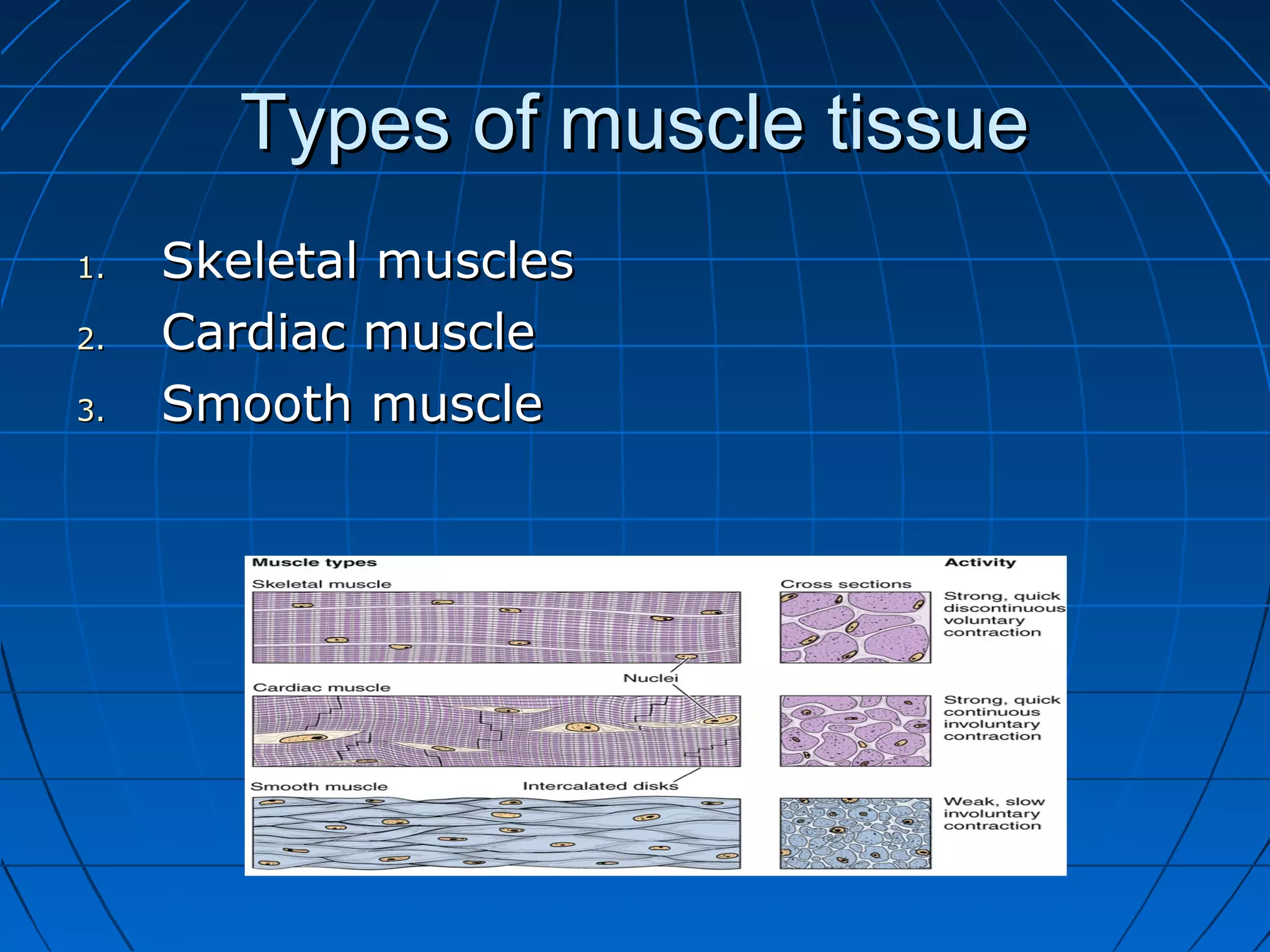
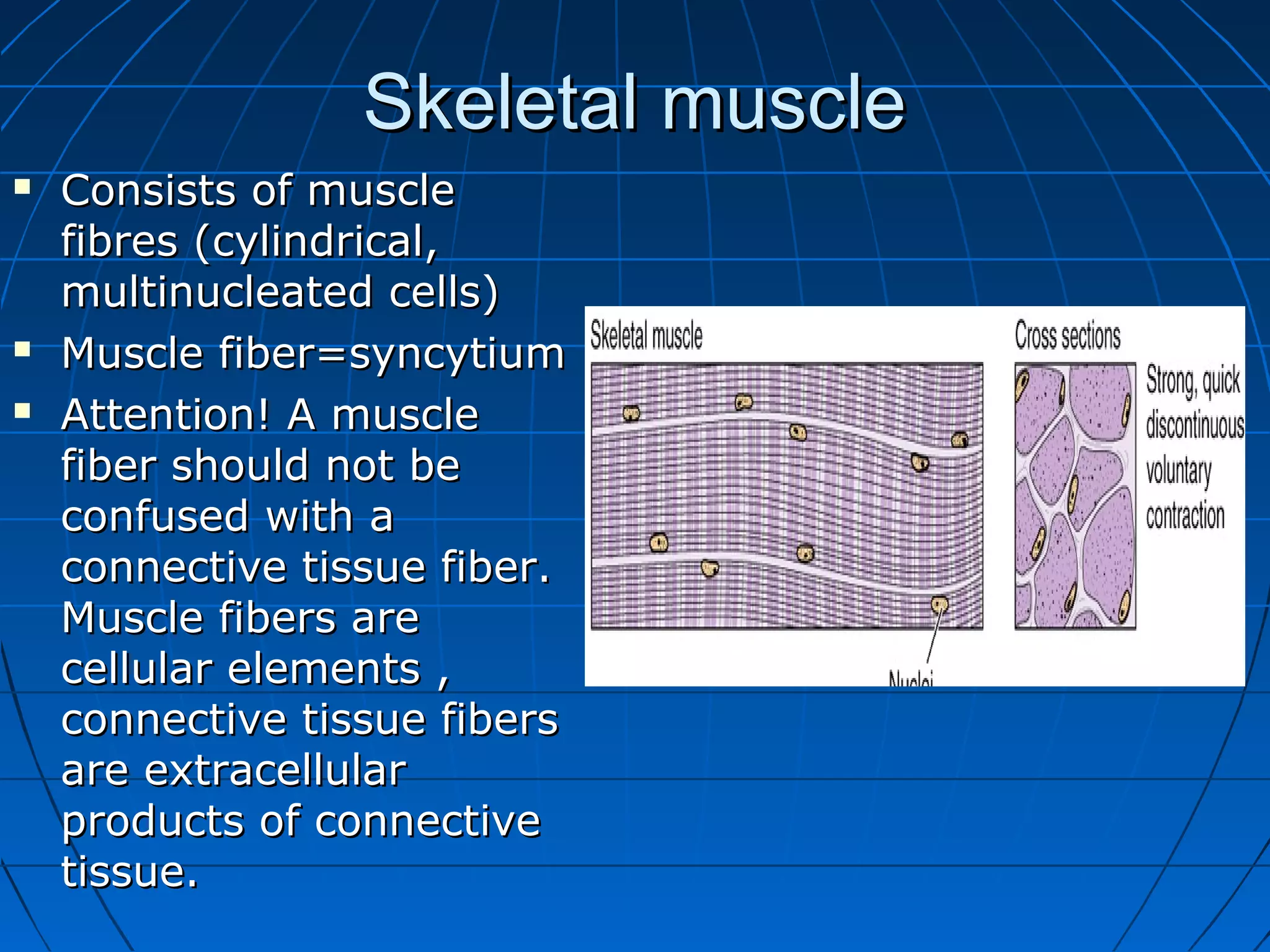
