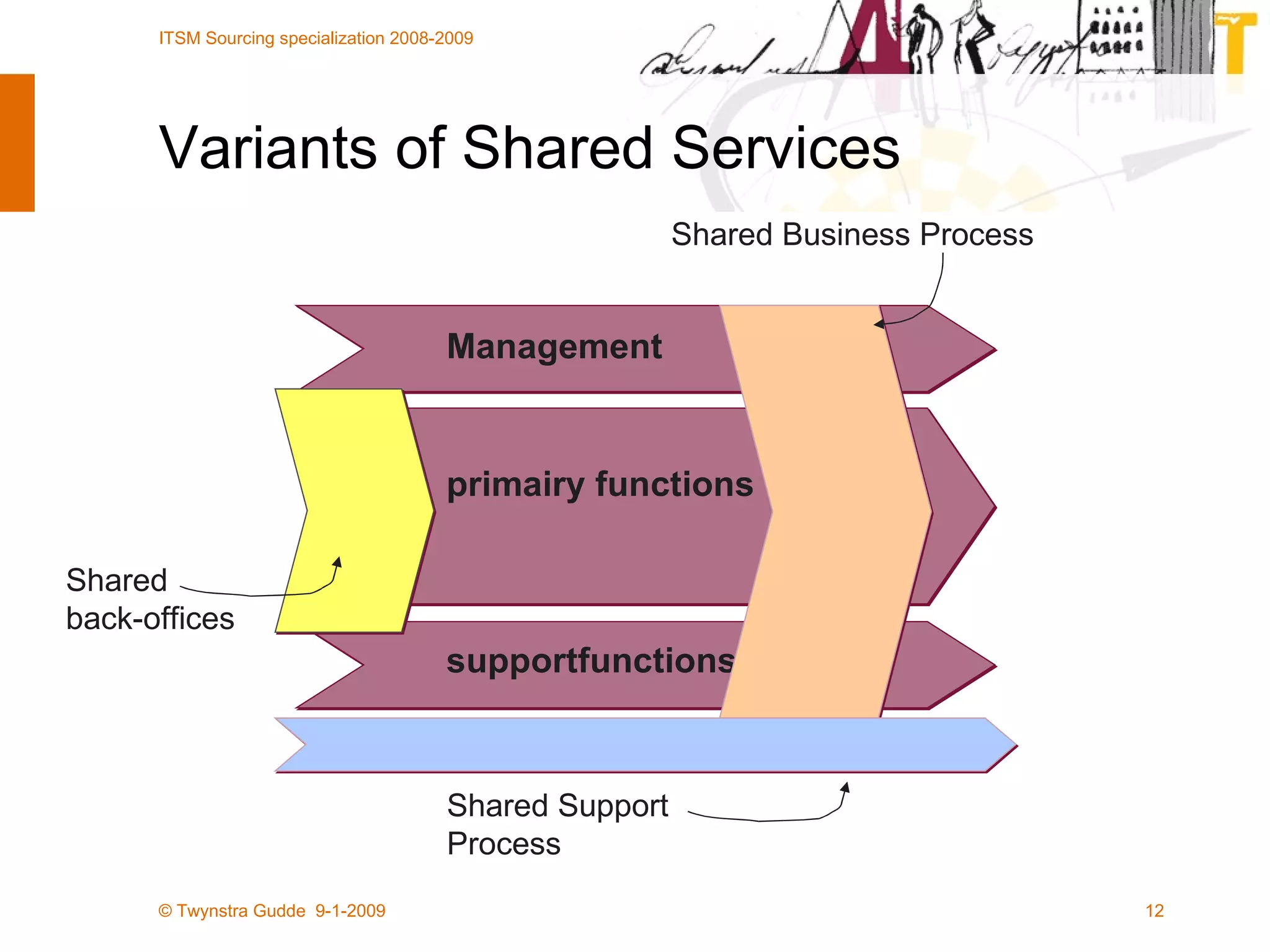
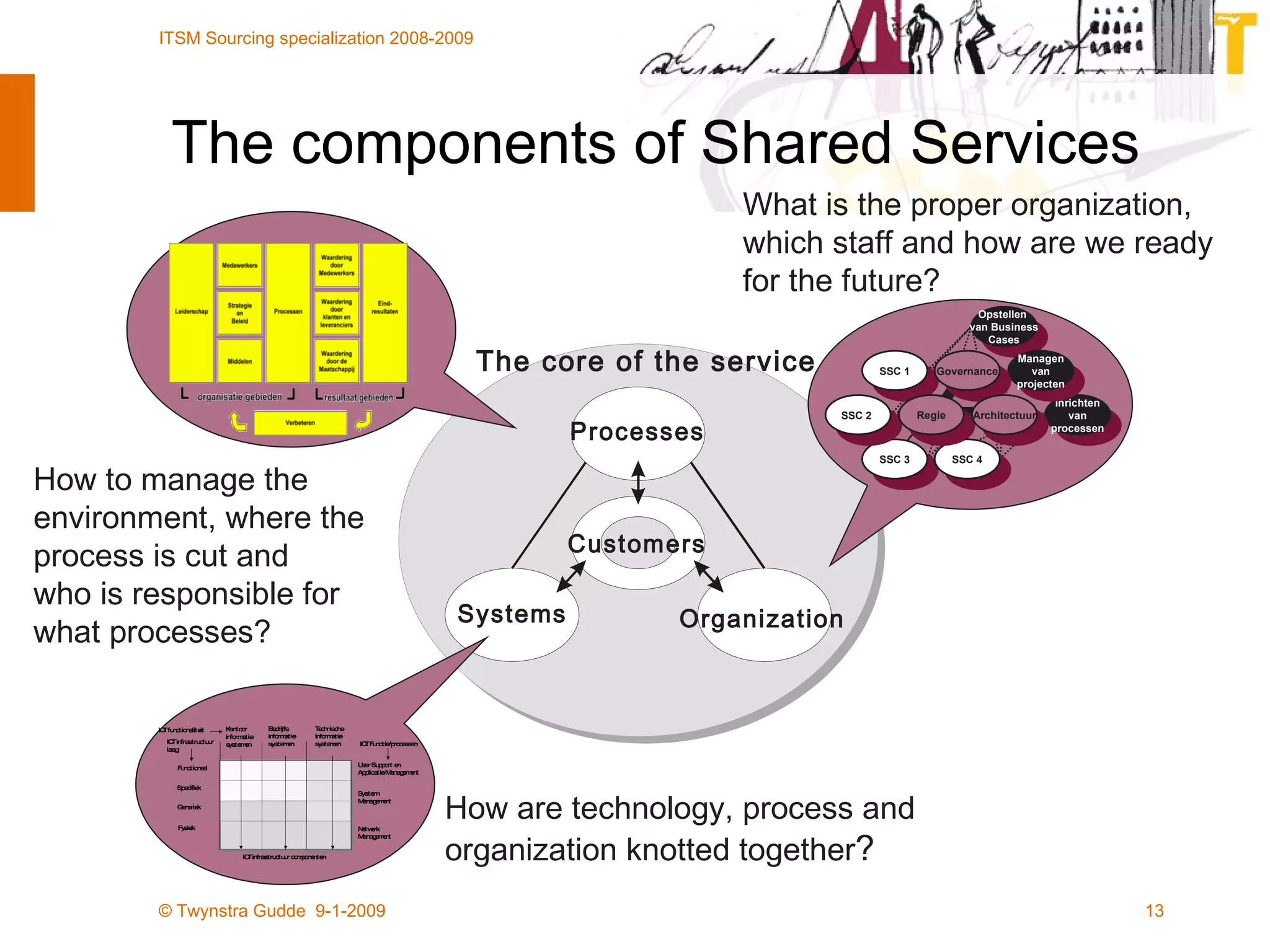
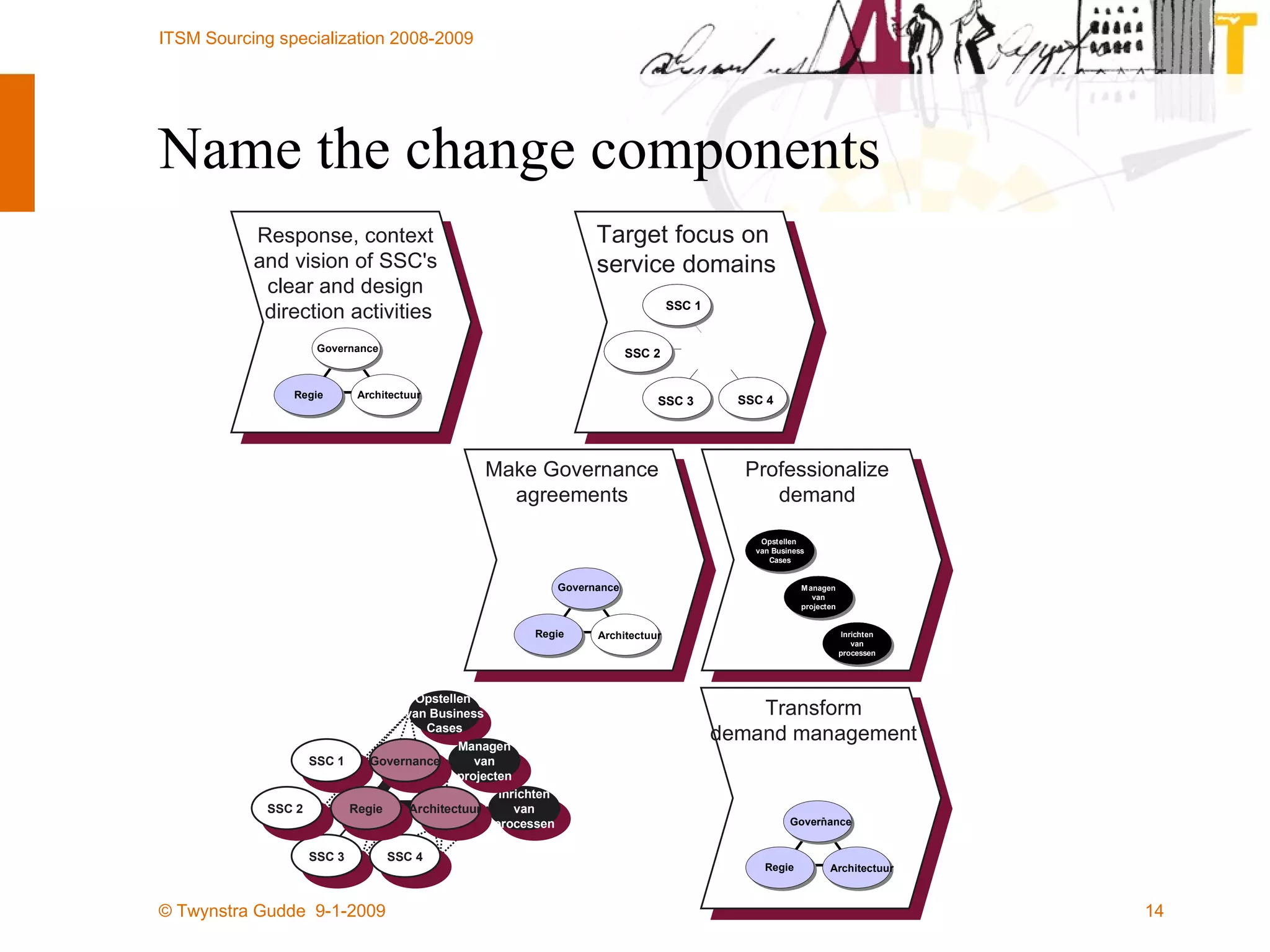
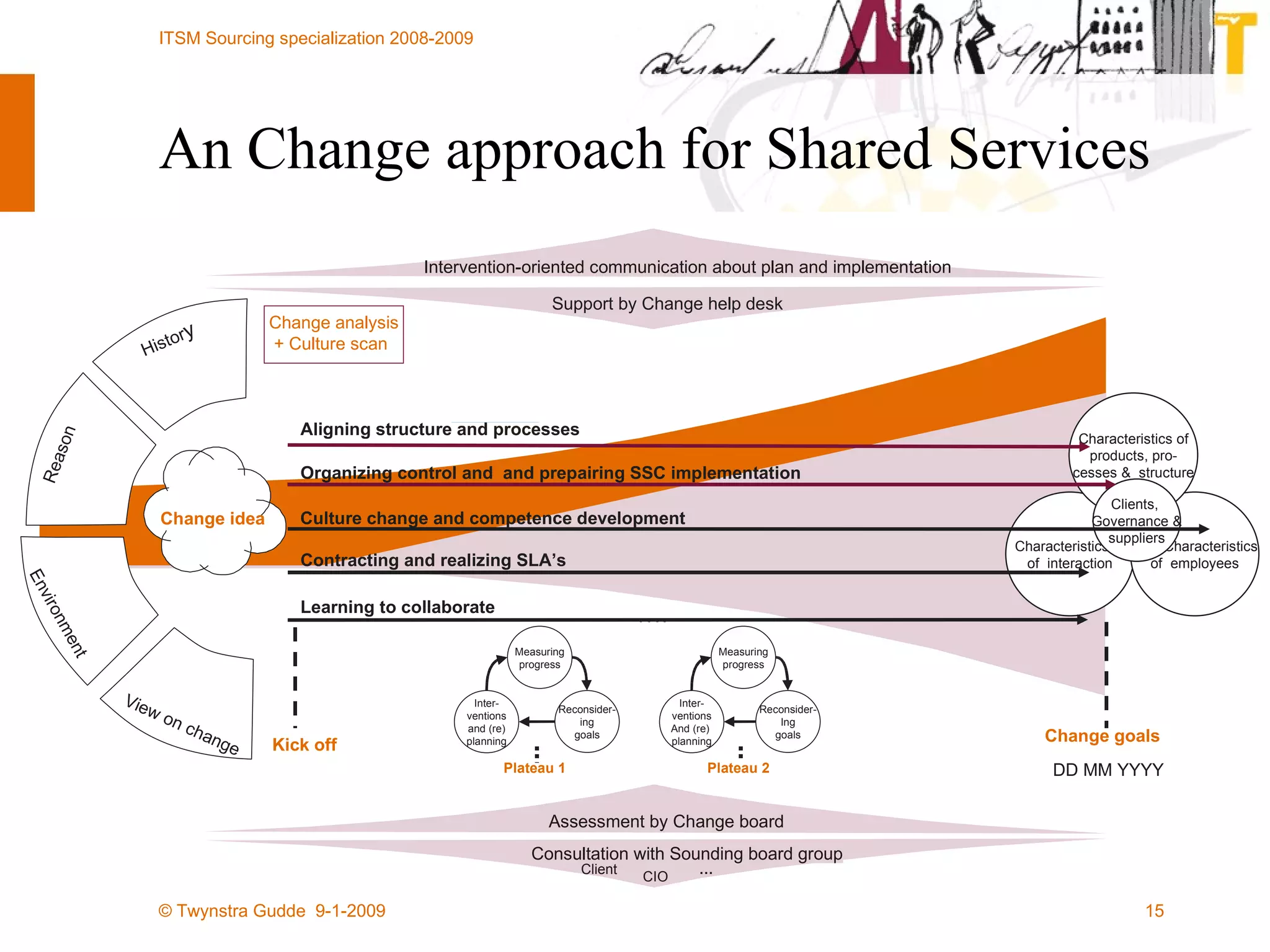
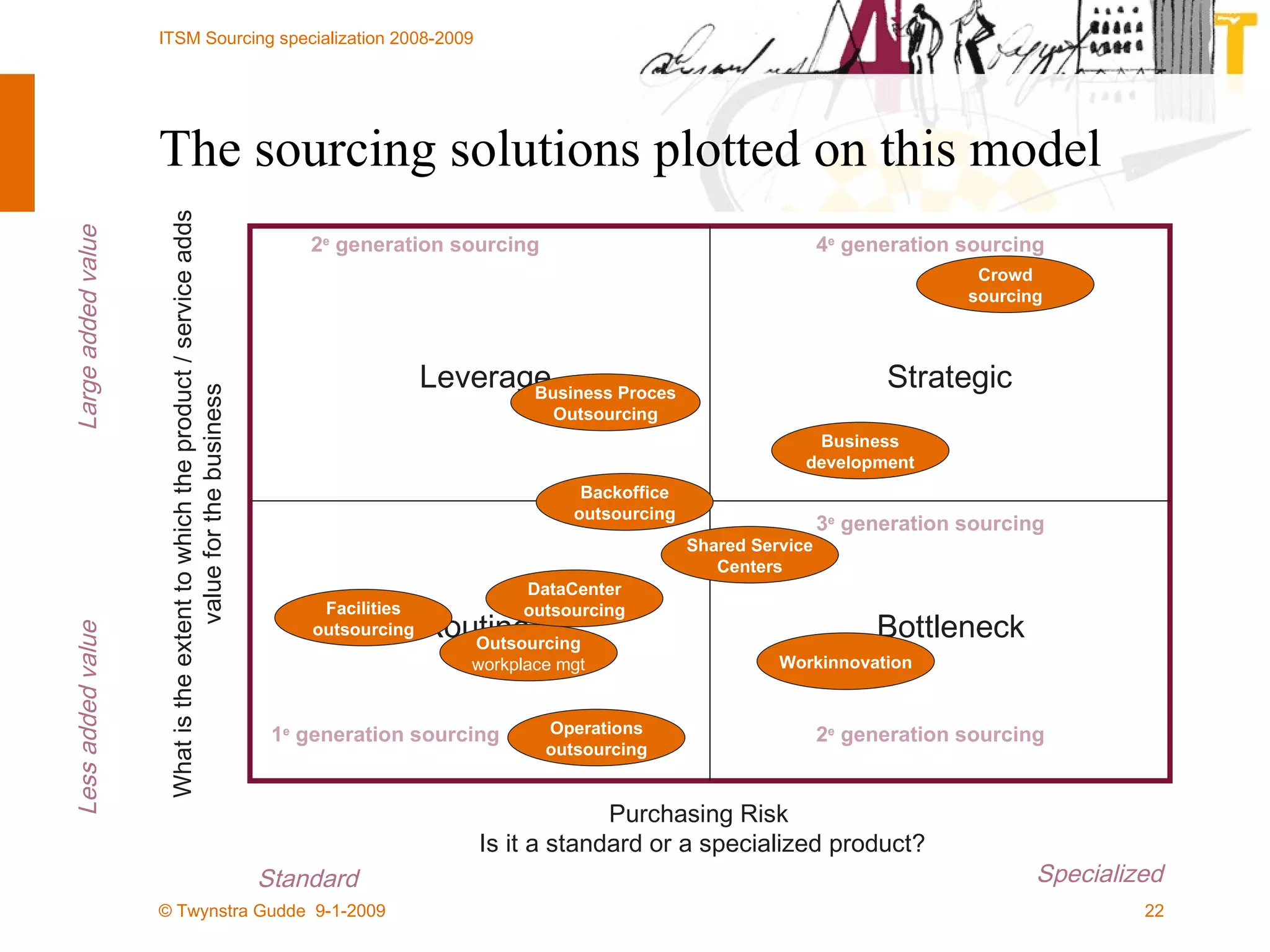
