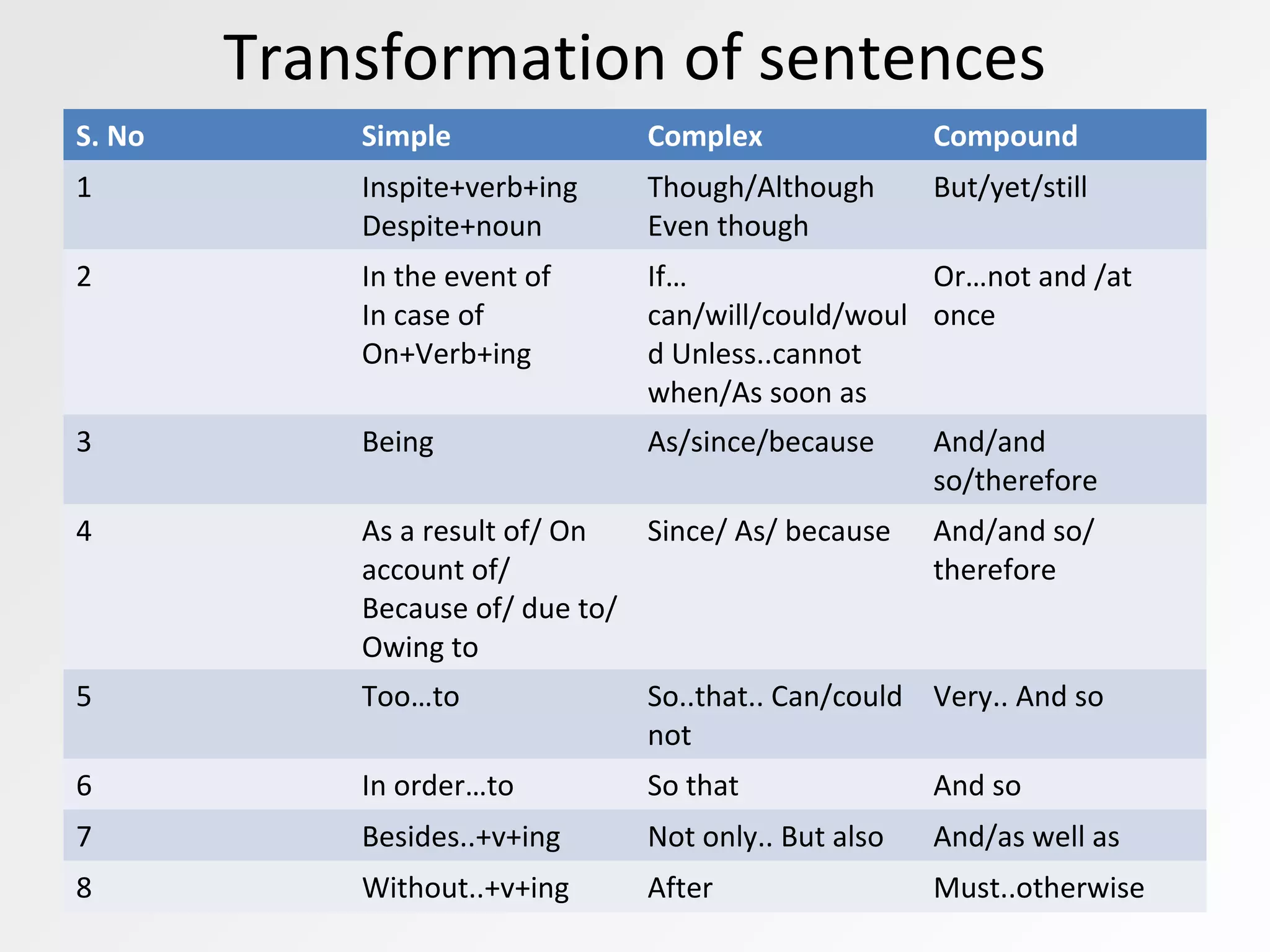
This document defines and provides examples of simple, compound, and complex sentences. It explains that a sentence contains a subject and predicate, a phrase does not, and a clause contains both. A main clause can stand alone while a subordinate clause cannot. A simple sentence has one main clause, a compound sentence has two or more main clauses joined by a conjunction, and a complex sentence has one main clause and one or more subordinate clauses. It also discusses the different types of conjunctions, relative pronouns, phrasal verbs, and provides examples of transforming sentences between simple, complex, and compound.