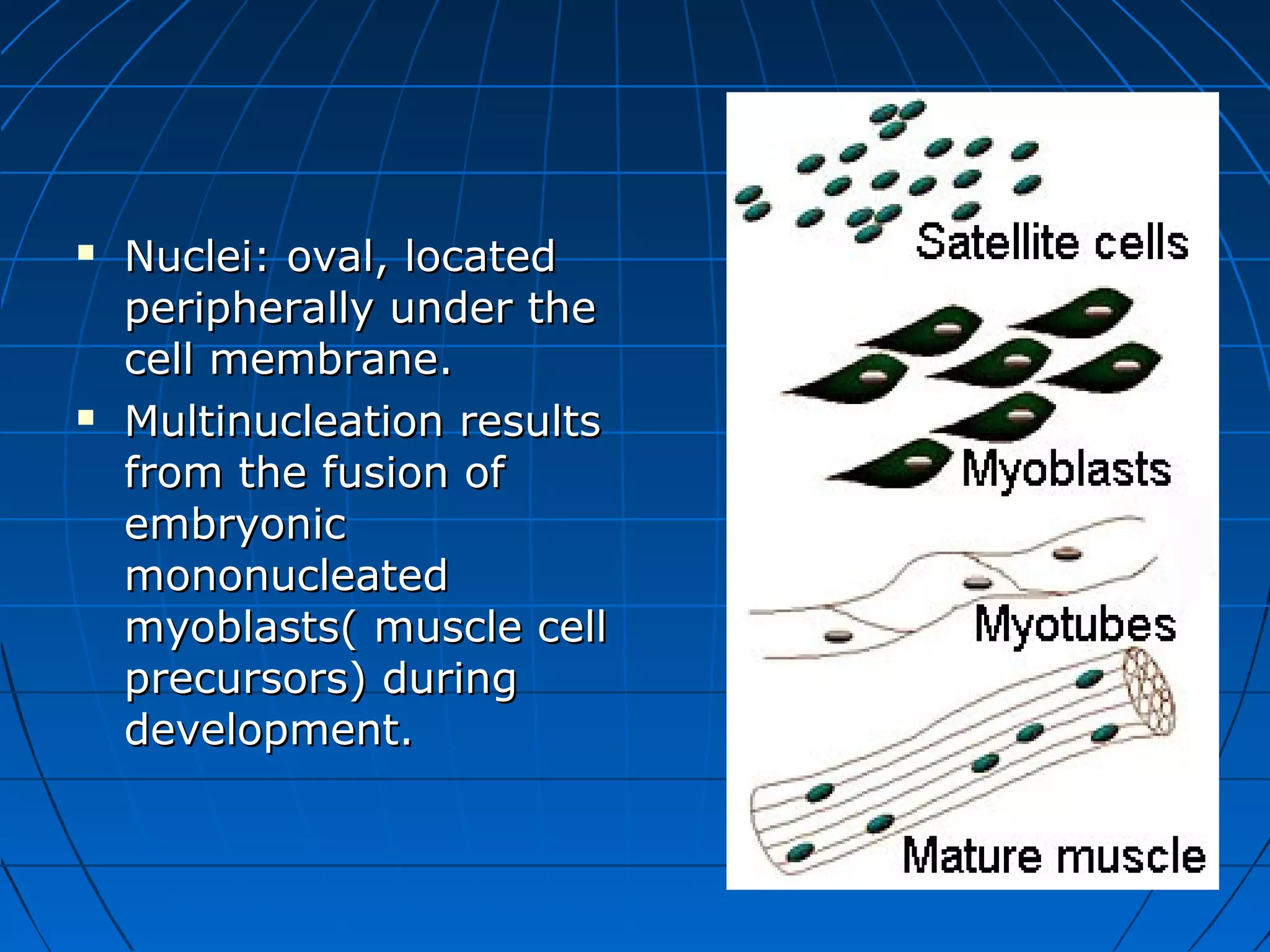
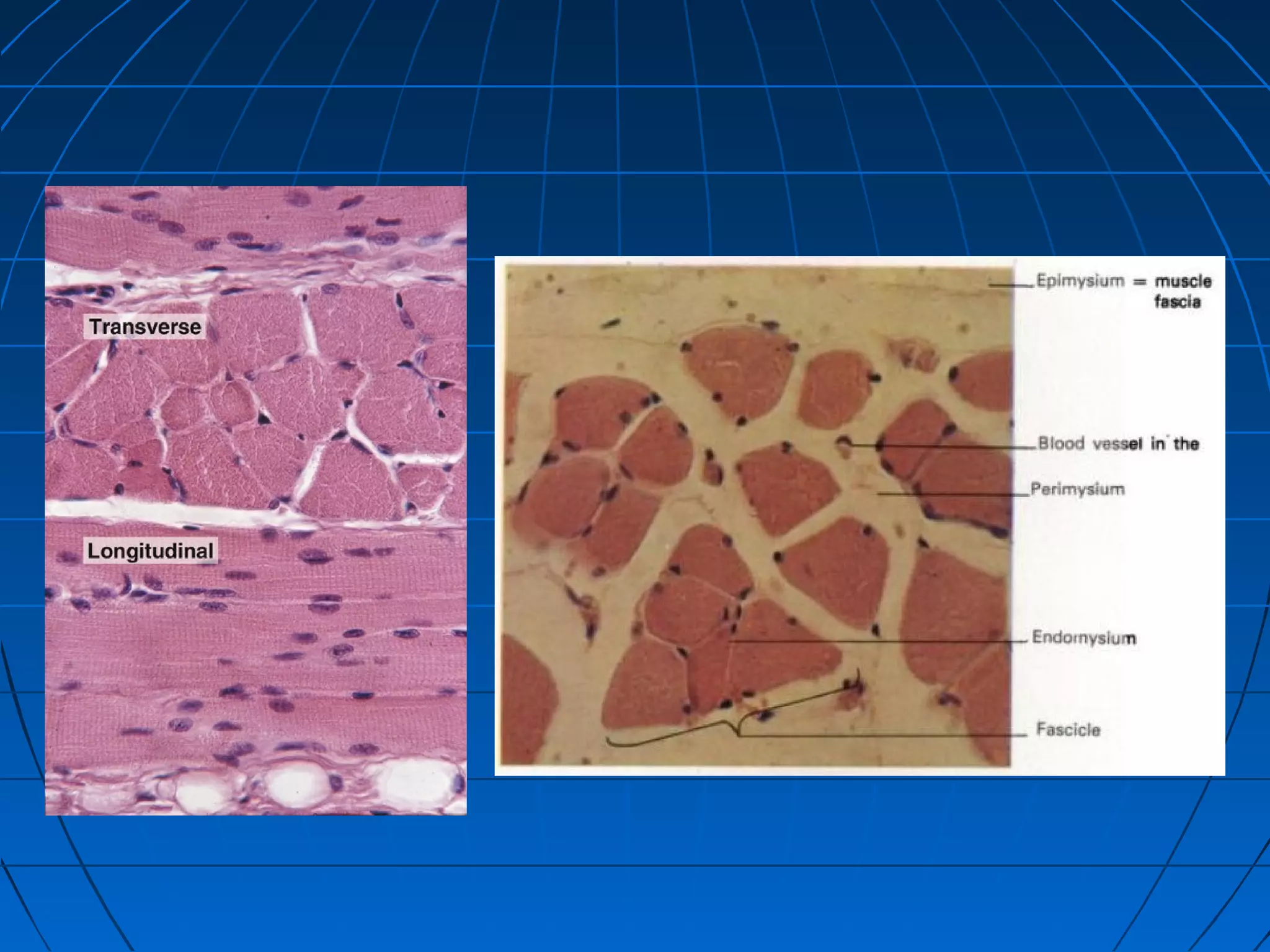
