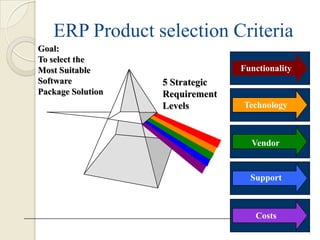
The document outlines various criteria for evaluating and selecting an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system, including functional fit, integration, flexibility, complexity, costs and customization requirements. It also lists factors for ERP success such as management support, training, adherence to schedules and change management. Some key benefits of ERP systems are easier access to information, automated business processes, reduced redundancy, improved communication and forecasting capabilities.