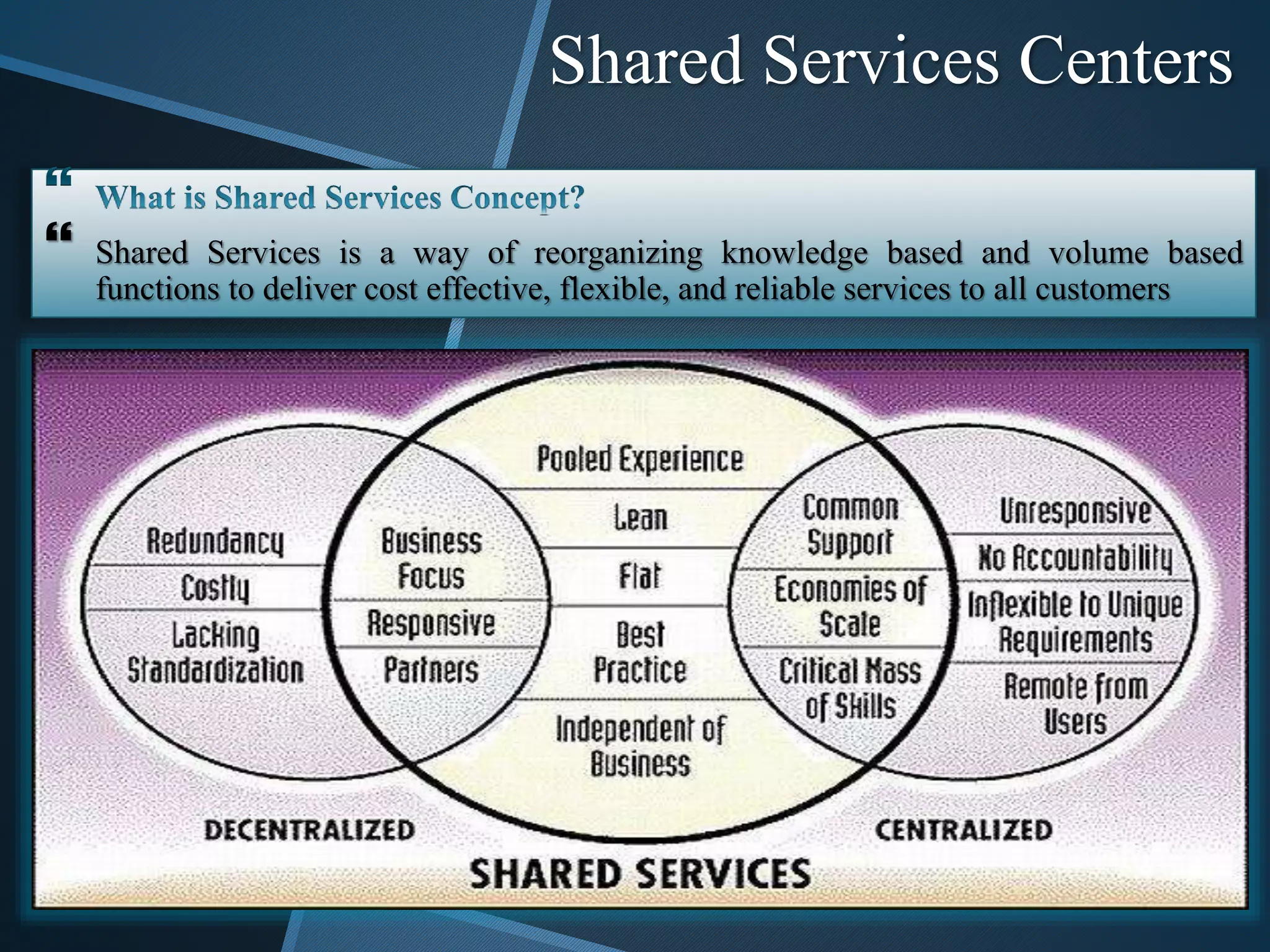
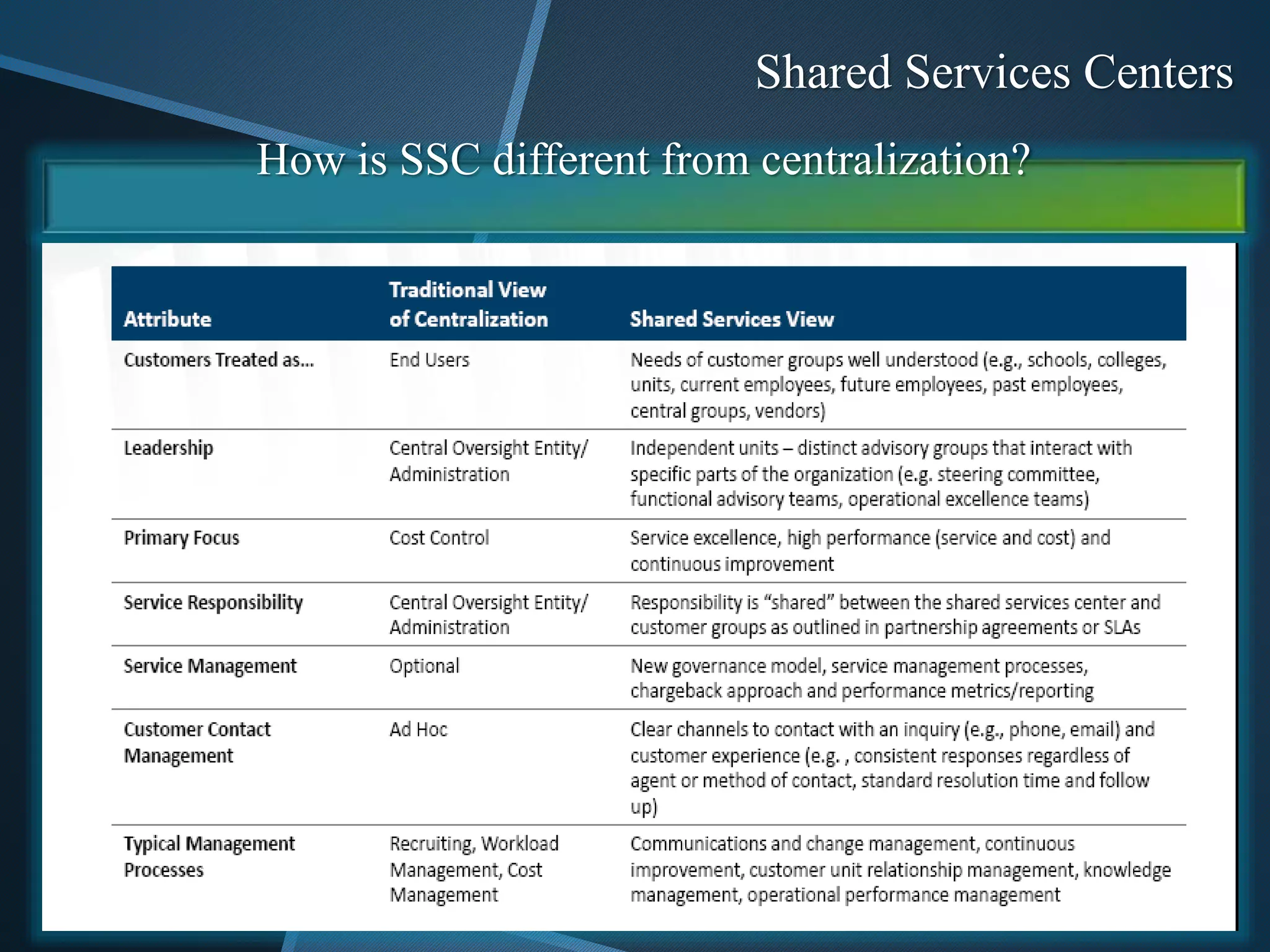
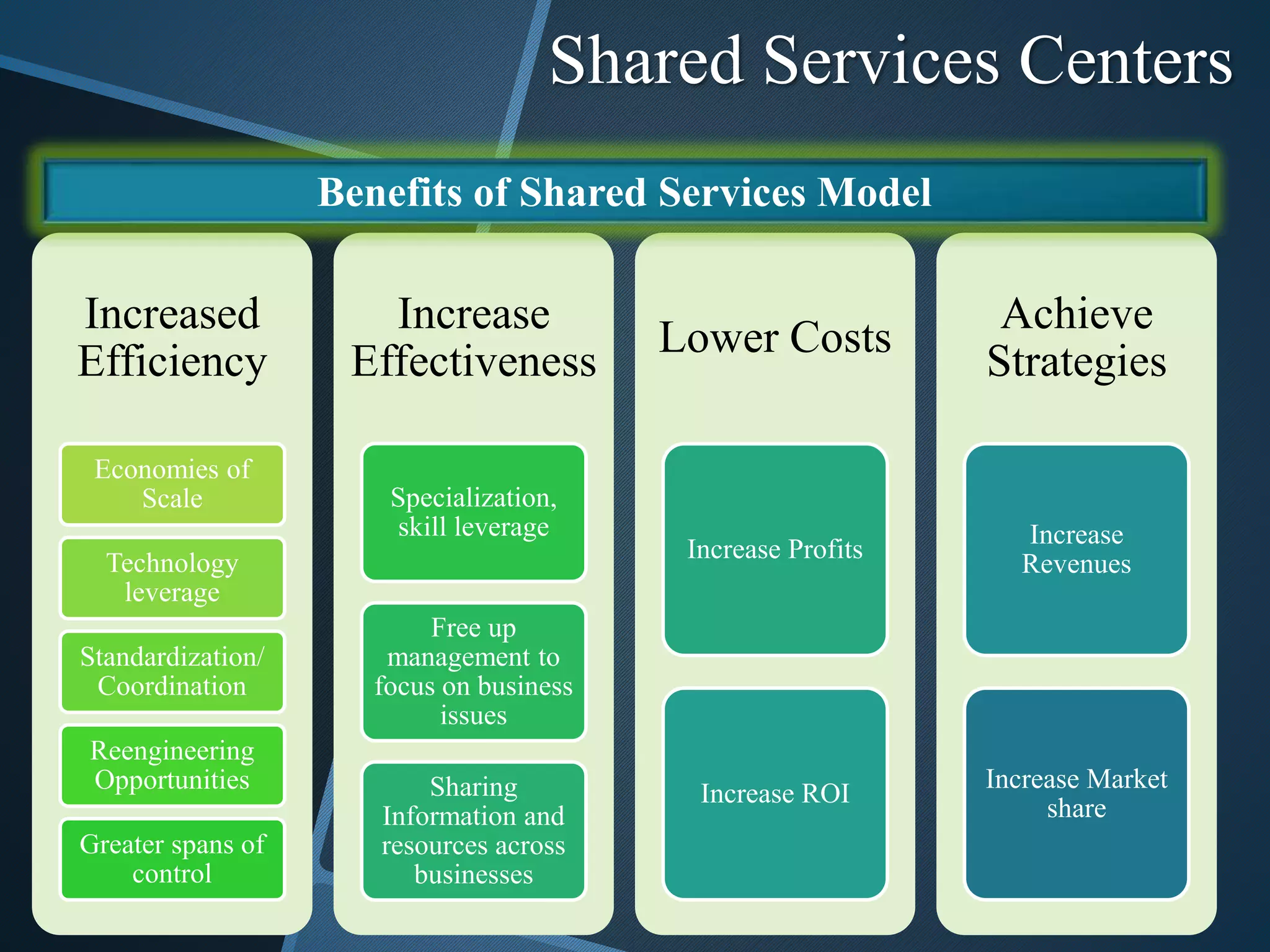
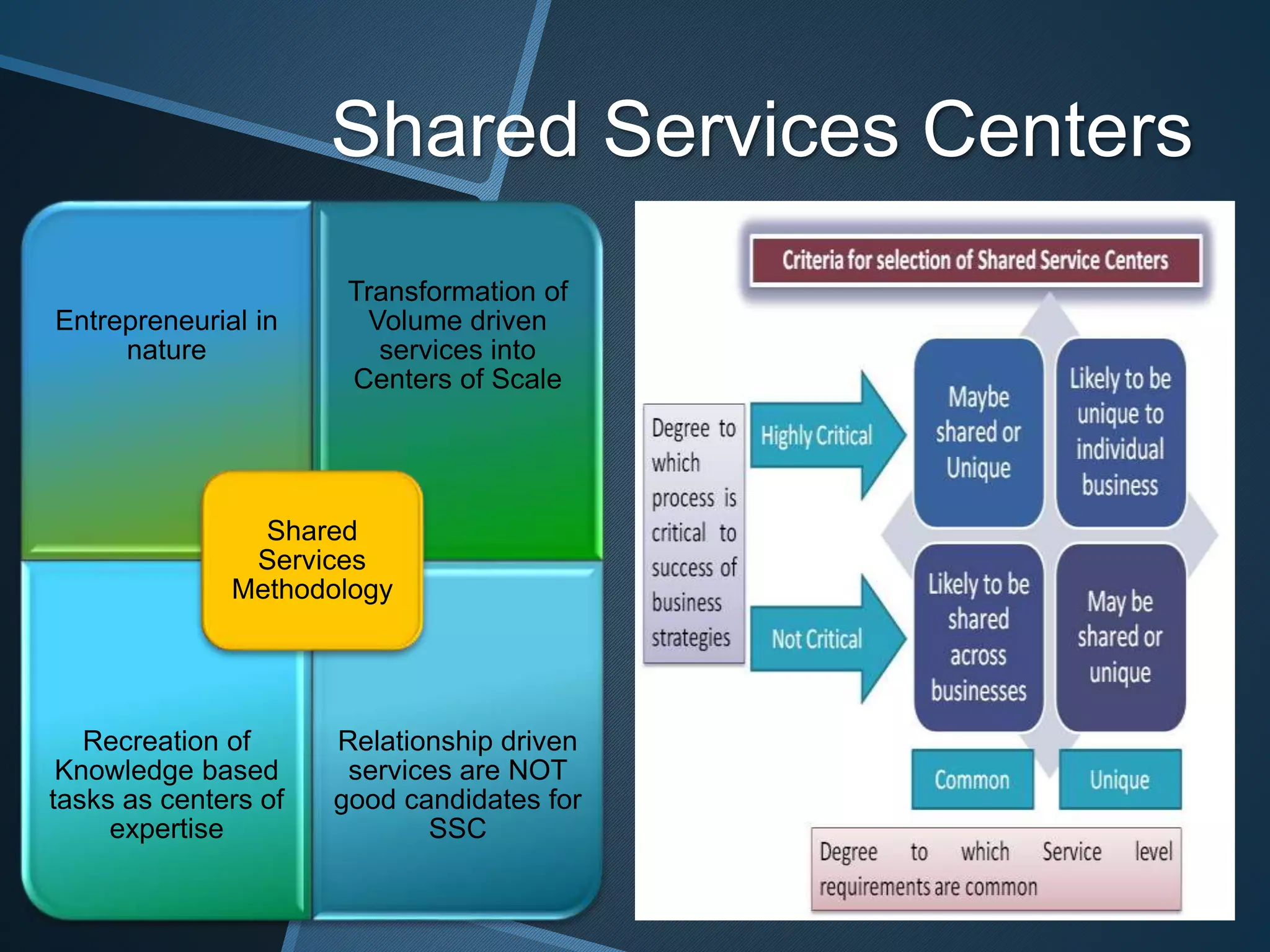