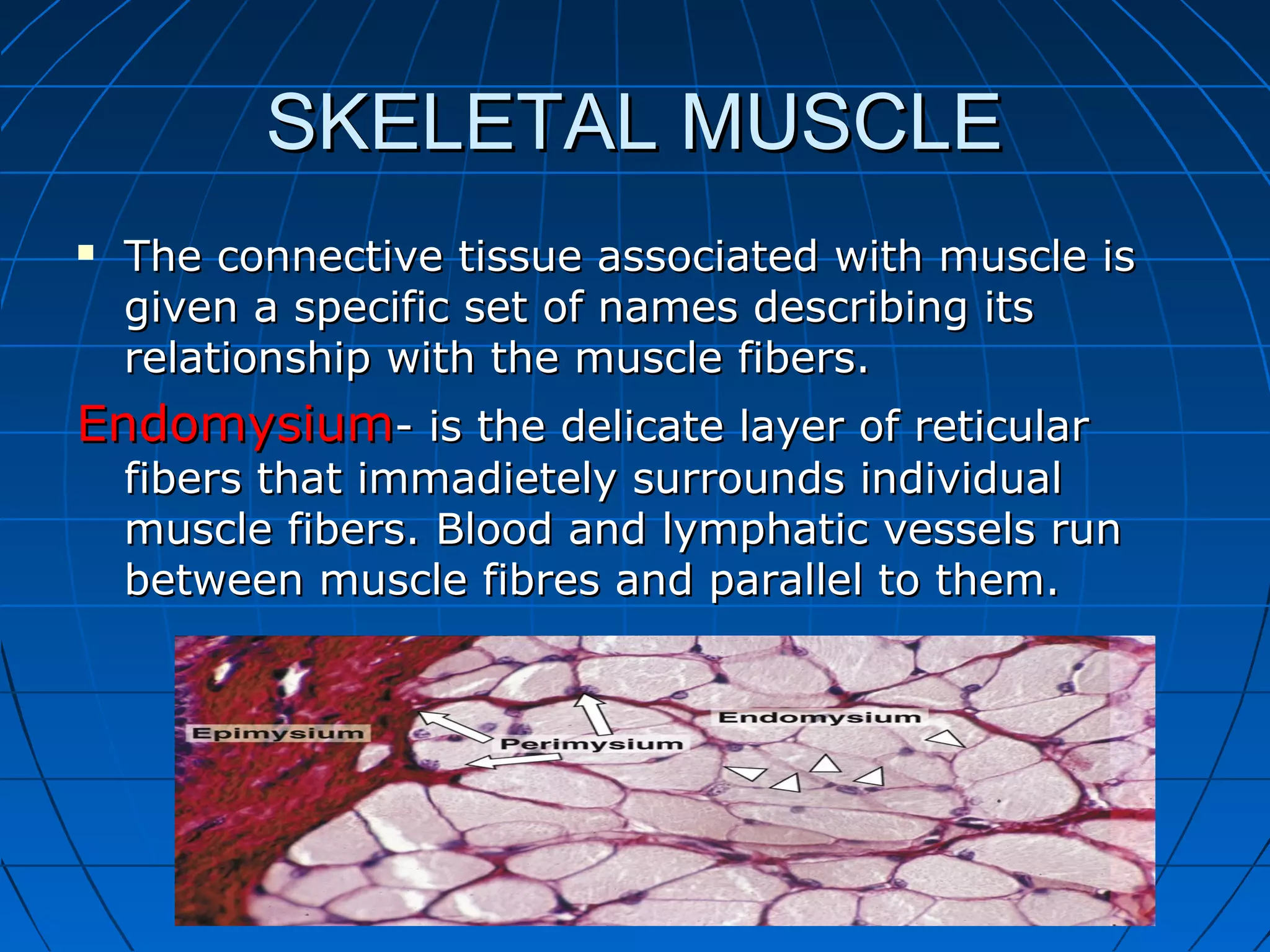
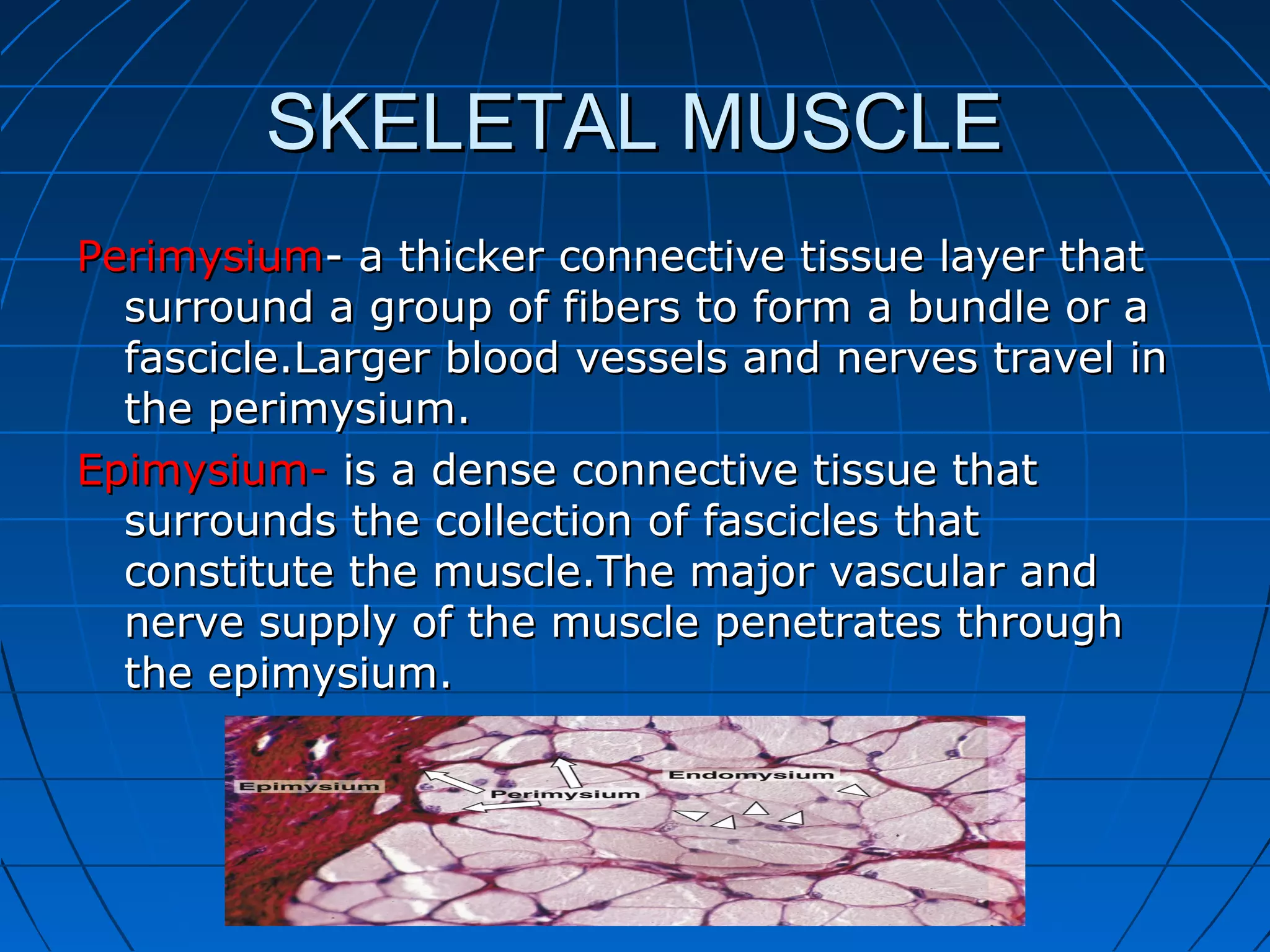
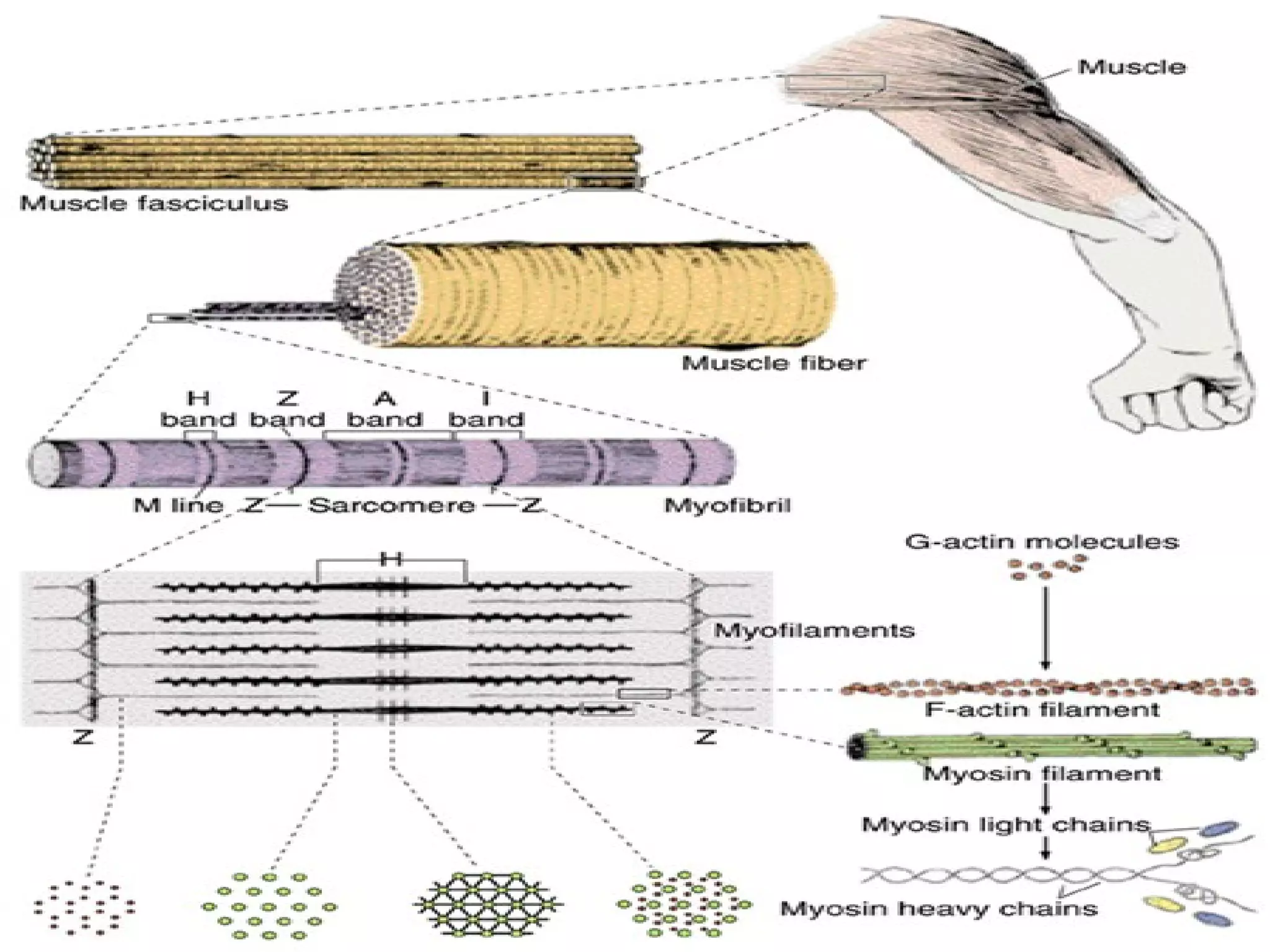
