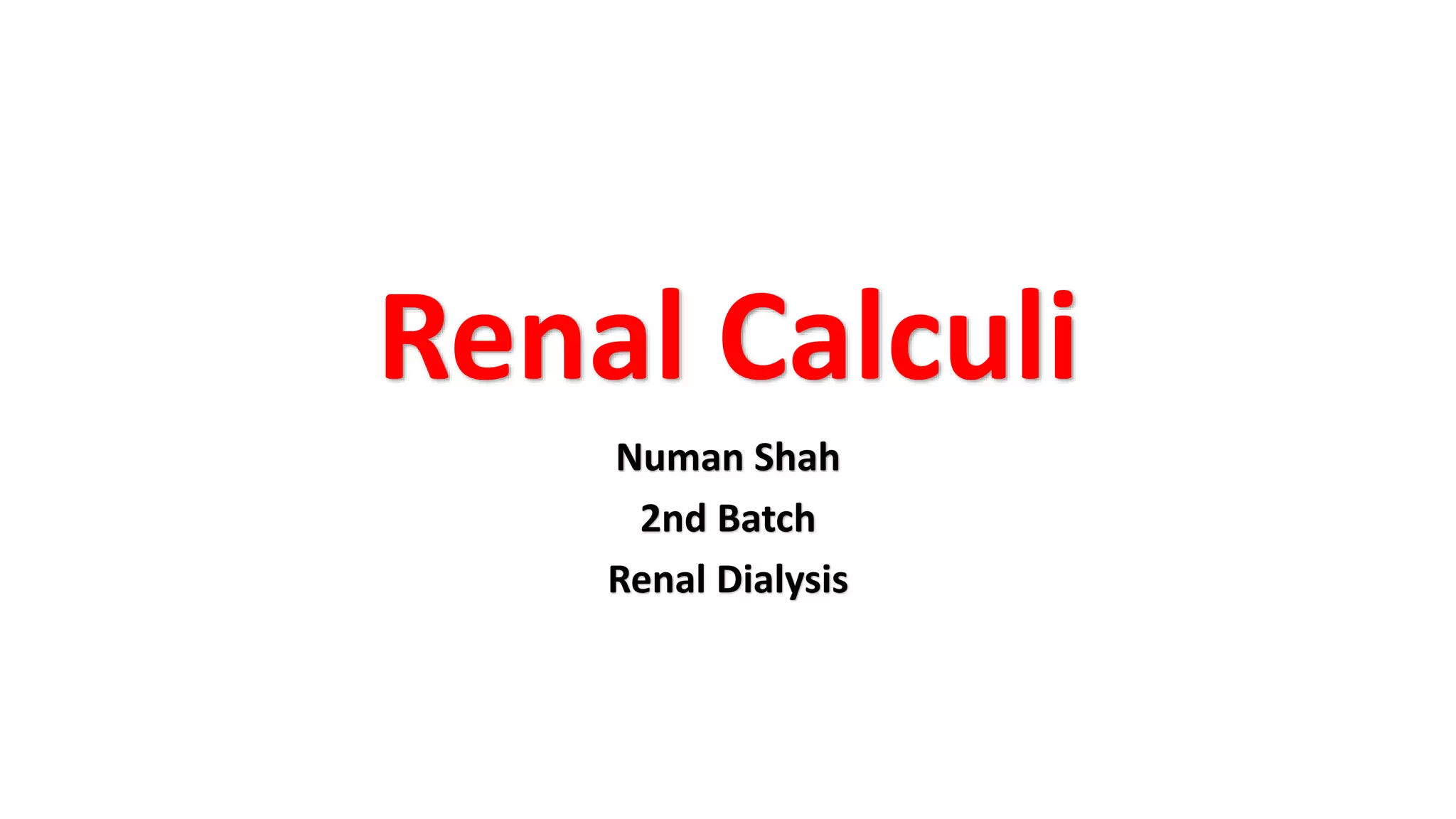
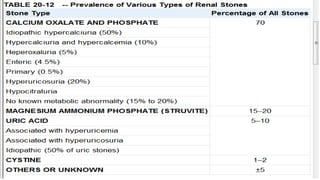
This document summarizes renal calculi (kidney stones). It defines renal calculi and lists its common types, including calcium oxalate, phosphate, uric acid, and cystine stones. The pathogenesis of different stone types is discussed, such as hypercalciuria leading to calcium oxalate stones and urinary tract infections causing struvite stones. Common sites of stone formation are the renal pelvis, calyces, and urinary bladder. Predisposing factors include metabolic abnormalities, dehydration, urinary stasis, and renal diseases. Complications include pyelonephritis, urinary retention, and renal failure. Clinical features range from gross hematuria and flank pain to symptoms of acute obstruction