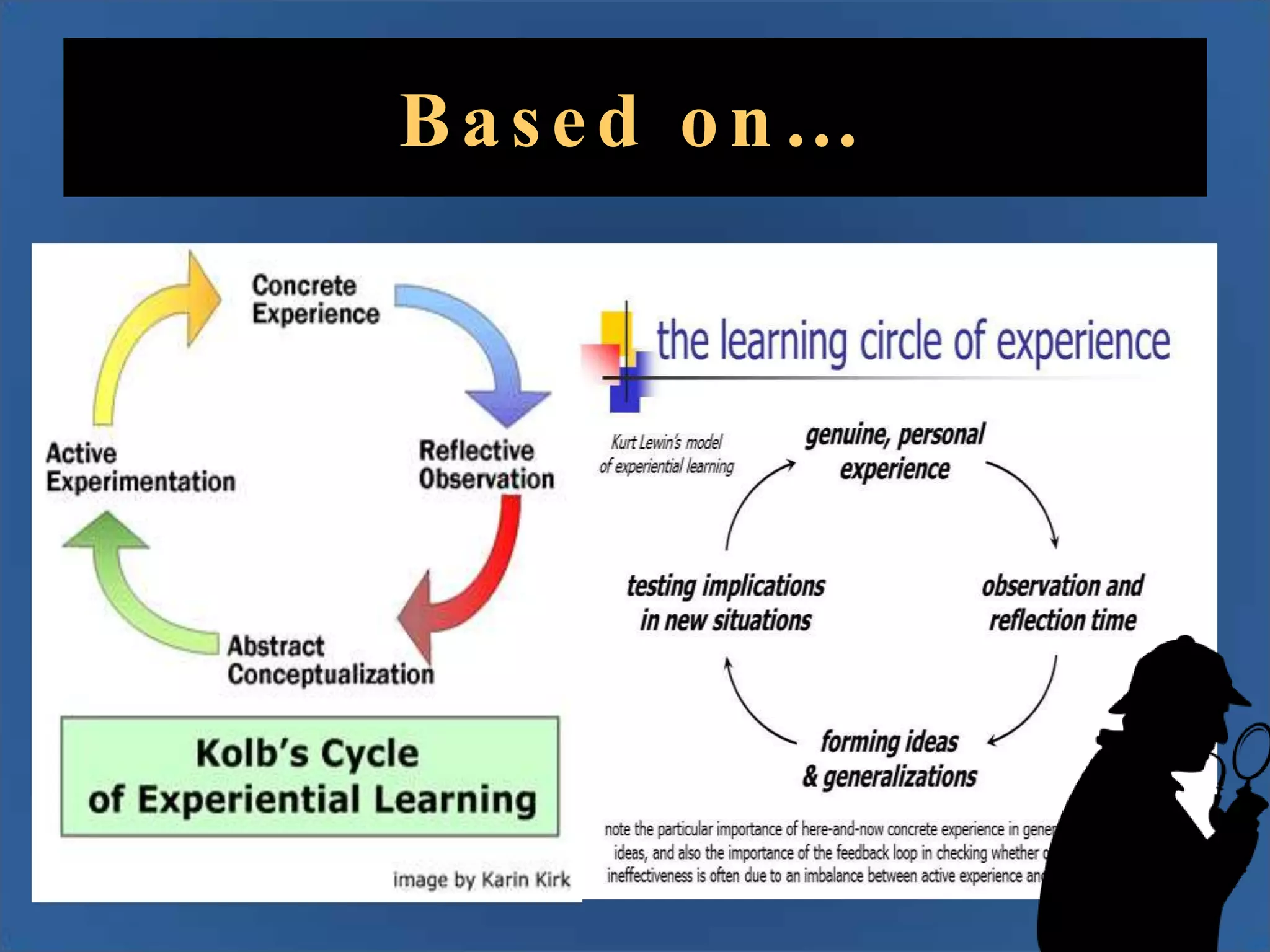
Team Five Star created an infographic for third-level lecturers to help teach critical thinking. The infographic will contain data on critical thinking research, definitions, tools, learning styles, leading thinkers, and a timeline. It is based on literature about using infographics as learning objects and principles of accessibility, usability, and cultural-historical activity theory. The infographic will have a Sherlock Holmes visual style and incorporate Victorian and steampunk aesthetics.