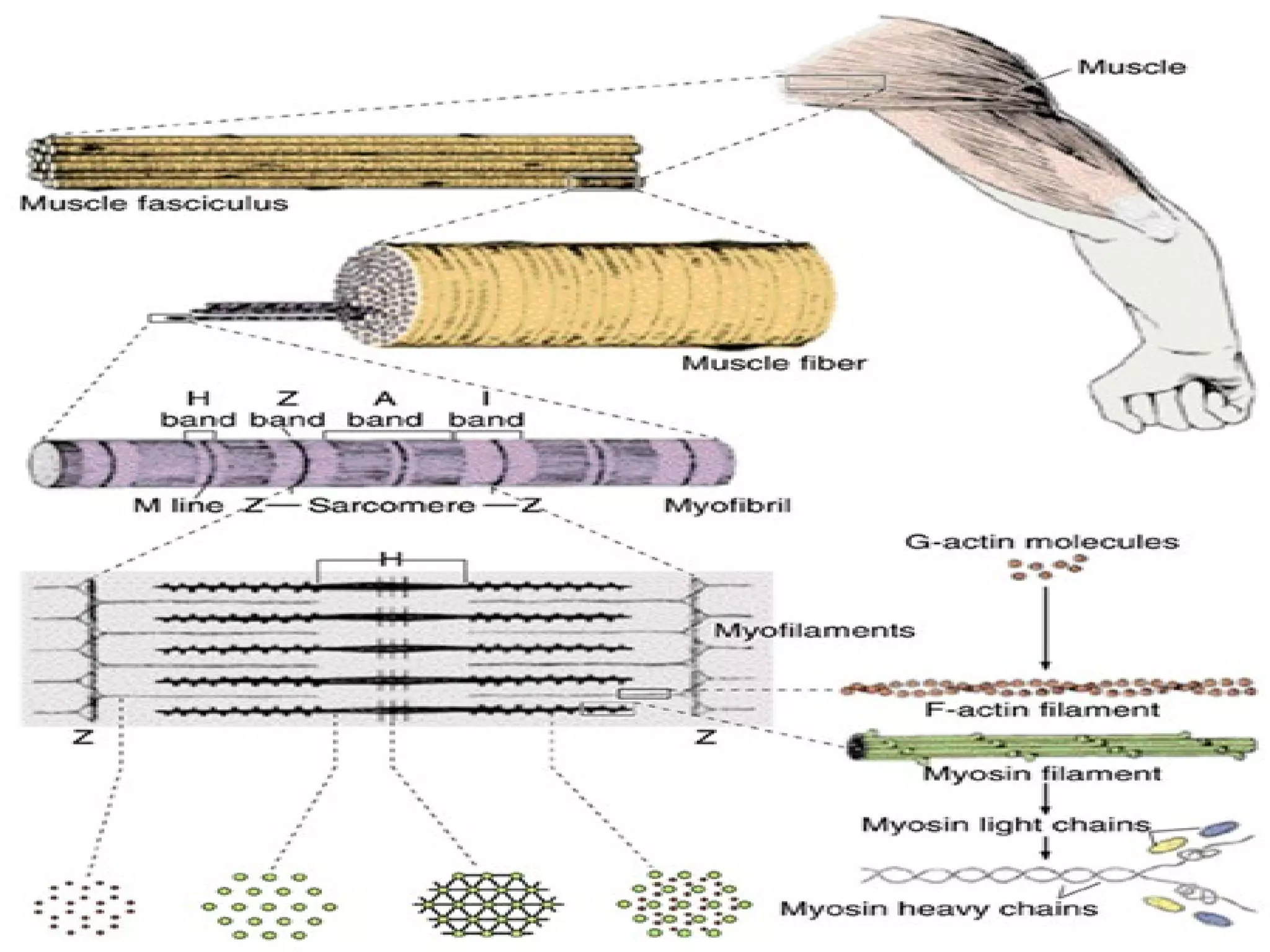
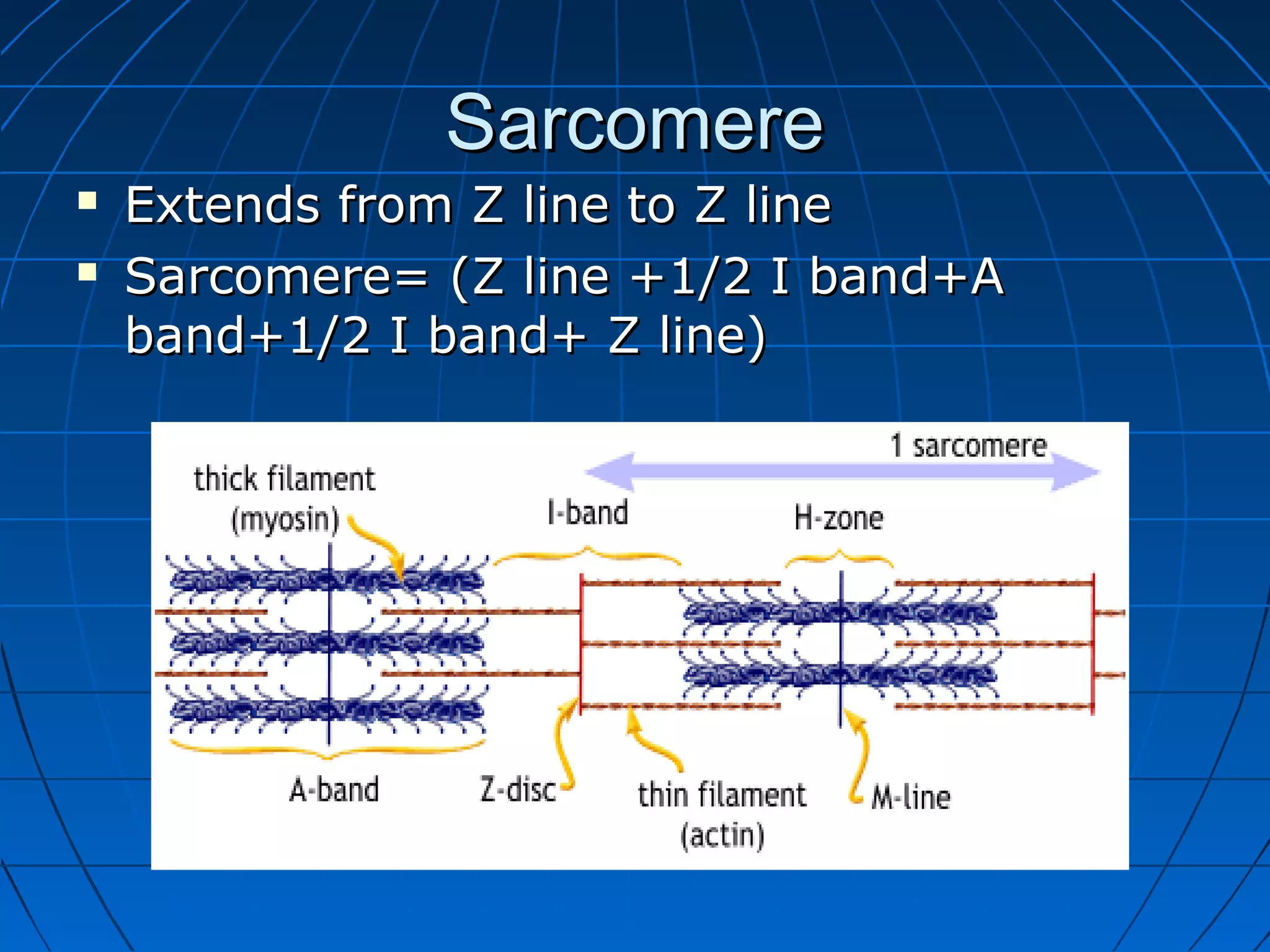
