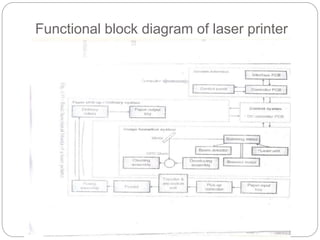
The document describes the functional block diagram of a laser printer, which contains four main sections: 1) the system interface for communication and data formatting; 2) the control system for coordinating all printing processes; 3) the image formation system using an OPC drum to form images through a six-step process; and 4) the paper pick-up/delivery system for feeding paper through the printer.