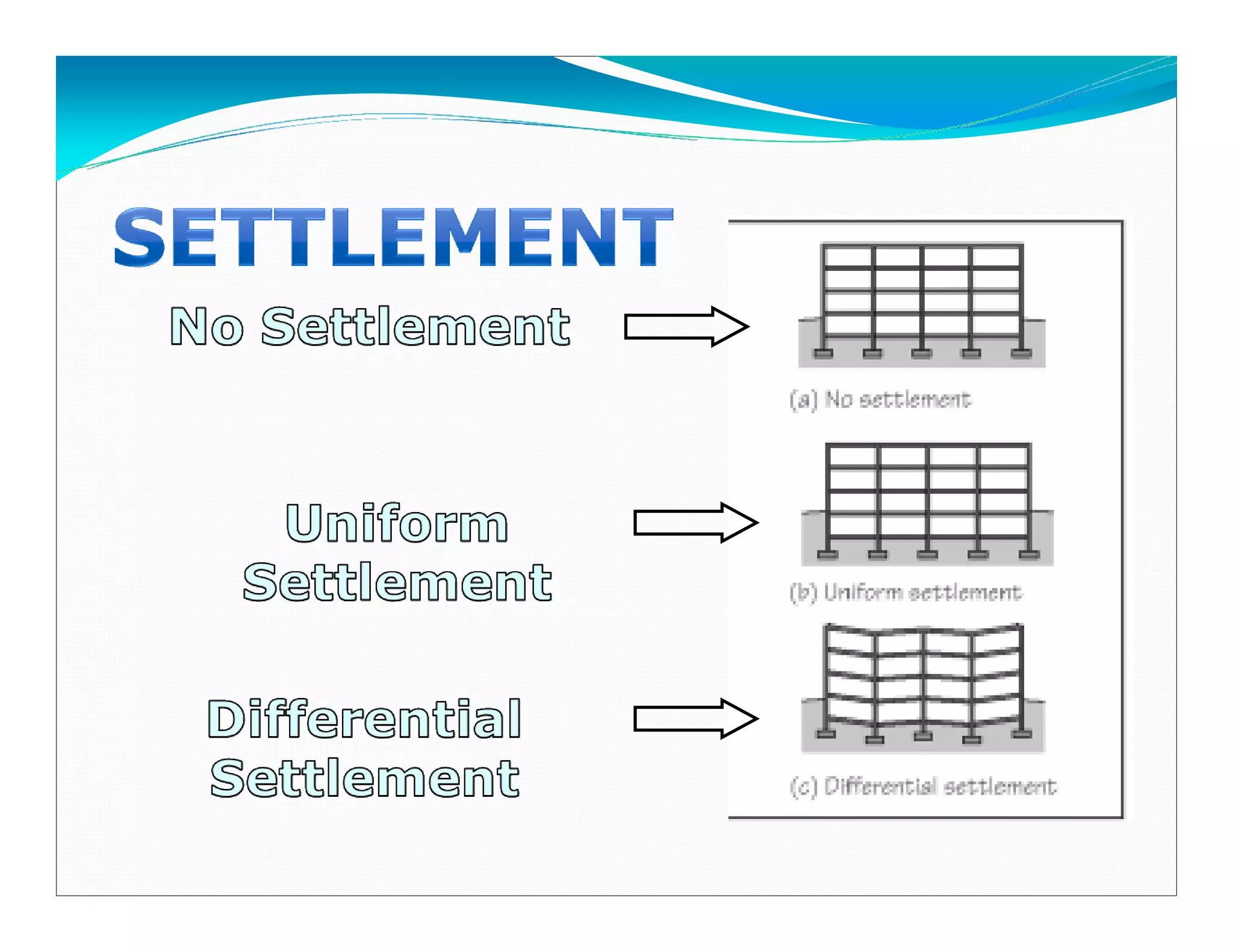
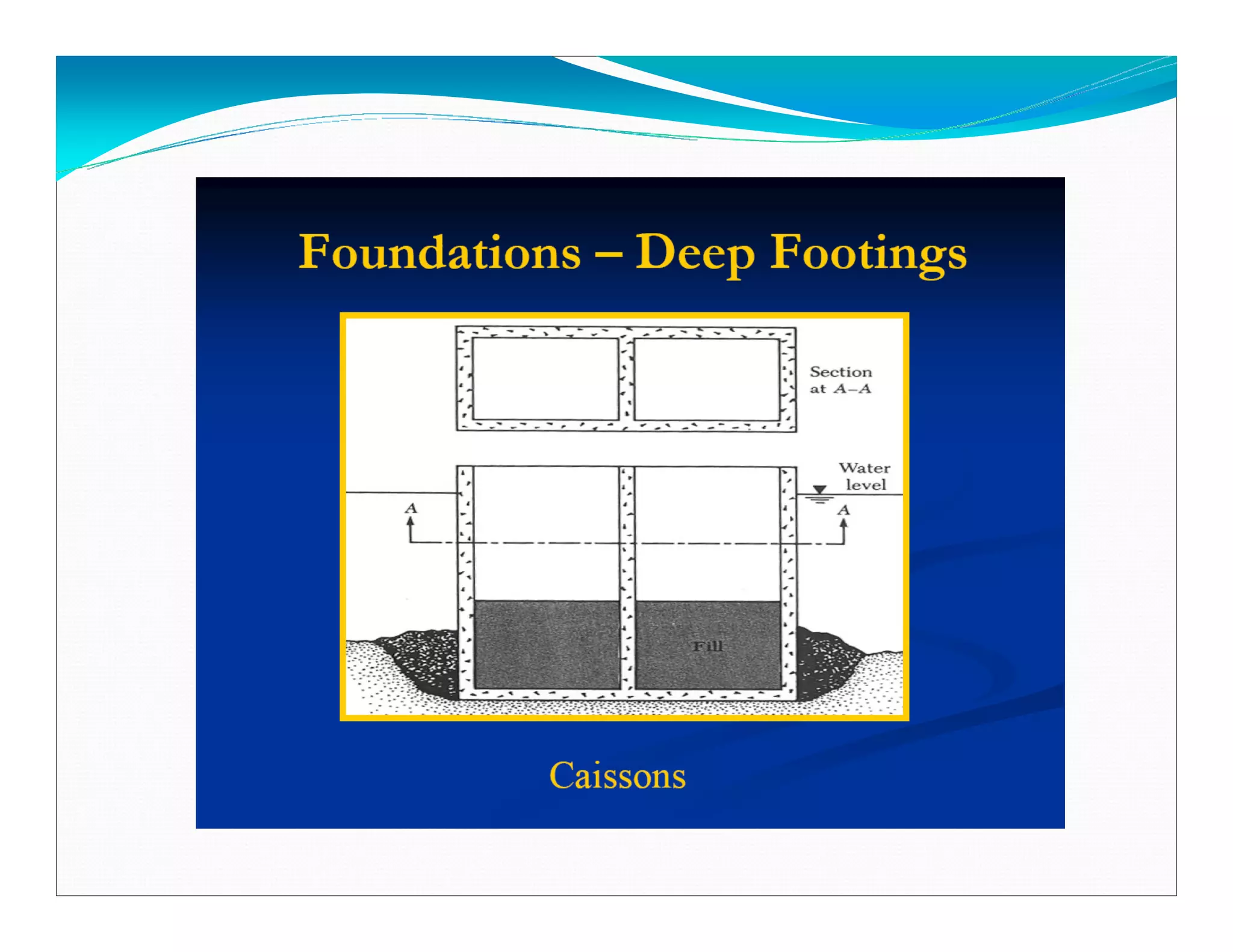
This document outlines the syllabus for a foundation engineering course. It covers topics such as soil exploration, shallow foundations, deep foundations, earthen dams, and foundations on difficult soils. The course will explore soil testing methods, bearing capacity calculations, pile load capacity, and dam design considerations. References textbooks on geotechnical engineering and foundation design are also listed.