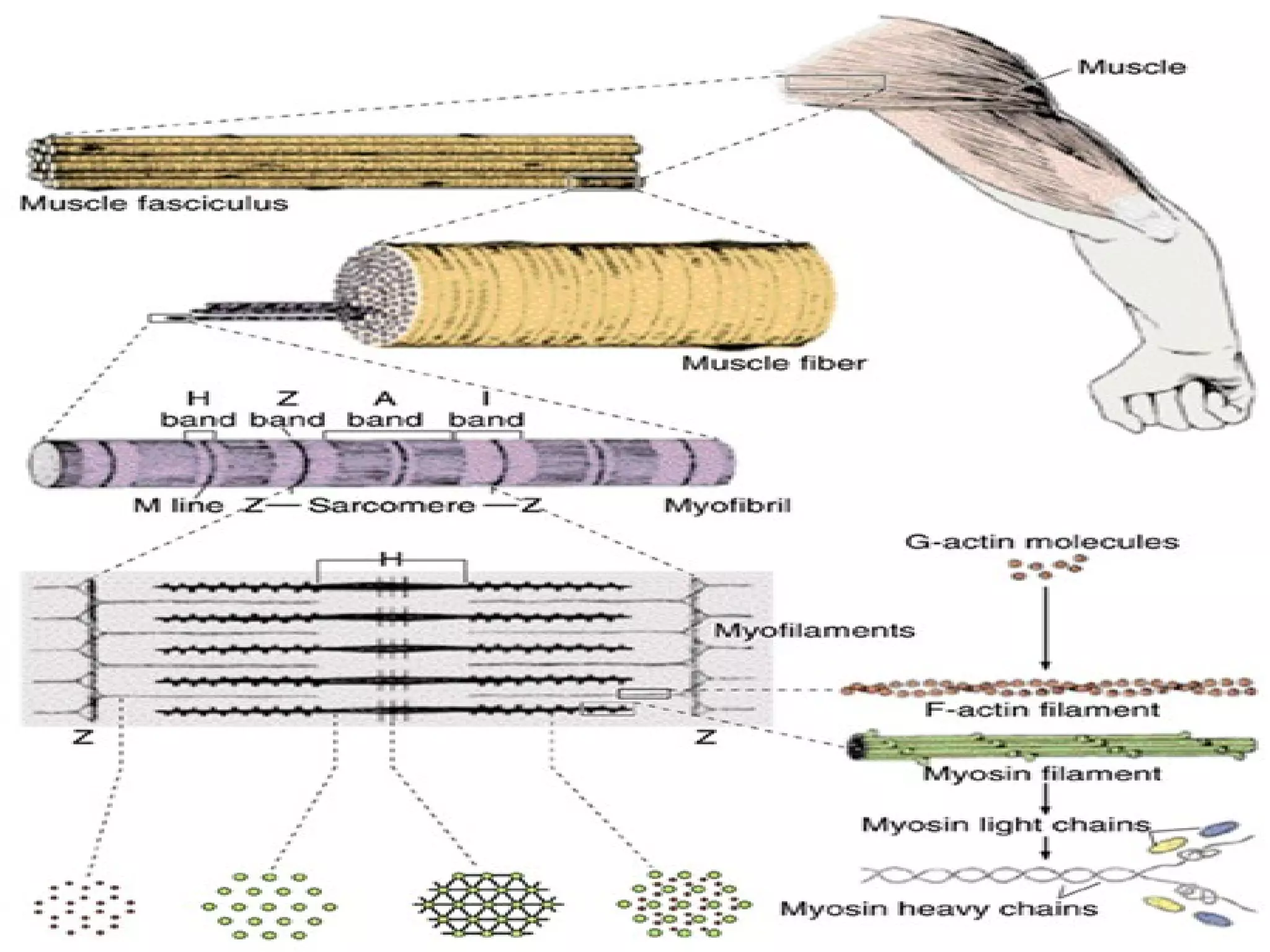
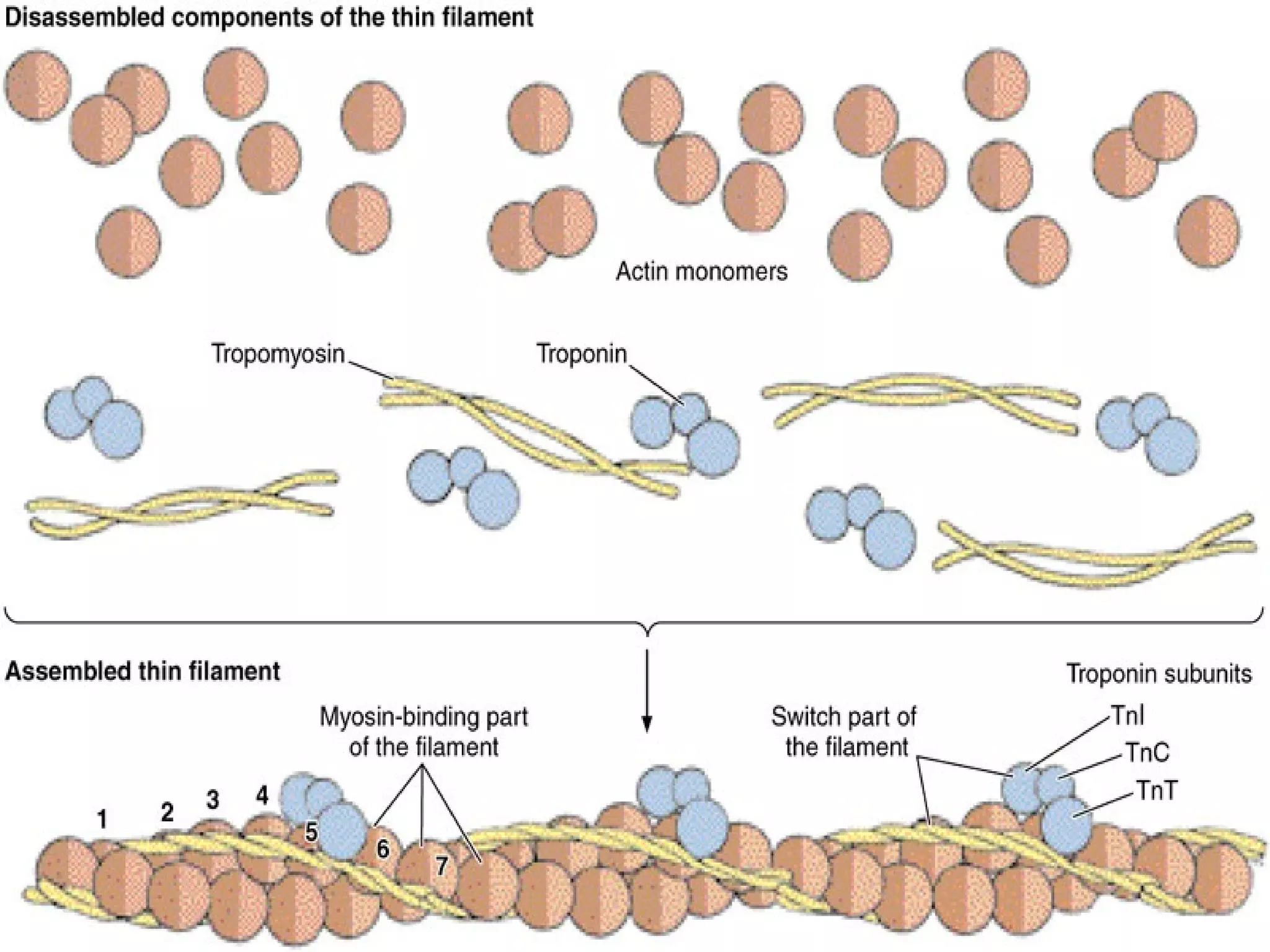