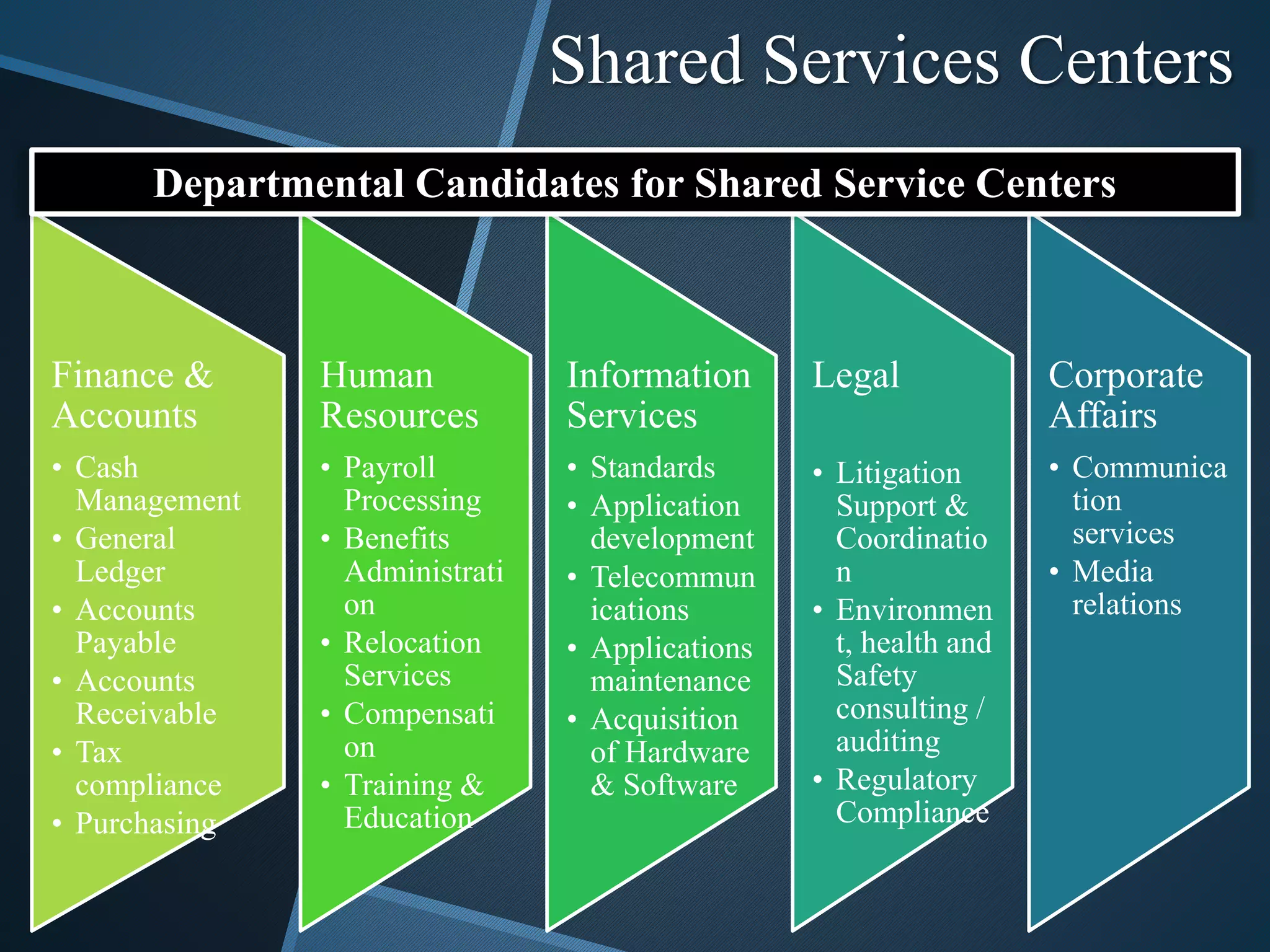
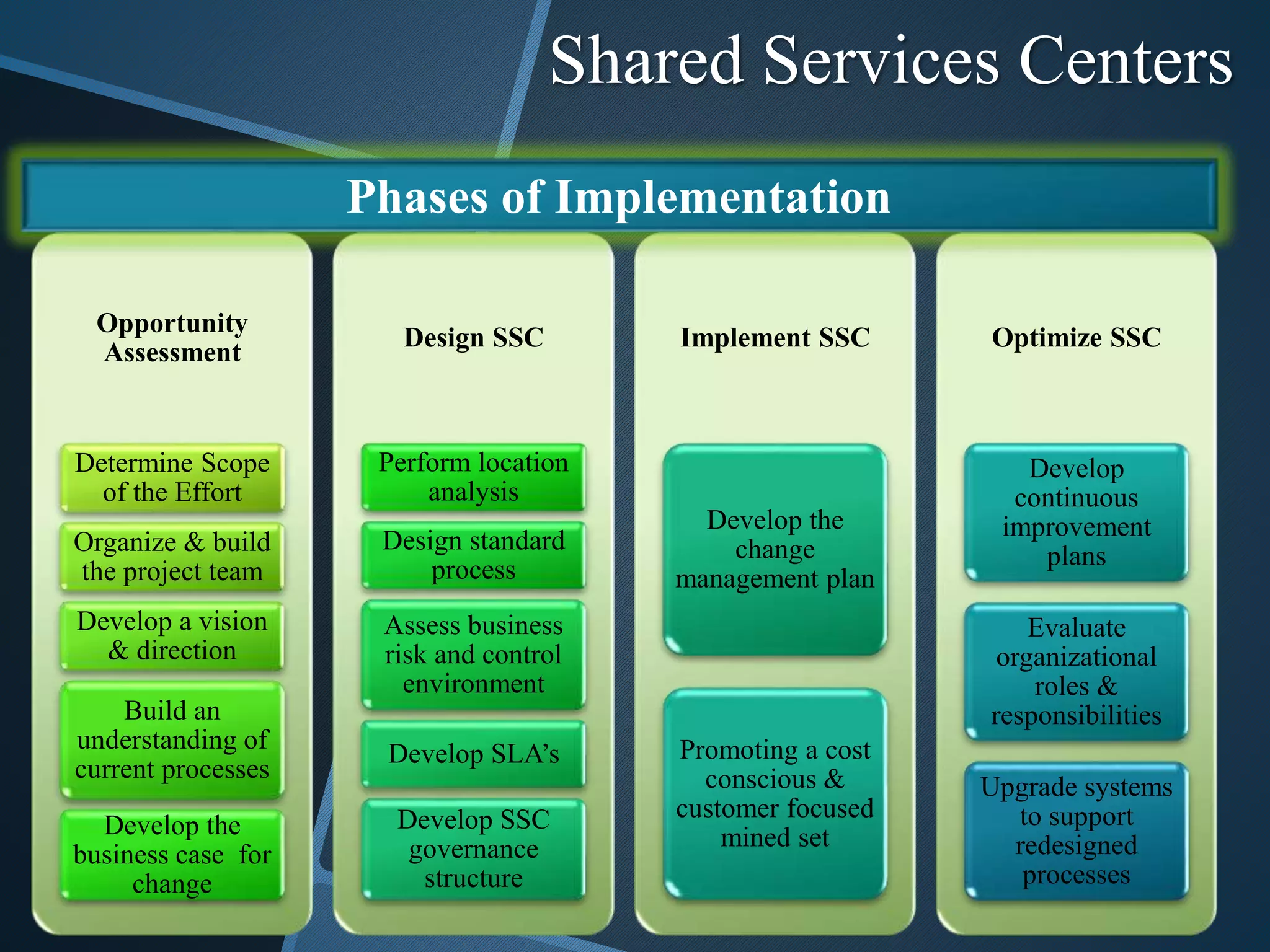
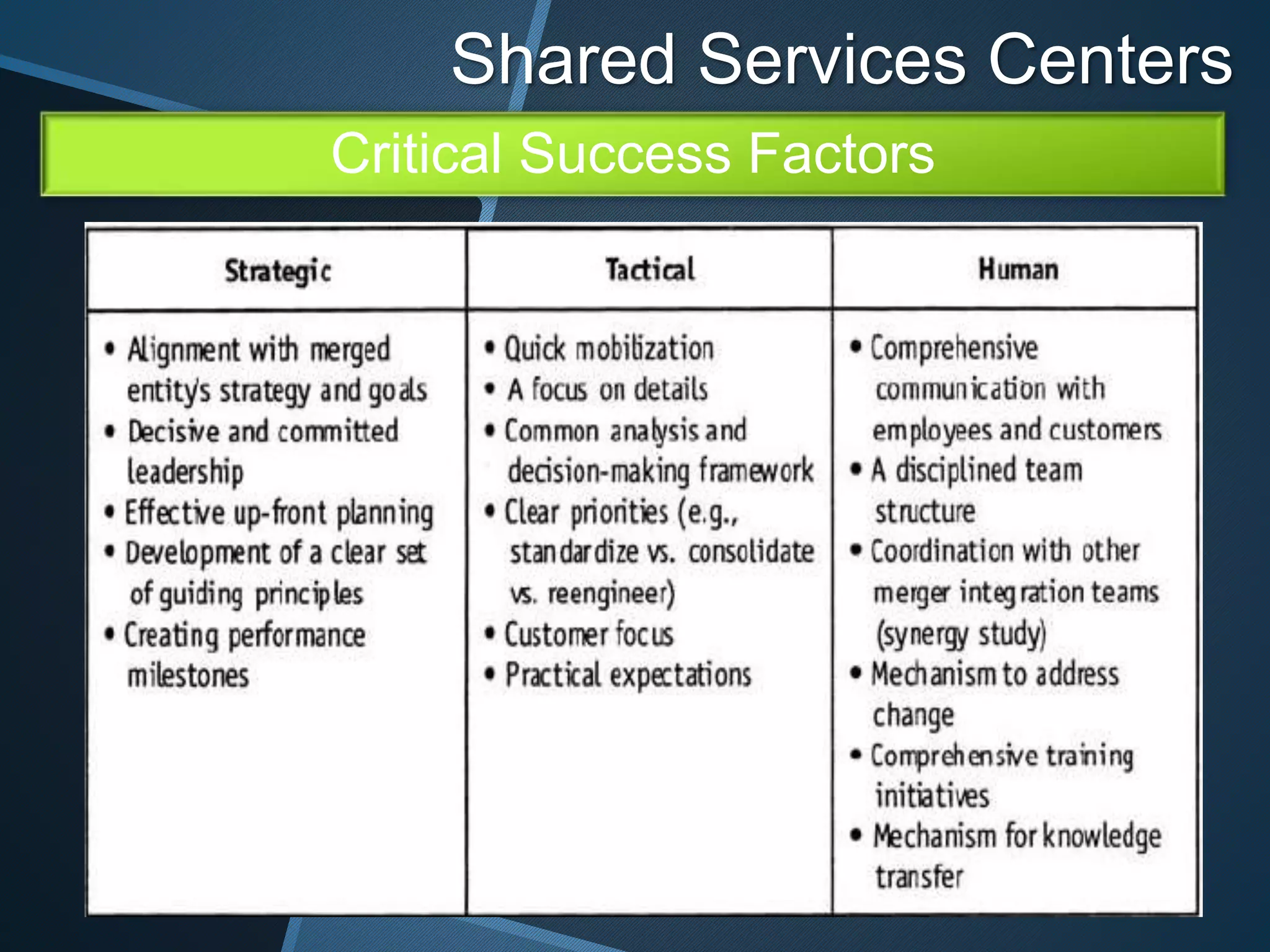
