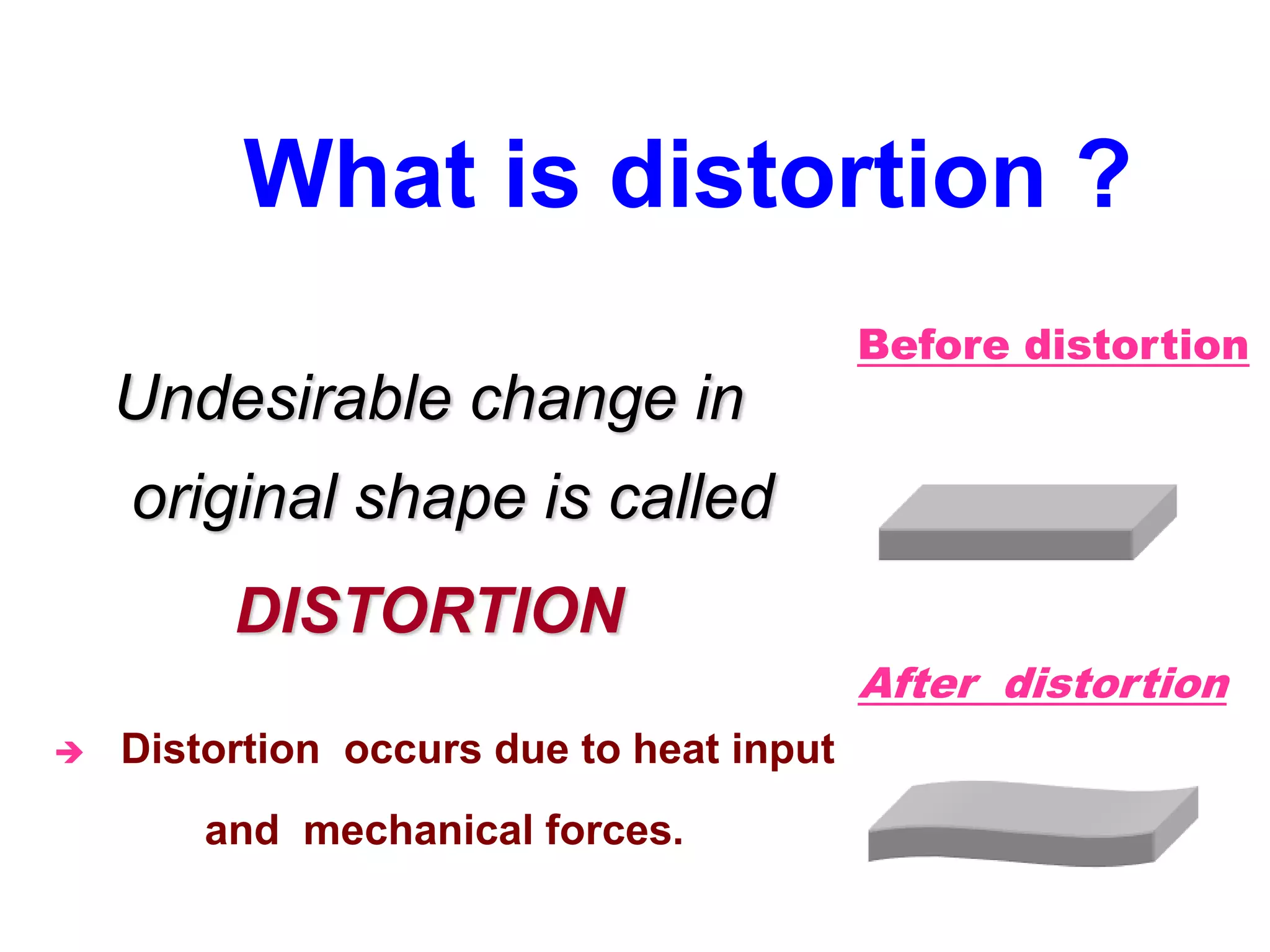
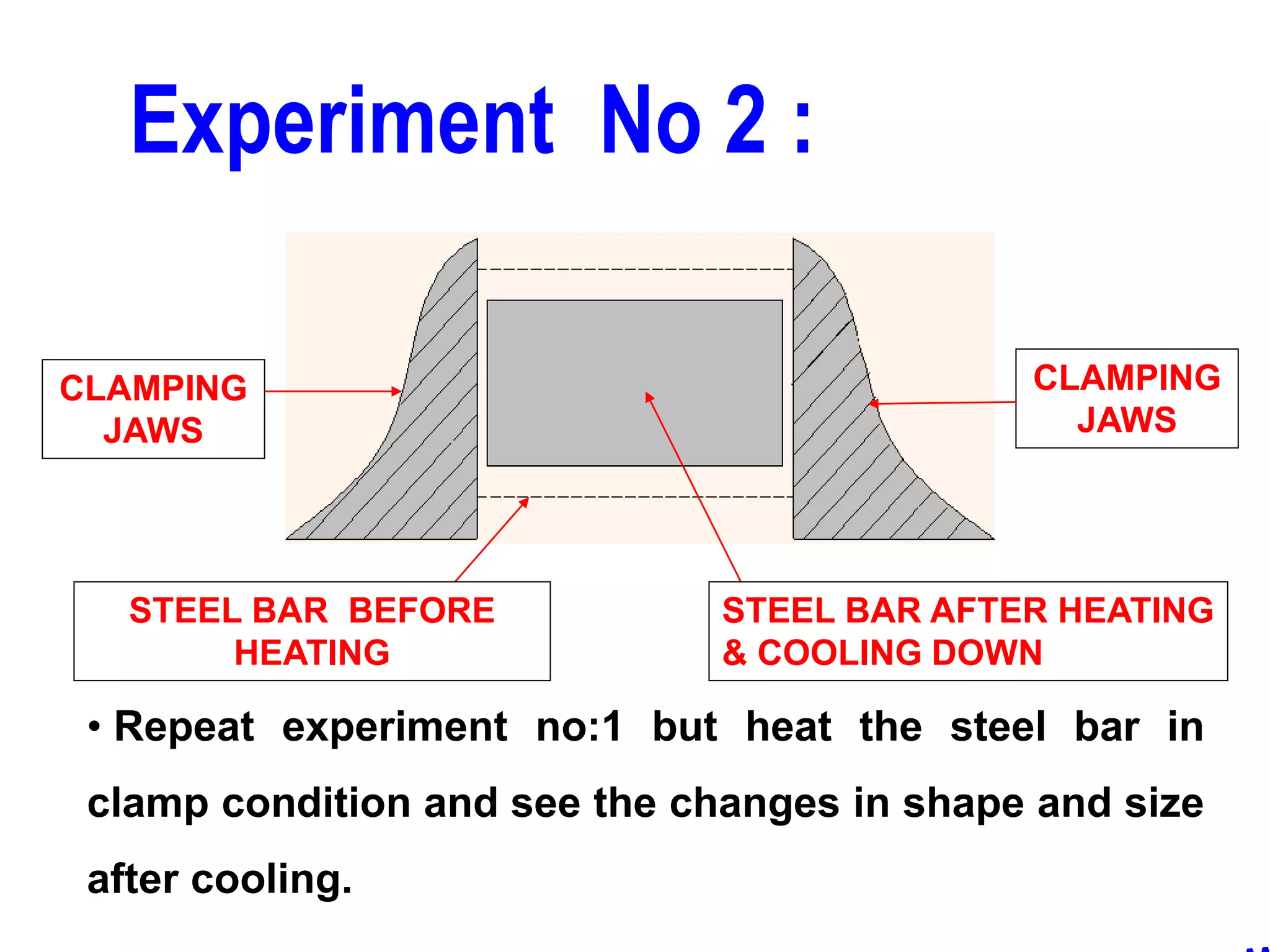
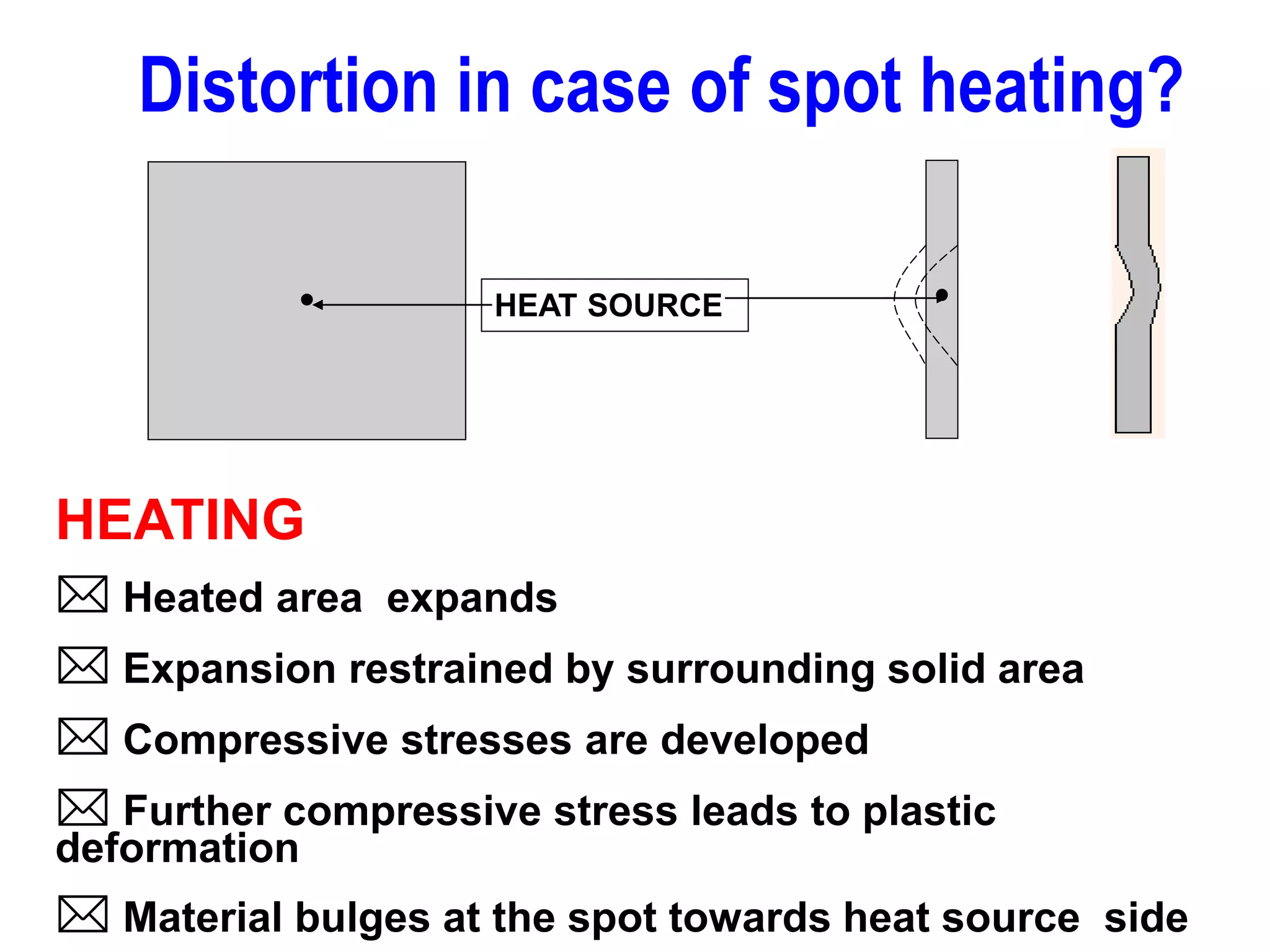
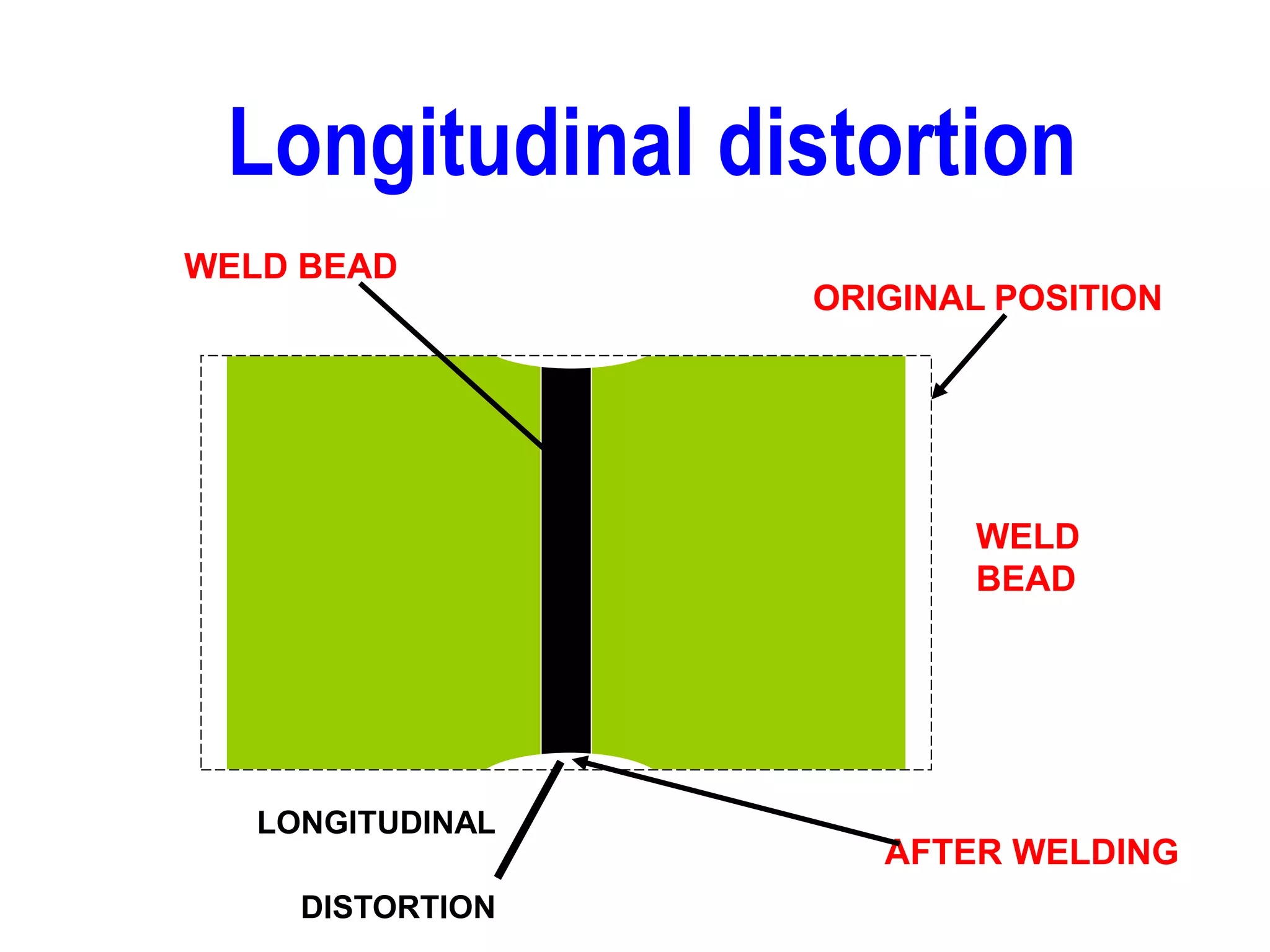
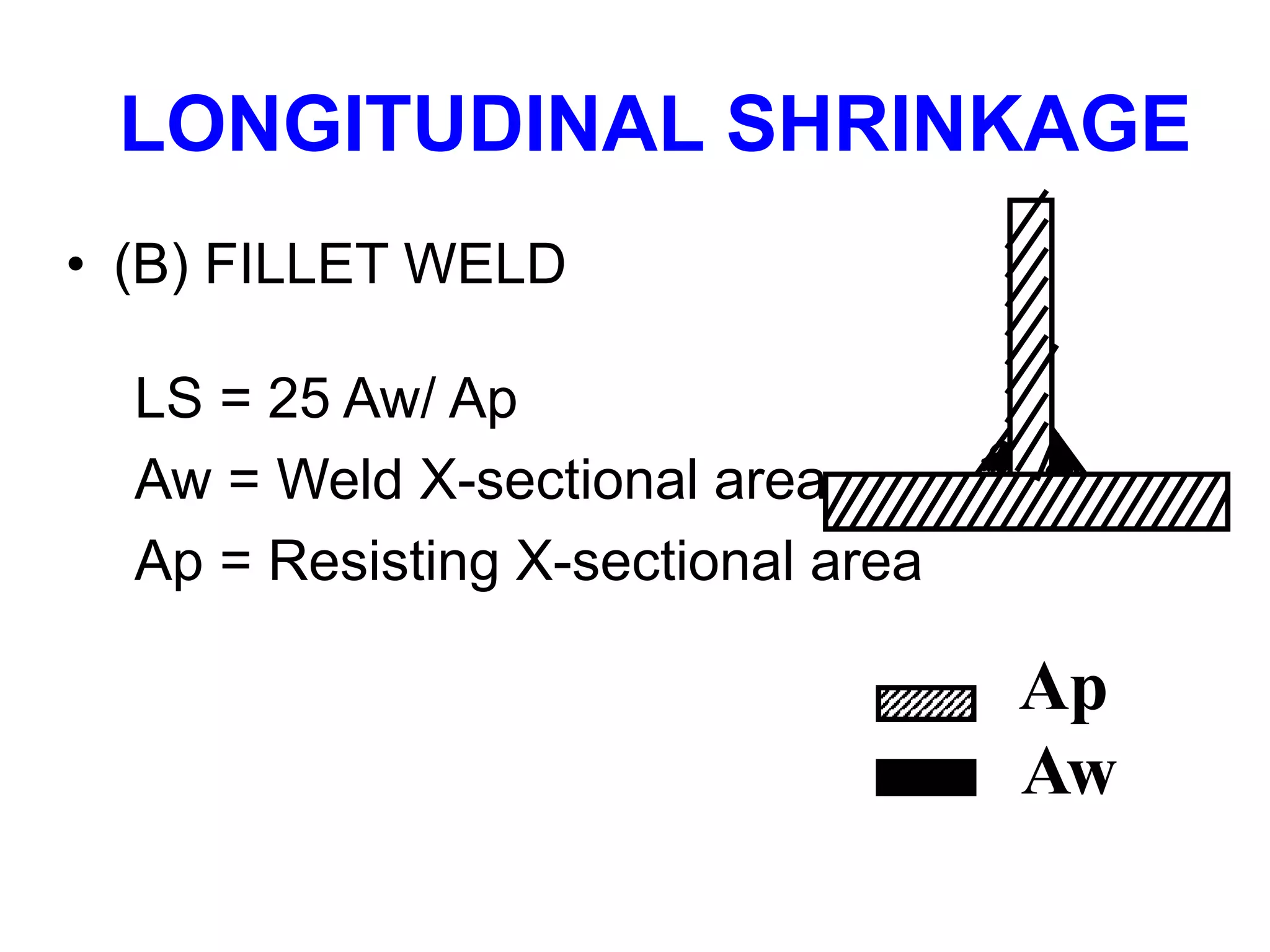
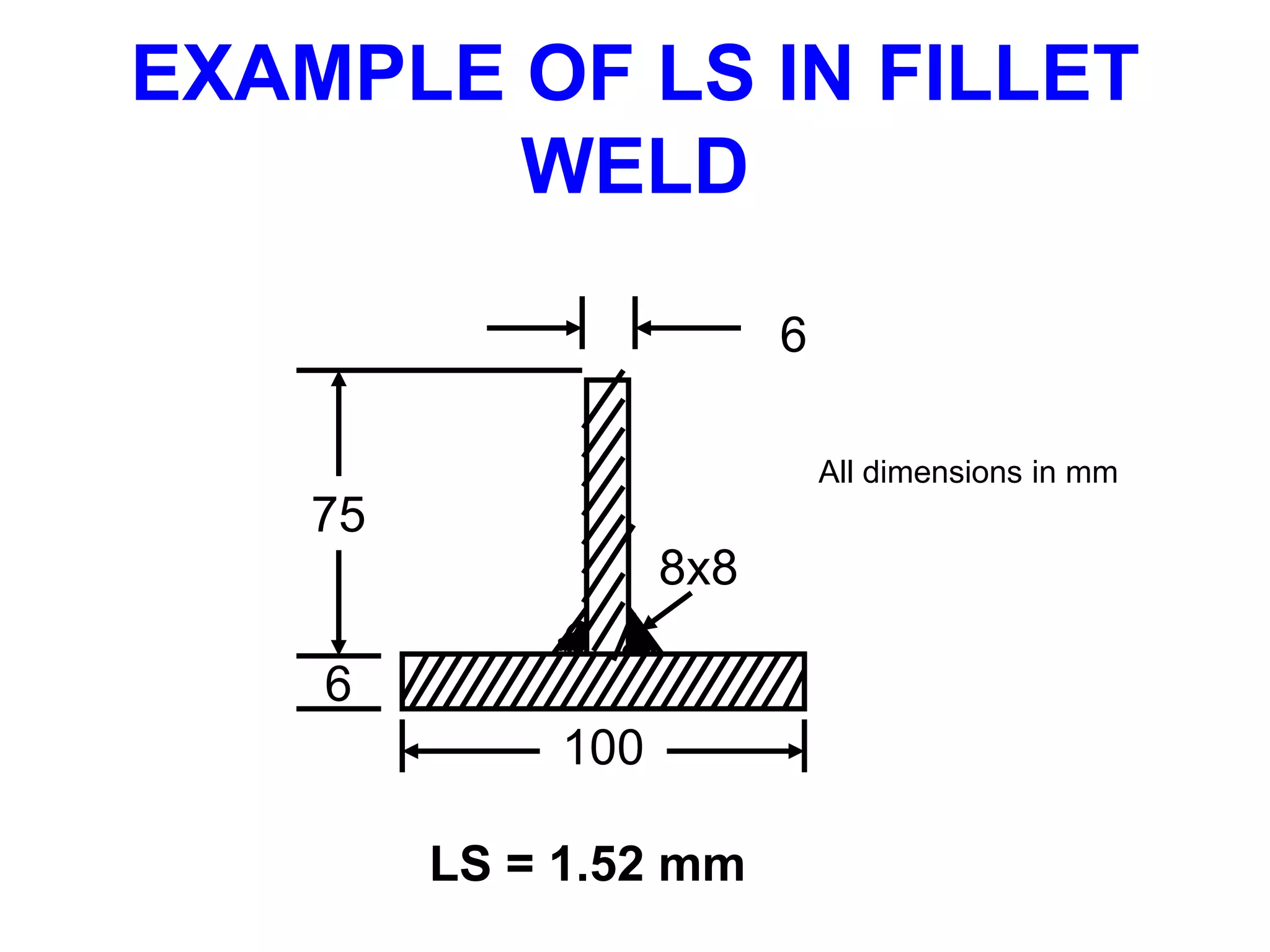
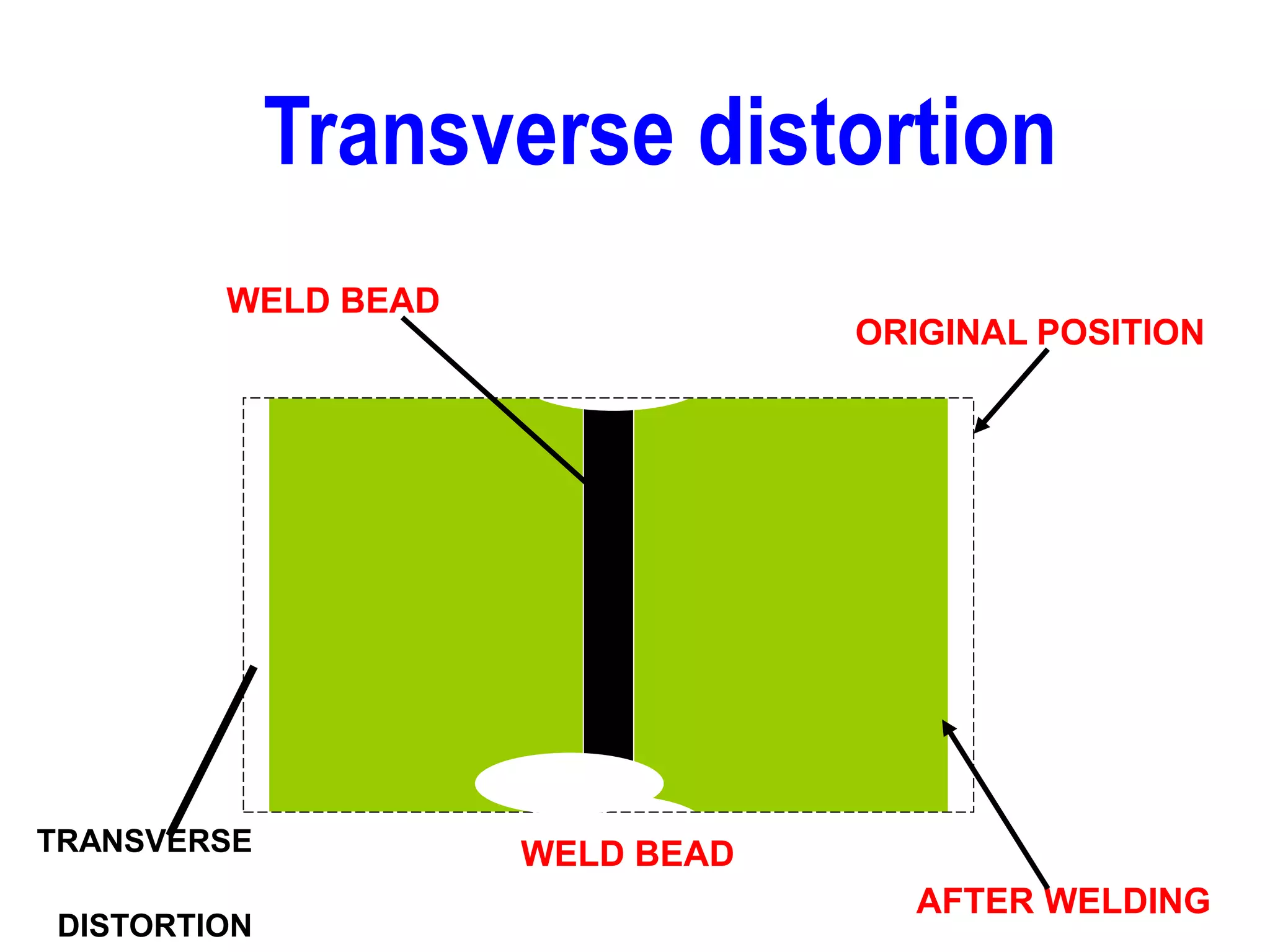