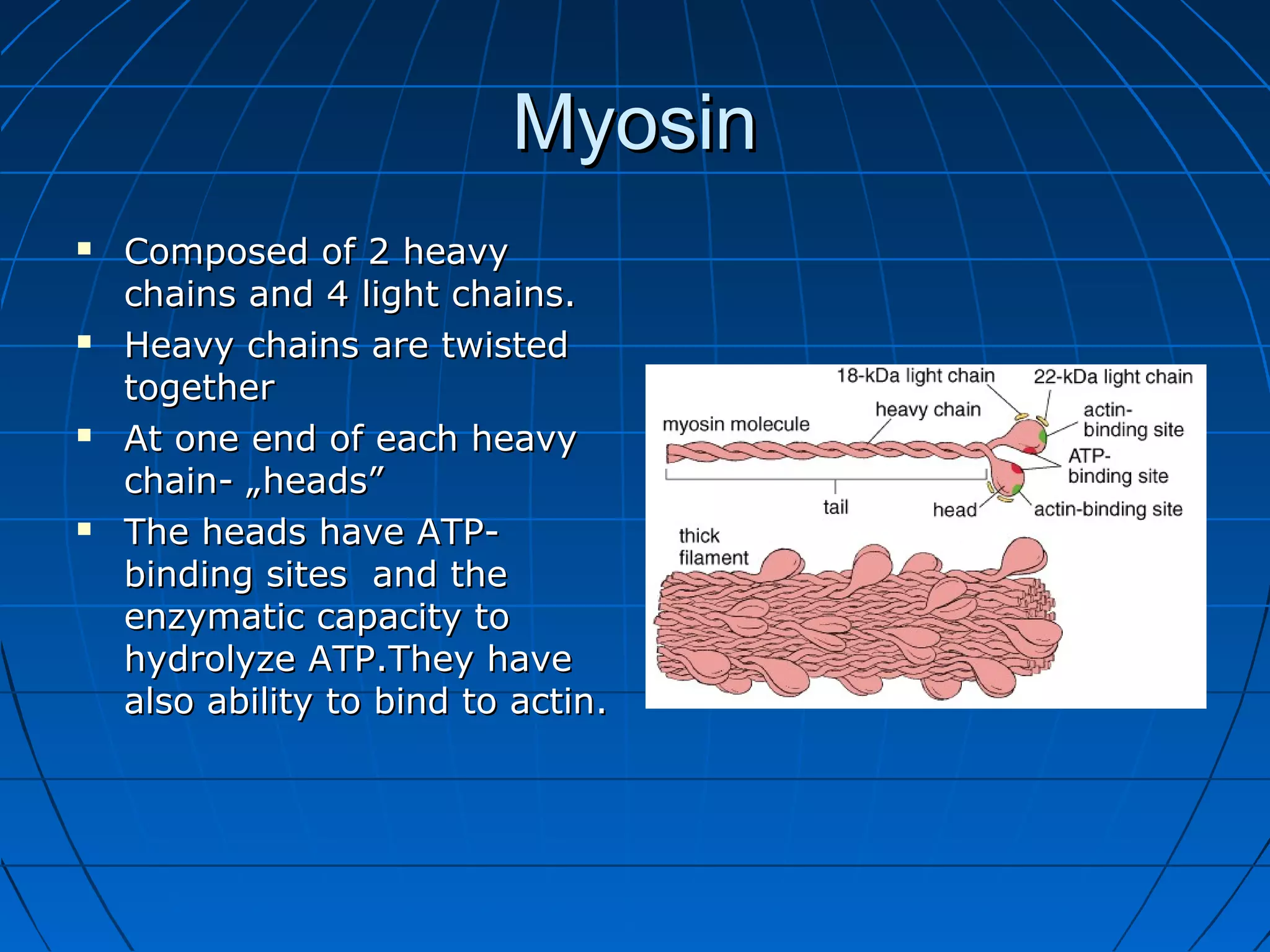
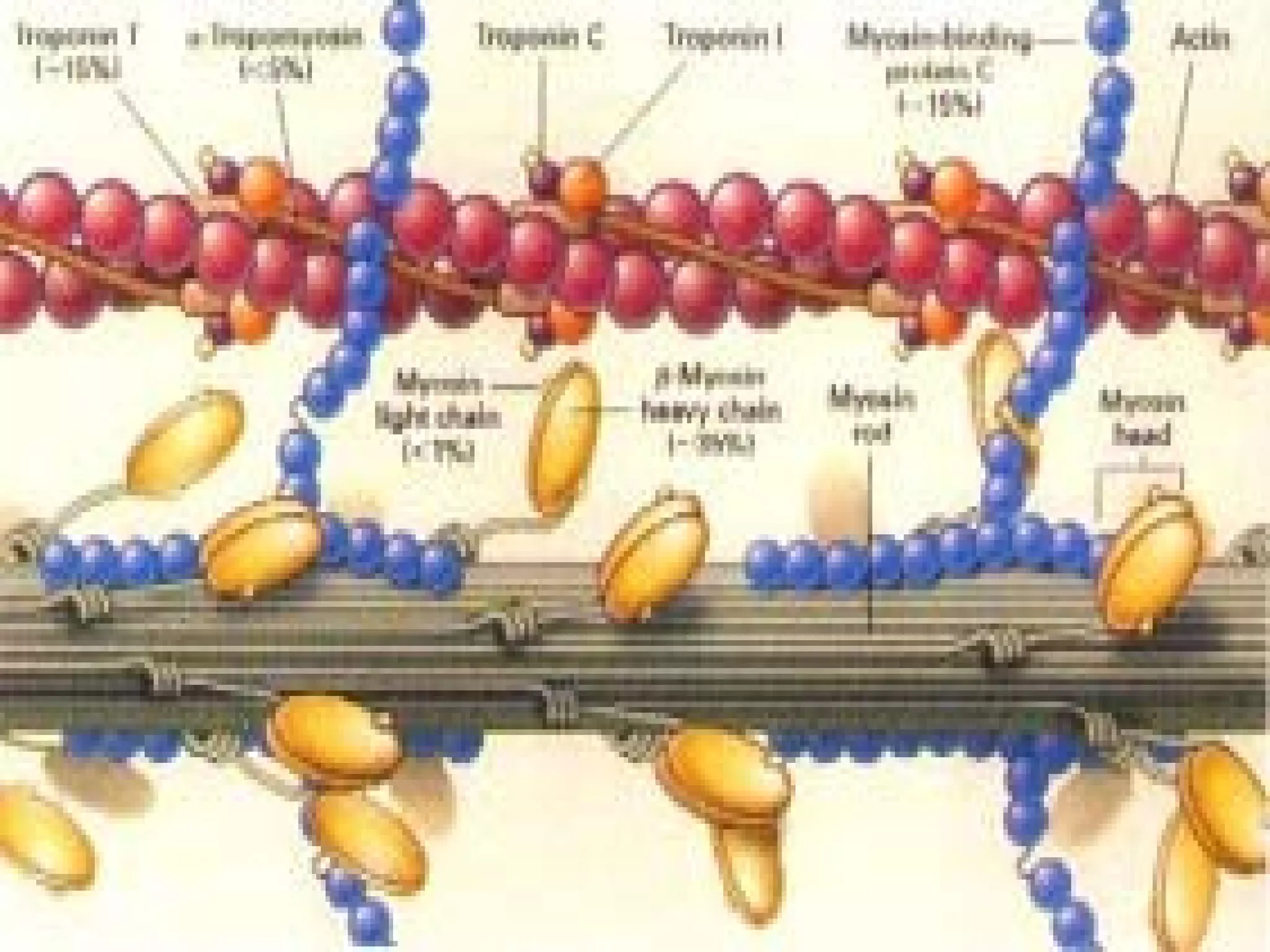
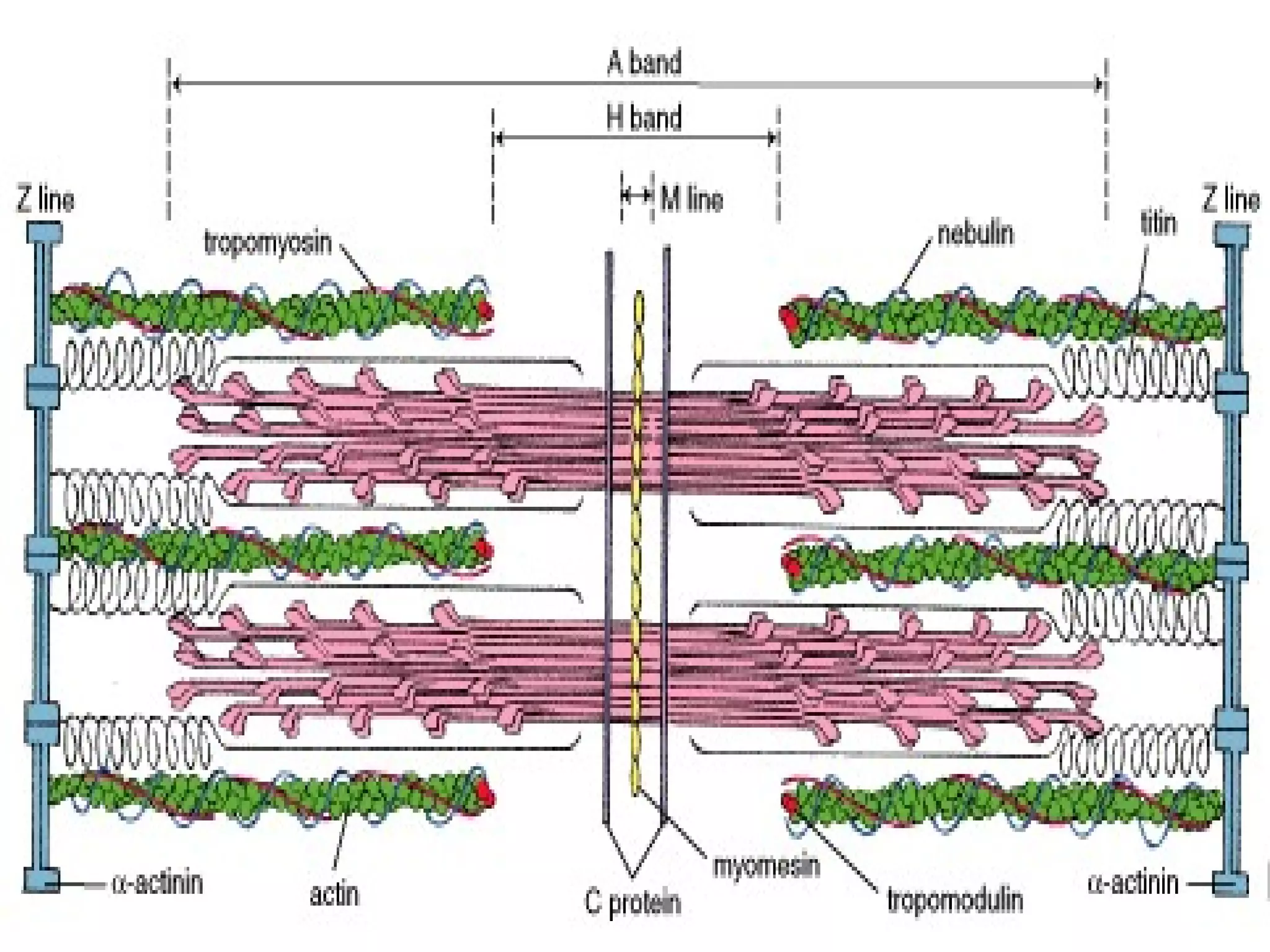
