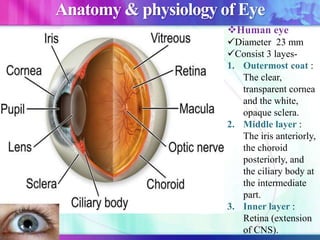
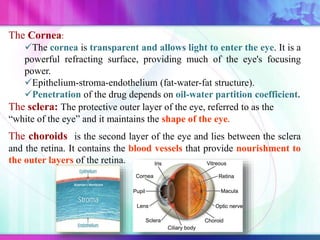
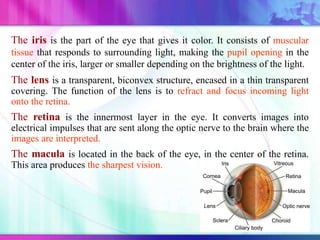
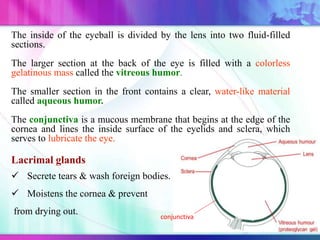
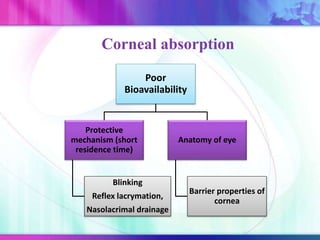
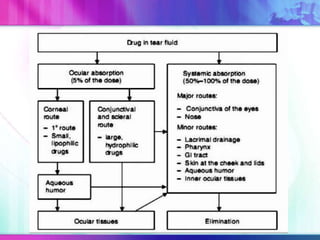
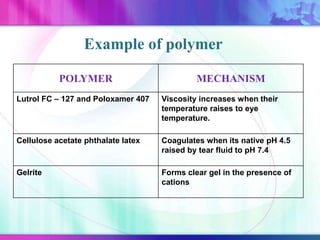
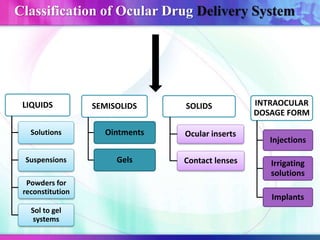
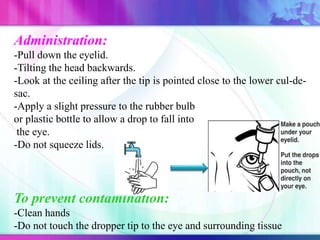
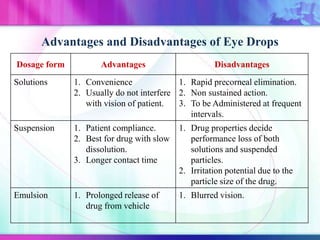
The document discusses various aspects of ocular drug delivery systems, including the anatomy and physiology of the eye, factors affecting intraocular bioavailability, and approaches to improve drug delivery. It classifies different ophthalmic preparations such as eye drops and ointments while analyzing their properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, it highlights methods to enhance drug absorption, including viscosity enhancers, prodrugs, and mucoadhesive systems.