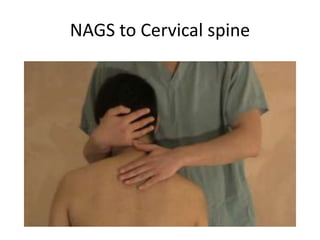
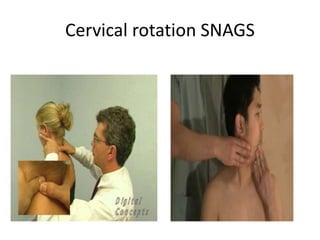
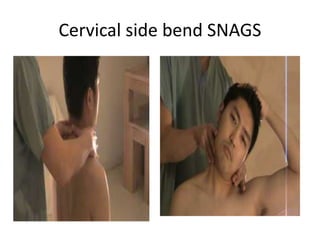
This document provides an introduction to NAGS (Natural Apophyseal Glides) and SNAGS (Sustained Natural Apophyseal Glides), manual therapy techniques developed by Brian Mulligan. It discusses Mulligan's background and credentials. The document describes the techniques, including that NAGS involve oscillatory glides along facet joints from C2-T3, while SNAGS involve sustained glides combined with symptomatic movements. Examples provided are cervical rotation, side bend, and traction SNAGS as well as NAGS techniques for the cervical and thoracic spine.