OBSTRUCTIVE UROPATHY PPT.pptx
- 2. OBJECTIVES Define obstructive uropathy List the etiology of obstructive uropathy Discuss the pathogenesis of urolithiasis and hydronephrosis List the types of renal stones and discuss the etiopathogenesis Describe the morphology of renal stone Define hydronephrosis and describe its pathogenesis
- 3. DEFINITION Obstructive lesions of the urinary tract increase susceptibility to infection and stone formation. Unrelieved obstruction almost always leads to permanent renal atrophy - Hydronephrosis or obstructive uropathy.
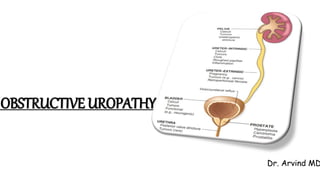
- 4. OBSTRUCTIVE UROPATHY / URINARY TRACT OBSTRUCTION
- 5. OBSTRUCTION • Sudden/ Insidious • Partial/ complete • Unilateral/ Bilateral • At any level of the urinary tract
- 6. ETIOLOGY - OBSTRUCTIVE LESIONS
- 7. URETER/ PELVIS CONGENITAL ACQUIRED INTRINSIC ACQUIRED EXTRINSIC PUJ narrowing/obstruction Calculi Pregnant uterus UVJ narrowing/obstruction Inflammation Retroperitoneal fibrosis Ureterocele Infection Aortic aneurysm Retrocaval ureter Trauma Uterine leiomyoma Sloughed papillae Carcinoma uterus, prostate, bladder, rectum Tumour Lymphoma PID Accidental surgical ligation
- 8. BLADDER OUTLET CONGENITAL ACQUIRED INTRINSIC ACQUIRED EXTRINSIC Bladder neck obstruction Benign prostatic hyperplasia Carcinoma cervix Ureterocele Cancer of prostate, bladder Carcinoma colon Calculi Trauma Diabetic neuropathy Spinal cord disease Anticholinergic drugs and Alpha adrenergic antagonists
- 9. URETHRA CONGENITAL ACQUIRED INTRINSIC ACQUIRED EXTRINSIC Posterior urethral valve Stricture Trauma Stricture Tumour Meatal stenosis Calculi Phimosis Trauma Phimosis
- 10. UROLITHIASIS Formed anywhere in the urinary tract, mostly in kidney M>F Age: Peak between 20 and 30 years Familial and hereditary predisposition; Many inborn errors of metabolism (like cystinuria & primary hyperoxaluria)
- 11. UROLITHIASIS - PATHOGENESIS • Increased urinary supersaturation – Stone constituents exceeds solubility (Hyperoxaluria, hypercalciuria, decreased urine volume, increased urine pH) Crystal nucleation Crystal growth Crystal aggregation Crystal-cell interaction Crystal retention within the kidney or renal collecting duct Stone formation
- 12. UROLITHIASIS - PATHOGENESIS • Stone formation - enhanced by deficiency of inhibitors of crystal formation in urine. • These inhibitors for crystal formation are pyrophosphate, diphosphonate, citrate, glycosaminoglycans, osteopontin and glycoprotein called nephrocalcin.
- 13. UROLITHIASIS TYPES: 1) Calcium oxalate stones • Incidence: 70% • Composition: calcium oxalate (OR) calcium oxalate + calcium phosphate
- 14. UROLITHIASIS -Calcium oxalate stones • Etiopathogenesis: Hypercalciuria without hypercalcemia (55%) Hypercalciuria and hypercalcemia (5%) Hyperuricosuria Hyperoxaluria: primary, enteric
- 15. UROLITHIASIS 2) Struvite stones or Triple stones • Incidence: 15% • Composition: Magnesium, Ammonium, Phosphate stones • Etiopathogenesis: • Urea splitting bacteria (protease, staphylococci) – convert urea ammonia resultant alkaline urine causes precipitation of magnesium ammonium phosphate salts Staghorn calculi
- 16. UROLITHIASIS Staghorn calculi Struvite stones
- 17. UROLITHIASIS 3) Uric acid stones • Incidence: 5-10 % • Etiopathogenesis: common with hyperuricemia (gout) and diseases involving rapid cell turnover (leukemias)
- 18. UROLITHIASIS 3) Uric acid stones However, more than 50% have neither hyperuricemia nor increased urinary uric acid • Predisposing factors: Acidic urine (pH <5.5) • RADIOLUCENT
- 19. UROLITHIASIS 4) Cystine stones • Incidence: 1-2% • Etiopathogenesis: genetic defects in renal reabsorption of aminoacids (cystine) cystinuria • Form at low urinary pH
- 20. UROLITHIASIS – Clinical features • Asymptomatic (OR) severe renal colic and abdominal pain (OR) significant renal damage • Small stones: may pass through (OR) ureteral obstruction “loin to groin” pain • Larger stones: often Haematuria
- 21. UROLITHIASIS – Complications • Hematuria • Hydronephrosis • Pyelonephritis and pyonephrosis
- 22. HYDRONEPHROSIS • Dilatation of renal pelvis and calyces associated with progressive atrophy of kidney due to obstruction to the outflow of urine
- 23. HYDRONEPHROSIS
- 24. HYDRONEPHROSIS • OBSTRUCTION -sudden/insidious - partial/complete -unilateral/bilateral This obstruction can occur at any level of the urinary tract.
