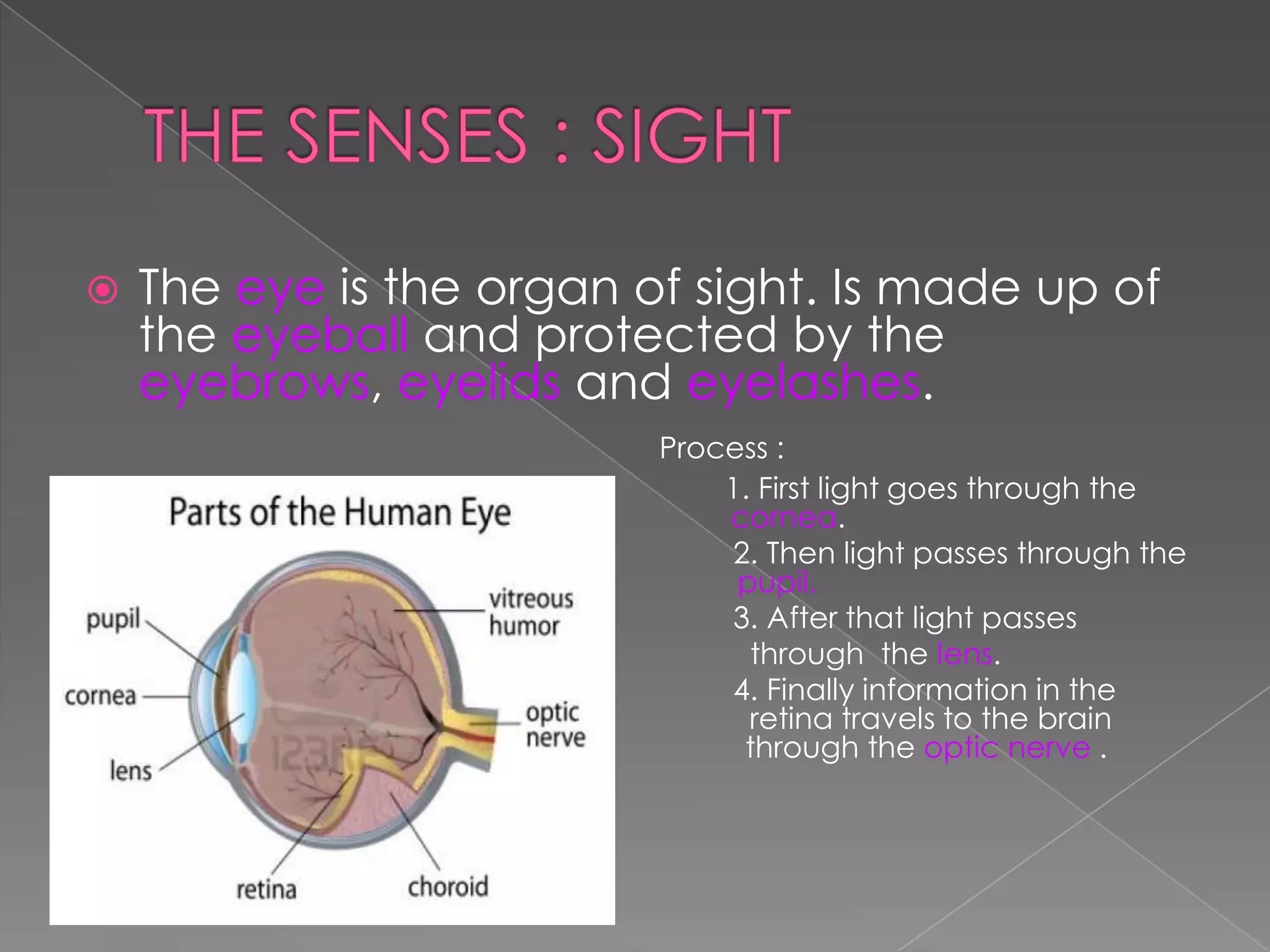
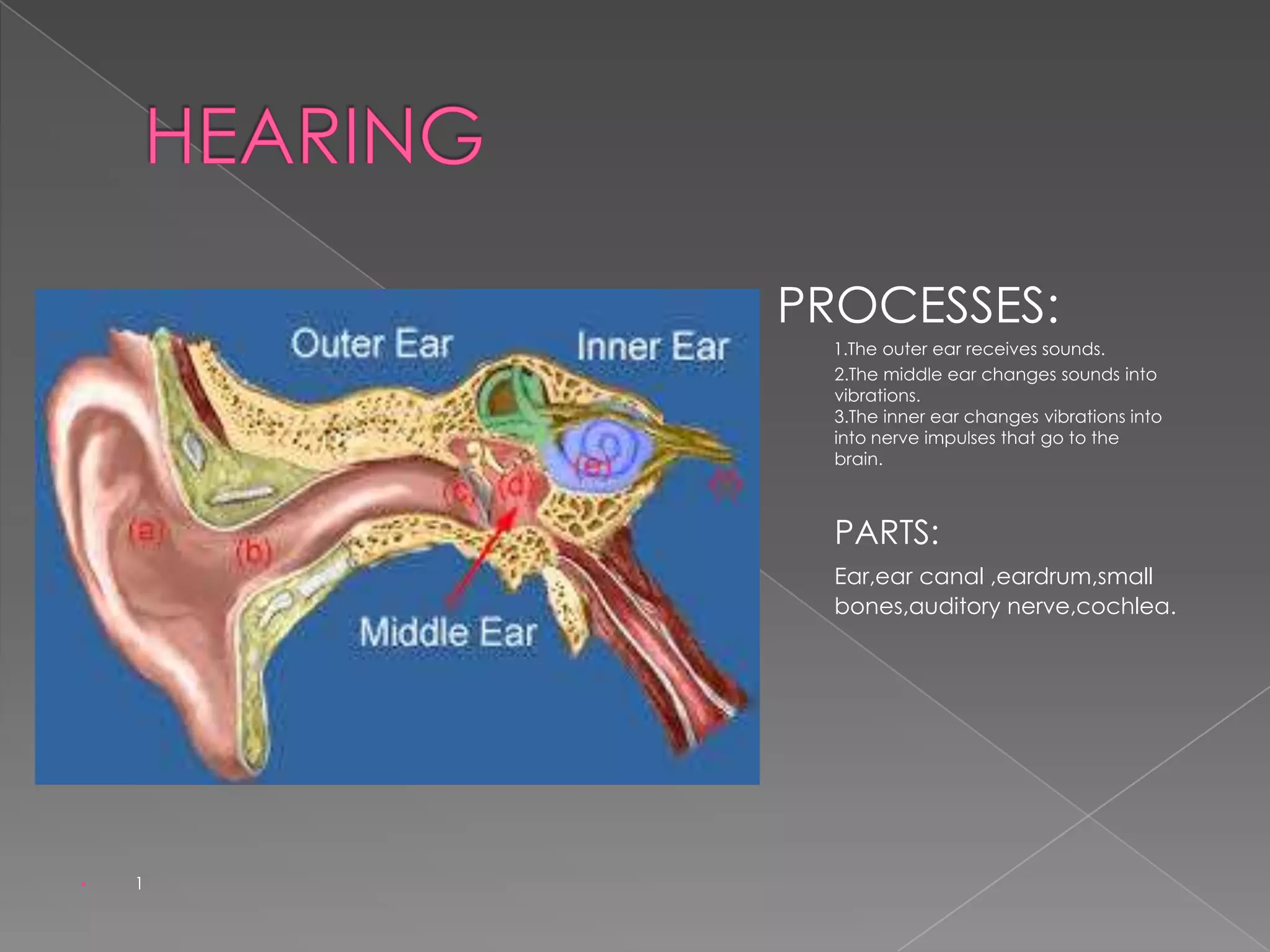
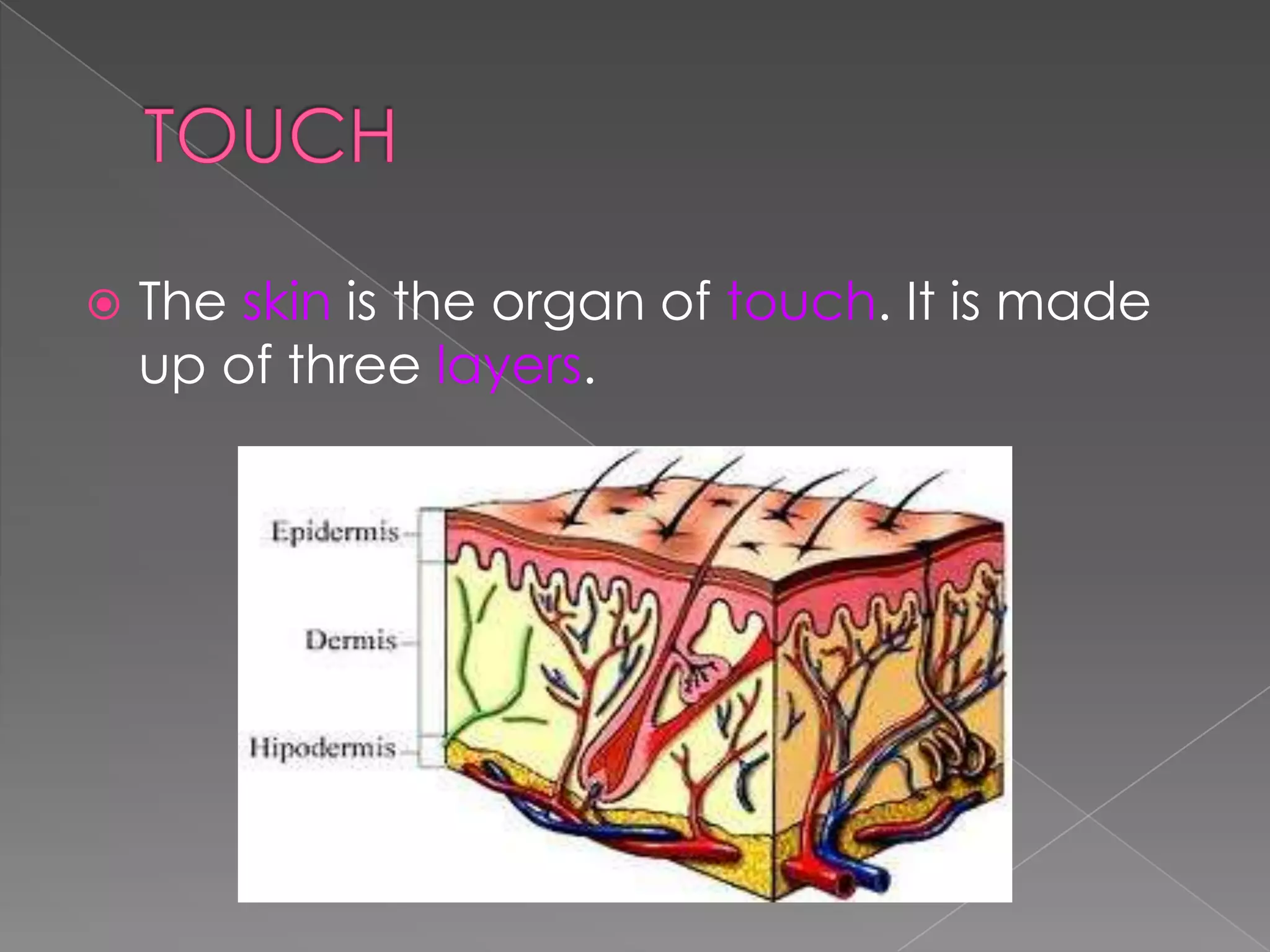
