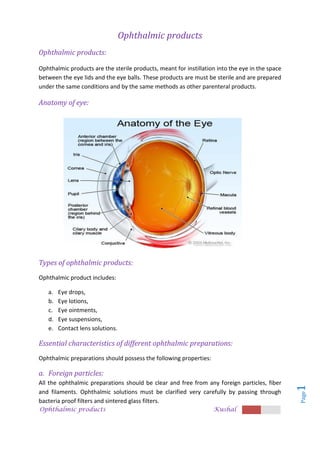
Ophthalmic products are sterile solutions, including eye drops, ointments, and solutions, designed for application in the eye, requiring strict adherence to sterility, viscosity, tonicity, and pH levels. They must be free from foreign particles and contain specific thickening agents and preservatives to ensure stability and comfort for users. Various types of ophthalmic products serve different purposes, such as treating infections, providing lubrication, or delivering sustained medication, with careful formulation processes to maintain their efficacy and safety.