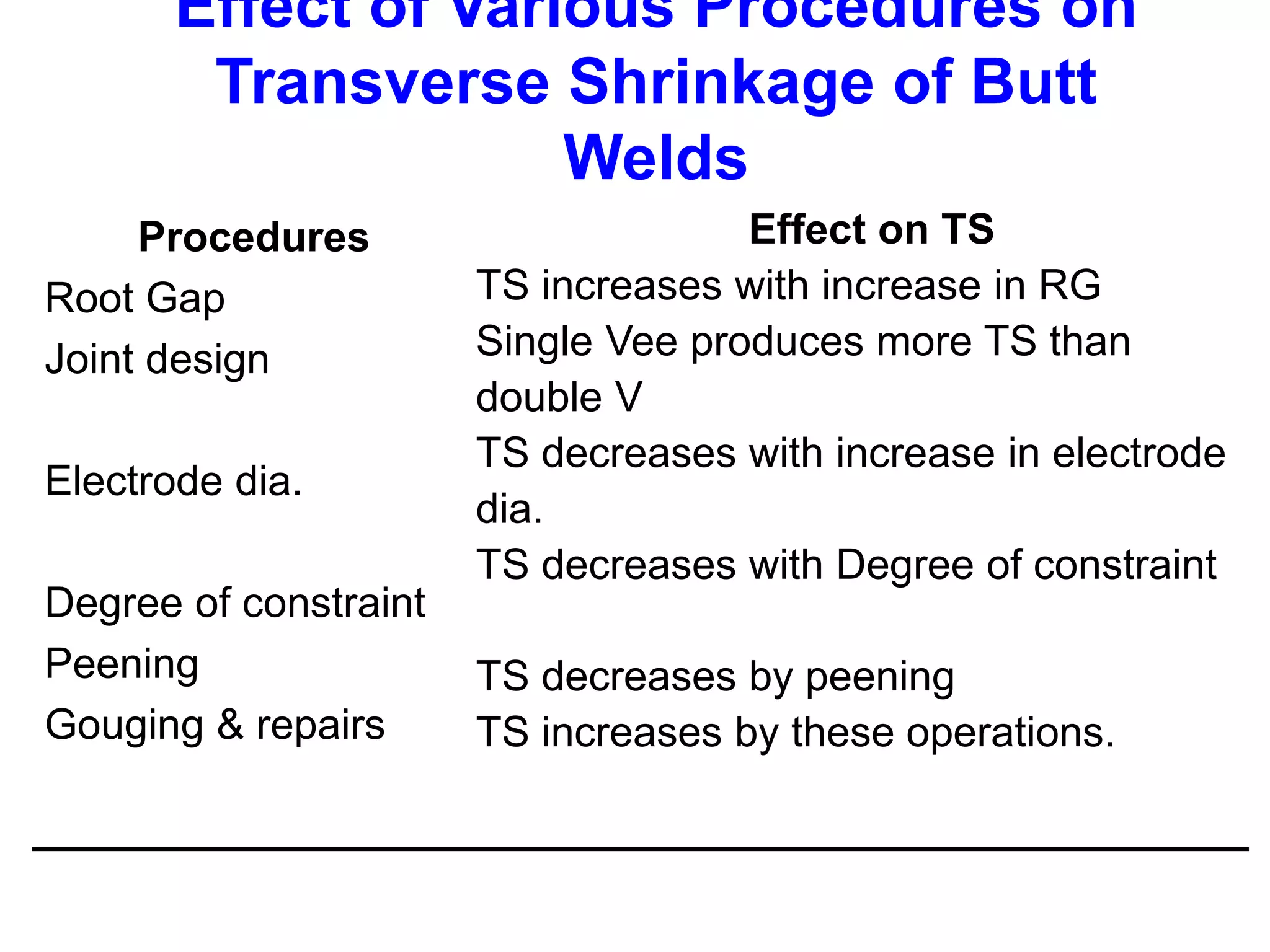
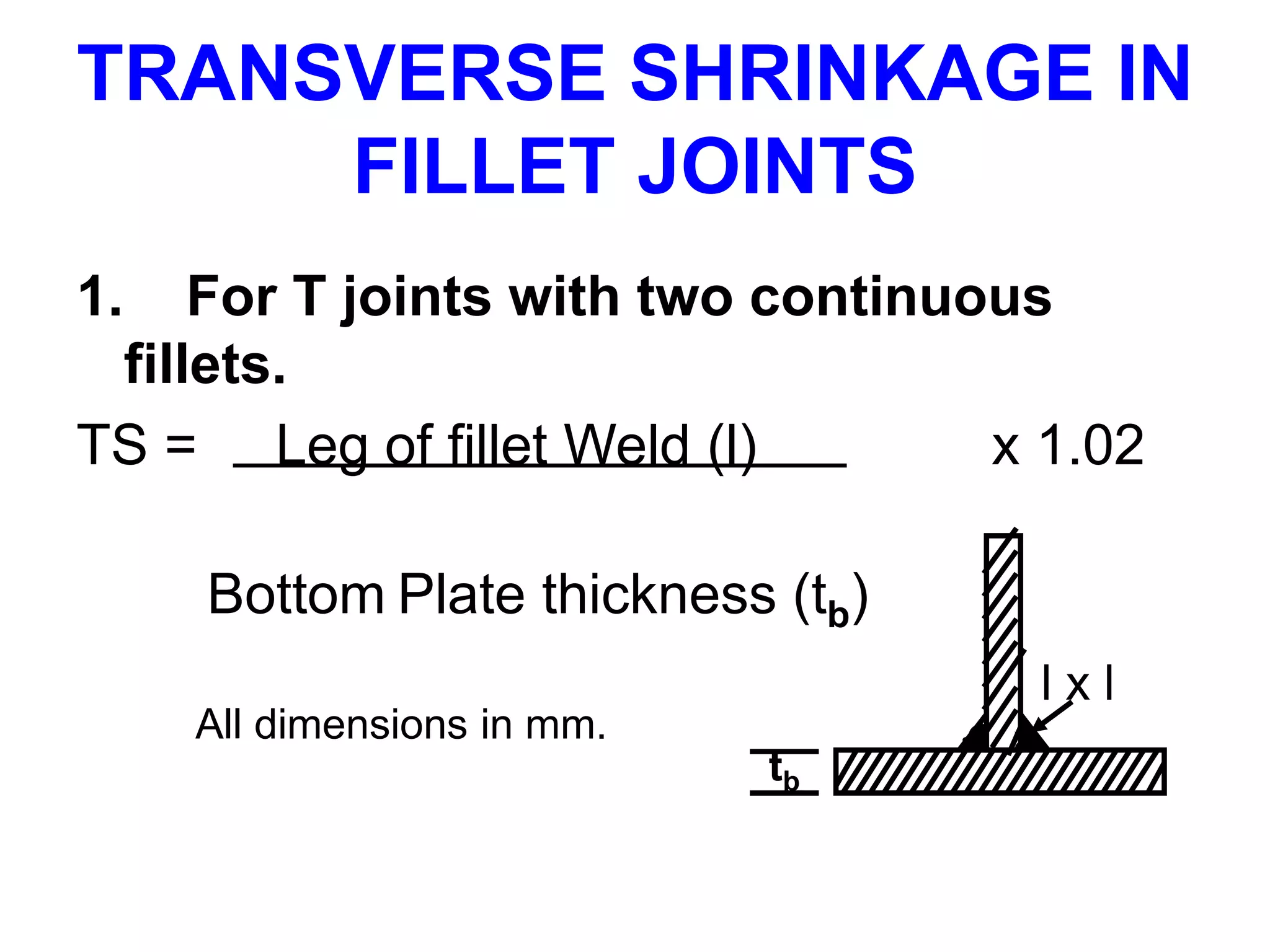
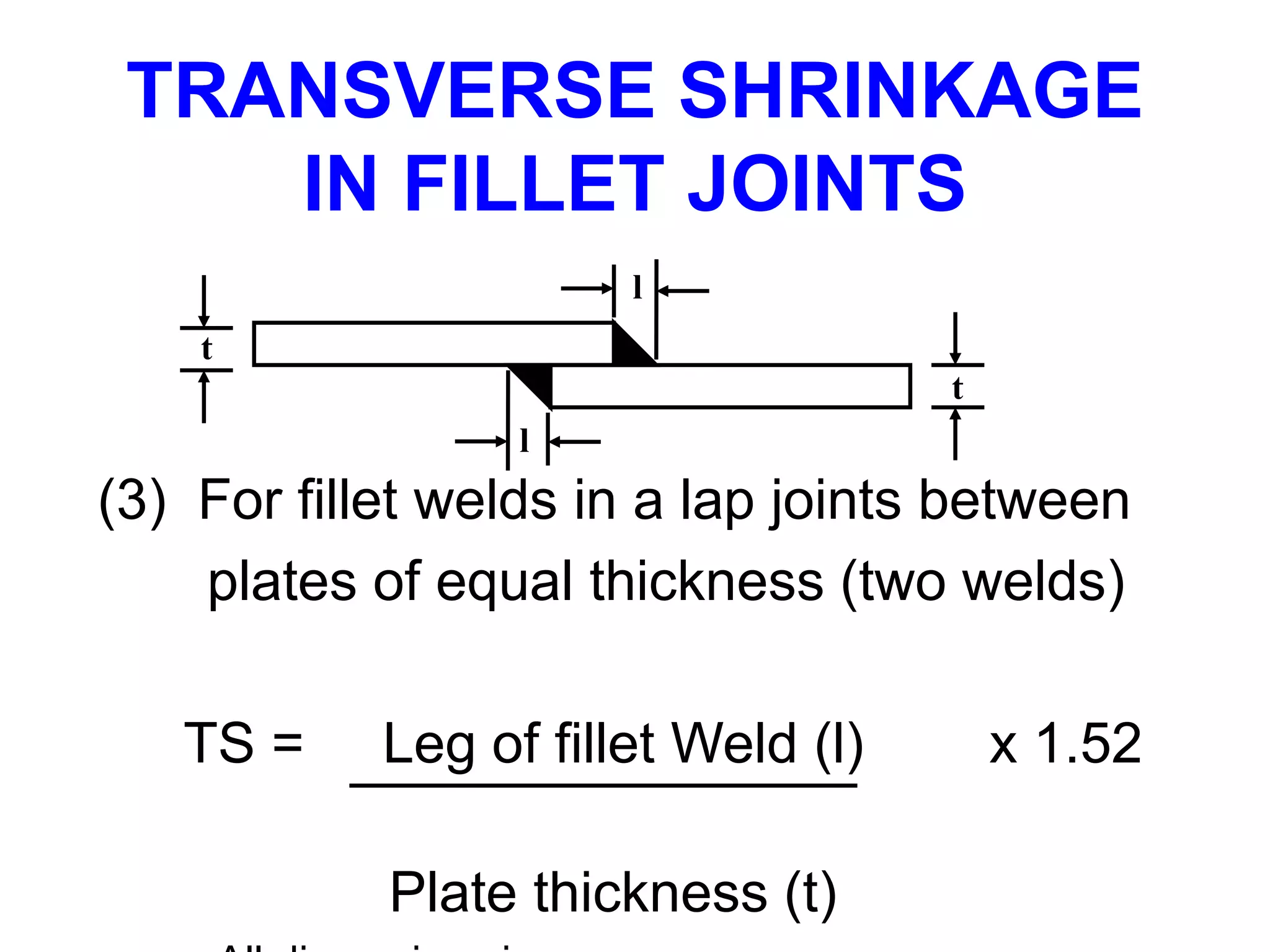
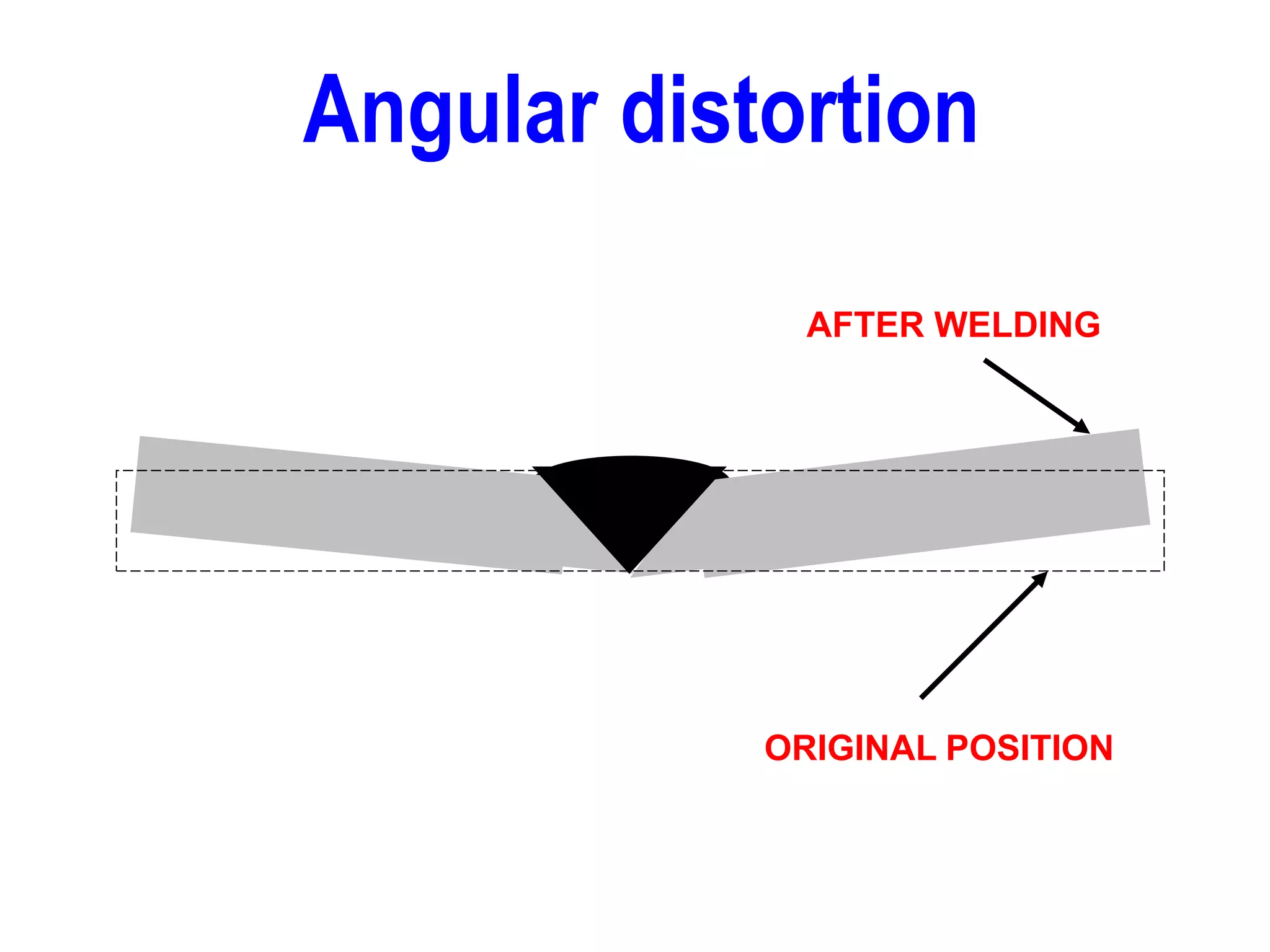
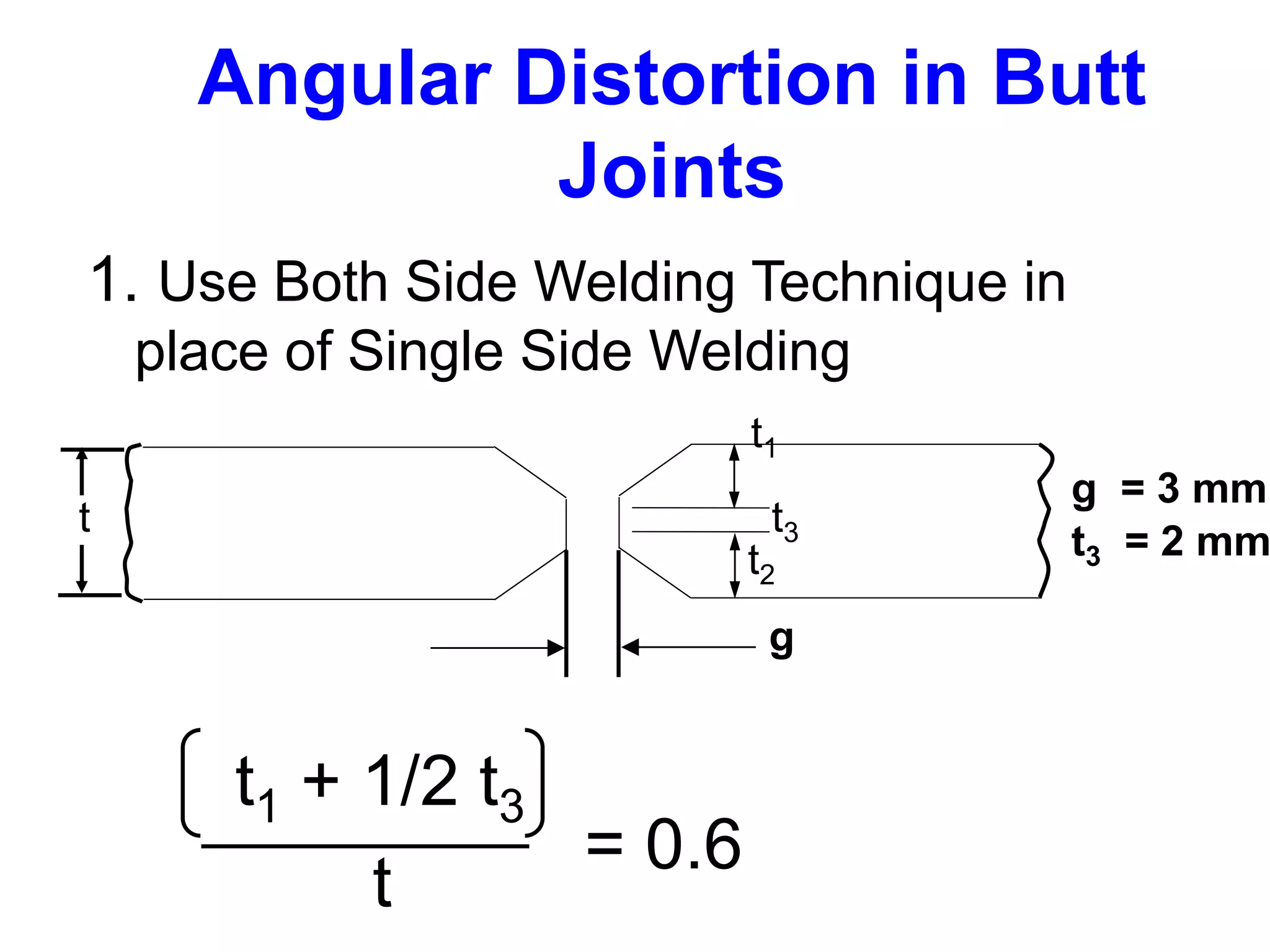
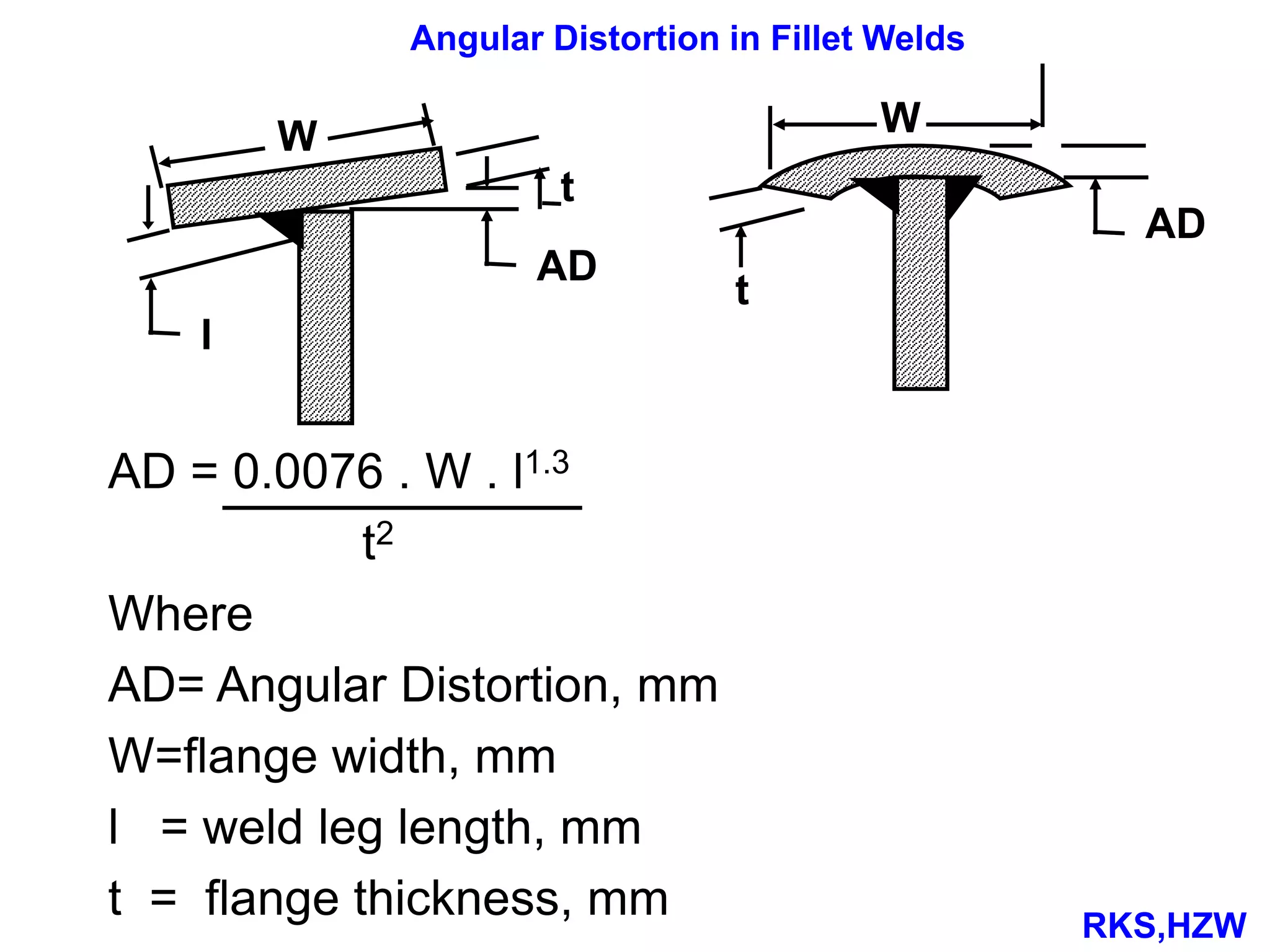