- 25. HYDRONEPHROSIS - Pathogenesis Obstruction in urinary tract + continued GF(Glomerular filtration) Dilatation of pelvis and calyces High pressure in the pelvis that transmits back through collecting duct Initially: renal vasculature of medulla Later: Cortical atrophy & decreased GFR is compressed Diminished inner medullary blood flow Deranged tubular function in the medulla (medullary vascular defects initially reversible) Manifested as: impaired concentrating ability Dilatation of pelvis and calyces and parenchymal atrophy HYDRONEPHROSIS
- 26. HYDRONEPHROSIS – Clinical features • Asymptomatic • Compensated by other kidney U/L -partial/complete hydronephrosis • Polyuria & Nocturia • Due to inability to concentrate the urine (tubular dysfunction) B/L partial obstruction • Oliguria or Anuria B/L complete obstruction
- 27. THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- WT is obstructive uropathy ?
- Obstruction in urinary tract and important because it increases the susceptibility to infection……chronic obstruction Any age
- Urinary tract obstruction leads to impairment in normal flow of urine-urinary stasis & increased pressure in part proximal to obstruction- increased pressure impairs renal and UT functions- increased susceptibility to hypertension, infection, and stone formation – chronic obstruction-cortical thinning -permentant loss of renal mass(renal atrophy) and excretory capacity lead to end stage disease
- Obstruction can be Complete bilateral obs.. Result in irreversible renal failure Long standing / partial – functional abnormalities & anatomical changes Level urinary tract – renal pelvis, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
- Intrinsic inside Extrinsic – outside
- Pelvic uretric junction narrowing – portion of collecting system that connects the renal pelvis to ureter Ureterovesical junction- blockage area where ureter meets bladder Ureterocele – swelling of ureter at bottom near bladder- birth defect – prevents flow of urine into urethra Urinary calculi Prostatitis, ureteritis, urethritis,
- Renal calculi /stones Hyperoxaluria provide examples of heridary disease – characterized by excessive production and excretion of stone forming substance
- There are many causes for initation and propagation of stone Most important determinant is increase urinary concentration of stone constituents such that it exceeds their solubility- supersaturation Nucleation of calcium oxalate by uric acid crystals in collecting ducts
- Hy[percalciuria- too much of calcium in urine 1- hyperabsorption of calcium from intestine (absortive hypercalcuria)- intrinsic impairement of renal tubular reabsorption of calcium 2-hyperparathyroidism – diffuse bone disease-sarcoidosis 3-20% stone ass with increased uric acid secretion 4- hereditary (primary)- acquired by interstinal overabsorption with enteric disease
- Formed after largely after infections by urea spitting bacteria (proteus and staphylococci) that converts urea to ammonia Result alkaline urine causes precipitation of magnesium ammonium phosphate salts. – large stone
- Uric acid stone will be radiolucent Calcium stone will be radioopaque
- Hematuria – blood in urine Hydronephrosis – dilation of renal pelvis and calyces Pyelonephritis-inflammation of kidney due to infection Pyonephrosis – collection of pus in renal pelvis - obstruction
- Hydronephrosis of kidney – marked dilation of the pelvis and calyces and thinning of renal parenchyma
- Affects pelvis and calyces – dilated High….. Collecting ducts into the cortex causing renal atrophy