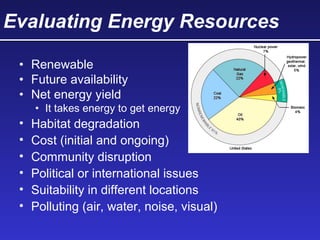
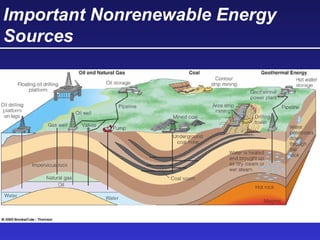
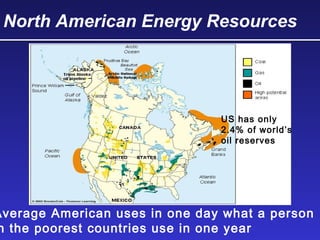
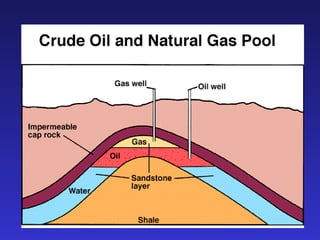
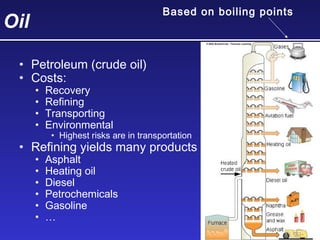
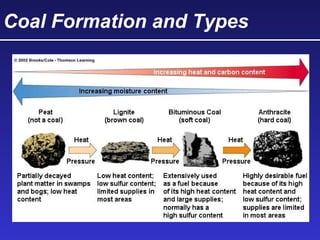
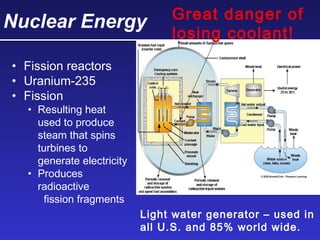
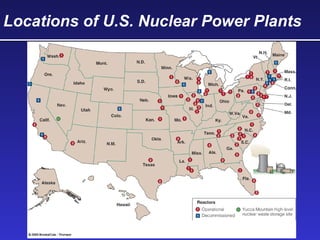
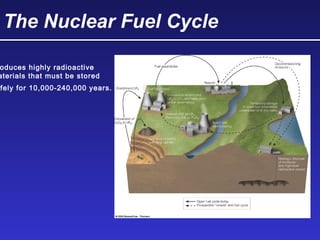
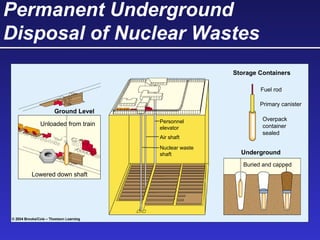
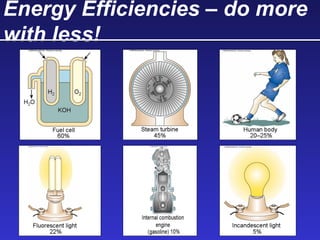
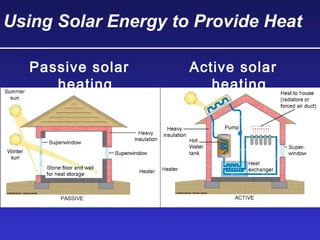
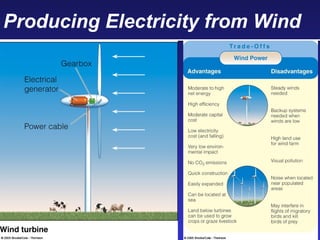
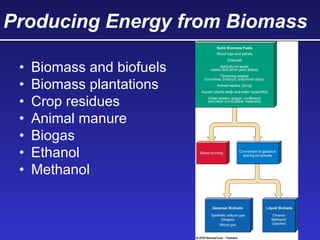
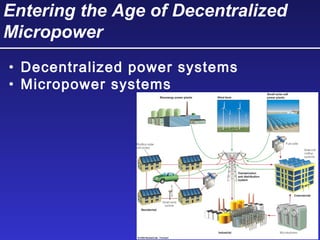
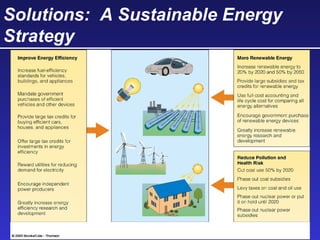
This document discusses various energy resources including renewable and non-renewable sources. It notes that 16% of energy comes from renewable sources such as solar, wind, water, and biomass while 84% comes from non-renewable sources like oil, natural gas, coal, and nuclear power. It provides details on the formation, extraction or production, uses, and trade-offs of different energy sources. These include discussions of oil and natural gas formation from dead marine organisms, coal formation over millions of years, nuclear fission reactions, and renewable options like solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy. The document emphasizes evaluating different energy sources based on factors like availability, yields, costs, environmental impacts, and sustainability