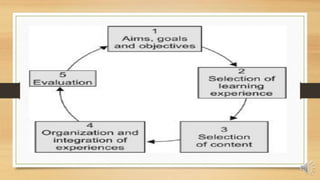
D.K. Wheeler was an educator who developed a cyclical curriculum model in 1967 consisting of 5 interdependent stages: 1) setting aims, goals and objectives; 2) selecting learning experiences; 3) selecting content; 4) organizing and integrating learning experiences and content; and 5) evaluation. Wheeler's model emphasizes flexibility, content selection, and integration of content to provide quality learning experiences. It also focuses on situational analysis and illustrates the dynamic nature of curriculum development as needs and interests change over time.