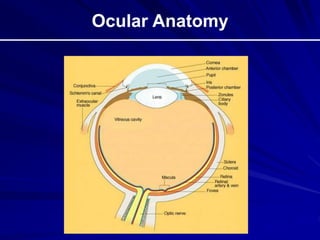
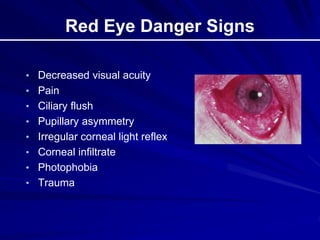
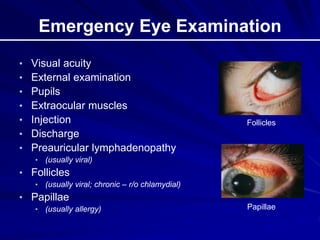
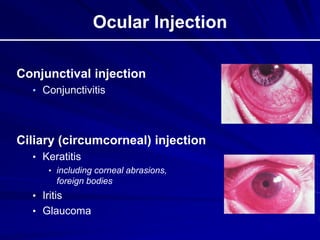
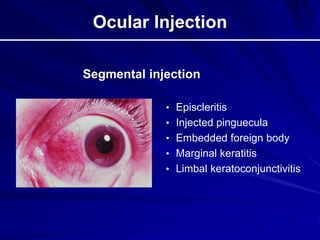
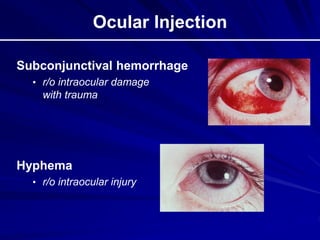
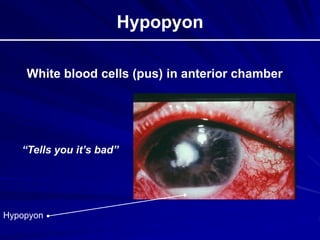
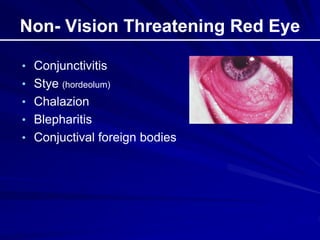
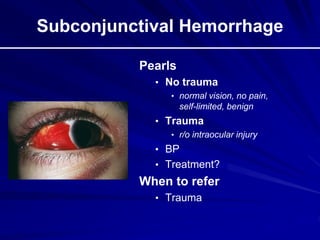
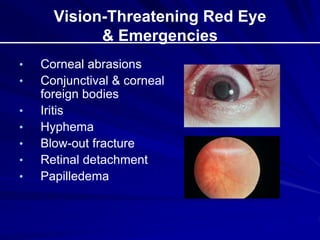
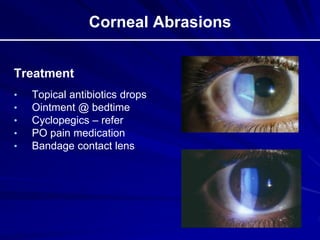
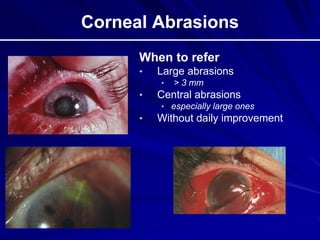
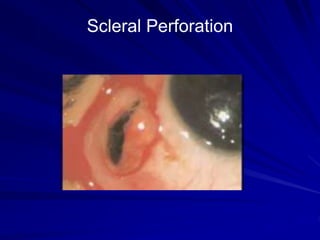
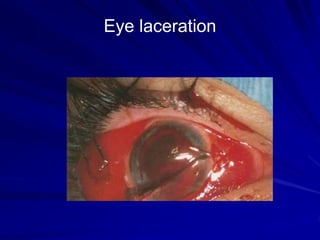
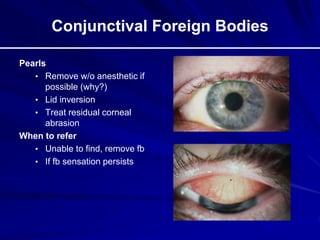
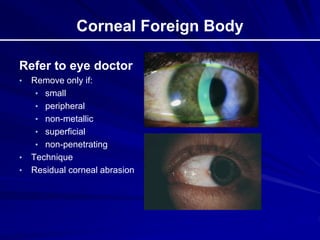
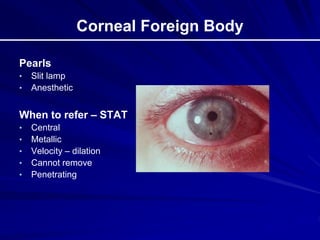
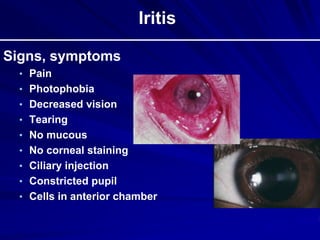
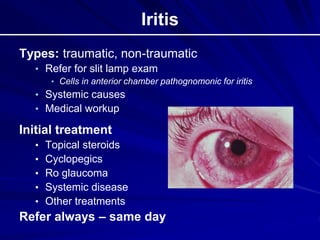
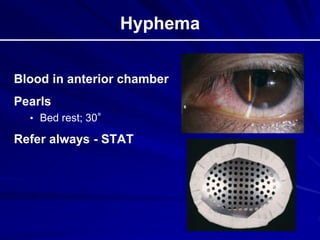
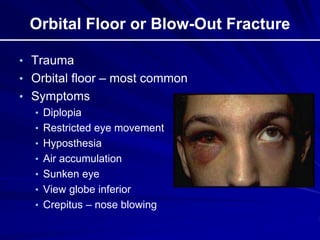
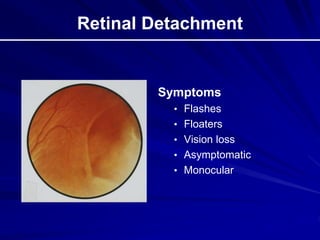
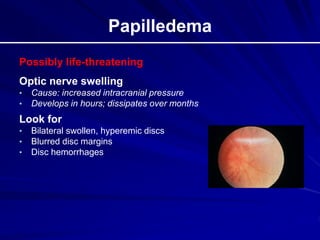
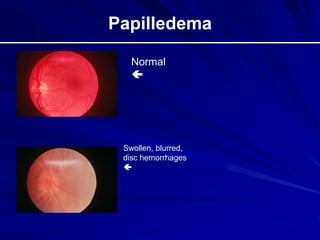
This document provides an overview of basic ocular emergencies for primary care physicians. It reviews red eye danger signs, examination techniques, common conditions like conjunctivitis and styes, as well as more serious issues like corneal abrasions, iritis, hyphema, retinal detachment and papilledema. For many conditions, pearls are provided on treatment and referral indications. Standards of care are also outlined, including not prescribing topical steroids without referral.