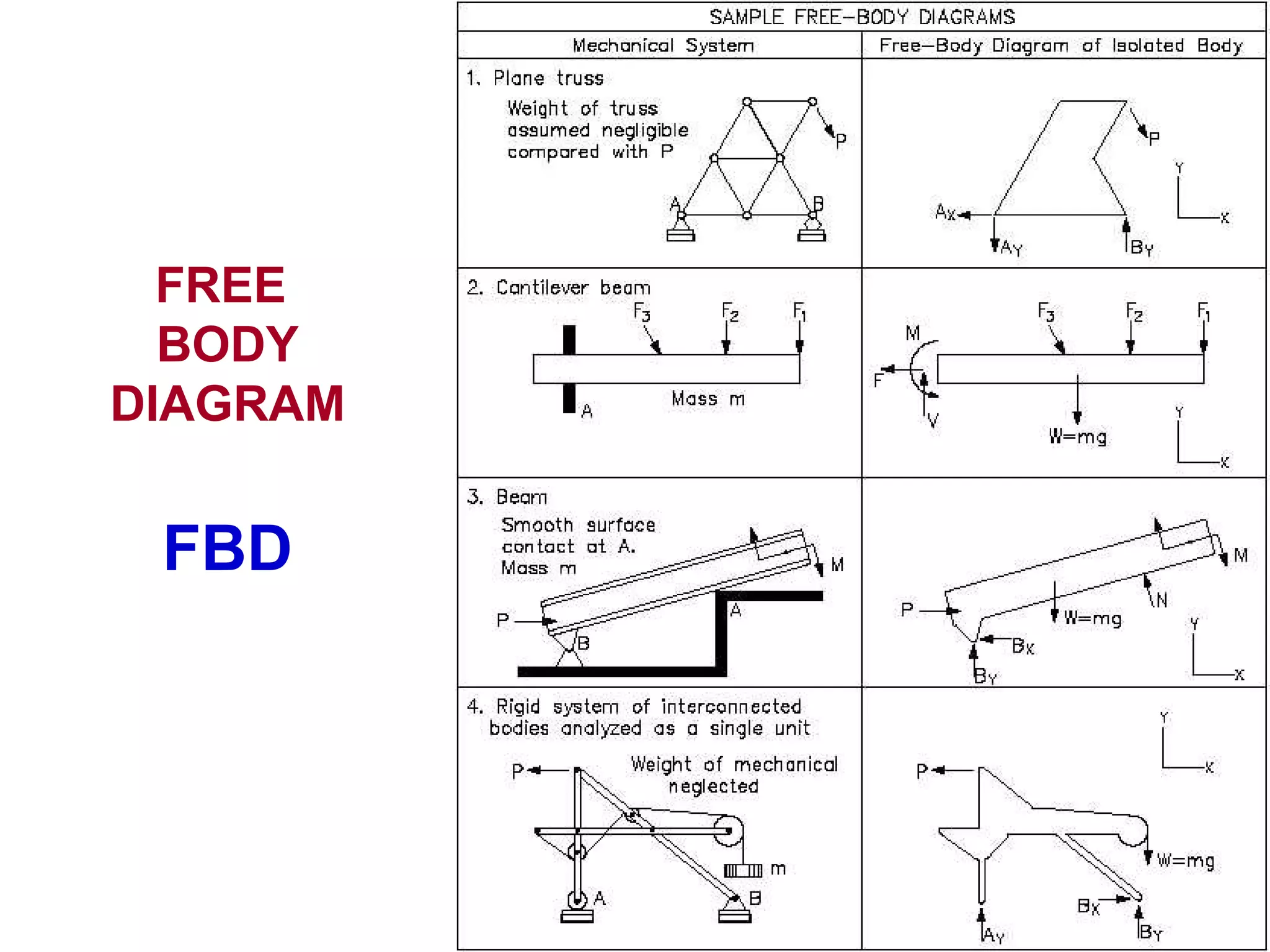
Free body diagrams show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. They include only physical forces touching the object like gravity, applied forces, friction, and reactions, drawn as arrows from a dot representing the object. To analyze motion, forces are resolved into horizontal and vertical components and Newton's second law is applied to each direction separately. For example, with an applied force at an angle on a block, the horizontal force component gives acceleration along the plane while the vertical forces sum to zero for no jump.