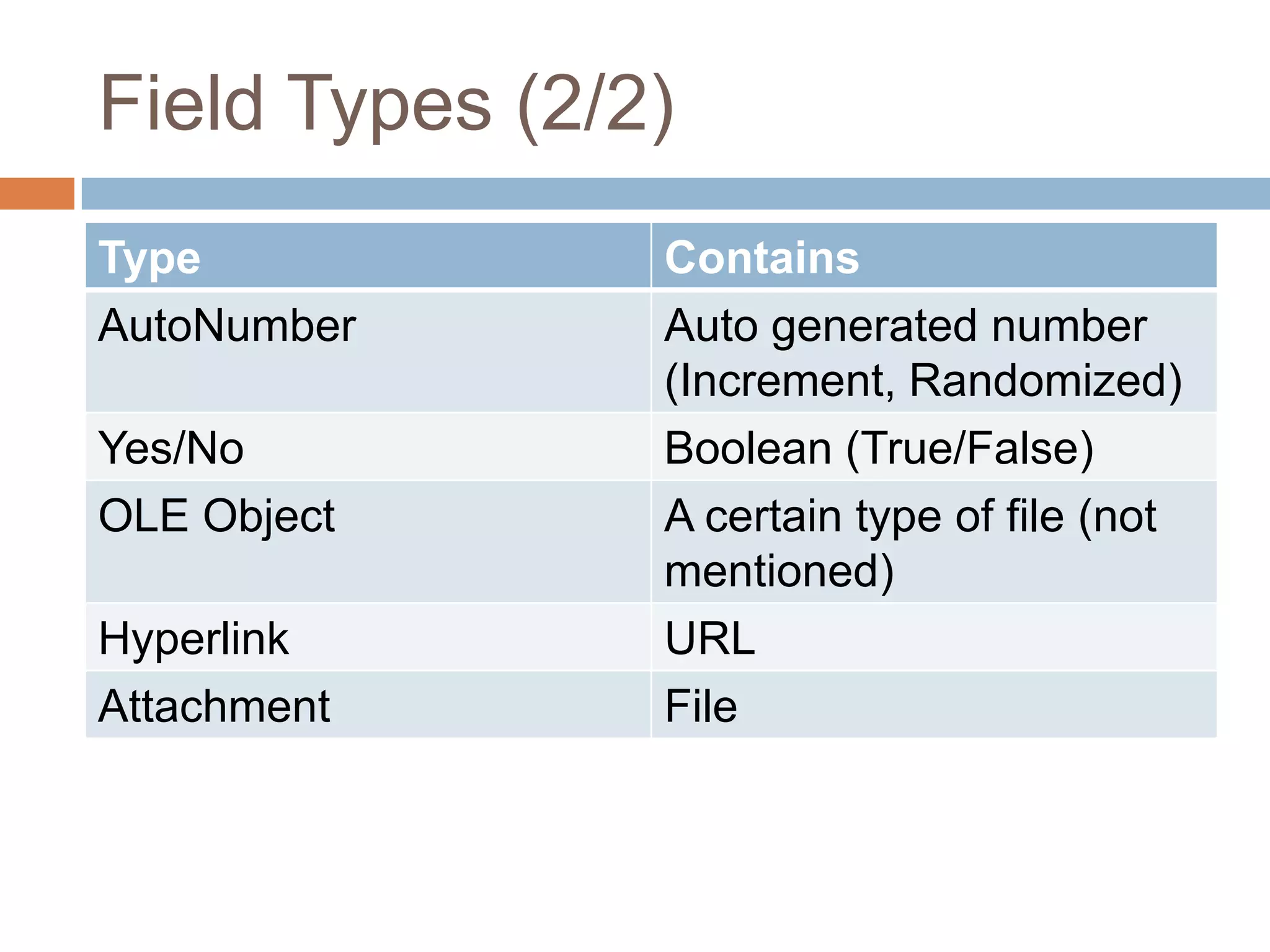
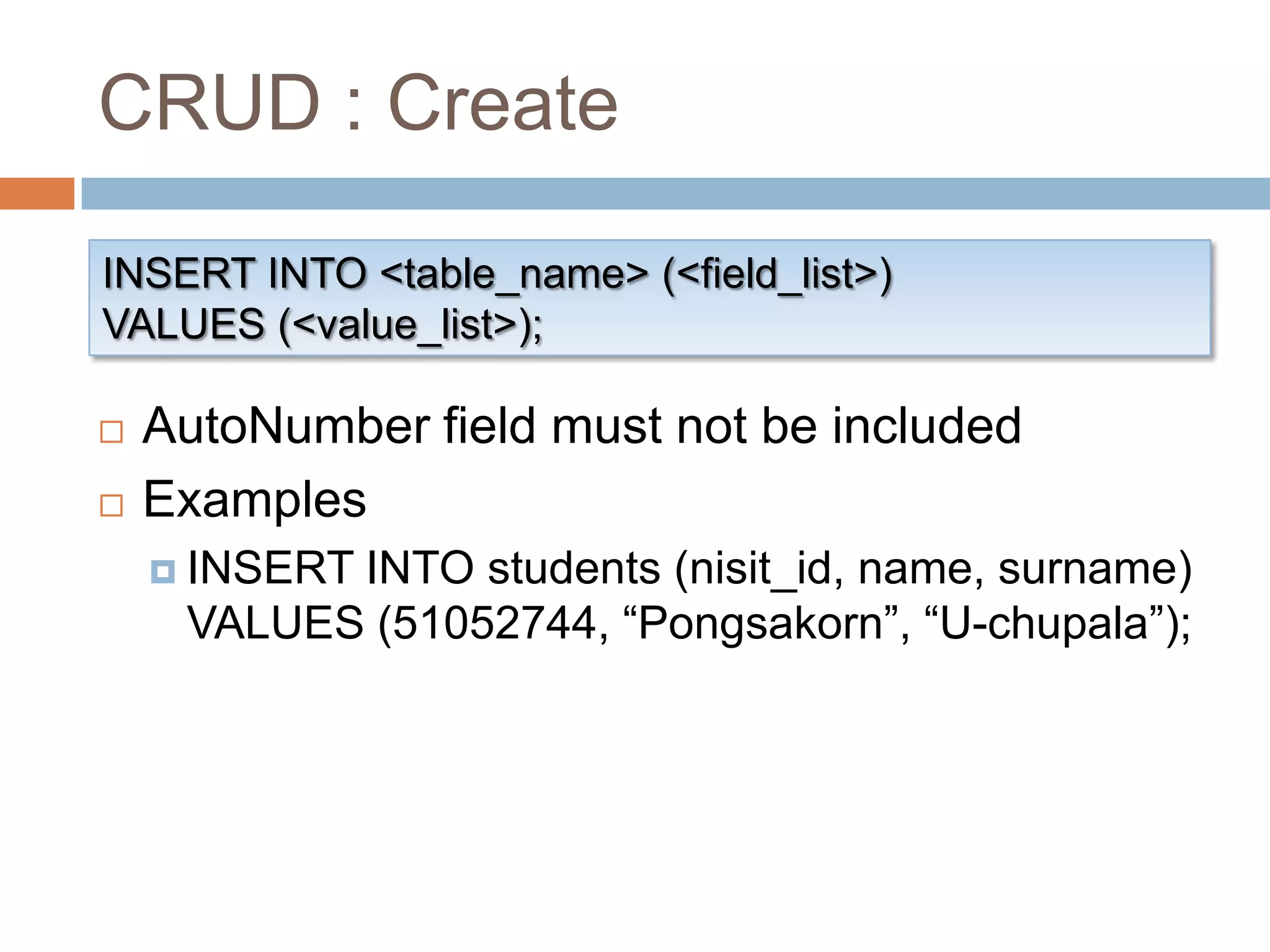
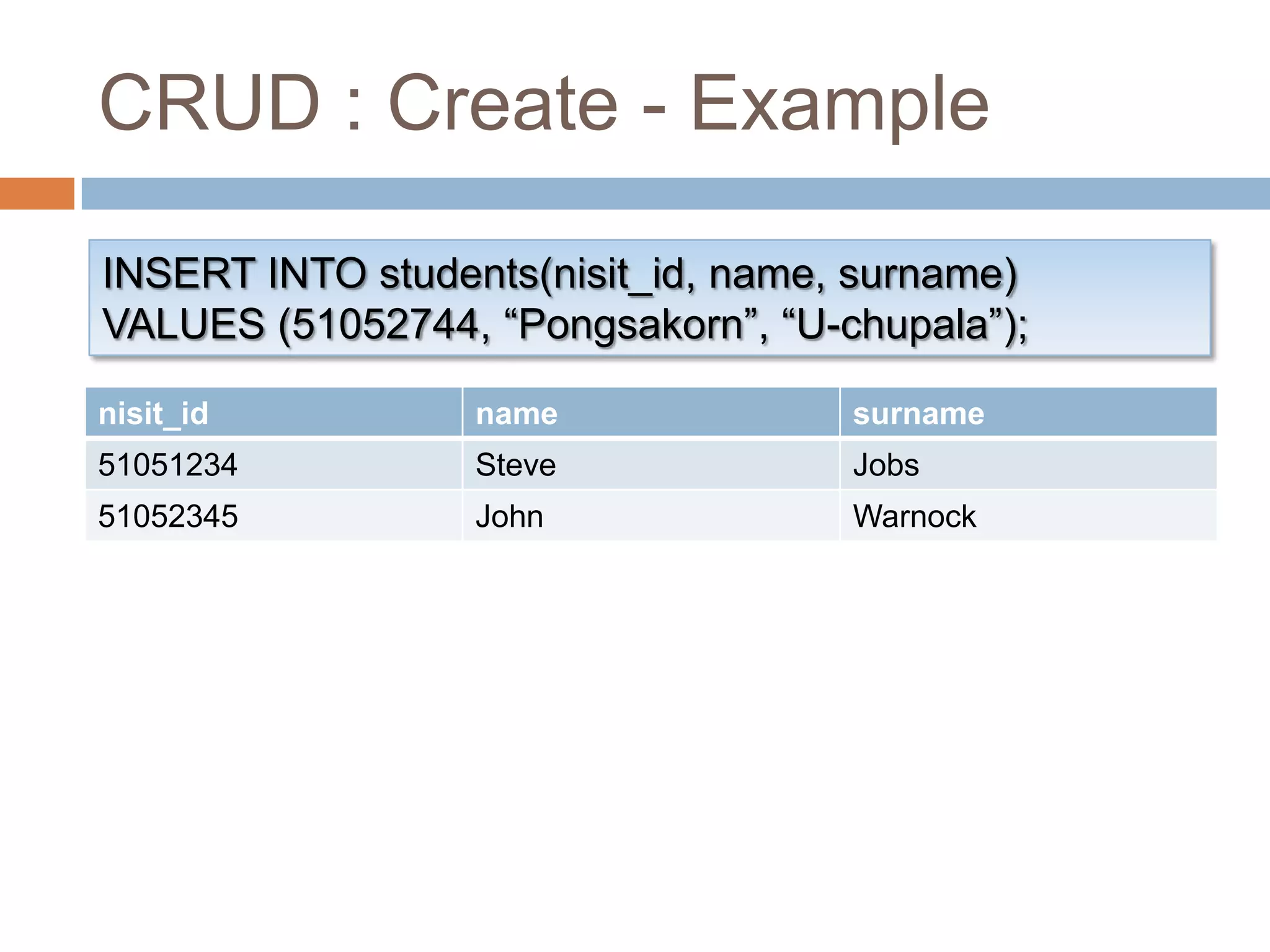
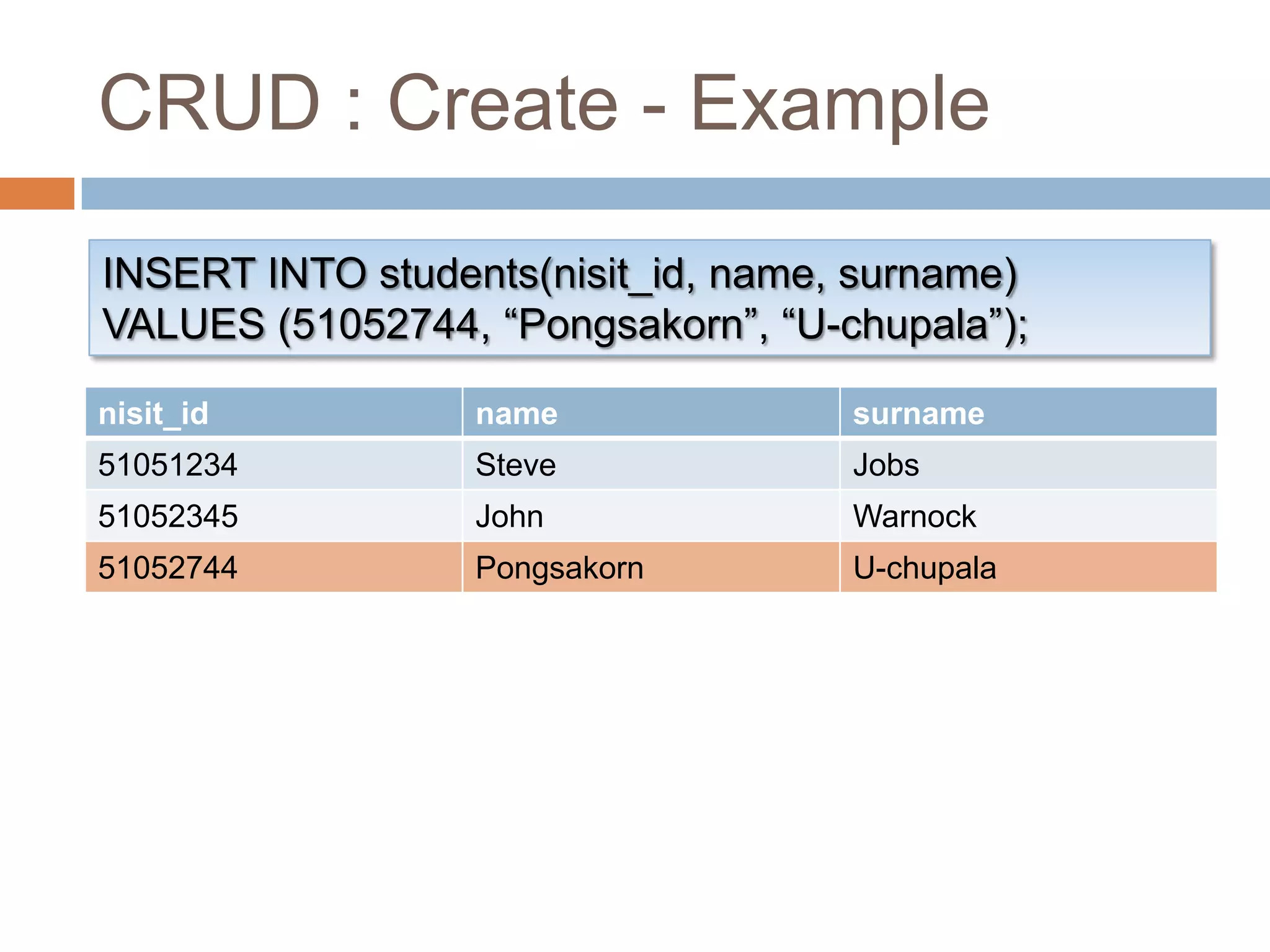
This document provides an introduction and overview of databases and the basic operations used to manage data in a database using Microsoft Access 2007. It defines what a database is, how data is organized in tables with rows and columns, and when it is appropriate to use a database. It also outlines and provides examples of the basic CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations used in structured query language (SQL) to manipulate data, including inserting, selecting, updating, and deleting records from database tables.








