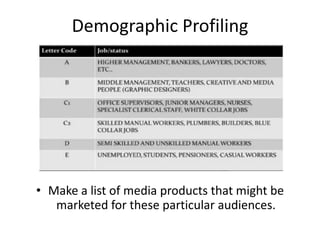
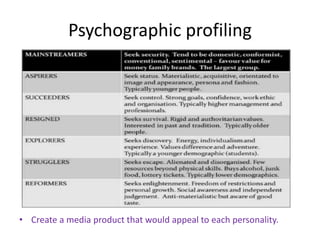
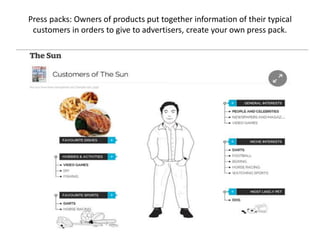
This document discusses key concepts relating to audiences and media effects theories. It defines what an audience is and discusses demographic and psychographic profiling. It also covers the differences between target and niche audiences. Several theories are summarized, including:
- Bandura's social learning theory which suggests media can influence behaviors through modeling
- Gerbner's cultivation theory which argues repeated media exposure shapes viewers' perceptions of social reality
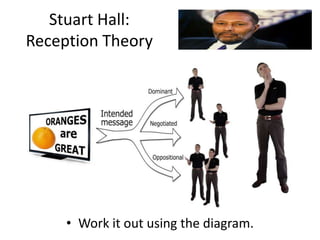
- Hall's reception theory which proposes encoding/decoding framework for analyzing how audiences make meaning from media texts.
The document provides examples and discussion questions to help apply these audience and effects theories.