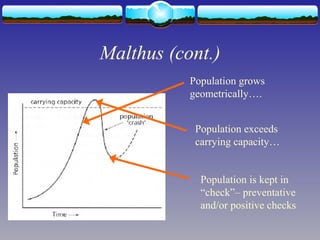
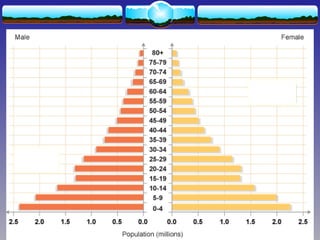
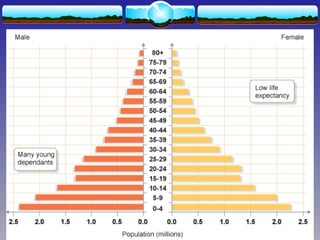
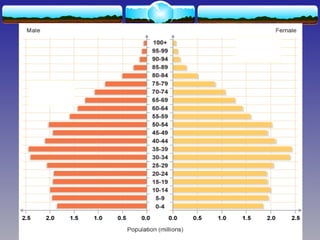
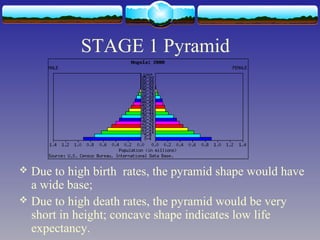
The document discusses population theories, primarily focusing on Malthus' theory, which posits that population growth will inevitably exceed food production, leading to checks such as famine and disease. It also explains the demographic transition model, which outlines four stages of population growth related to economic development: high stationary, early expanding, late expanding, and low stationary, each characterized by varying birth and death rates. The model suggests that as societies develop, mortality and fertility rates decline, leading to changes in population dynamics.