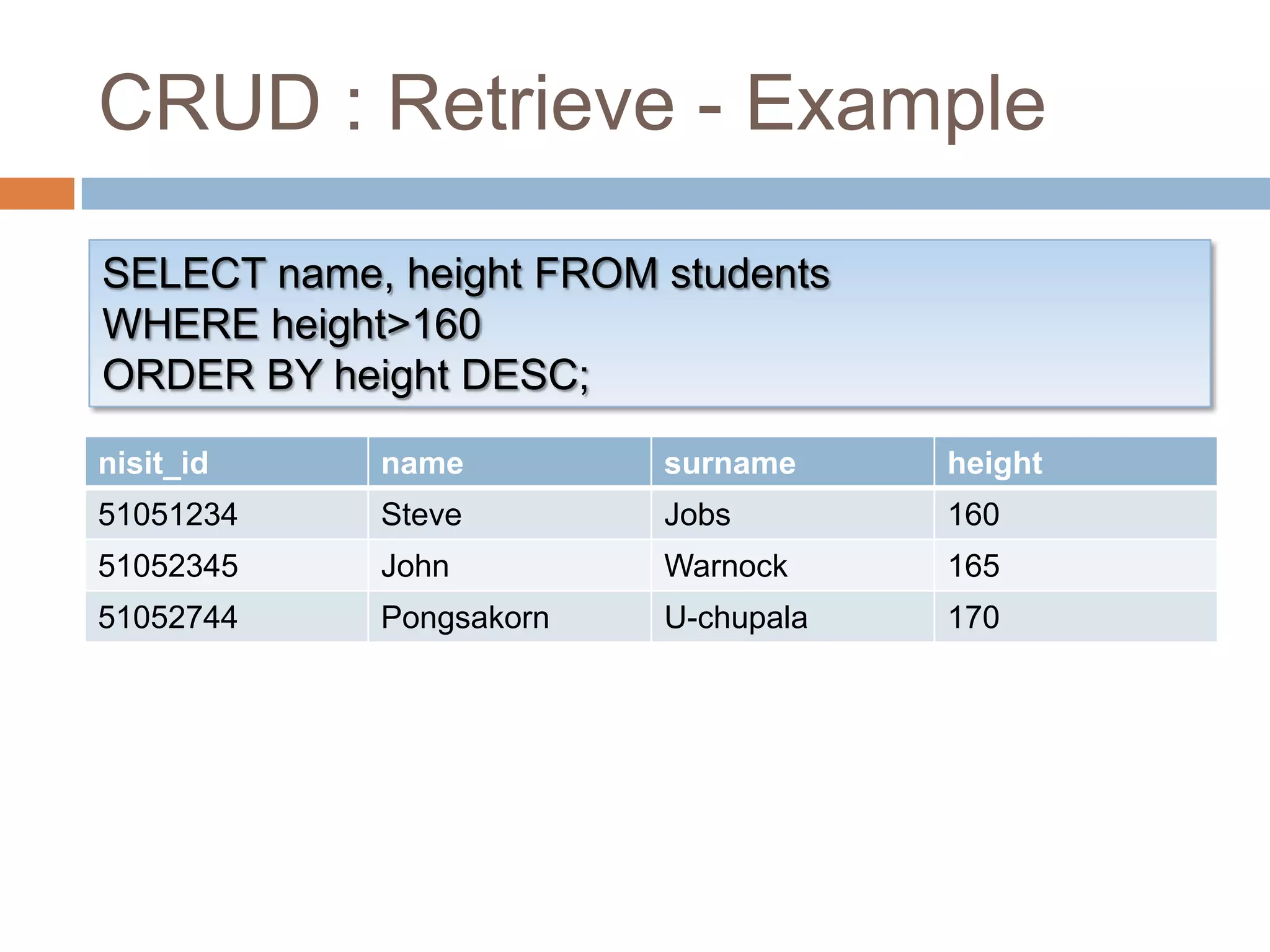
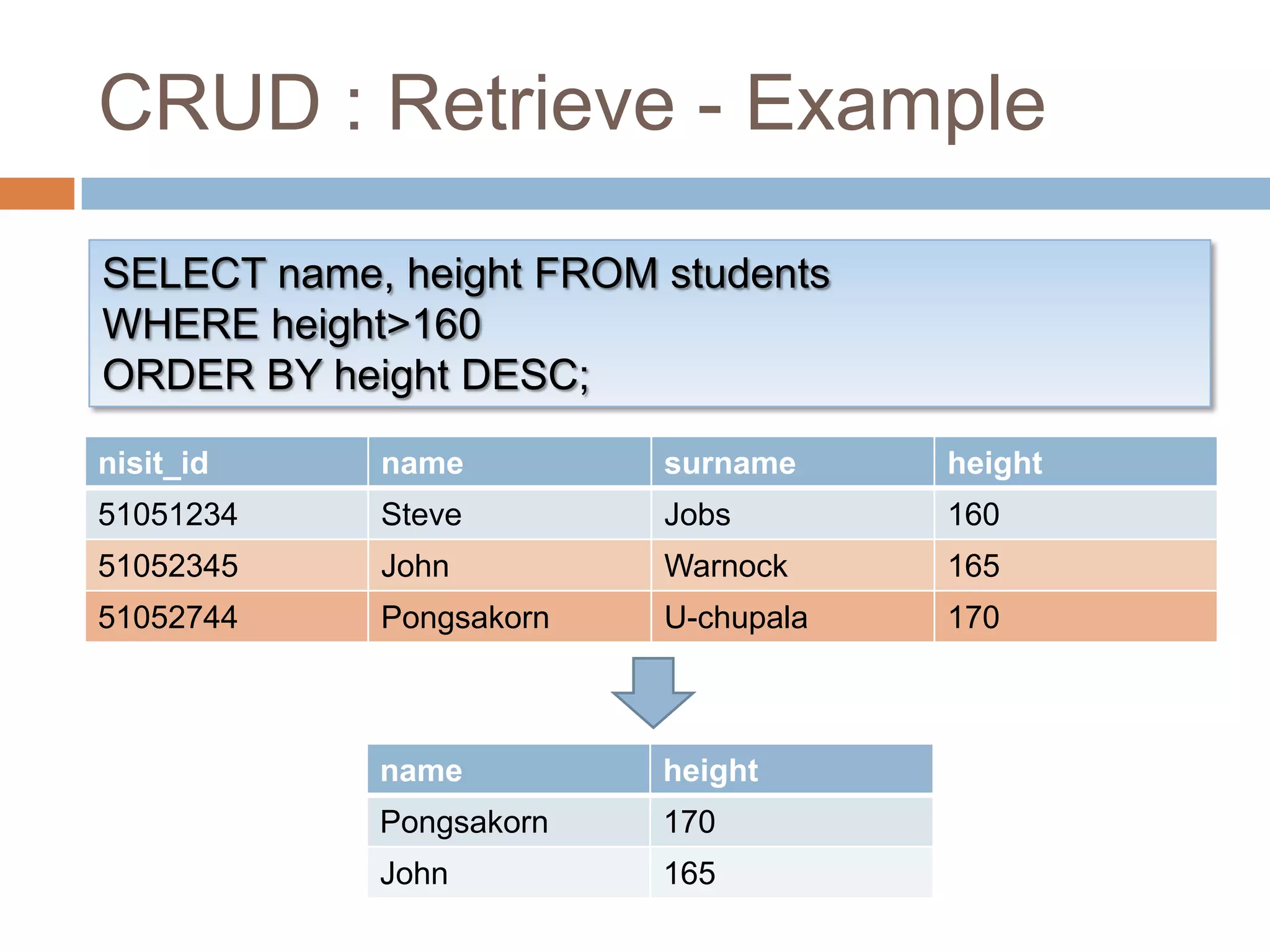
![CRUD : RetrieveSELECT <select_list> FROM <table_name>[ WHERE <search_condition> ][ ORDER BY <order_expression> [ ASC | DESC ] ];Select which fields to retrieve ExamplesSELECT field_1, field_2 FROM table_name …SELECT * FROM table_name …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatabase-100518082143-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-database-22-2048.jpg)
