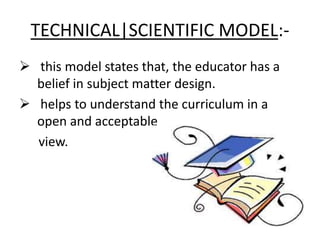
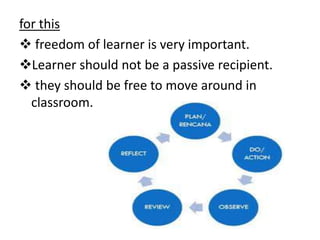
The document outlines models of curriculum development, categorizing them into technical and non-technical models. Technical models focus on structured educational objectives and include notable theories like Tyler's and Taba's models, while non-technical models, such as the open classroom model, emphasize learner autonomy and self-directed learning. Each model offers distinct approaches to curriculum design, implementation, and evaluation, reflecting different educational philosophies.