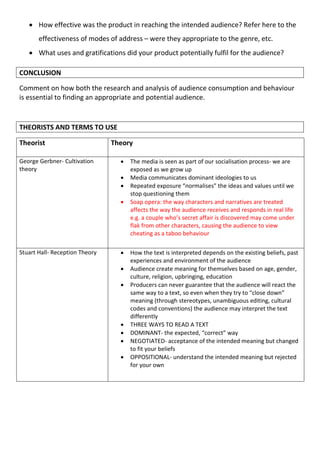
The document provides guidance for writing a response analyzing the role of audience in a soap trailer or music video production piece. It outlines key areas of focus, including audience research conducted to identify the target audience and their consumption trends, as well as the modes of address implemented to appeal to that audience. Feedback on audience response to the final product is also identified as important to analyze, such as how effectively the intended audience was reached and what uses and gratifications the product provided viewers. Theorists like Gerbner and Hall are referenced to aid in analyzing how the media socializes audiences and how audiences interpret media texts based on their own experiences and beliefs.