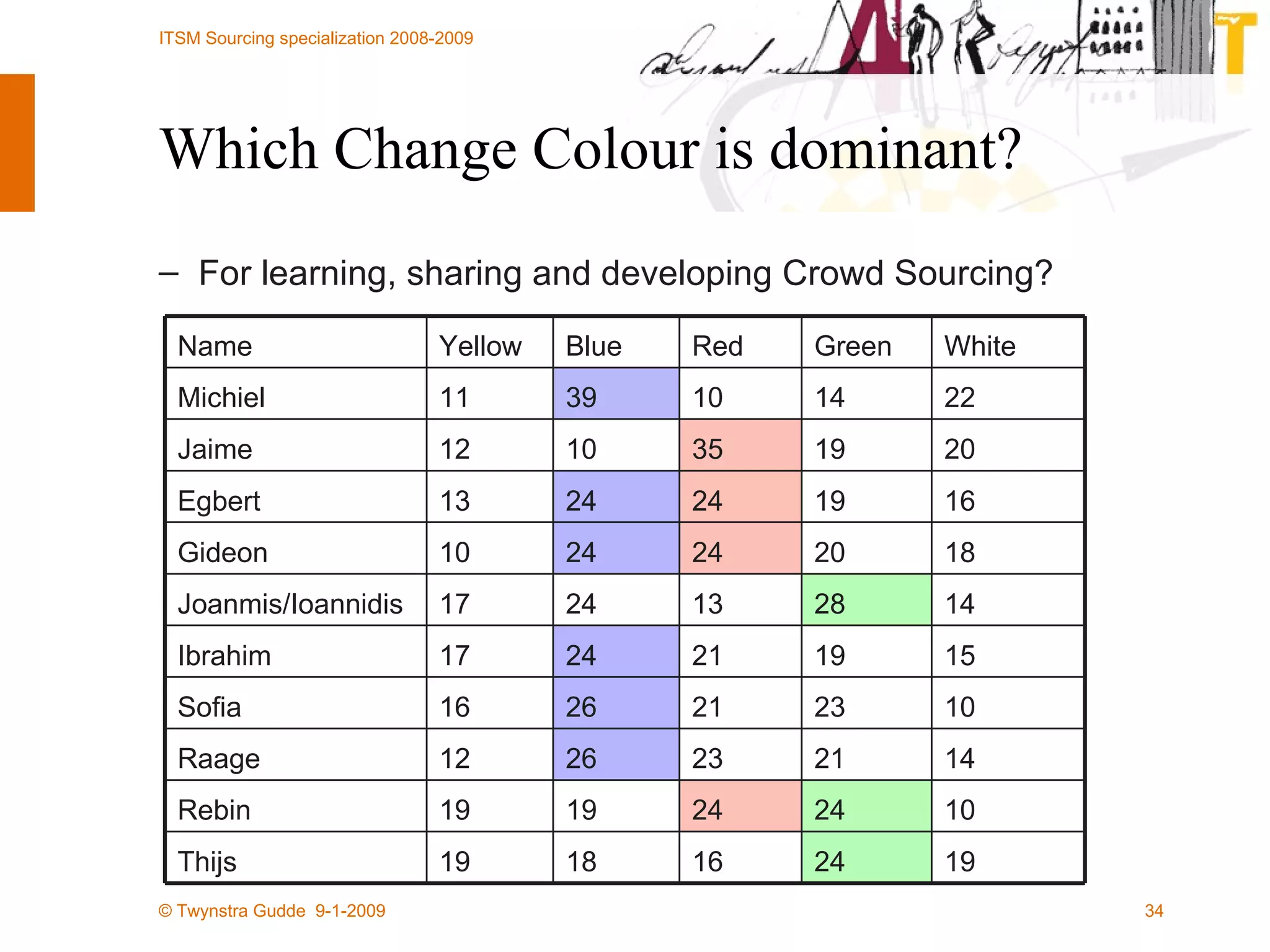
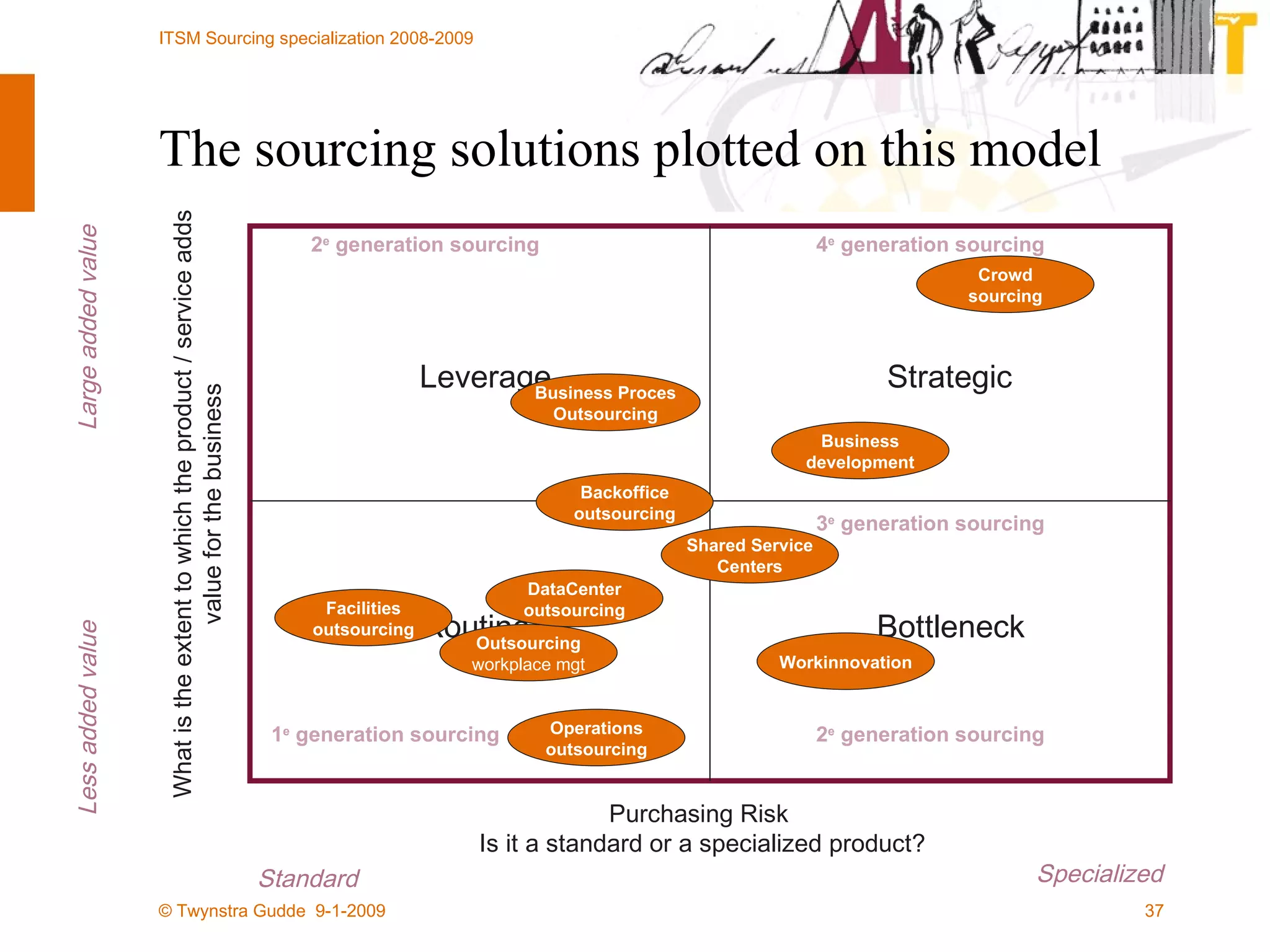
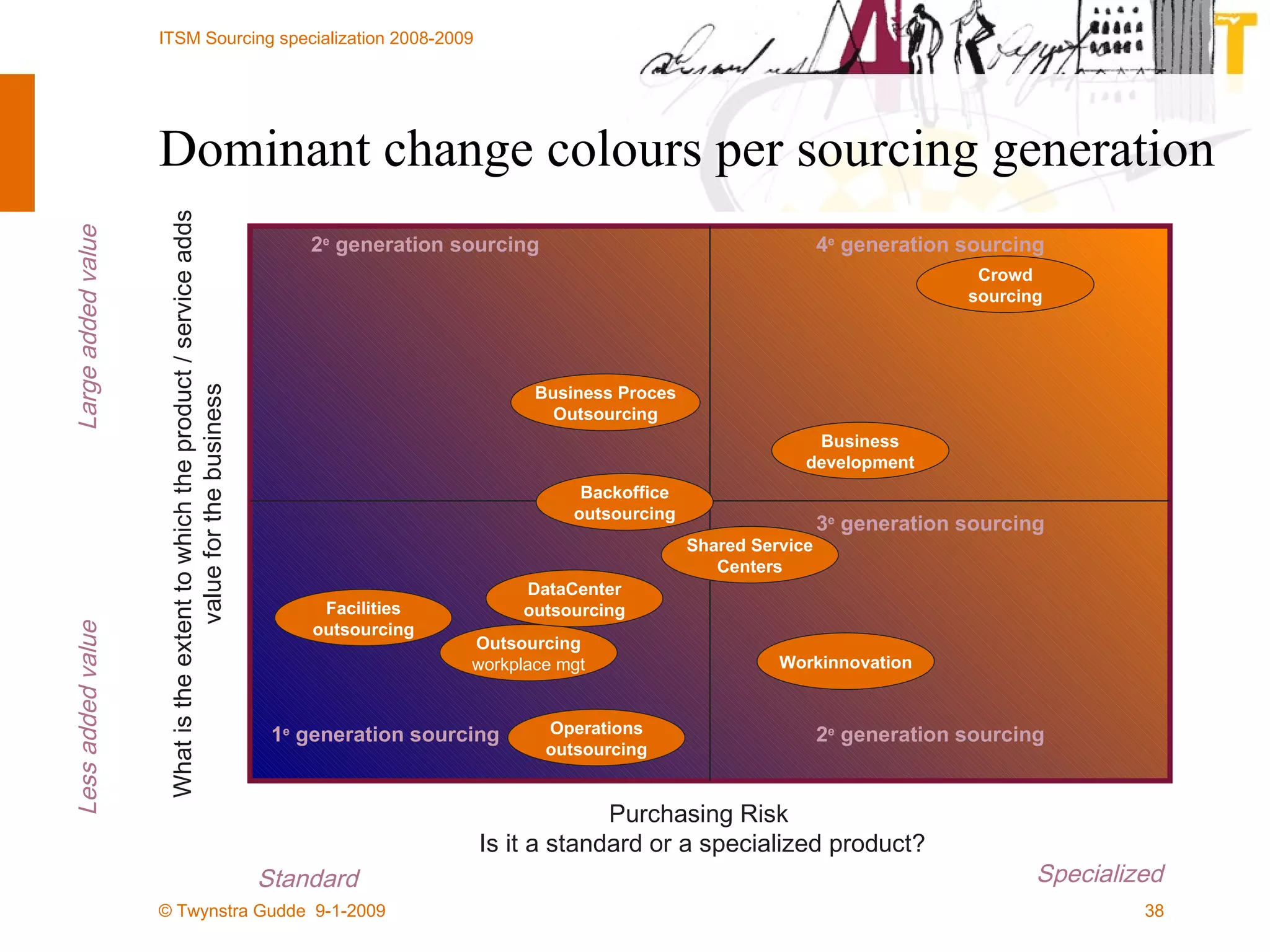
The document discusses the evolution of sourcing