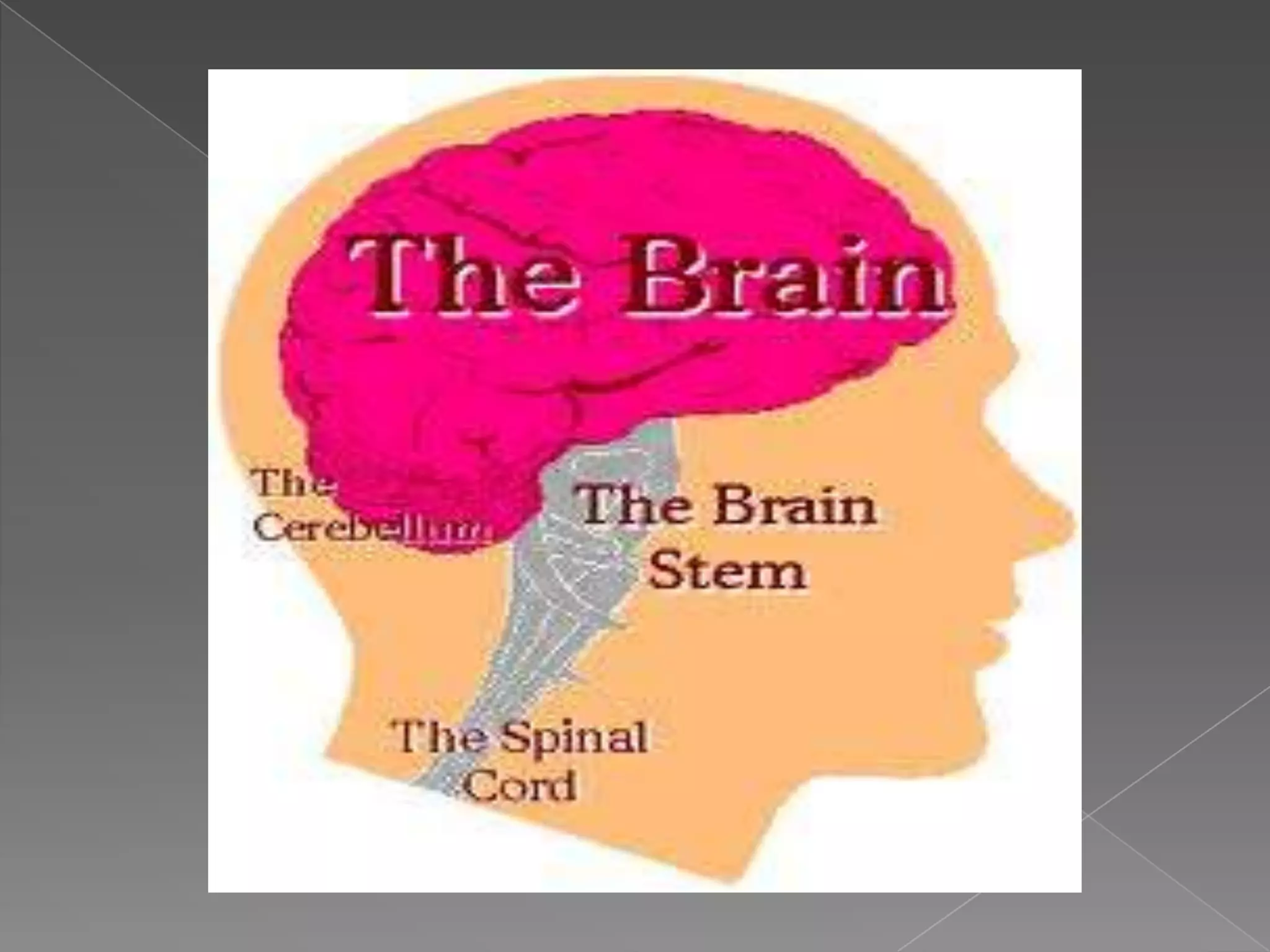
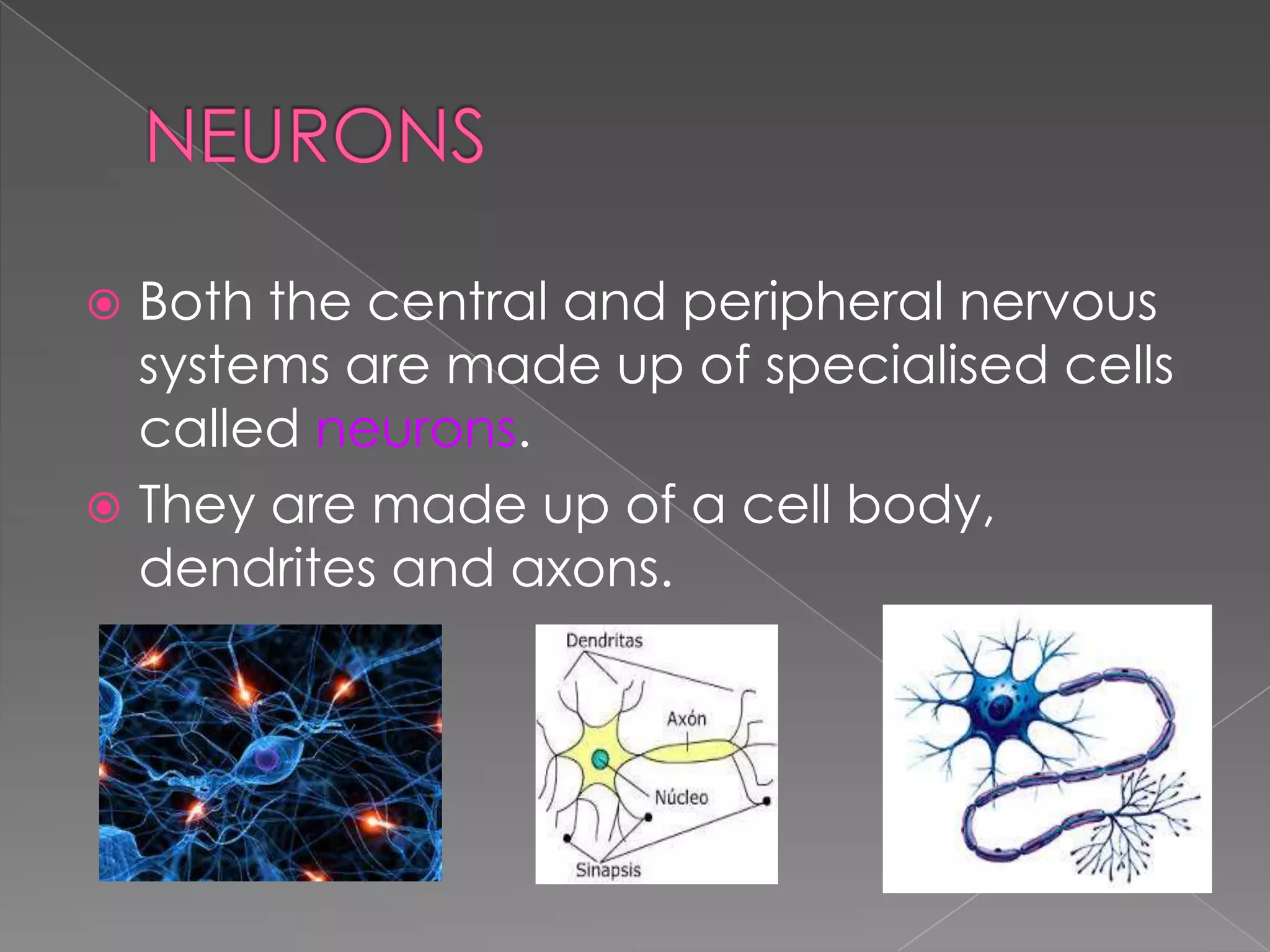
