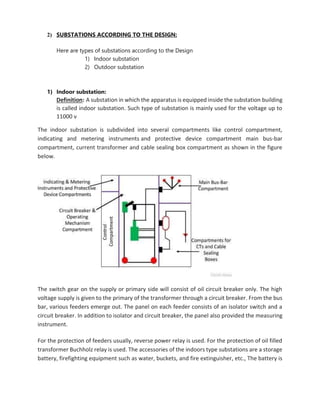
An electrical substation receives power from generating stations via transmission lines and distributes power via outgoing transmission lines. It performs several key functions:
- Transforming voltage levels for efficient long-distance transmission and local distribution using step-up and step-down transformers.
- Balancing loads, switching circuits, detecting and isolating faults to maintain stable grid operations.
- Regulating voltage, monitoring and controlling parameters, and implementing protection systems to safeguard equipment.
Substations can be indoor or outdoor and are classified by their service (e.g. distribution, industrial) or design (e.g. pole-mounted, foundation-mounted). They facilitate renewable energy integration and allow remote control and monitoring for efficient power system