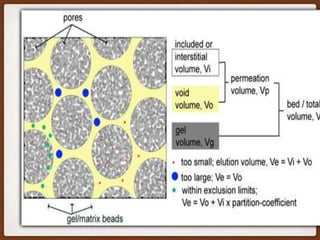
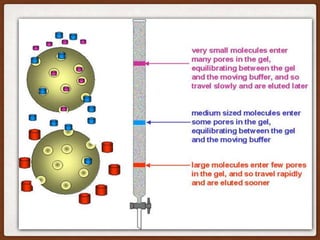
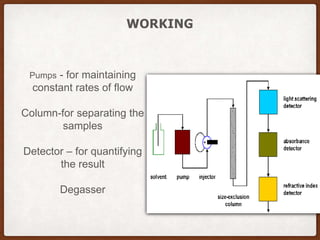
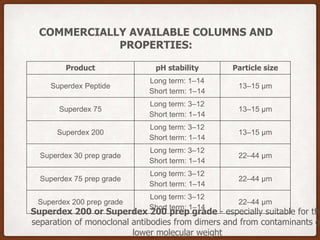
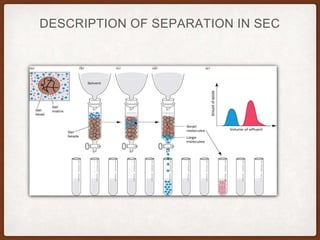
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a method for separating molecules based on their size, using two main types: gel permeation chromatography (GPC) for organic solvents and gel filtration chromatography (GFC) for aqueous solutions. It is widely used for purifying and analyzing biological and synthetic polymers, including proteins and nucleic acids, with various advantages like room temperature operation and rapid analysis, though it has disadvantages such as high investment cost and limitations for small molecular weight samples. Recent advancements include absolute size-exclusion chromatography (ASEC) for accurate size measurements and improvements in purifying DNA-wrapped carbon nanotubes.