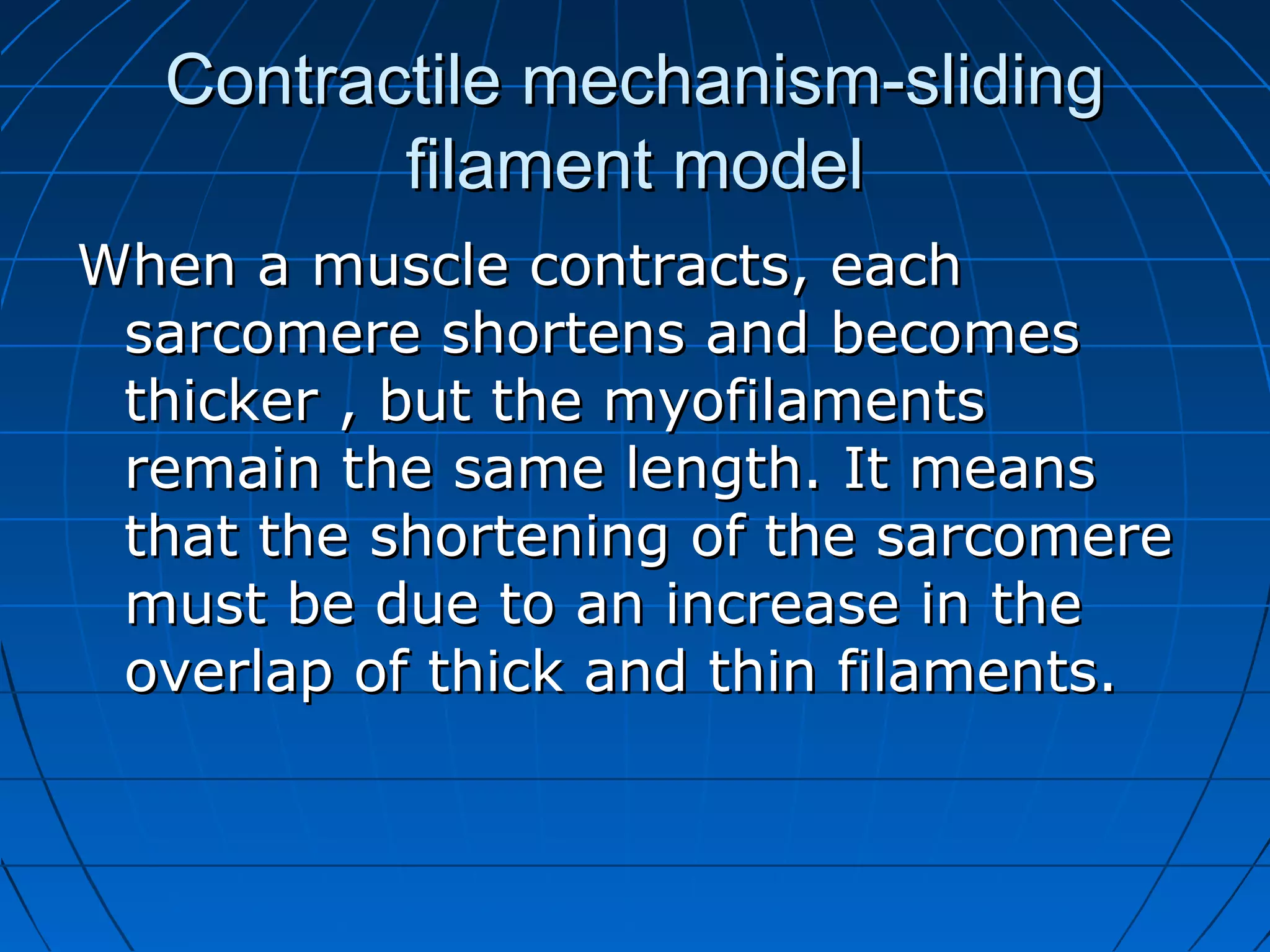
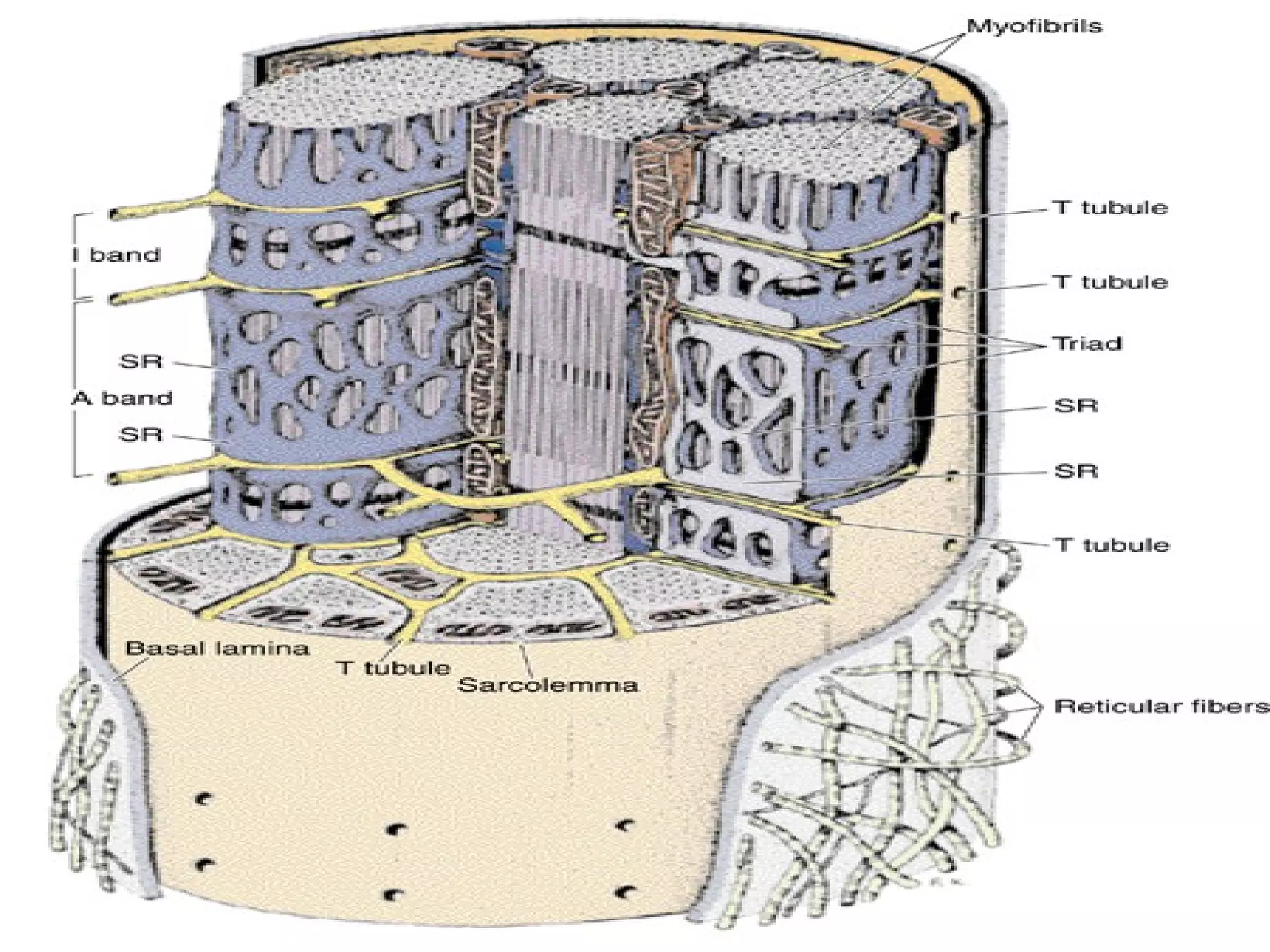