![CRUD : RetrieveSELECT <select_list> FROM <table_name>[ WHERE <search_condition> ][ ORDER BY <order_expression> [ ASC | DESC ] ];Available operators: =, <, >, <=, >=, <>Modifiers: AND, OR, NOT, ()Examples… WHERE student_id=1 …… WHEHE (<cond1>) AND (<cond2>) …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatabase-100518082143-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-database-23-2048.jpg)
![CRUD : RetrieveSELECT <select_list> FROM <table_name>[ WHERE <search_condition> ][ ORDER BY <order_expression> [ ASC | DESC ] ];Sort results by order expression ascending (default) or descendingExpression can be chained togetherExamples… ORDER BY date DESC …… ORDER BY name ASC, surname ASC …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatabase-100518082143-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-database-24-2048.jpg)

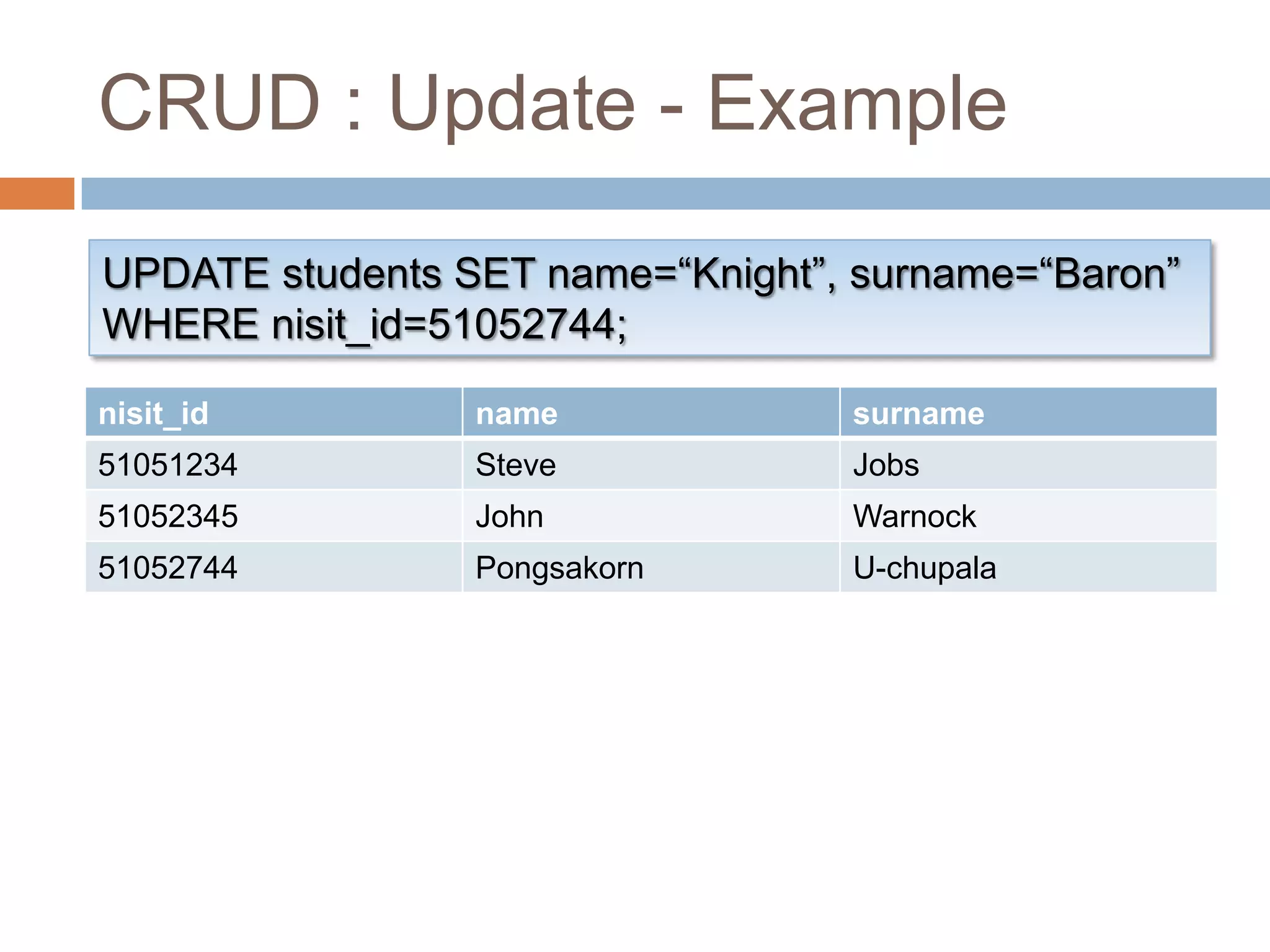