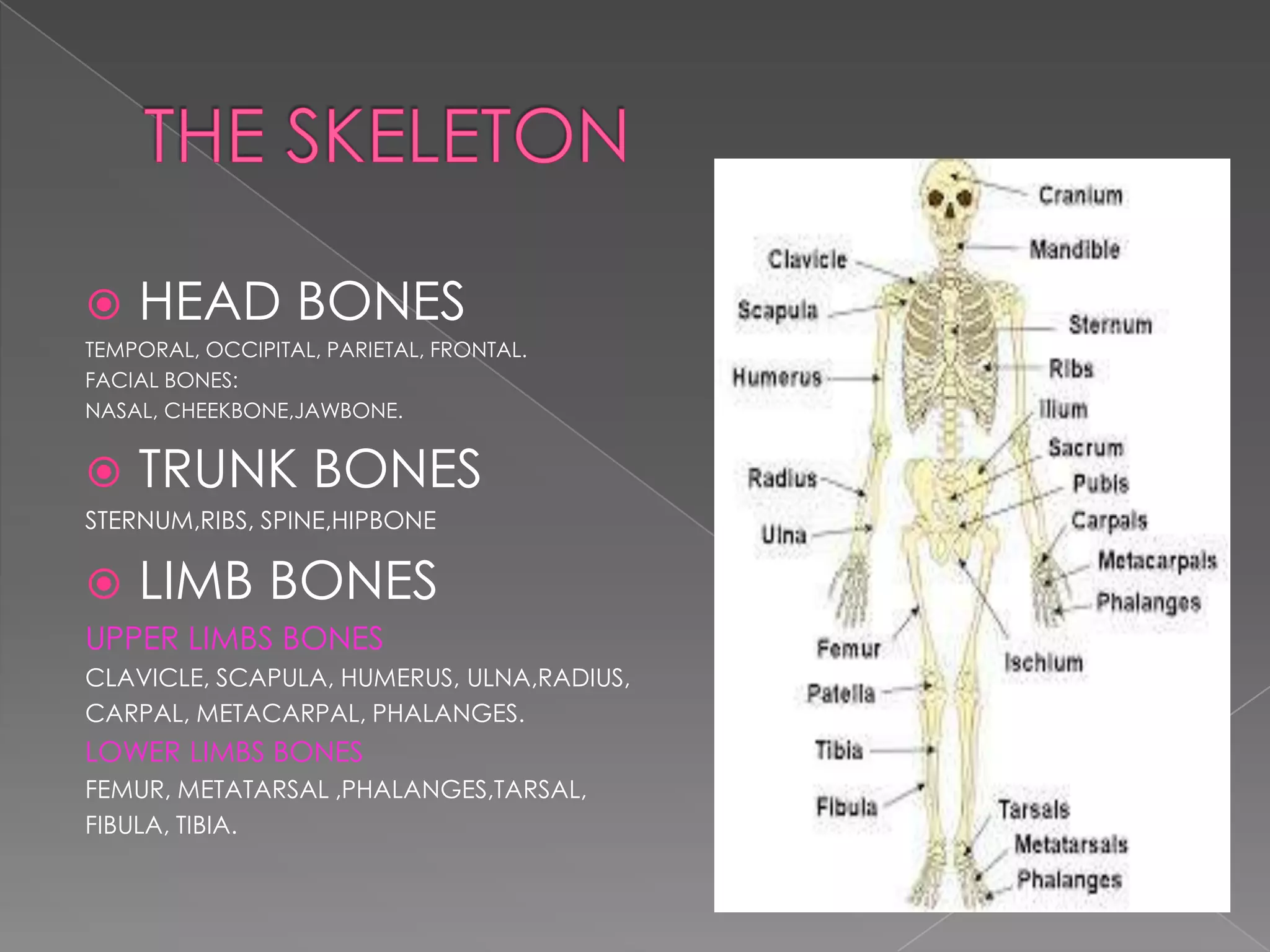
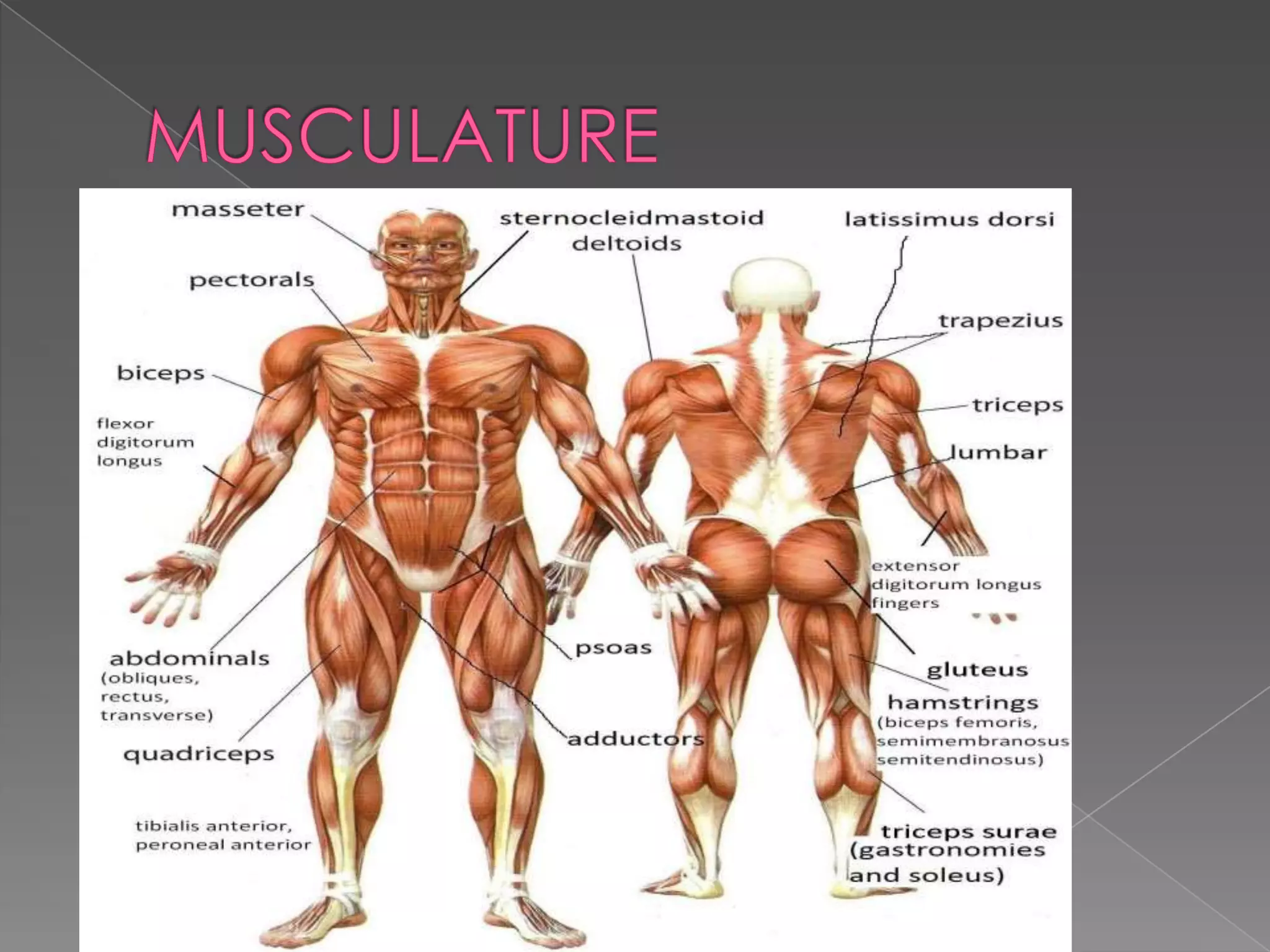
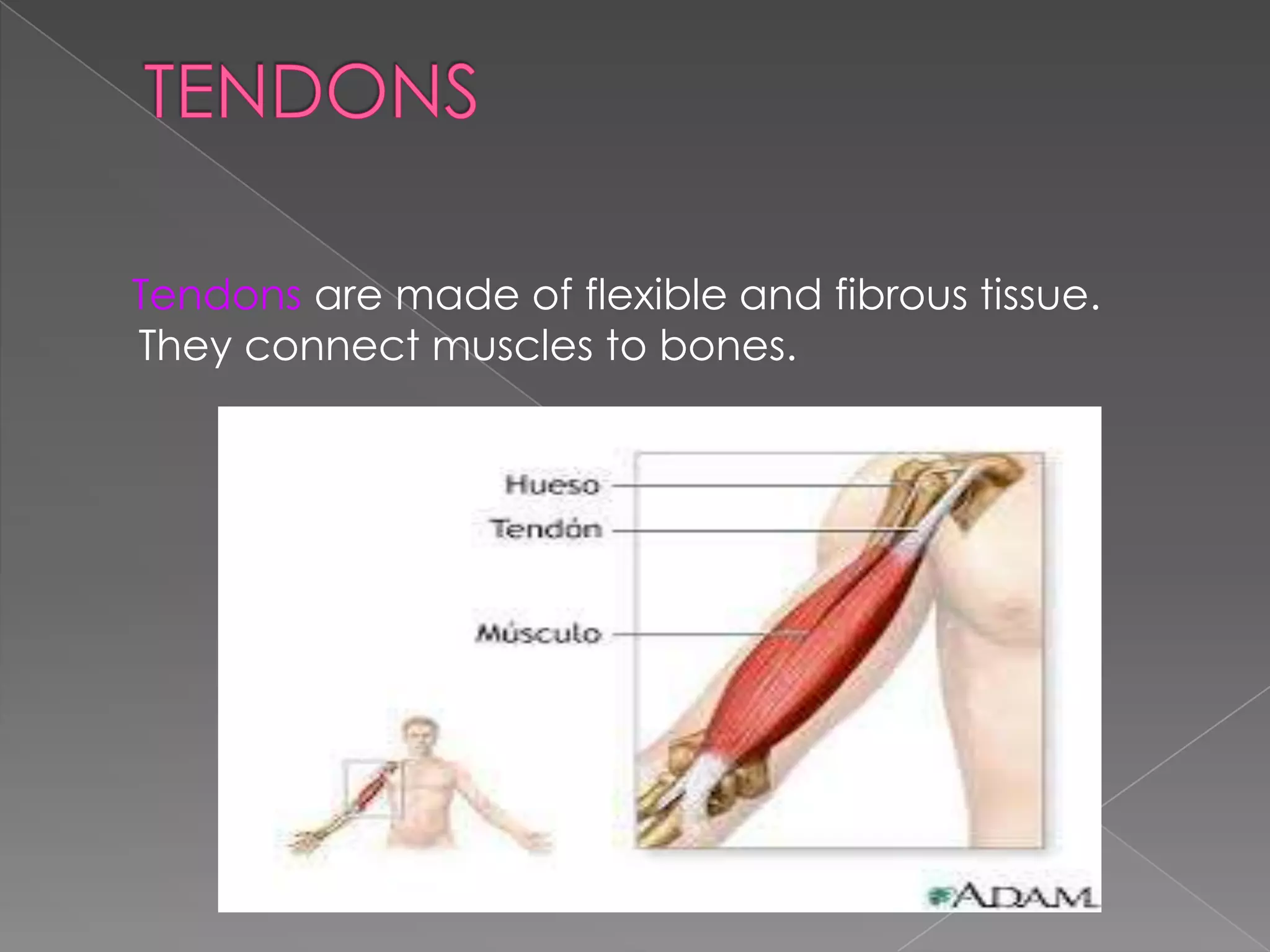
This document summarizes the key human sensory and motor systems. It describes the main organs for sight (eye), smell (nose), hearing (ear), touch (skin), and taste (tongue). It outlines the main parts and processes for each sensory organ. It also discusses the nervous system, including the central and peripheral divisions, neurons, and voluntary and involuntary movements controlled by the brain and spinal cord respectively. Finally, it briefly mentions the main bones of the body and types of joints that connect bones.