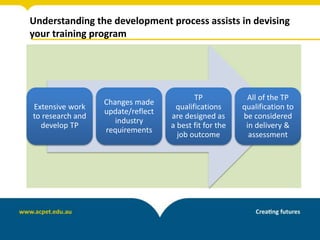
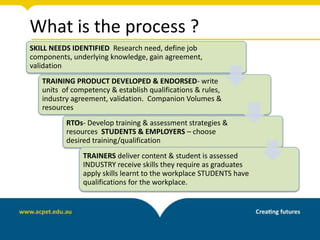
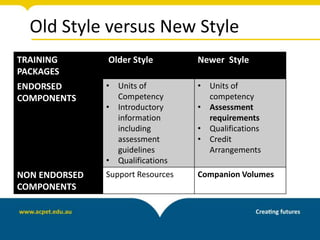
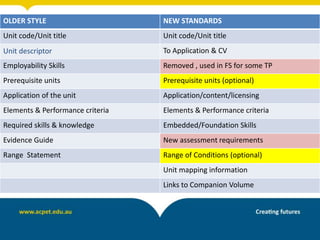
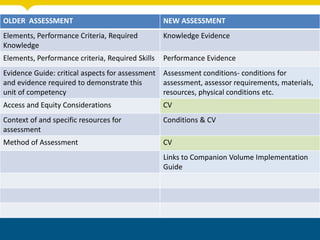
The document discusses unpacking training packages and their components to plan training programs. It begins by outlining the aims of understanding how training packages are developed and their key components. It then explains the changes in training packages, including moving to a new standards format. The main components of training packages are described, including units of competency, qualifications, and assessment requirements. The document outlines a process for unpacking training packages which involves establishing needs, identifying participant needs, and planning program organization. It concludes by discussing implications for RTOs, including ensuring compliance with standards regarding training delivery and assessment.