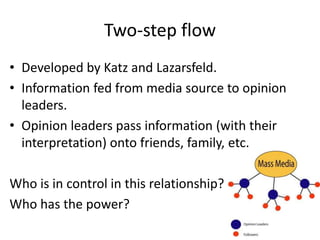
This document discusses different types of media audiences and theories about how audiences interact with media. It addresses television and film audiences, techniques used to appeal to audiences, and whether audiences are passive or active. It also covers several media effects theories: the hypodermic needle theory which sees audiences as entirely passive; the two-step flow theory which involves opinion leaders influencing others; and cultivation theory which proposes media shape beliefs over long periods of exposure. The document also discusses uses and gratifications theory and its limitations, as well as defining target audiences.