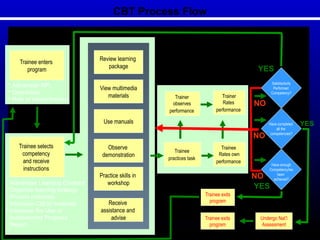
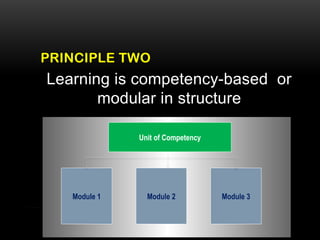
The document outlines a training program for Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) certifying individuals for employment and competency in Zamboanga City. It emphasizes a competency-based training approach that individualizes learner experiences, focuses on practical skills, and leverages both on-the-job and off-the-job components. The program details the roles of trainers and trainees, training methods, assessment methods, and the overall curriculum structure aimed at developing essential welding skills and knowledge.











![PRINCIPLE FIVE
Training materials are directly related
to the competency standards and the
curriculum
CS to CBC to LMs
[CS-Competency Standards/
CBC-Competency-Based Curriculum/
LMs-Learning Materials]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysmawintro-240903152839-55e04c92/85/TESDA-Shielded-Metal-And-Welding-presentation-13-320.jpg)