strategies in IT service management, emphasizing the importance of shared services, collaboration, and crowdsourcing as a means to improve efficiency and reduce costs. It outlines various aspects of organizational change management, the role of technology in facilitating collaboration, and considers the implications of crowd-based production models in today's economy. It concludes by highlighting key principles for effective crowdsourcing and offering insights into successful implementation within organizations.



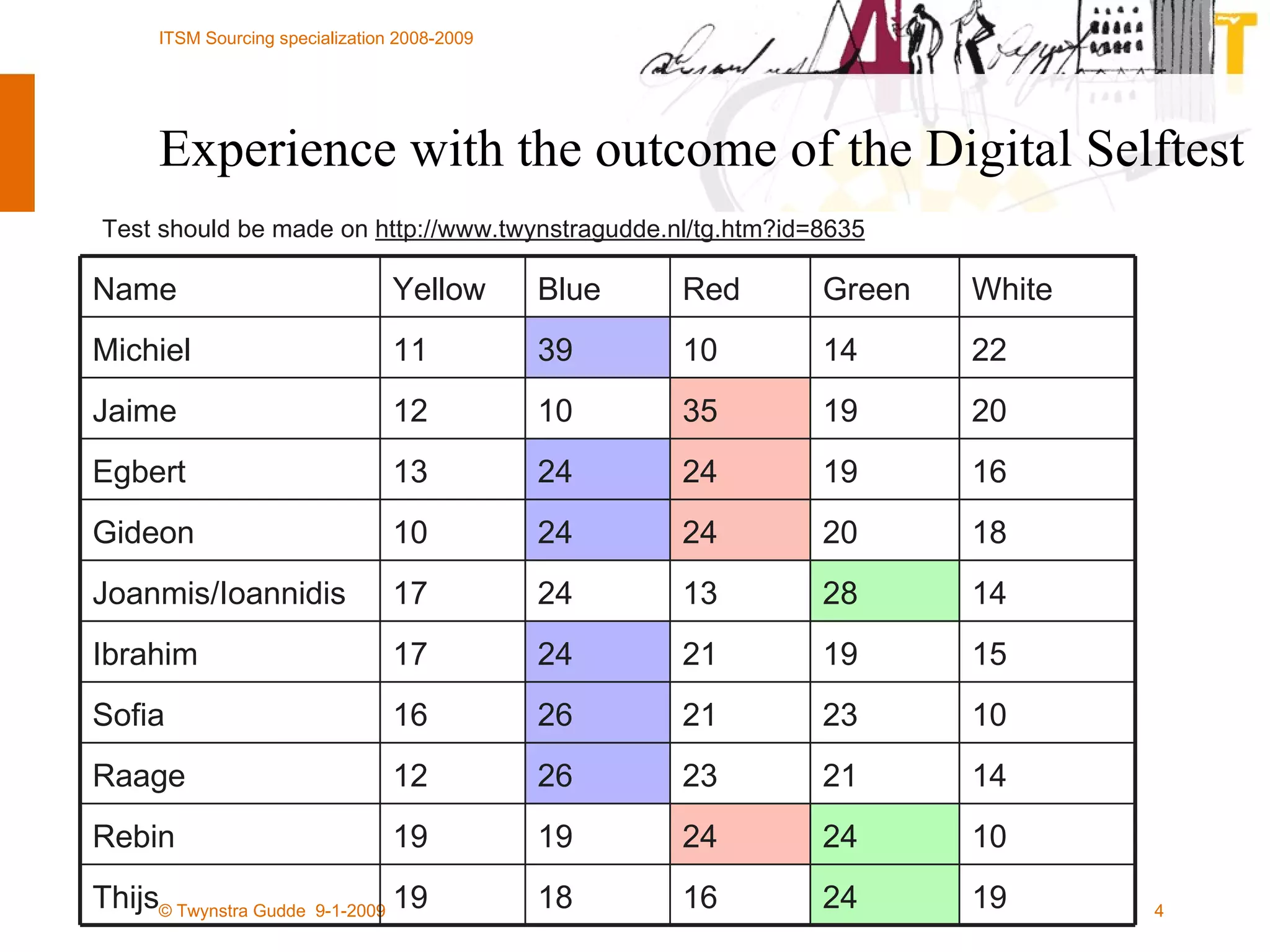



