This document discusses various definitions, characteristics, principles, domains, and theories of learning. It begins by defining learning as a process of adopting new behaviors through experience in order to overcome obstacles. Some key points discussed include:
- Learning results in enduring changes in behavior and involves adjusting to new situations.
- Important factors in learning include motivation, practice, feedback, and the learning environment.
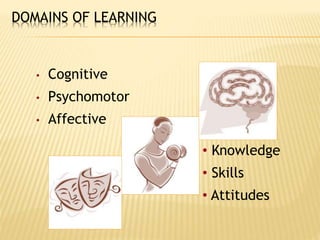
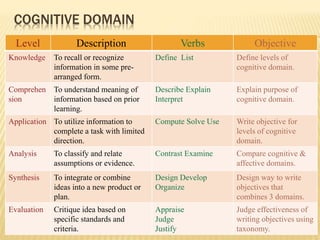
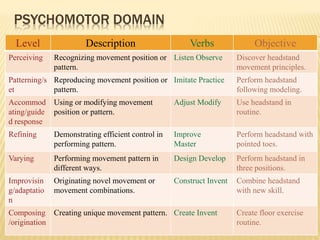
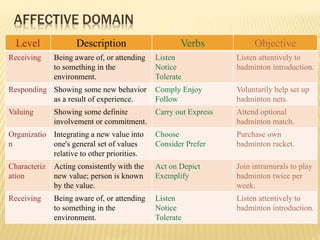
- Learning involves cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains and can be measured based on knowledge, skills, and attitudes gained.
- Learning theories discussed include behavioral, cognitive, and constructivist approaches. Conditioning and reinforcement play a role in behavioral theories of learning.