![Teaching & Learning Styles
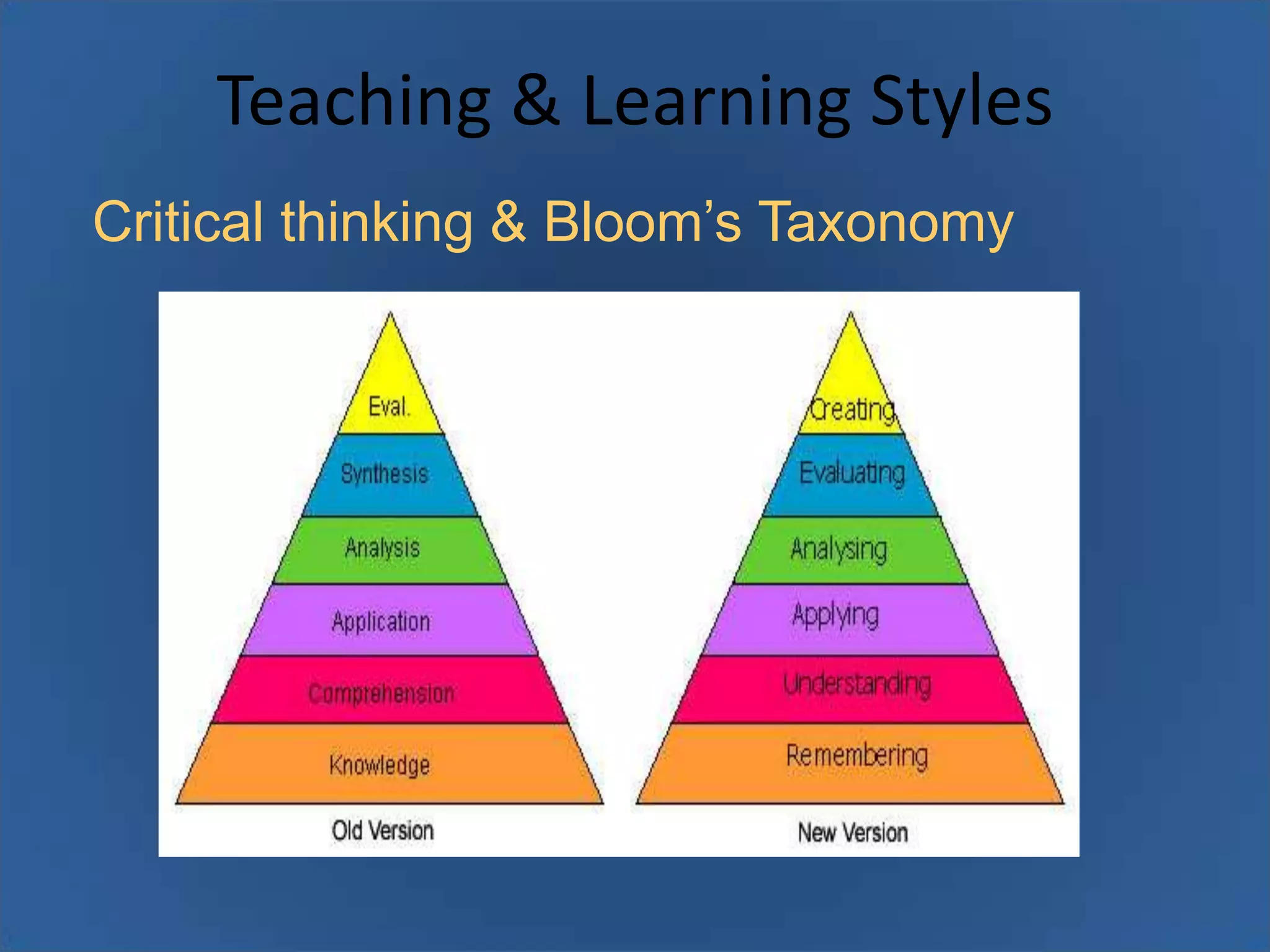
Critical thinking & Bloom’s Taxonomy
• Higher-order skills classified in the Taxonomy such as
analysis, synthesis and evaluation.
• It may be thought that all that needs to be done to
incorporate critical thinking in the classroom is to call for
analysis, synthesis and evaluation of problems.[1]
• However, this would not be sufficient for example the
process of learning is not a linear process for example the
acquisition of knowledge does not merely rely on the
acquisition of facts but rather it requires an
analysis, synthesis and evaluation of the facts in order for it
to become knowledge.
• Critical thinking in the classroom - foster a learning
environment which combines the presenting of facts for the
learner to examine and question and use in order to construct
their knowledge.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teamfivestar-final-140225111648-phpapp02/75/Team-Project-work-on-Critical-Thinking-Infographic-19-2048.jpg)
![Teaching & Learning Styles
• Behaviourism
Behaviourism concentrates on observable behaviour without
considering motivation or other mental processes. With this
teaching style the main implication is that the learner is
completely passive, and the teacher holds the key to
learning success, so how can critical thinking be considered
with this approach. Taking a behaviourism approach the
goal is to change a behaviour and to measure that
change, so the change is critical thinking.
Using this approach the material presented should be
presented in (1) chunks and (2) questioning of the material
should be introduced at the beginning. (3) Frequent
feedback should be provided to the learner.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teamfivestar-final-140225111648-phpapp02/75/Team-Project-work-on-Critical-Thinking-Infographic-21-2048.jpg)
![Teaching & Learning Styles
• Cognitivism
Cognitivism focuses on the way in which the learner gains
and organises their knowledge. This approach to learning
develops strategies for thinking and so aligns well with critical
thinking. With this approach facts are presented to the
learner and the learner encodes these facts in their long-term
and due to the encoding the information can be retrieved.
This approach of encoding information involved the learners
analysis, synthesis and evaluation of the material thus a
process of developing their critical thinking.
Using this approach the use of (1) mind-maps as a
presentation of the facts aligns well with developing critical
thinking skills through cognitive approaches of learning.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teamfivestar-final-140225111648-phpapp02/75/Team-Project-work-on-Critical-Thinking-Infographic-22-2048.jpg)
![Teaching & Learning Styles
• Social Constructivism
Social constructivism involves learning based on the
interaction with others. It is believed that thinking
does not exist independently of the world, nor of other
people.
Using this approach the use of (1) peer tutoring is very
valuable as the learner has to construct their and then
present it to their peer, this presentation of the facts to
the peer in then challenged, encouraging a deeper
level of learning and could be used to promote critical
thinking.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teamfivestar-final-140225111648-phpapp02/75/Team-Project-work-on-Critical-Thinking-Infographic-23-2048.jpg)