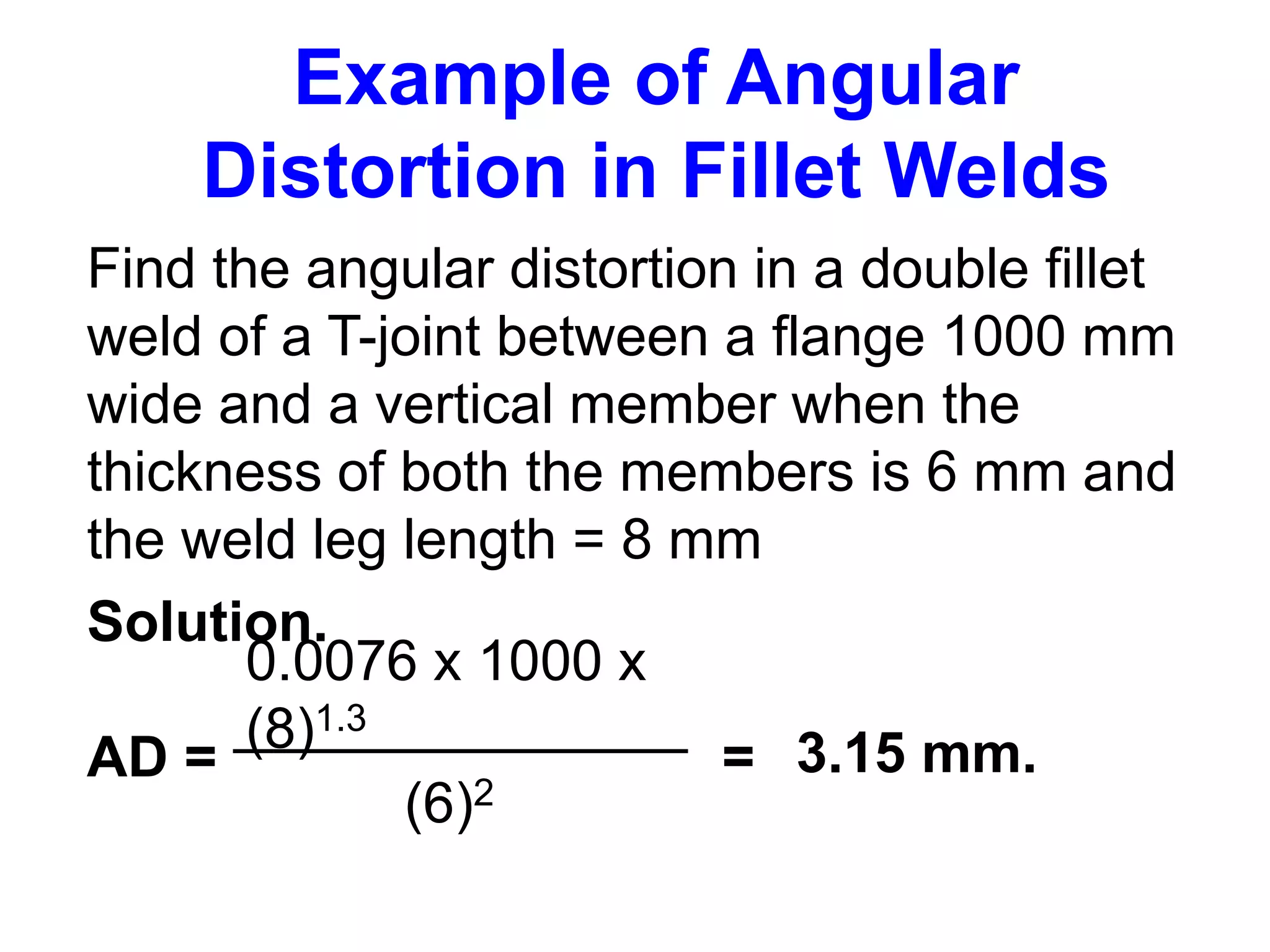
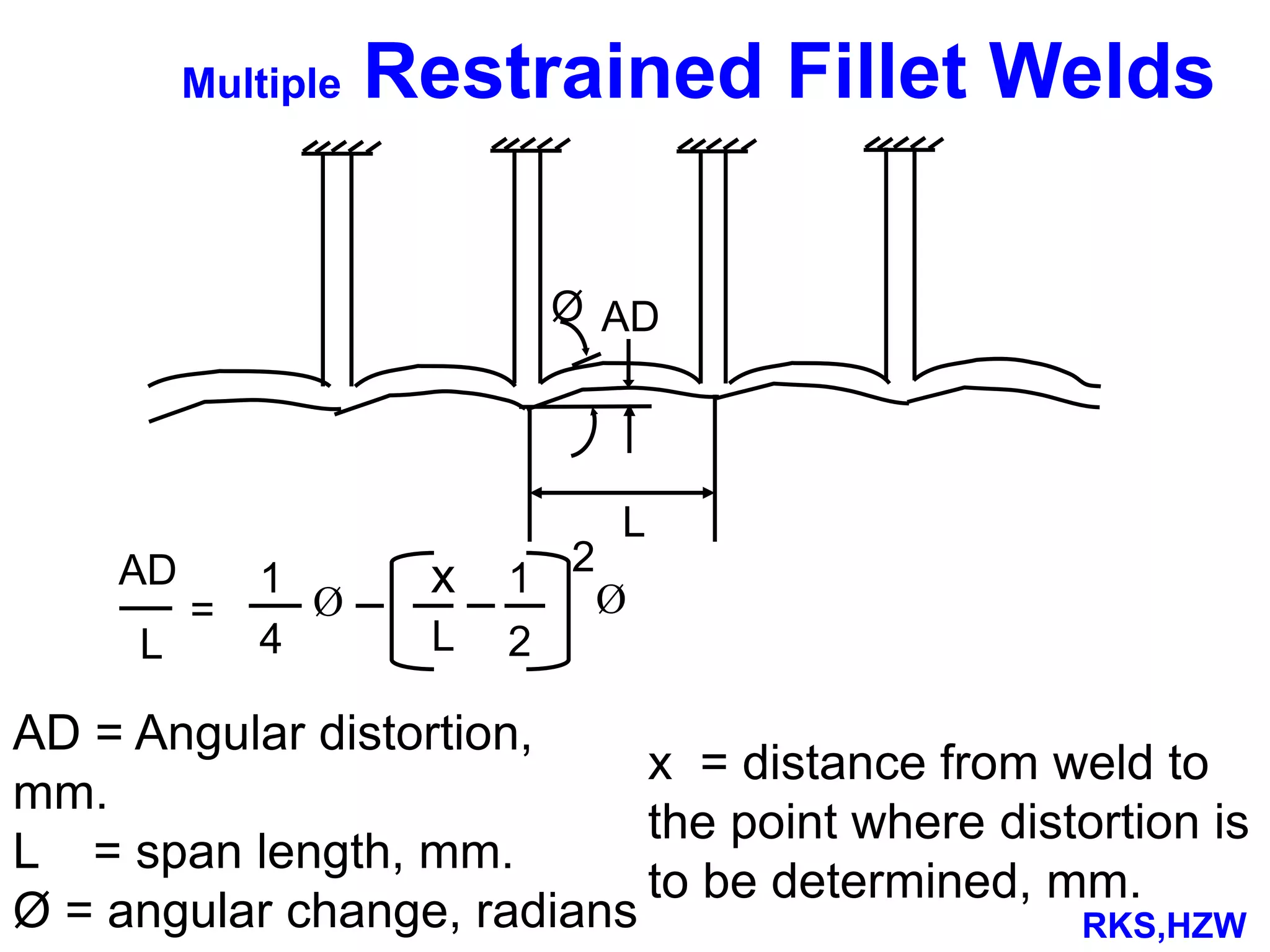
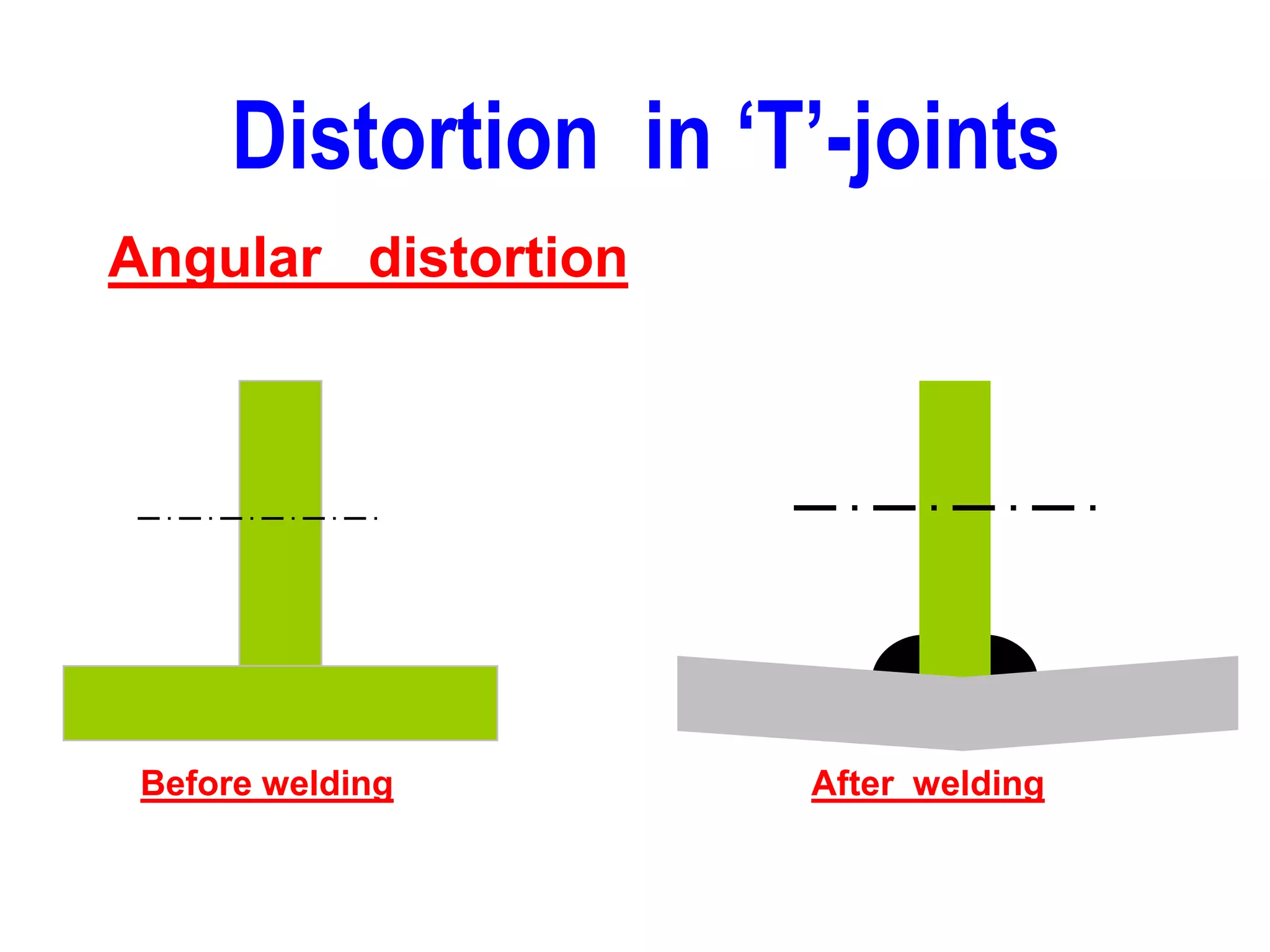
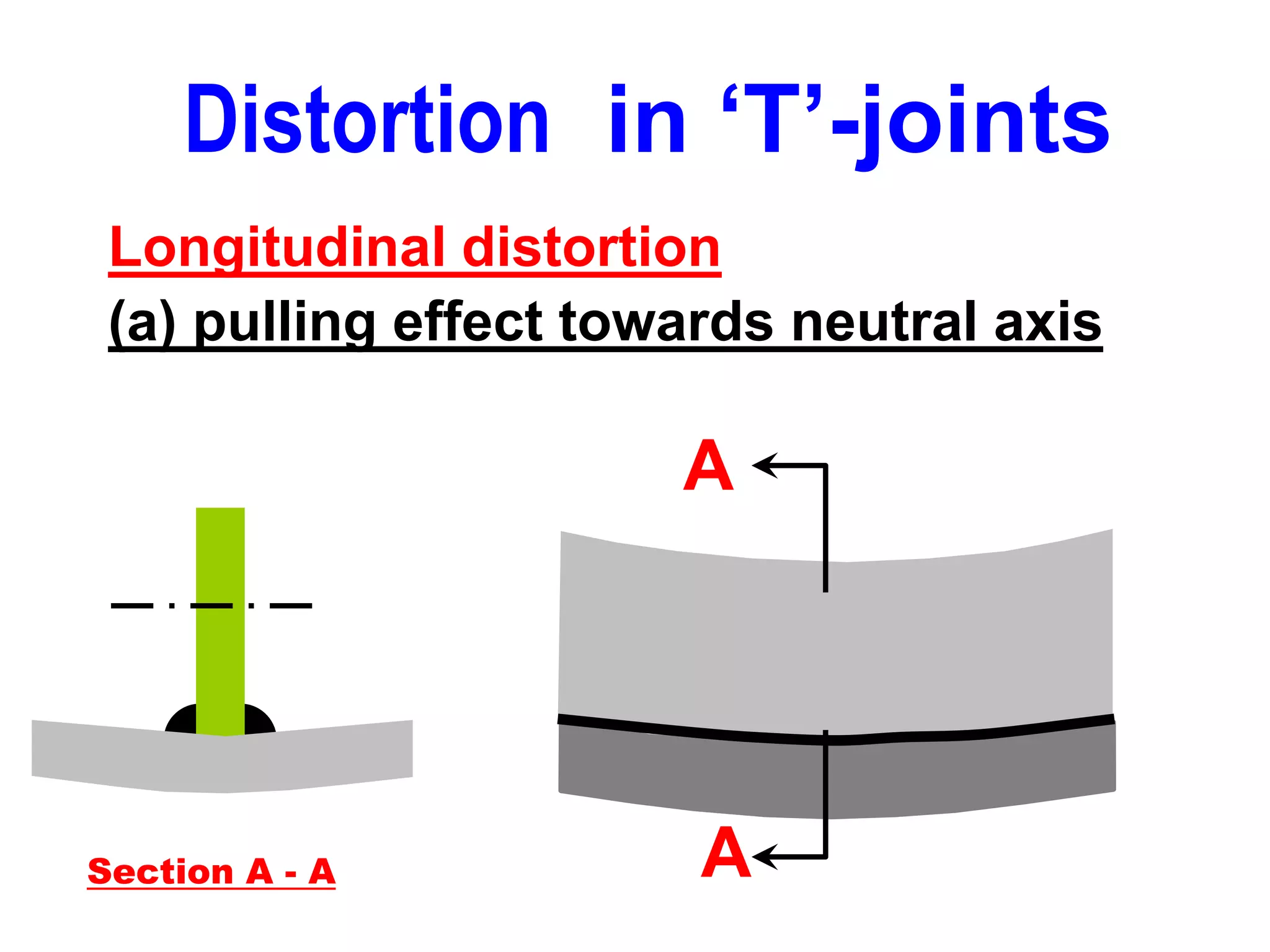
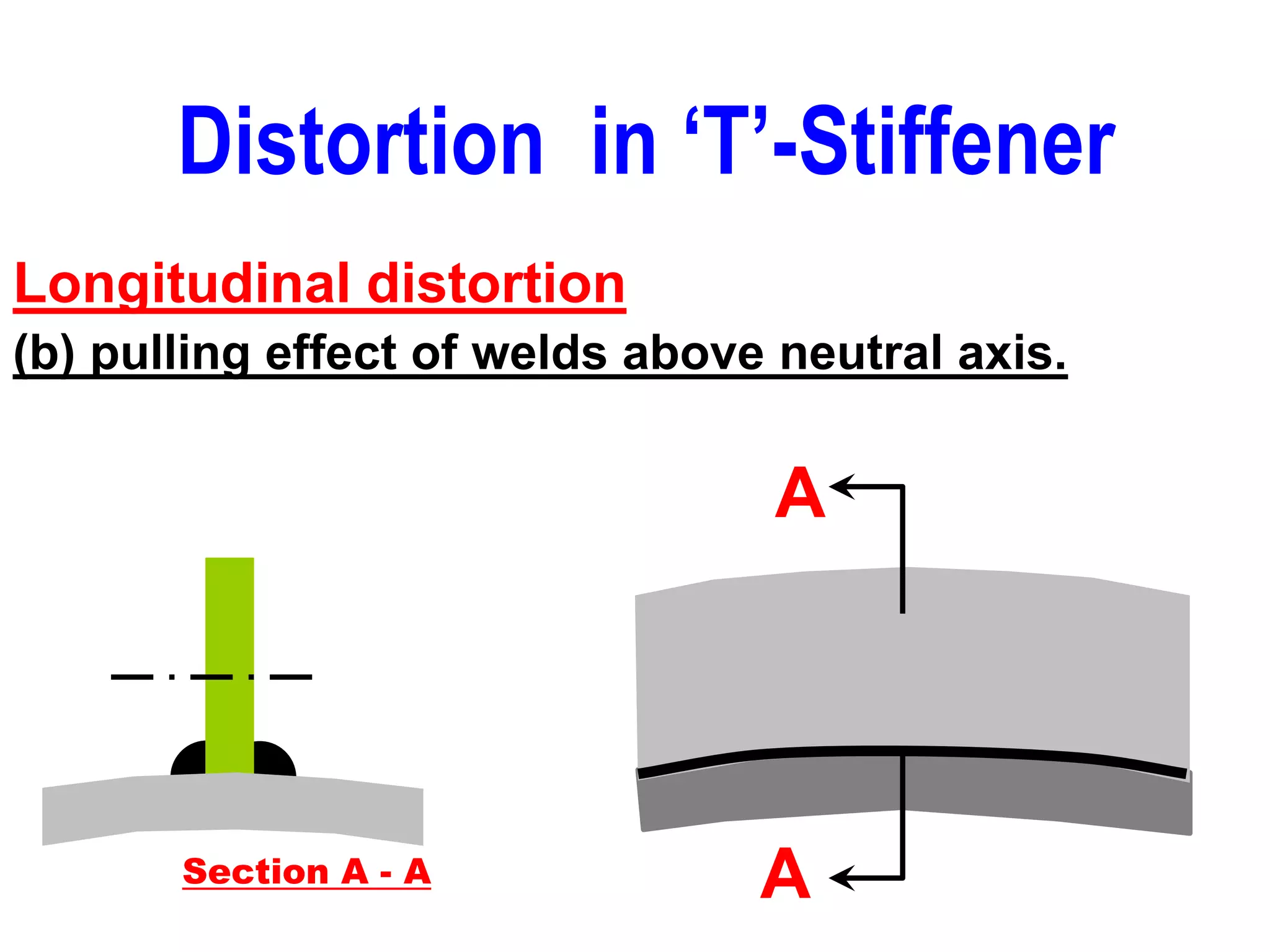
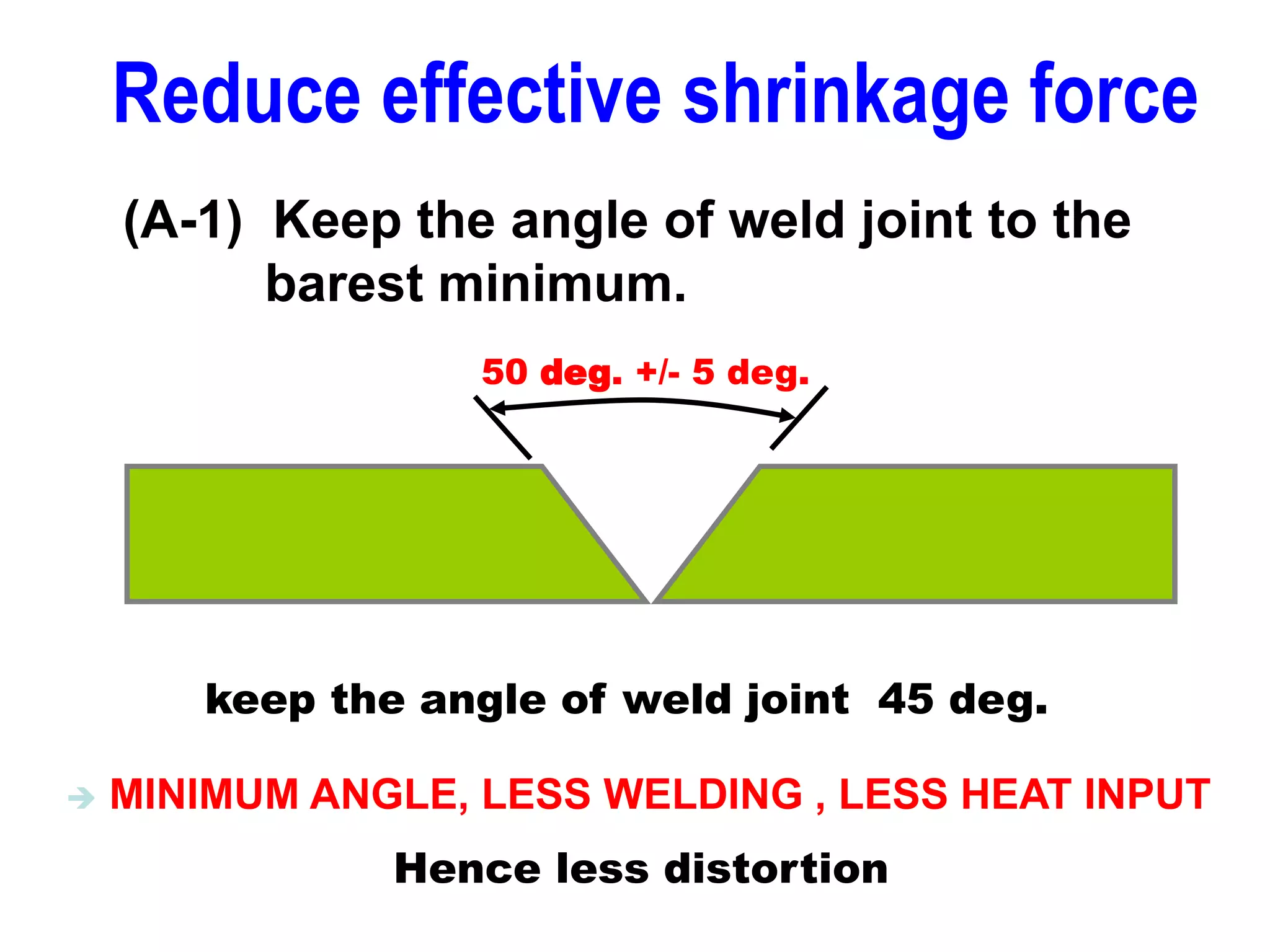
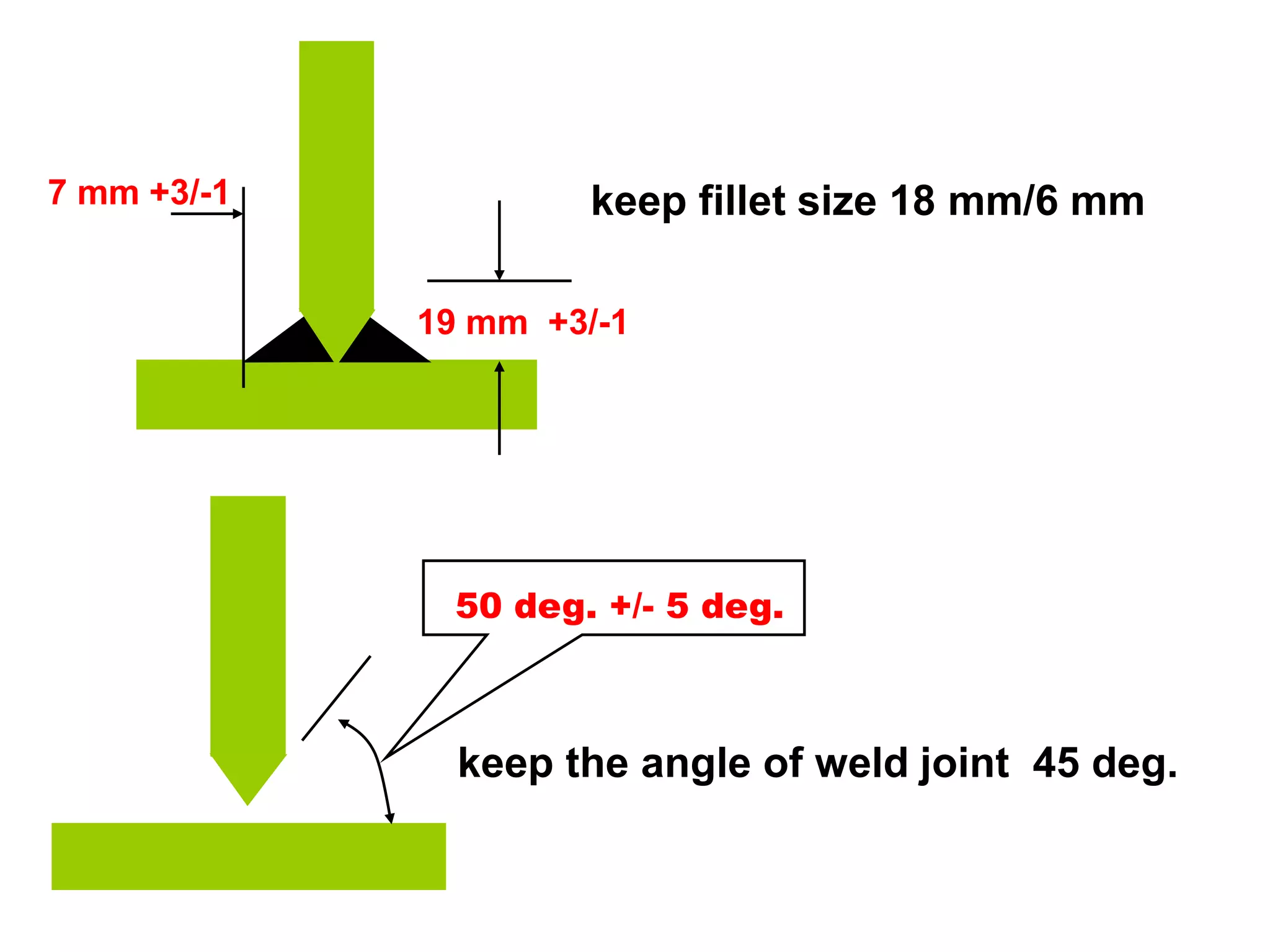