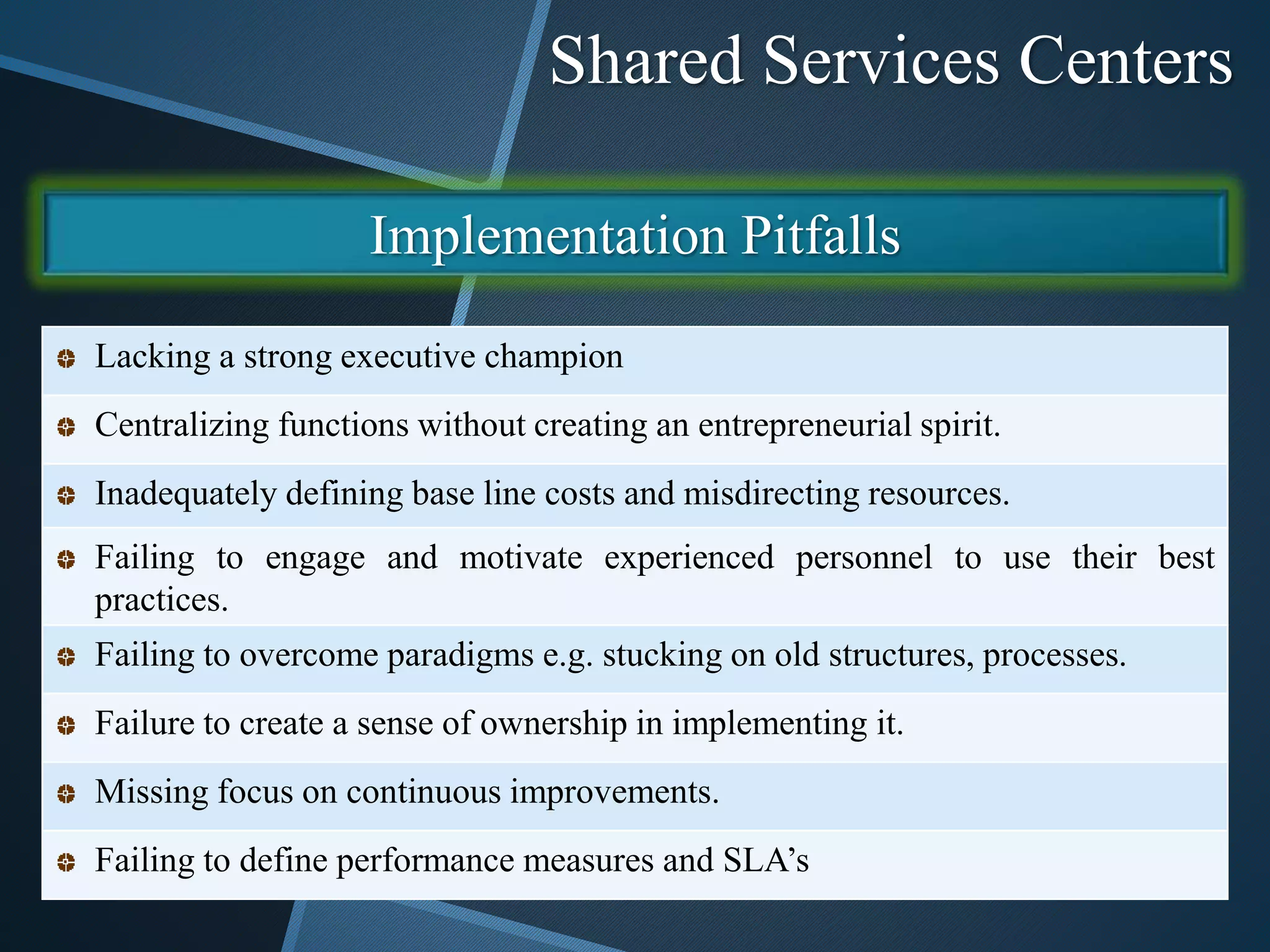
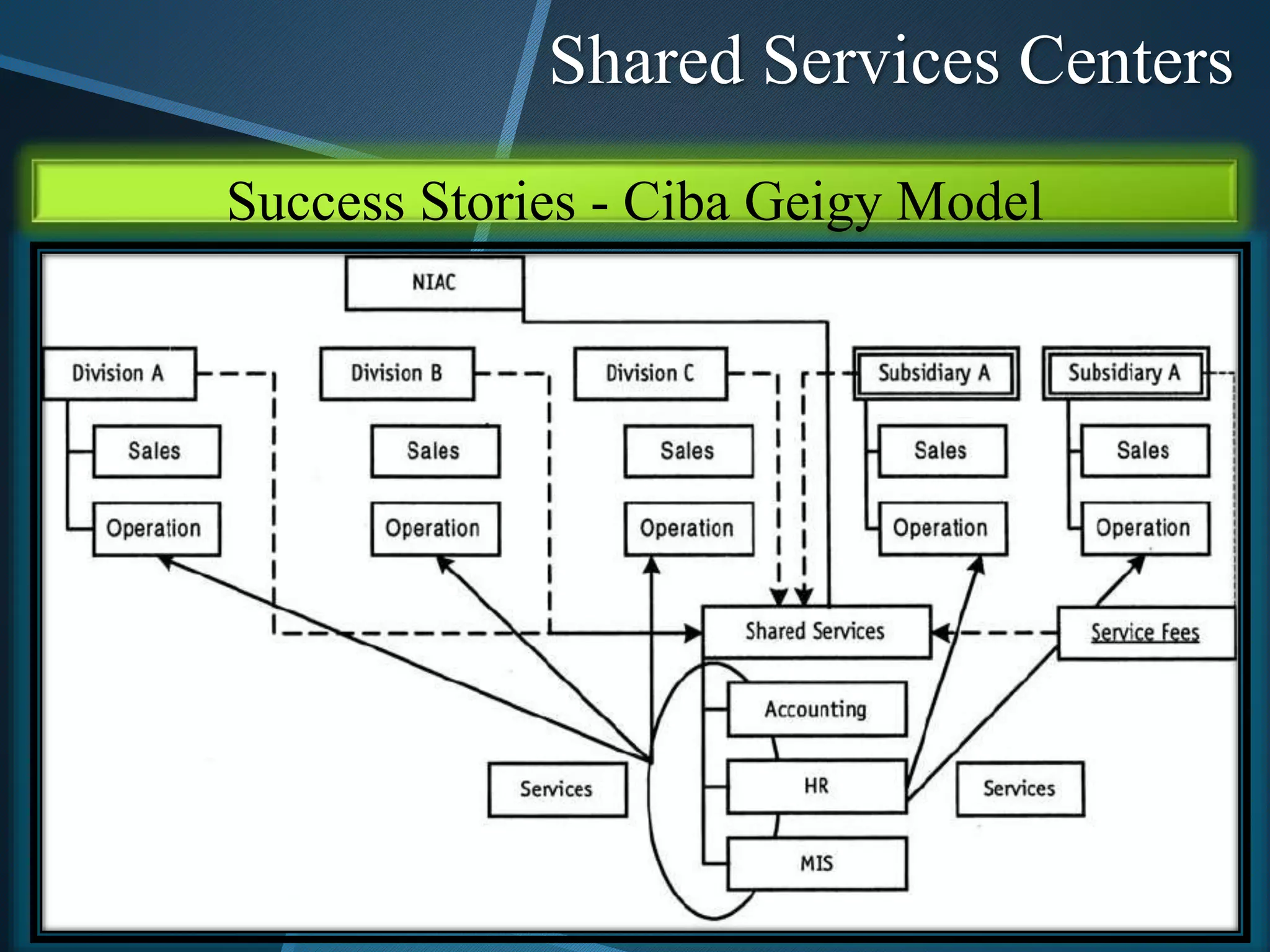
The document discusses shared services centers (SSCs) and their benefits over centralized functions. SSCs aim to deliver cost-effective and reliable services through increased efficiency, economies of scale, standardization, and technology leverage. Common functions considered for SSCs include finance, accounting, HR, IT, legal and corporate services. The implementation of SSCs involves opportunity assessment, defining the scope, building a project team, developing a vision, analyzing current processes, designing the SSC, and change management. Critical success factors include strong executive support, engaging experienced staff, and defining performance measures. The conclusion states that SSCs can help control non-essential costs and ensure efficient service delivery across divisions in the long run.