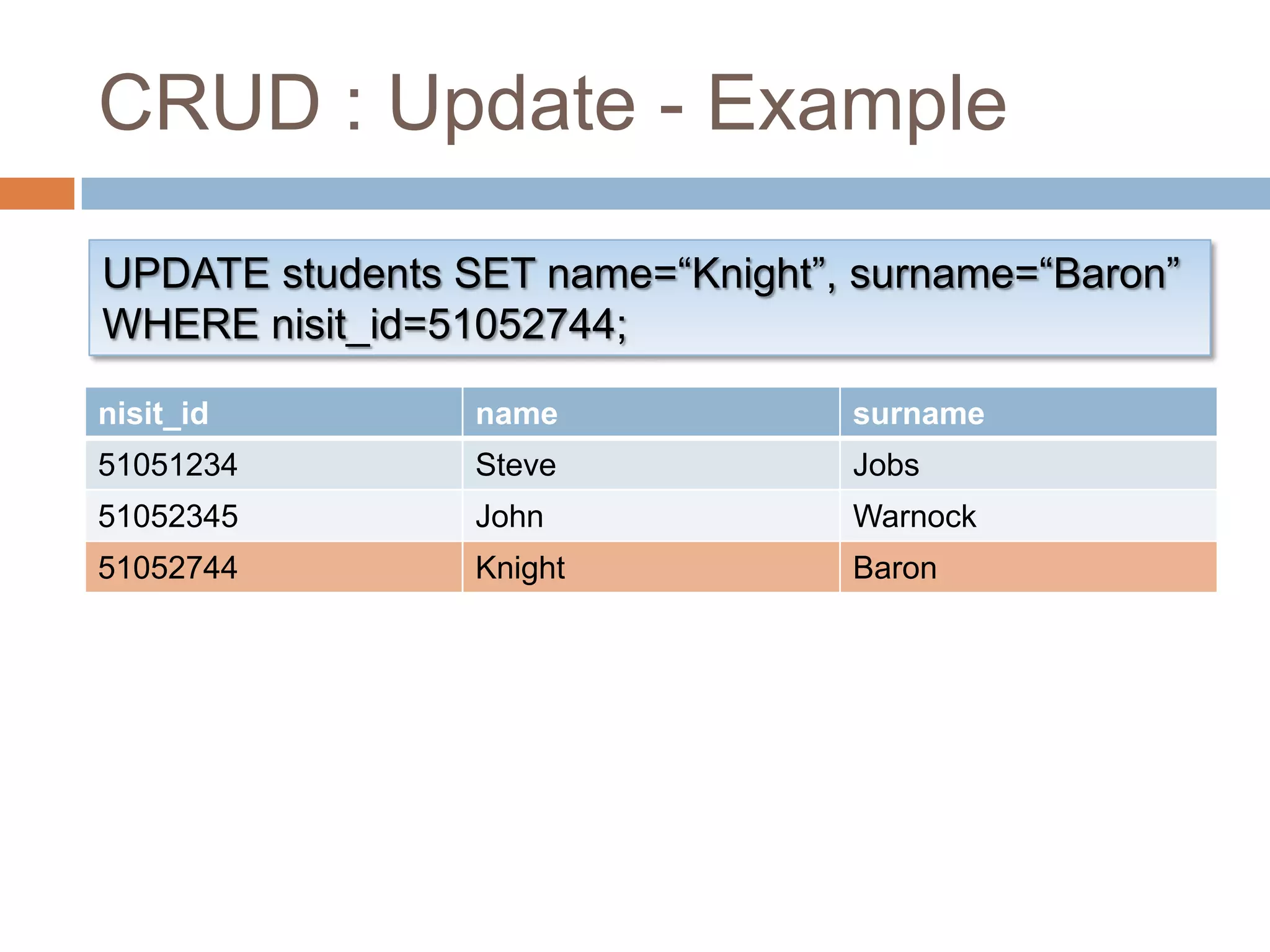
![CRUD : UpdateUPDATE <table_name> SET <field_value_list>[ WHERE <search_condition> ];Update every record that match the search conditionWe usually use primary key for thisExamplesUPDATE students SET name=“Knight”, surname=“Baron” WHERE nisit_id=1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatabase-100518082143-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-database-28-2048.jpg)