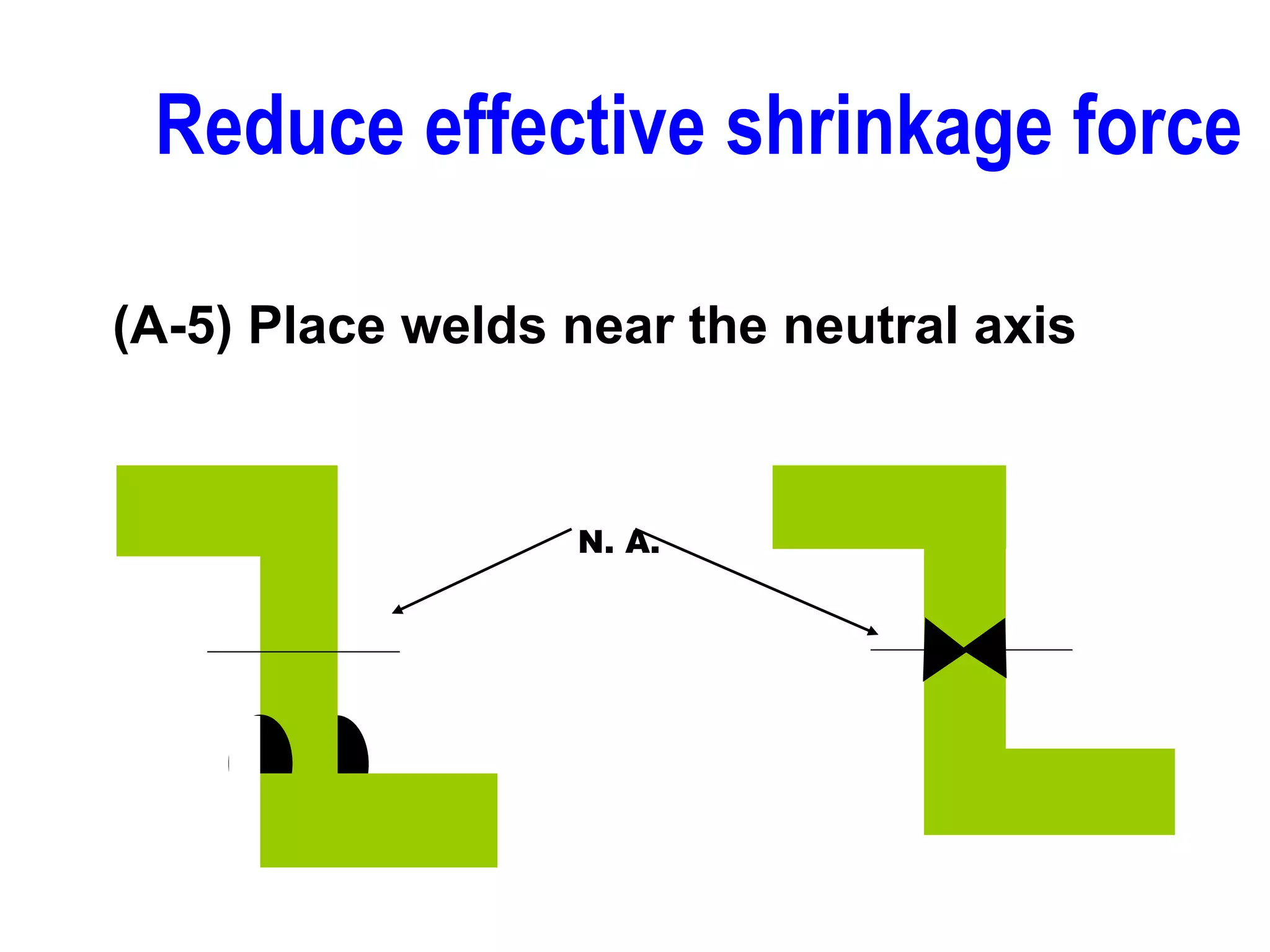
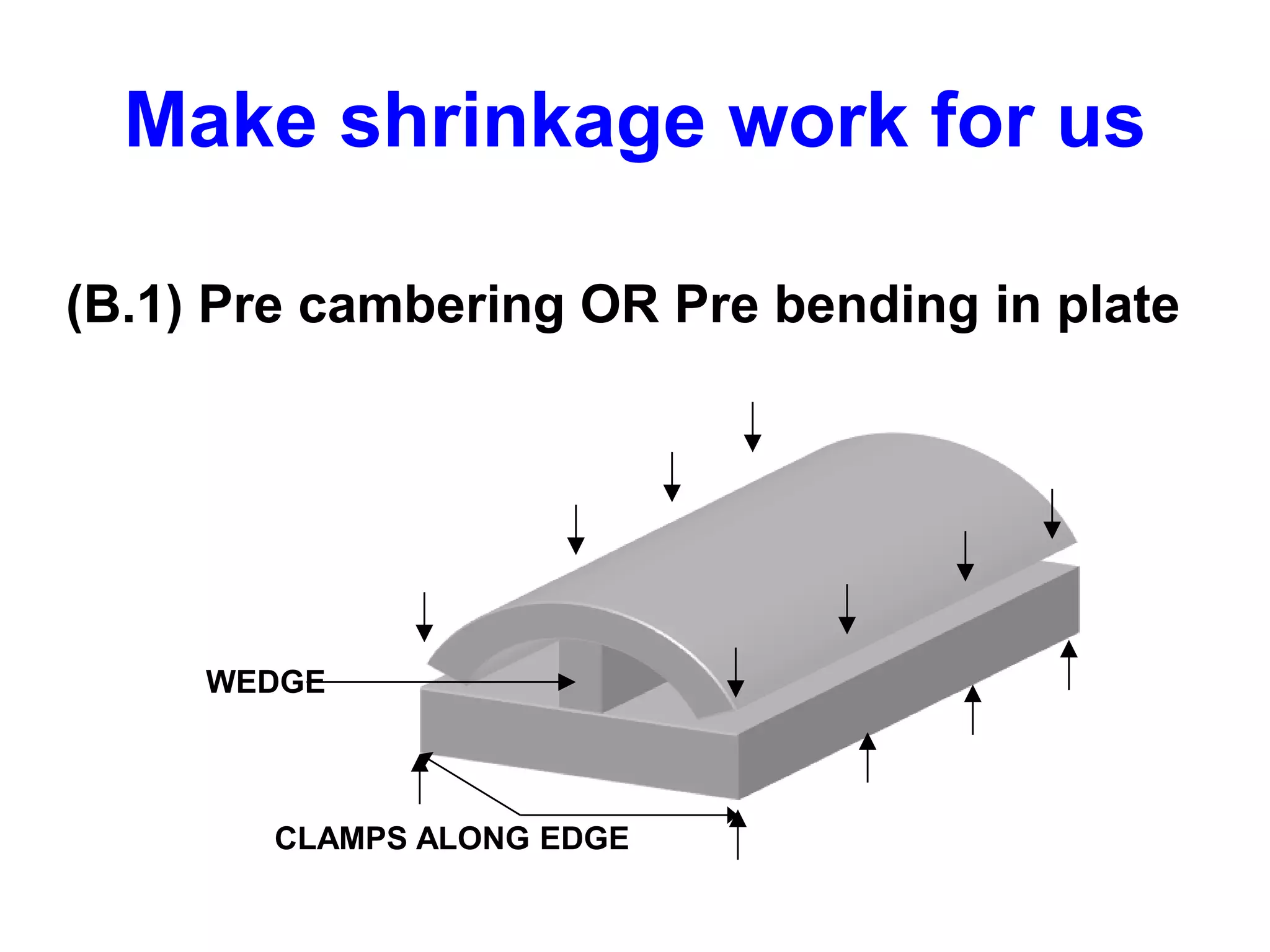
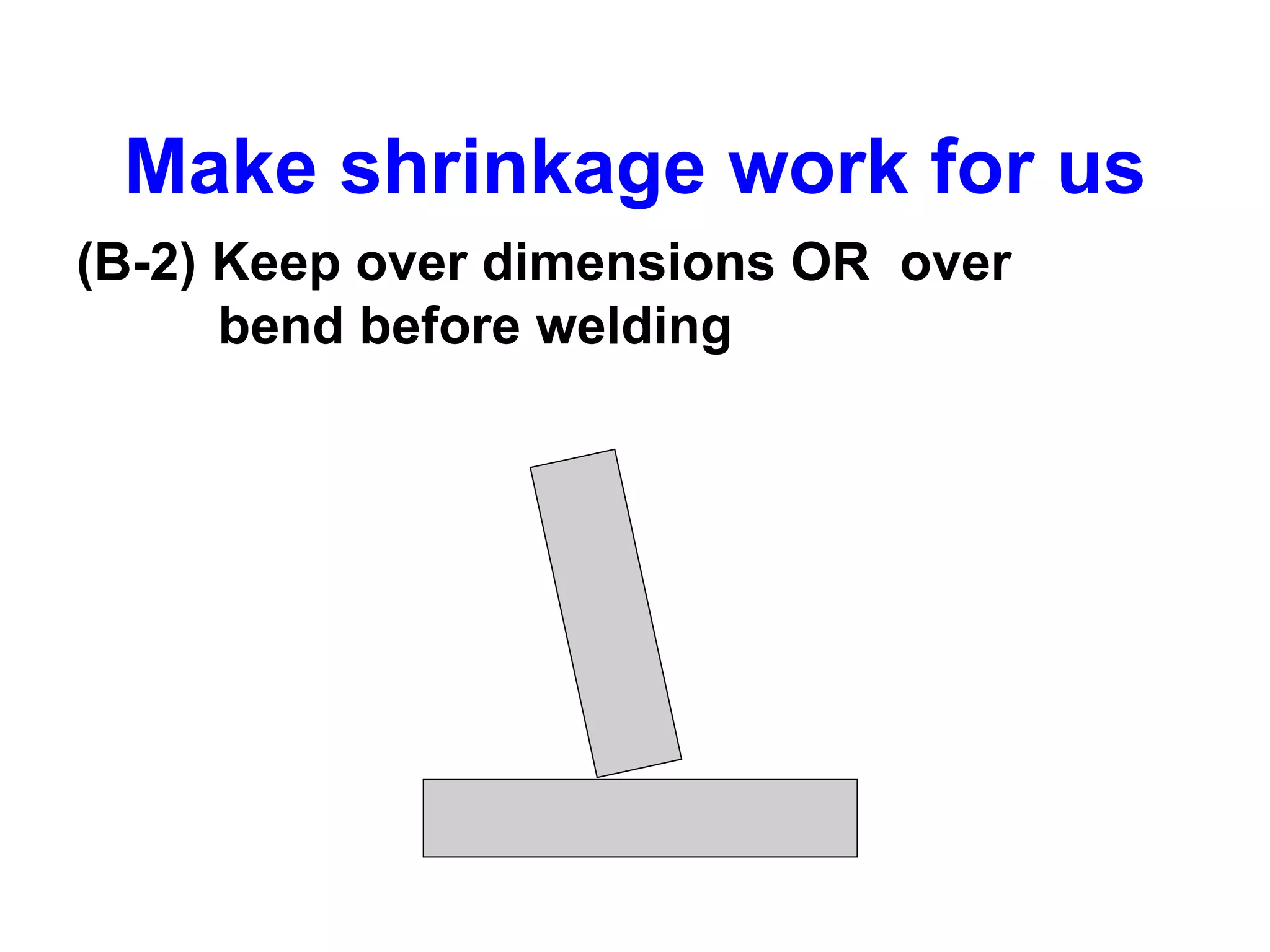
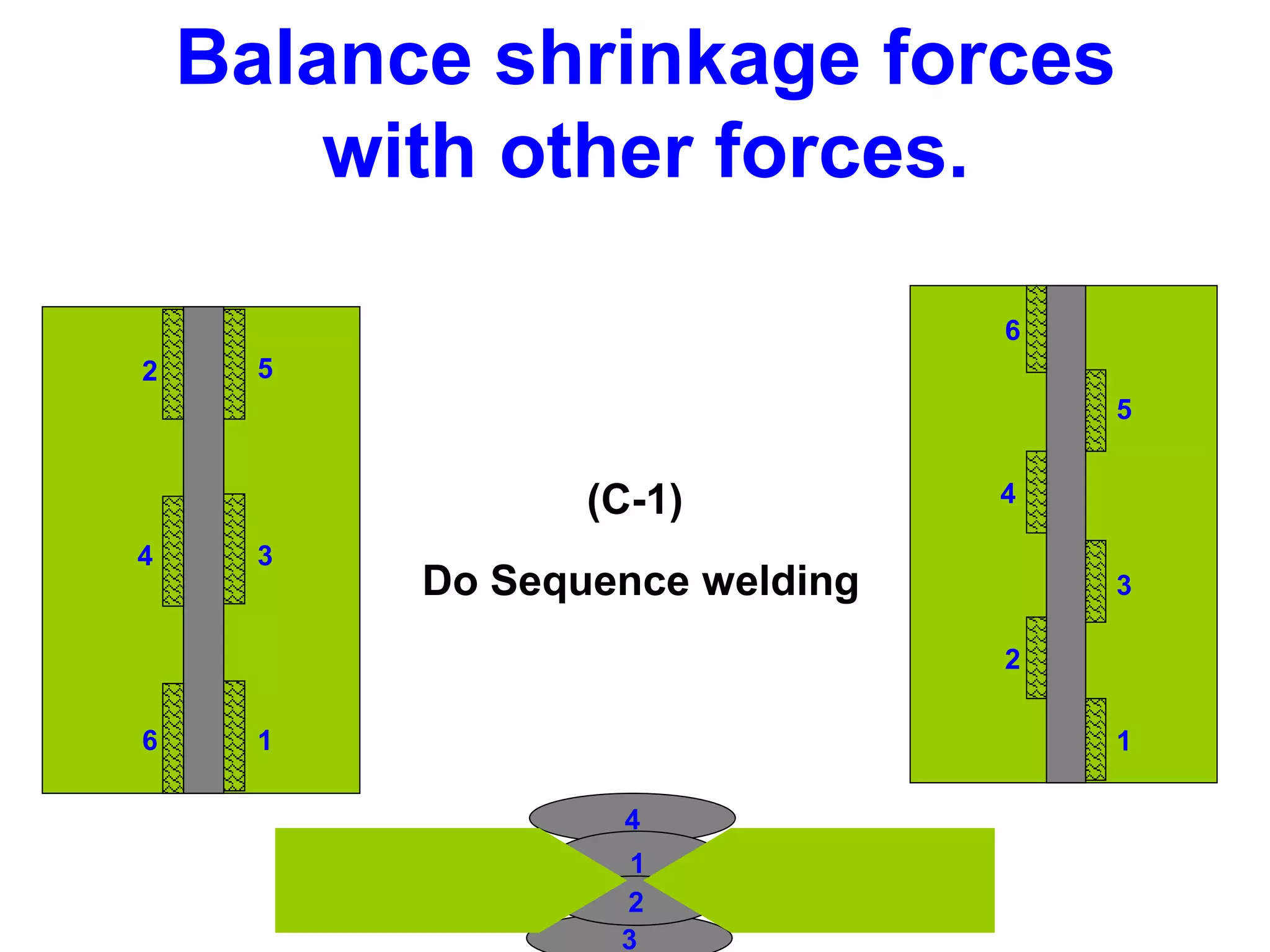
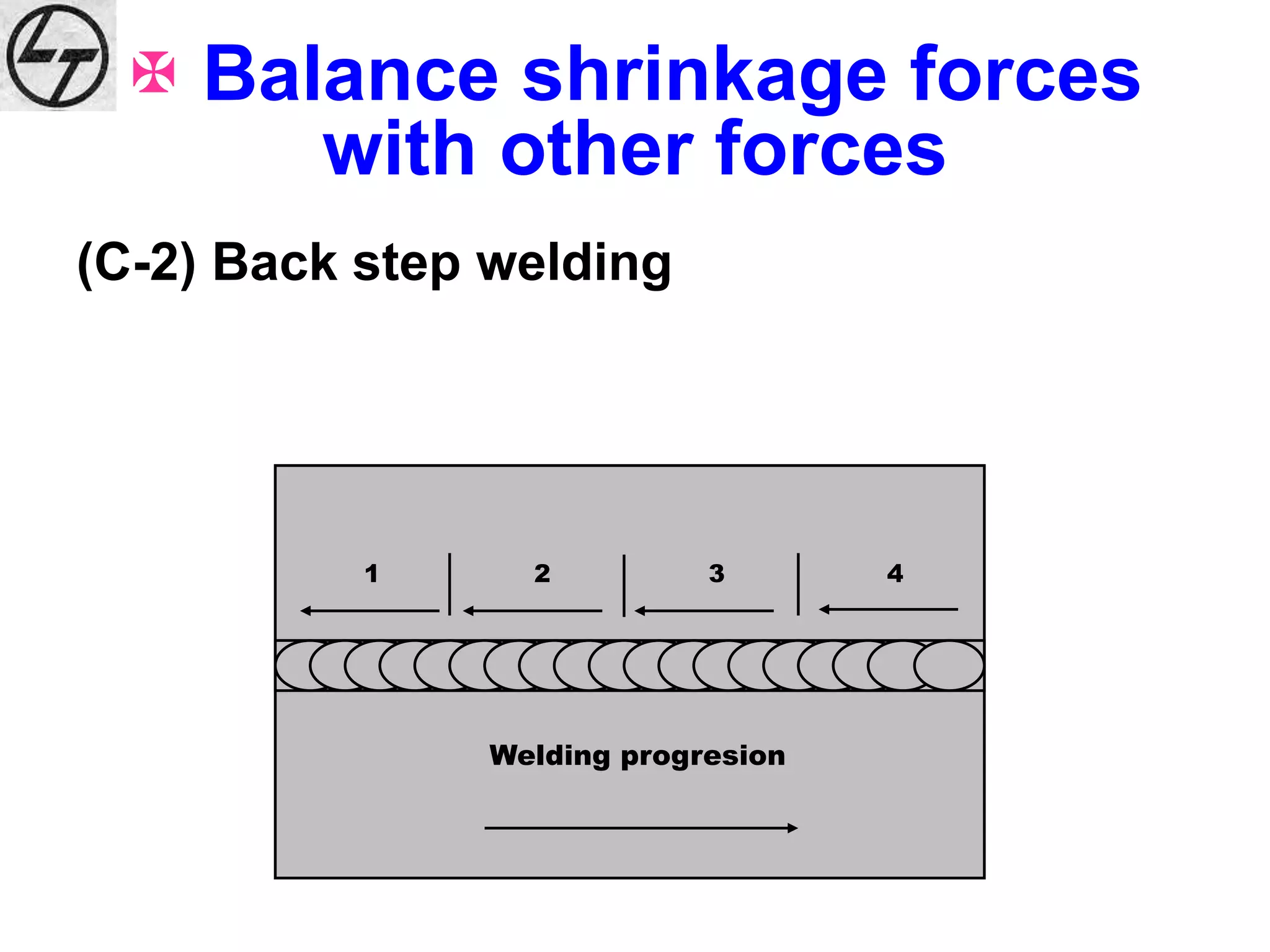
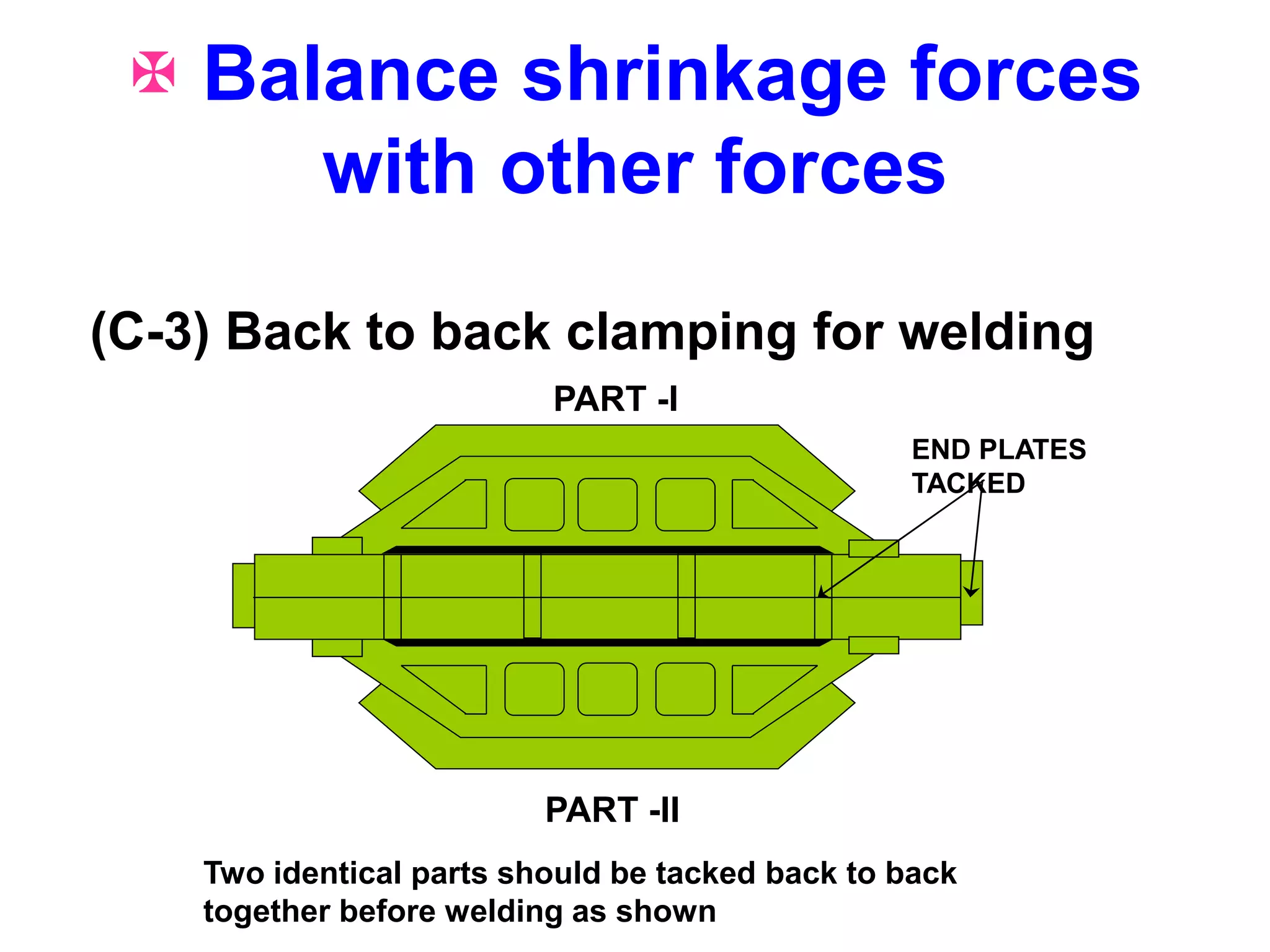