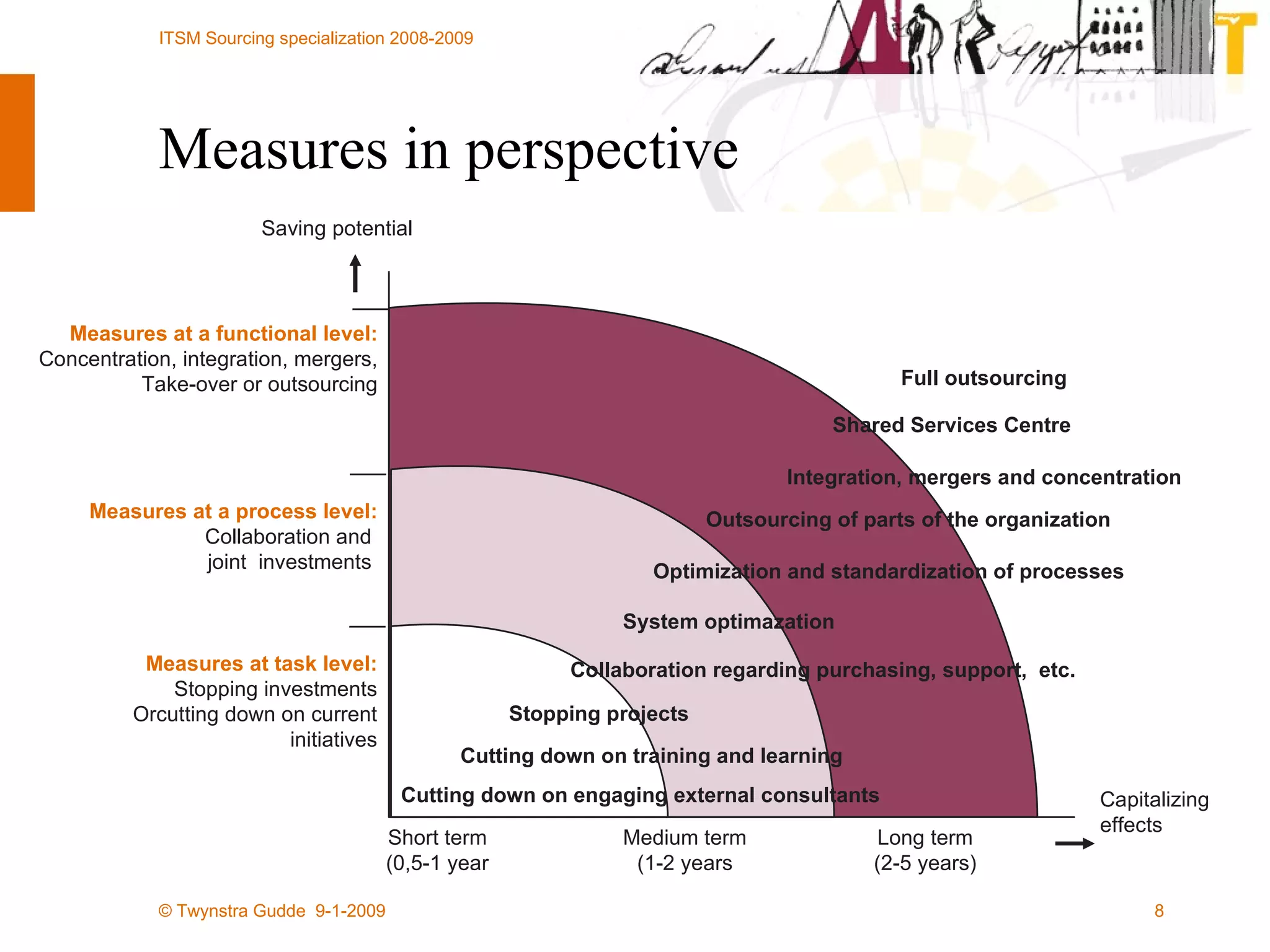
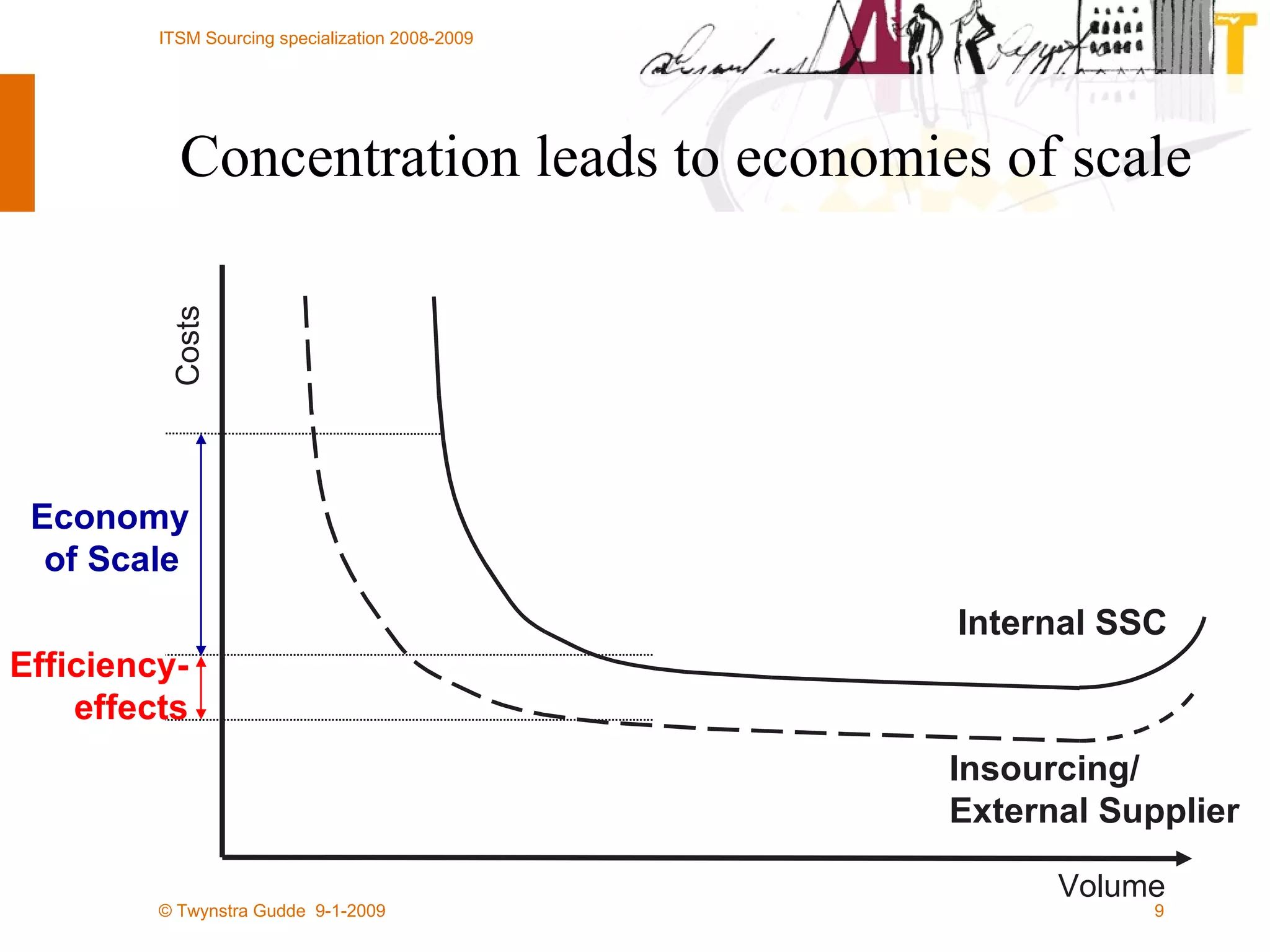
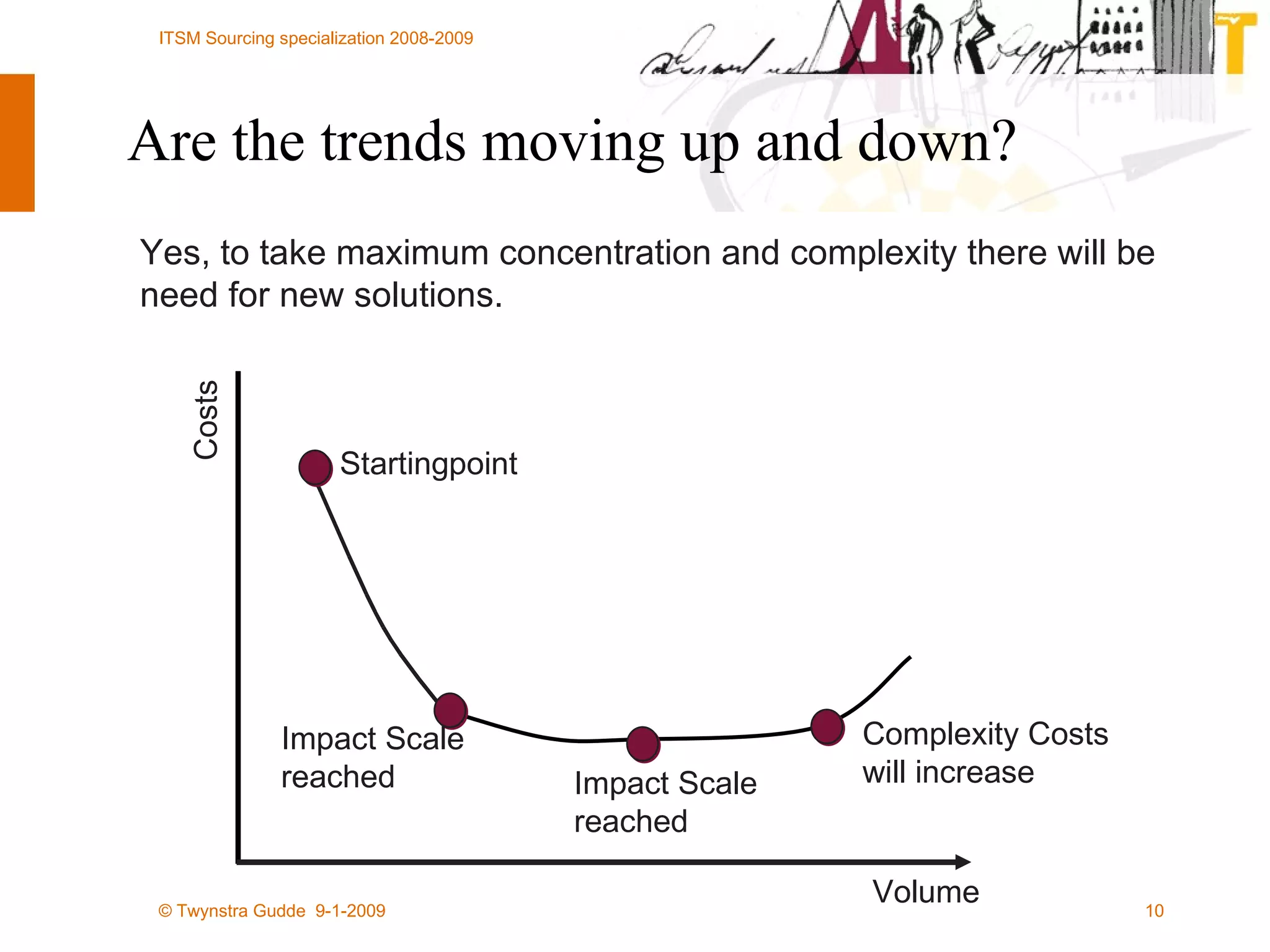
















![All rights reserved. No part of this presentation may be reproduced or published in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Twynstra Gudde. Frank Willems [email_address] www.twynstragudde.nl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hg-itsm-sourcing-lecture-4-shared-services-collaboration-and-crowdsourcing-1232313903668620-2/75/Sourcing-Lecture-4-Shared-Services-Collaboration-And-Crowdsourcing-39-2048.jpg)