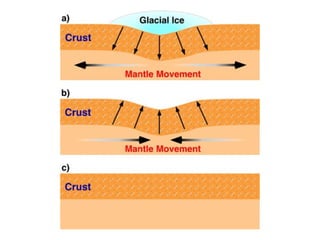
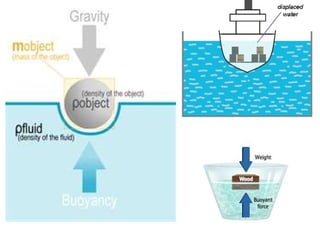
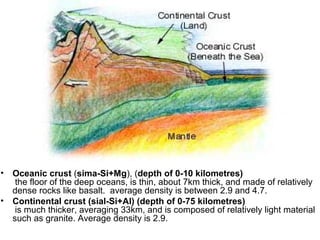
The document discusses the geological concept of isostasy. Isostasy refers to the principle of buoyancy where land masses float on the denser underlying mantle material. It explains that mountains create indentations in the earth's crust similar to placing a heavy object on a rubber ball. It also describes early theories on isostasy from Clarence Dutton, who coined the term, and Sir George Airy, who proposed that land masses float with varying thickness but uniform density. The concept was later refined by A. Pratt to propose uniform depth but varying density between land masses.