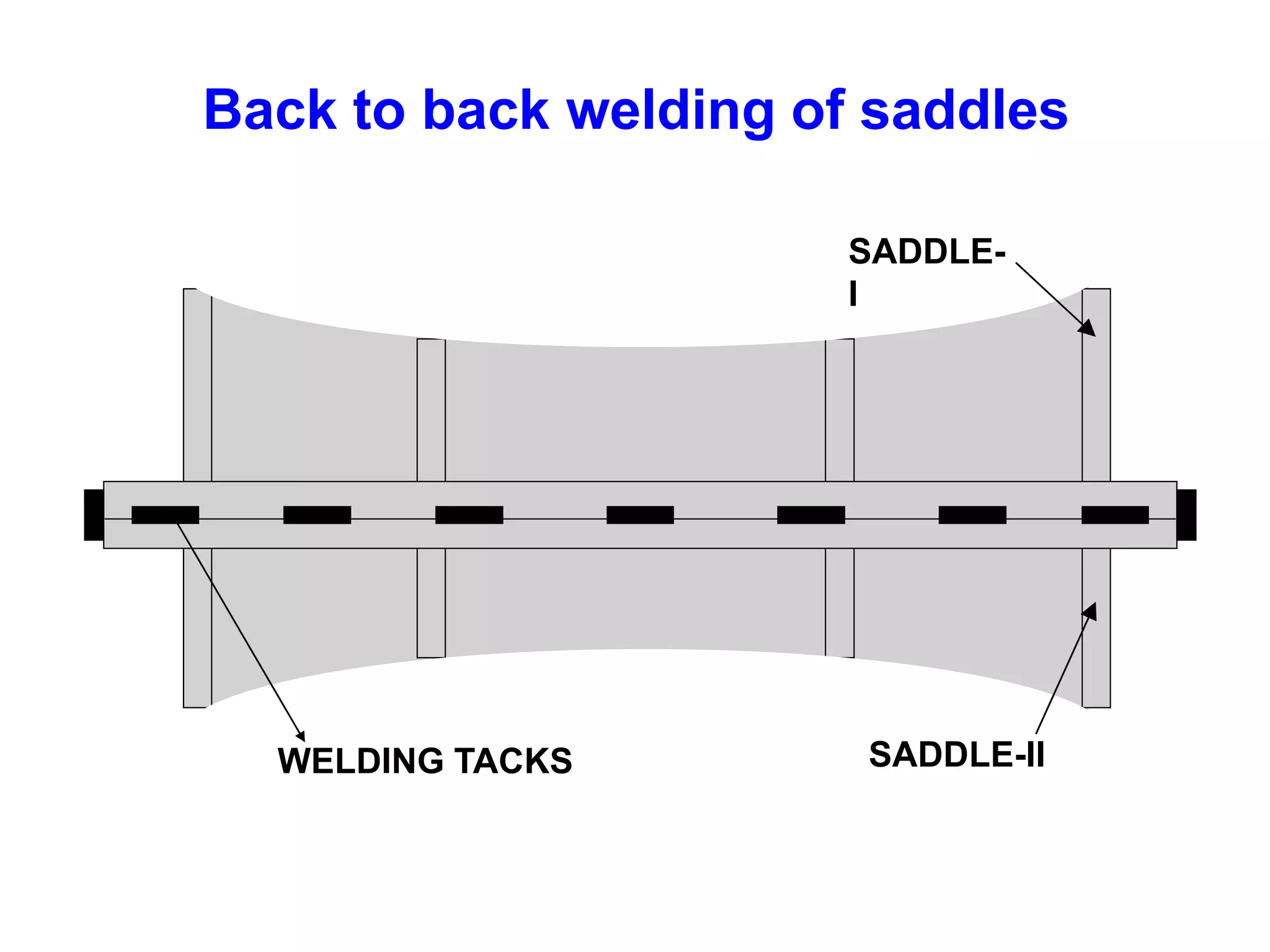
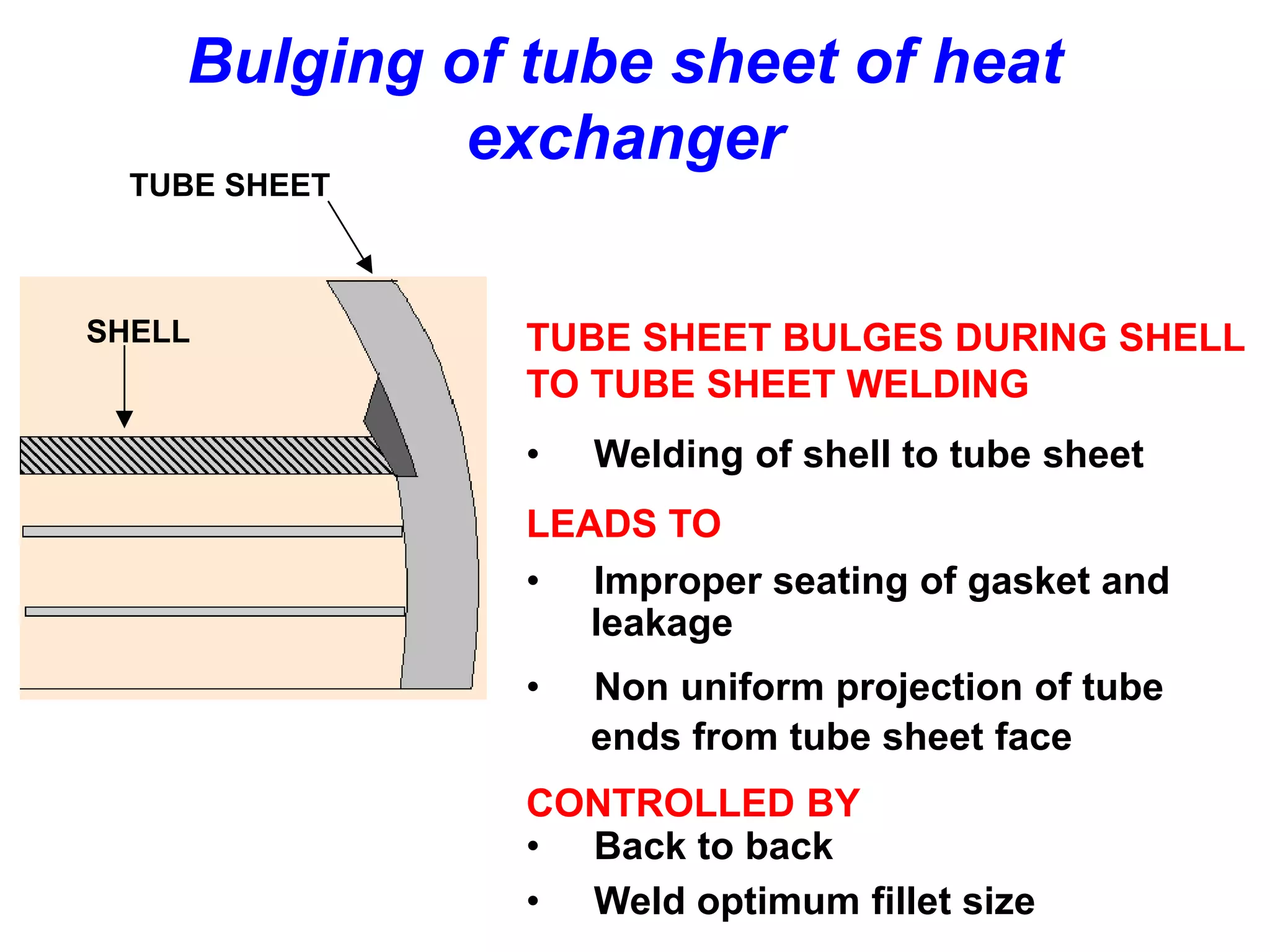
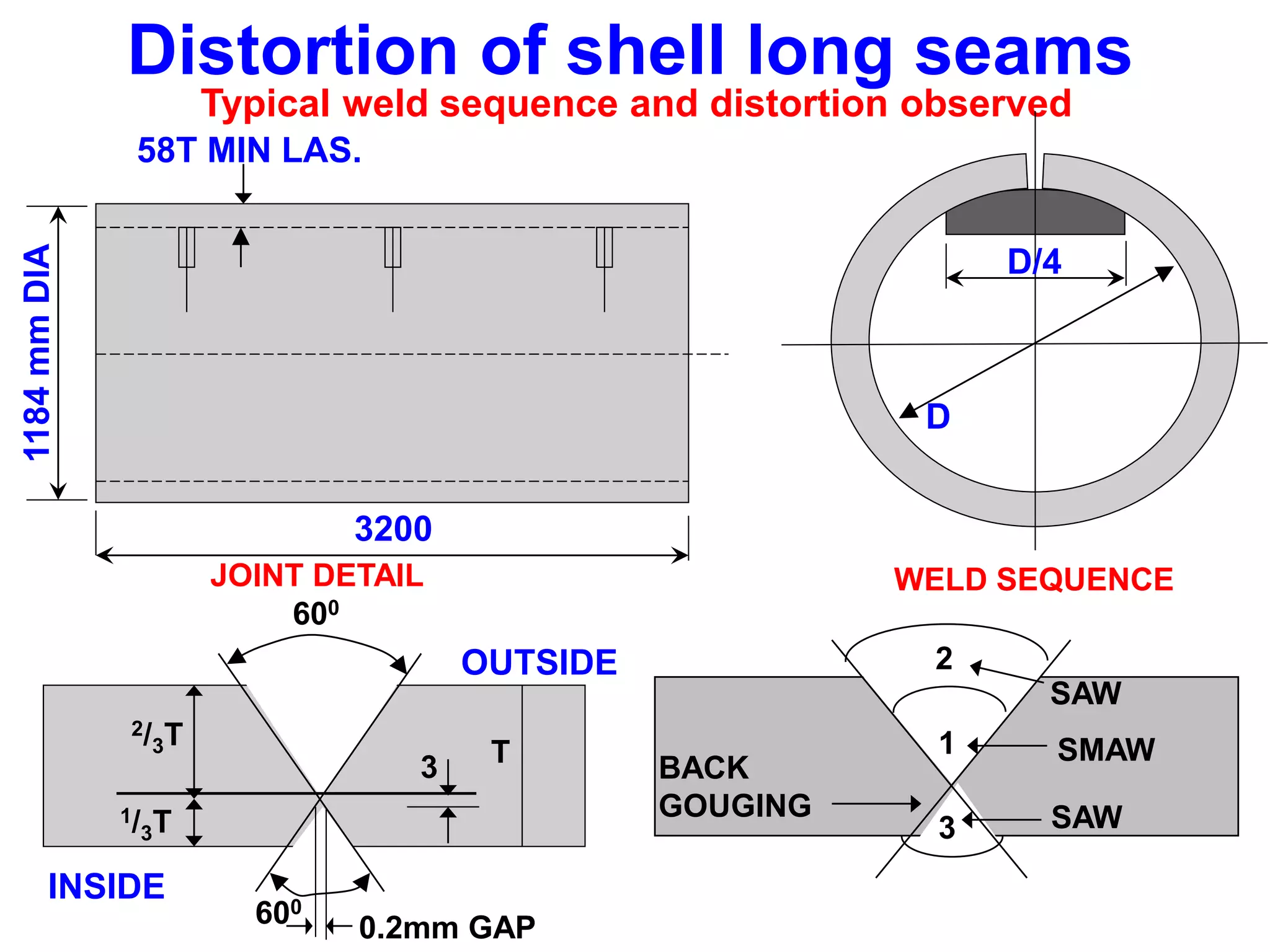
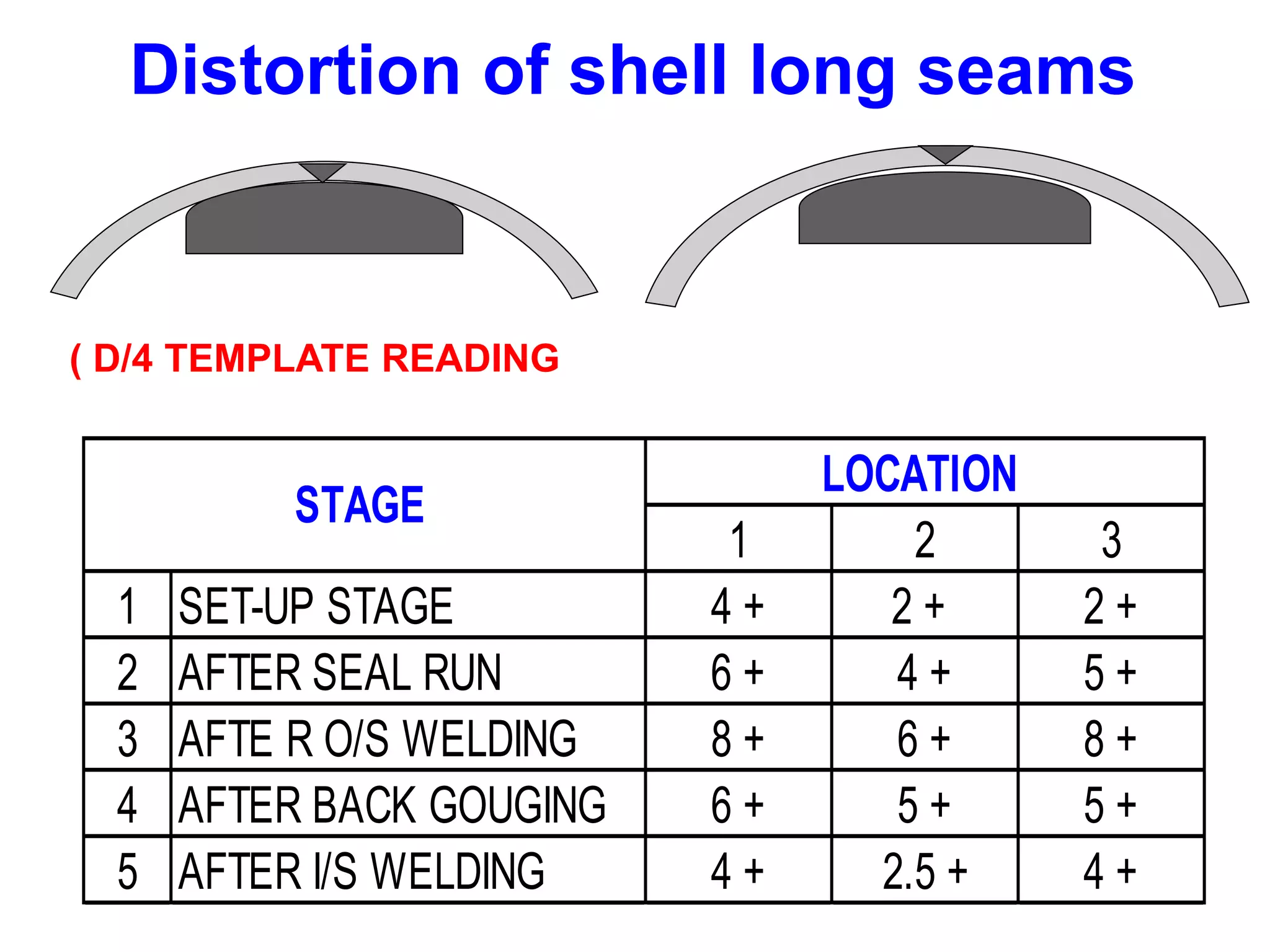
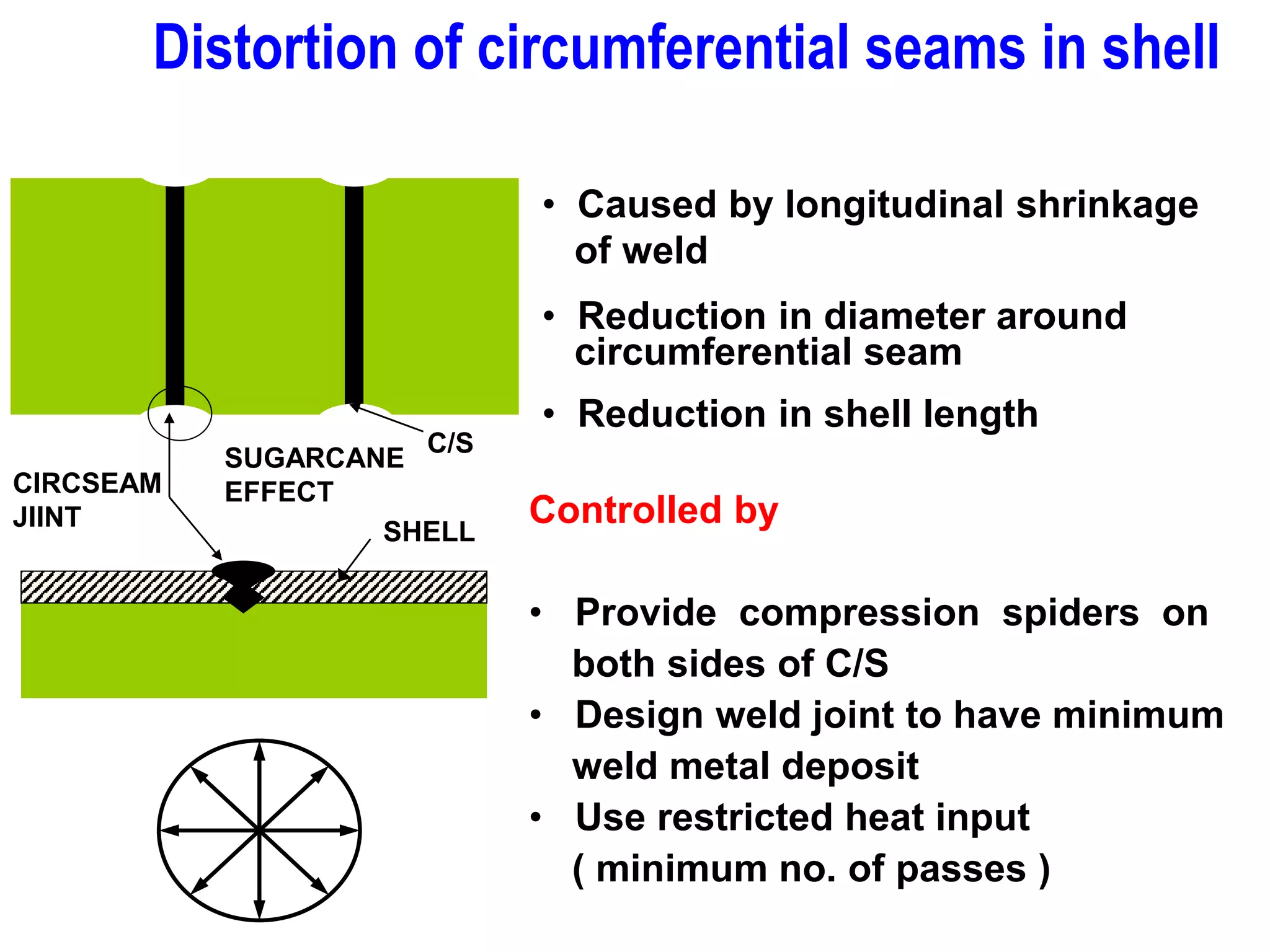
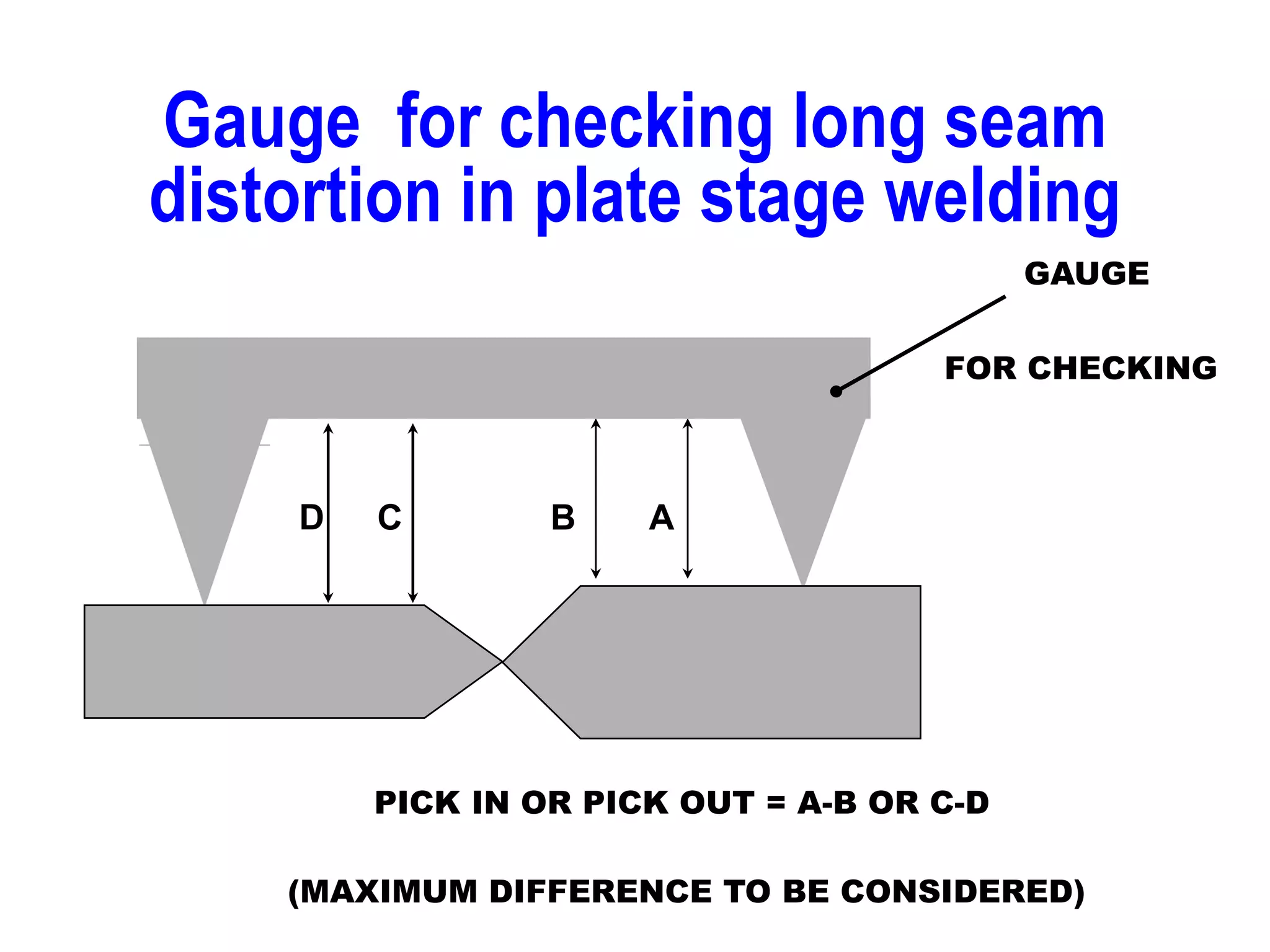
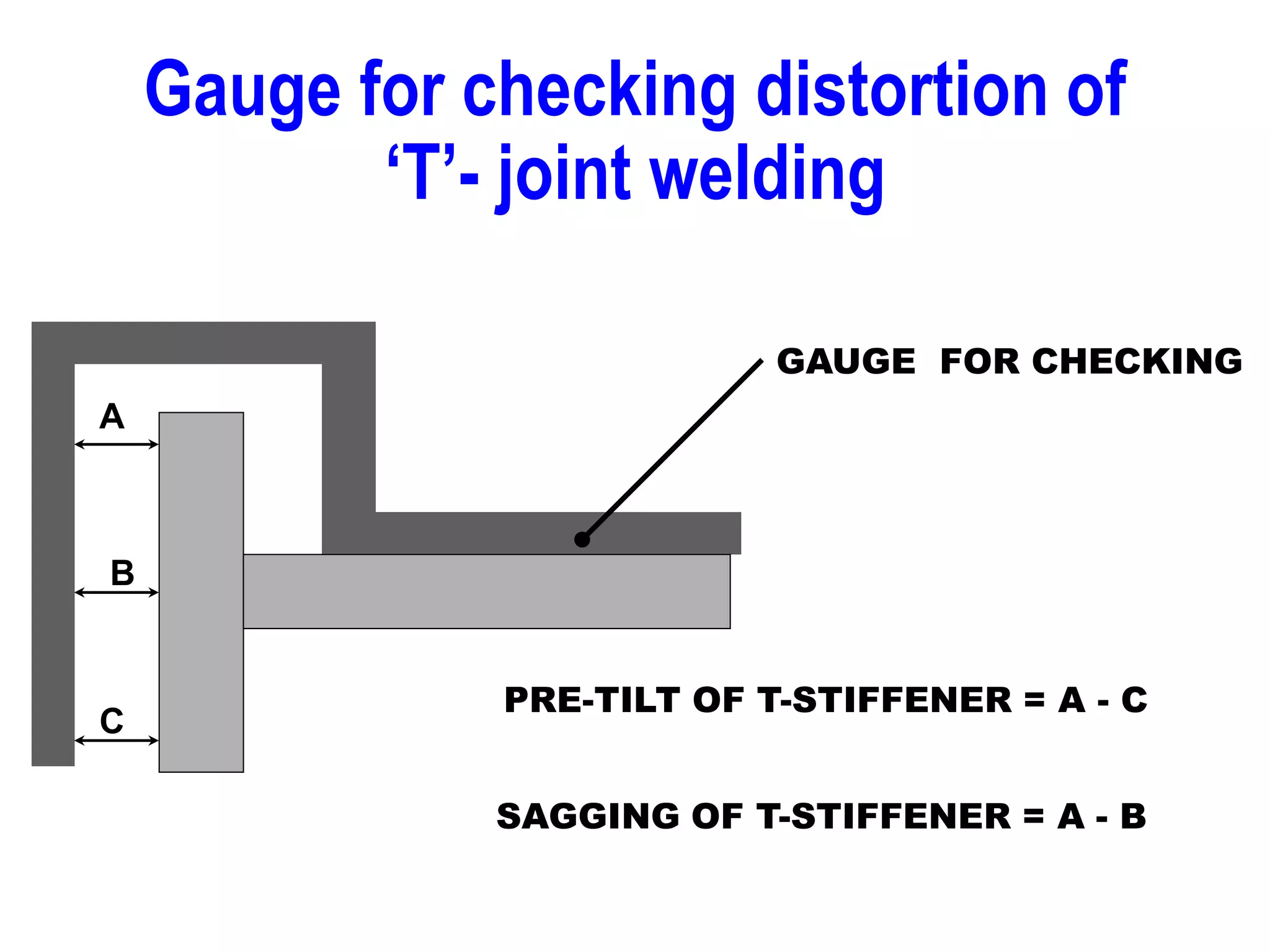
