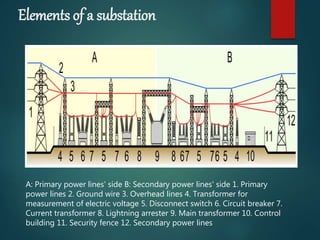
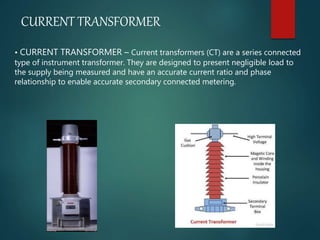
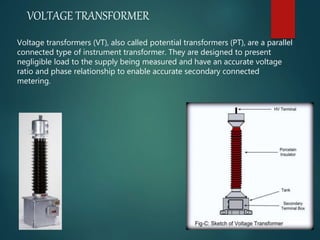
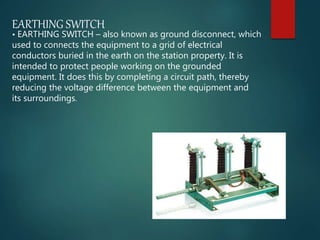
A substation is a crucial component in the electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system that transforms voltage levels and routes electric power to consumers. Substations can be classified by function, voltage, and installation type, serving purposes such as stepping down high voltage for residential use and ensuring optimal efficiency and reliability of supply. Key components include transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and lightning arresters, which together ensure safe and efficient operation.