This document discusses sociolinguistics and the relationship between language and society. It covers several topics:
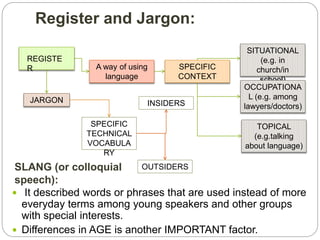
- Sociolinguistics studies how social factors like class, education, occupation, age and gender influence language use.
- Social dialects vary based on social class - working class speakers tend to use different features than middle class speakers.
- Education level impacts language through exposure to formal written language influencing spoken language.
- Social markers like pronunciation features can identify what social group a speaker belongs to consciously or not.
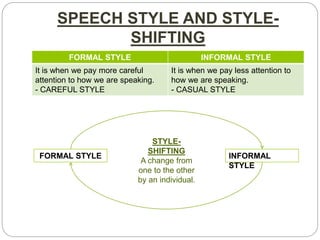
- Style shifting refers to changing between formal and informal speech styles depending on the social context and audience.



![SOCIAL
MARKERS
It is a FEATURE which occurs frequently in our
SPEECH.
It MARKS you as a member of a PARTICULAR
SOCIAL GROUP, whether you realize it or not.
PRONUNCIATION FEATURES:
Example: - The final pronunciation of –ING.
- [h] dropping: It makes the words at and hat
sounds the same.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thestudyoflanguage-171101034532/85/The-study-of-language-Chapter-19pptx-4-320.jpg)