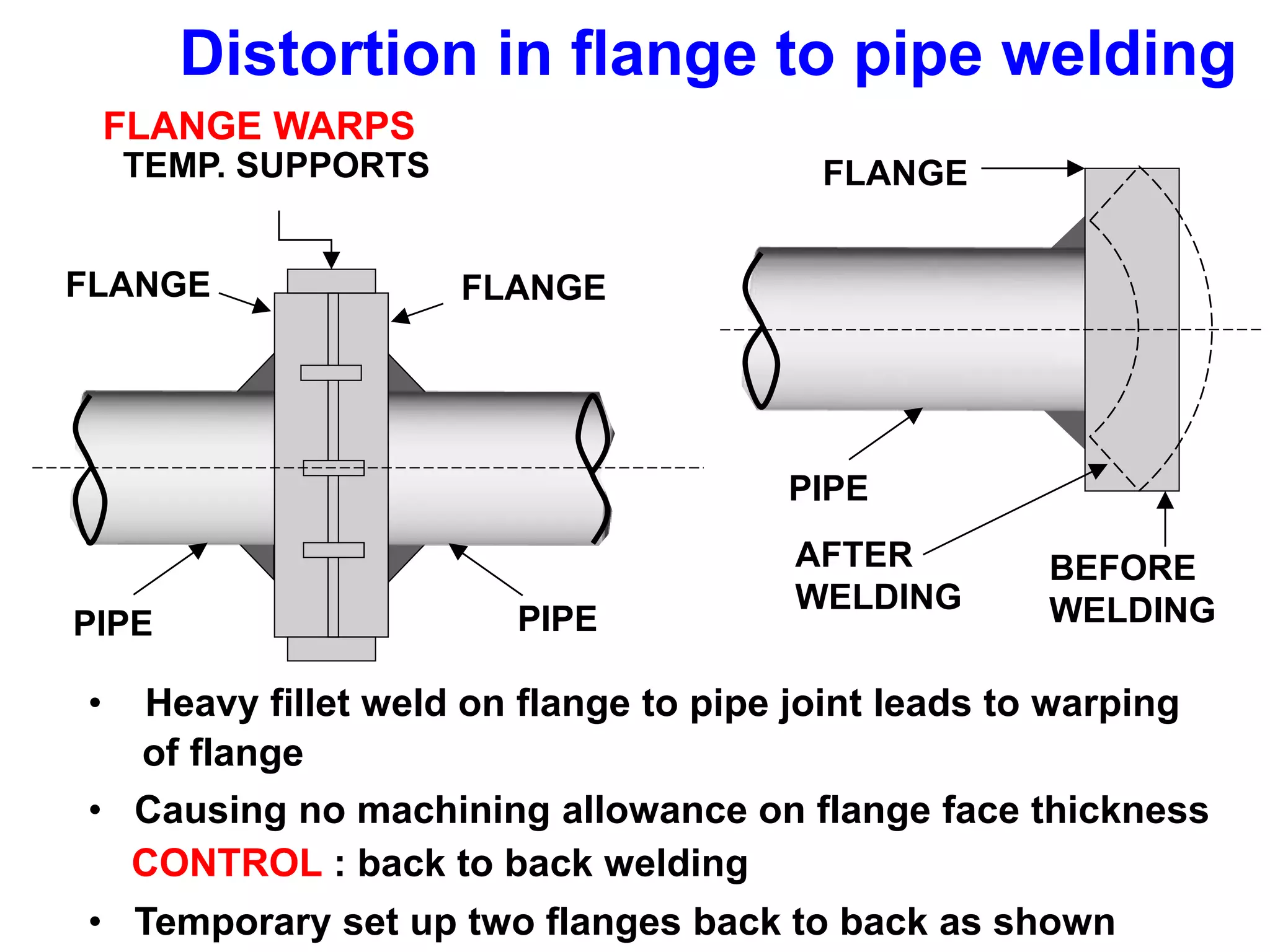
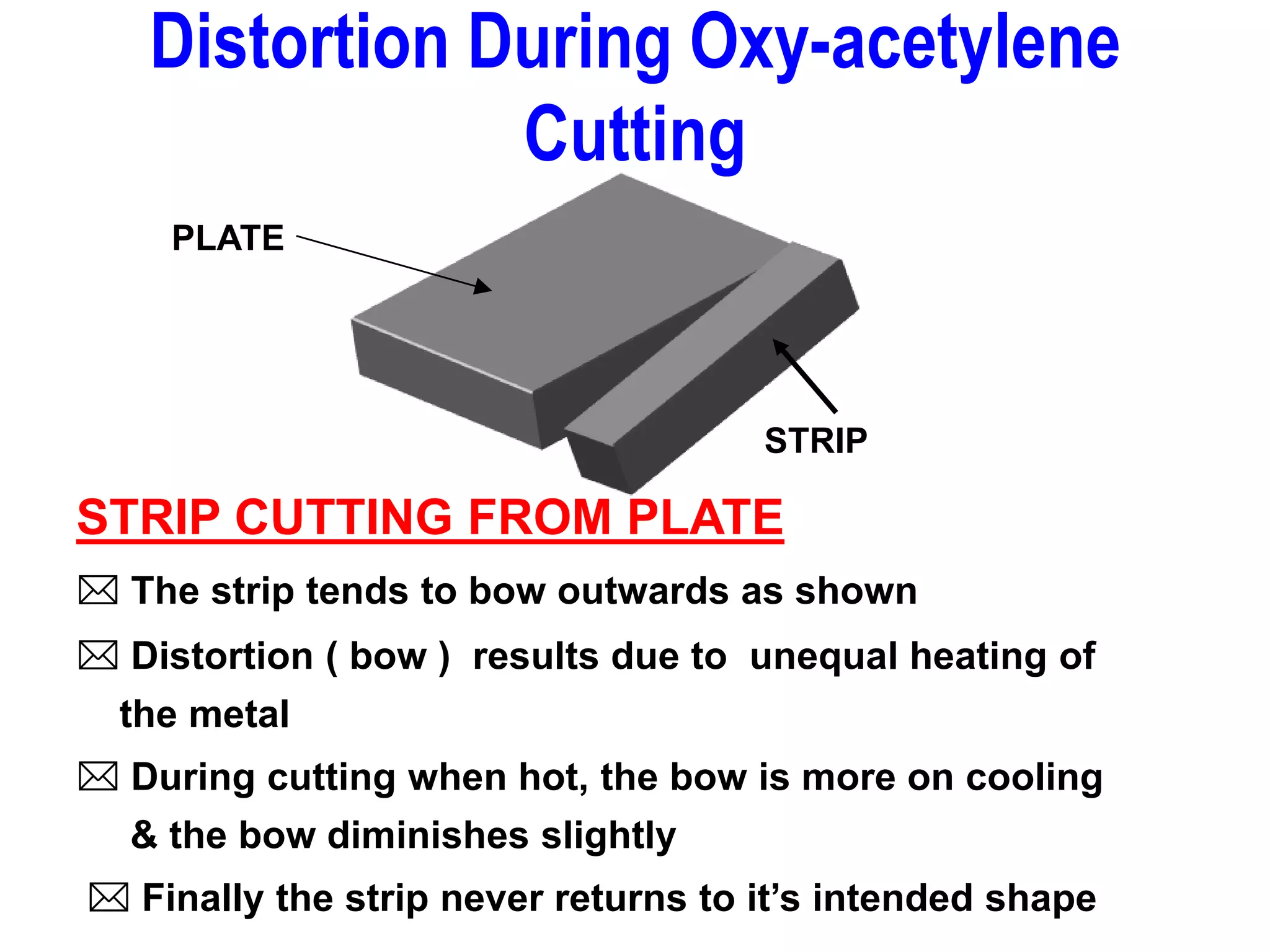
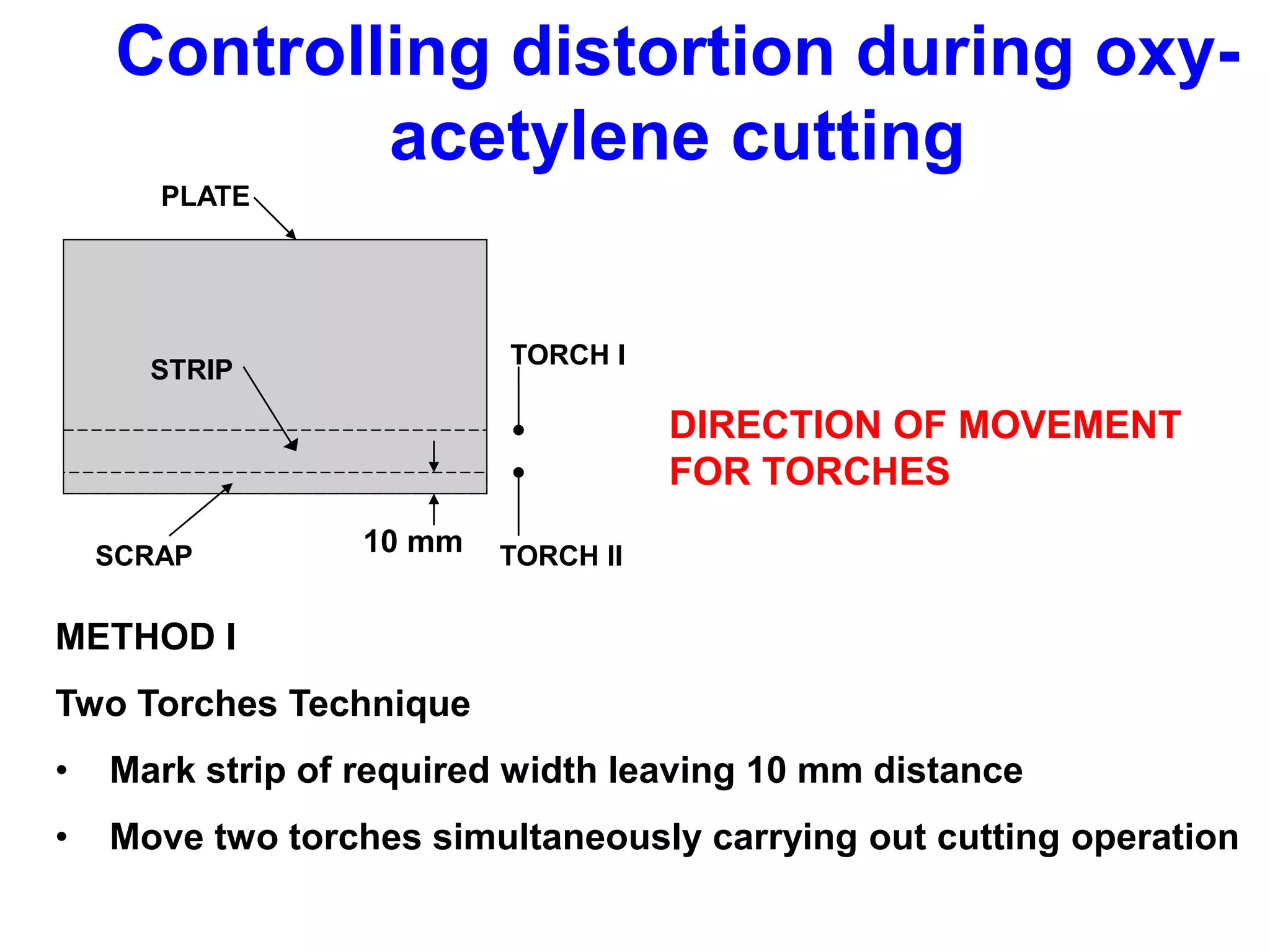
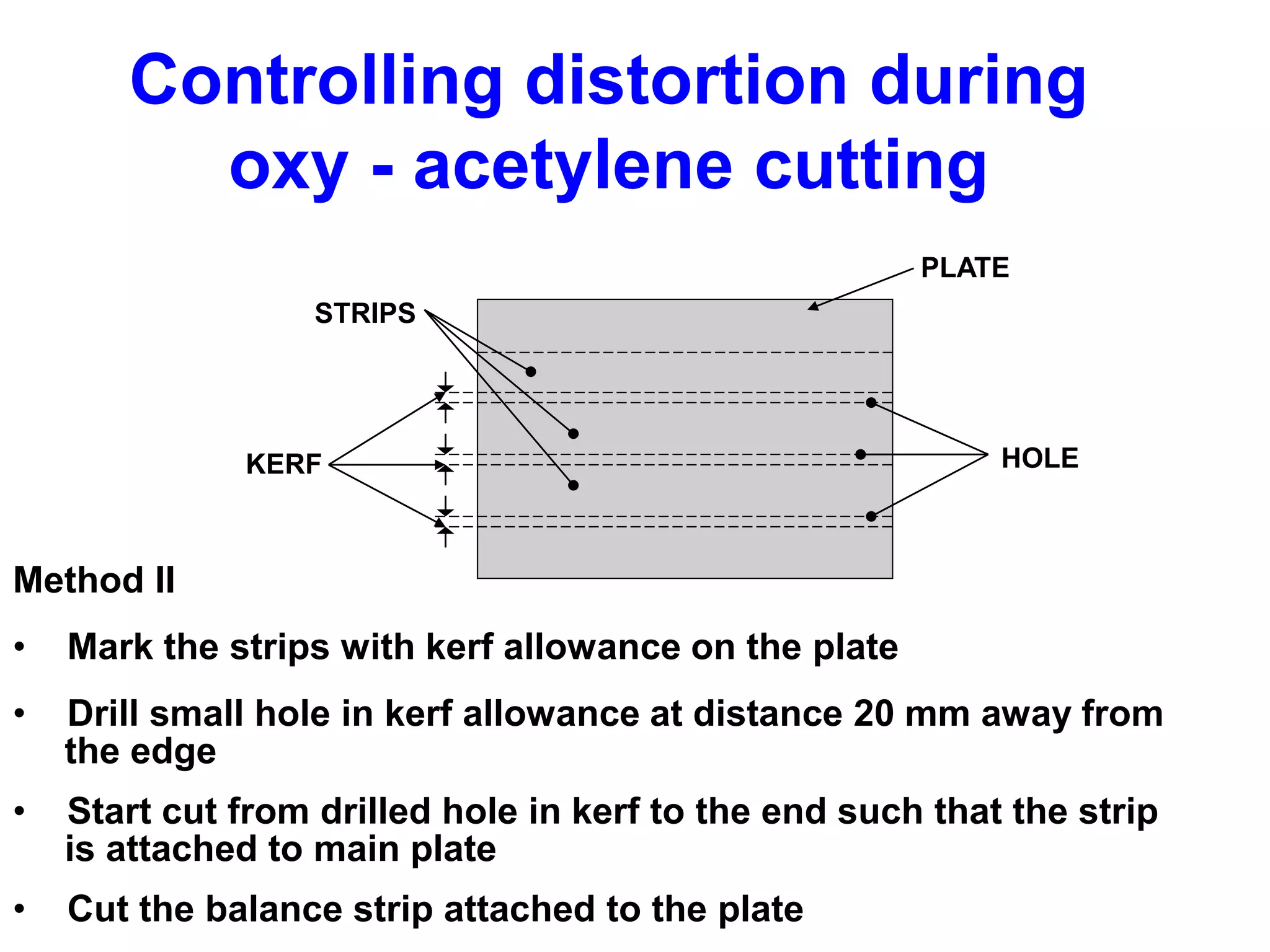
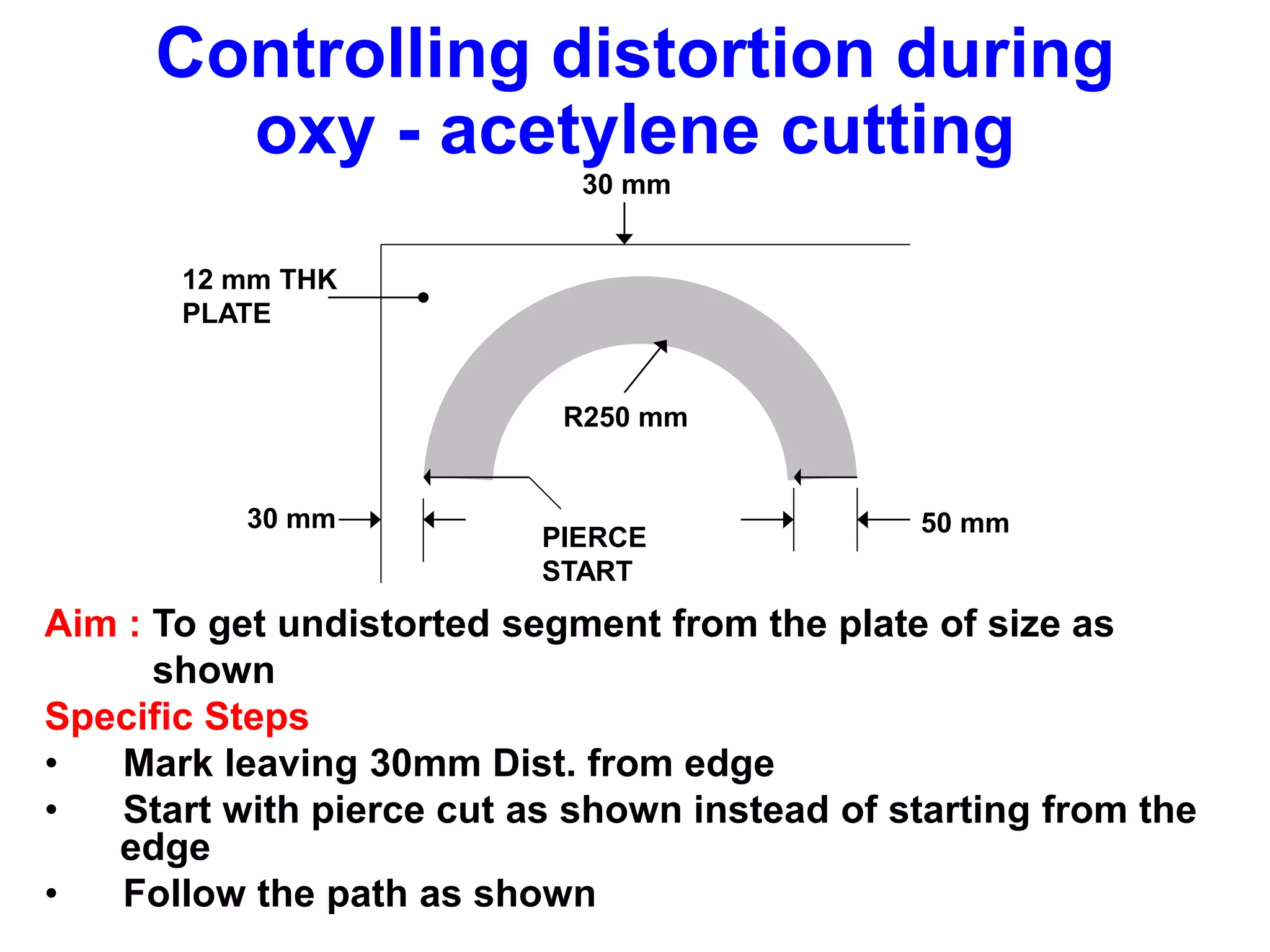
This document discusses various types of welding distortion including longitudinal, transverse, and angular distortion. It provides examples of how distortion occurs in butt welds, fillet welds, and T-joints due to restraint of expansion and contraction during the welding process. Methods to control and reduce distortion are covered, such as preheating, using proper joint design and welding sequence, and temporarily clamping components in a way that balances shrinkage forces. The importance of minimizing restraint and heat input is emphasized for limiting distortion in welded structures.