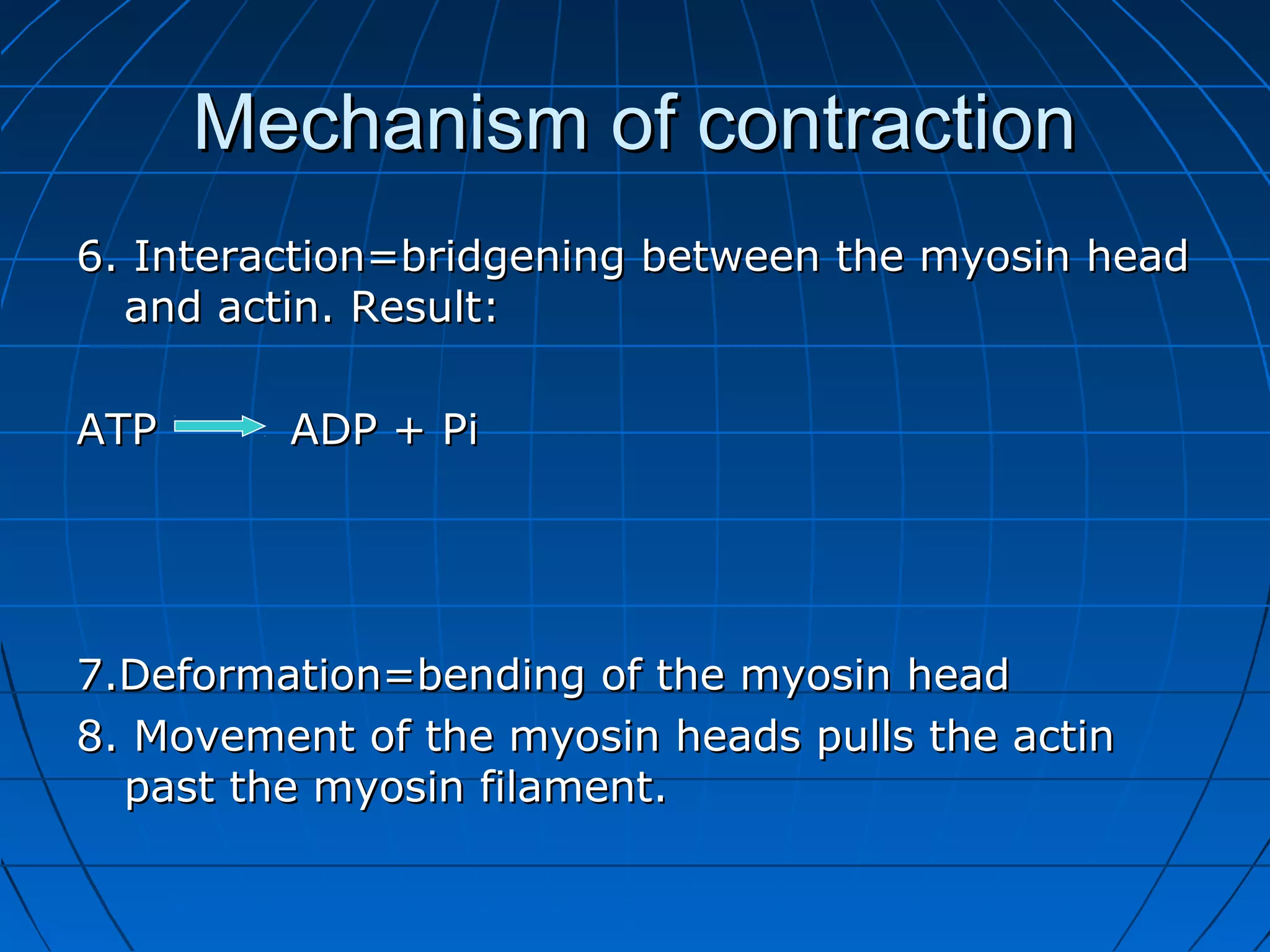
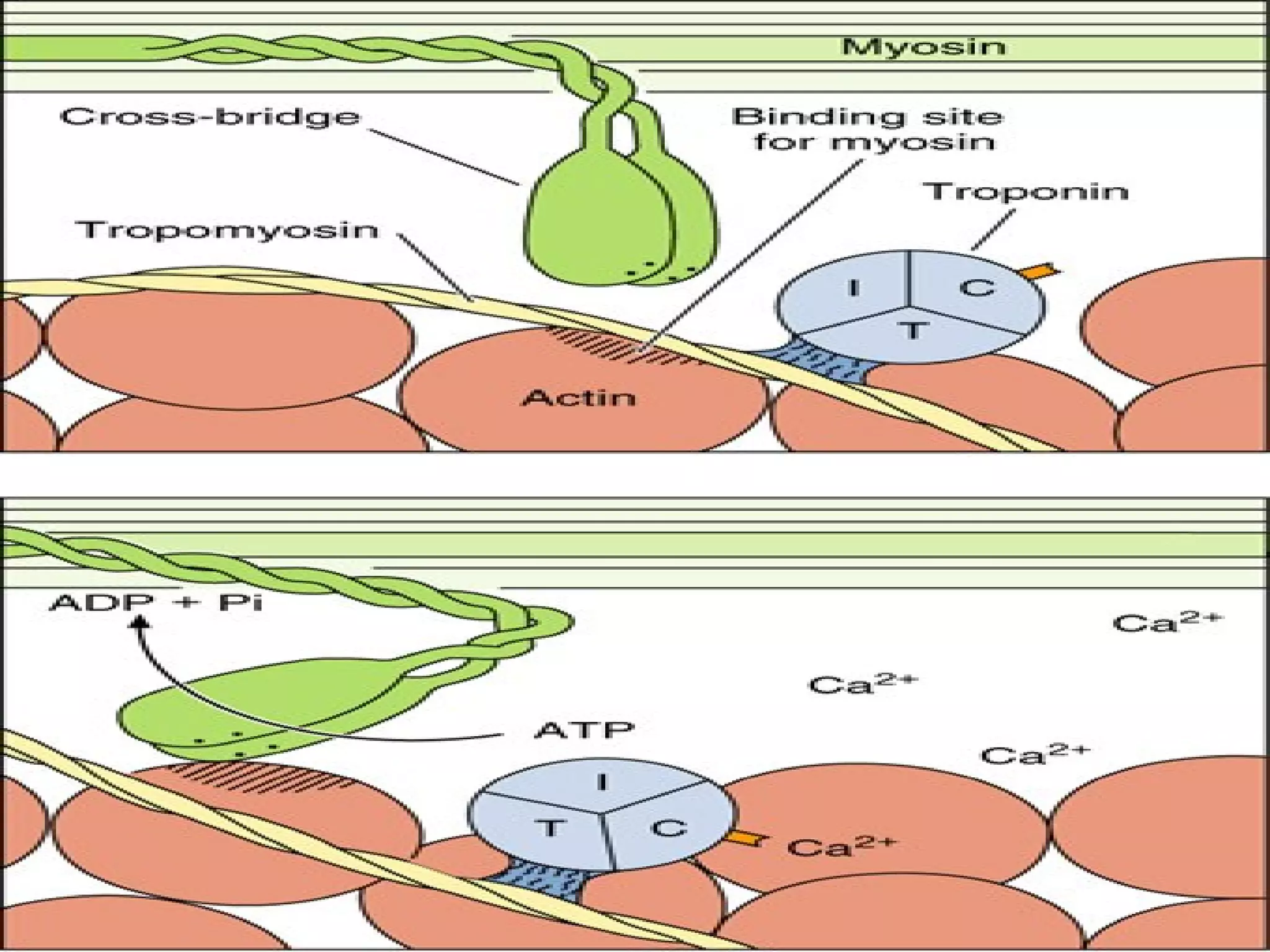
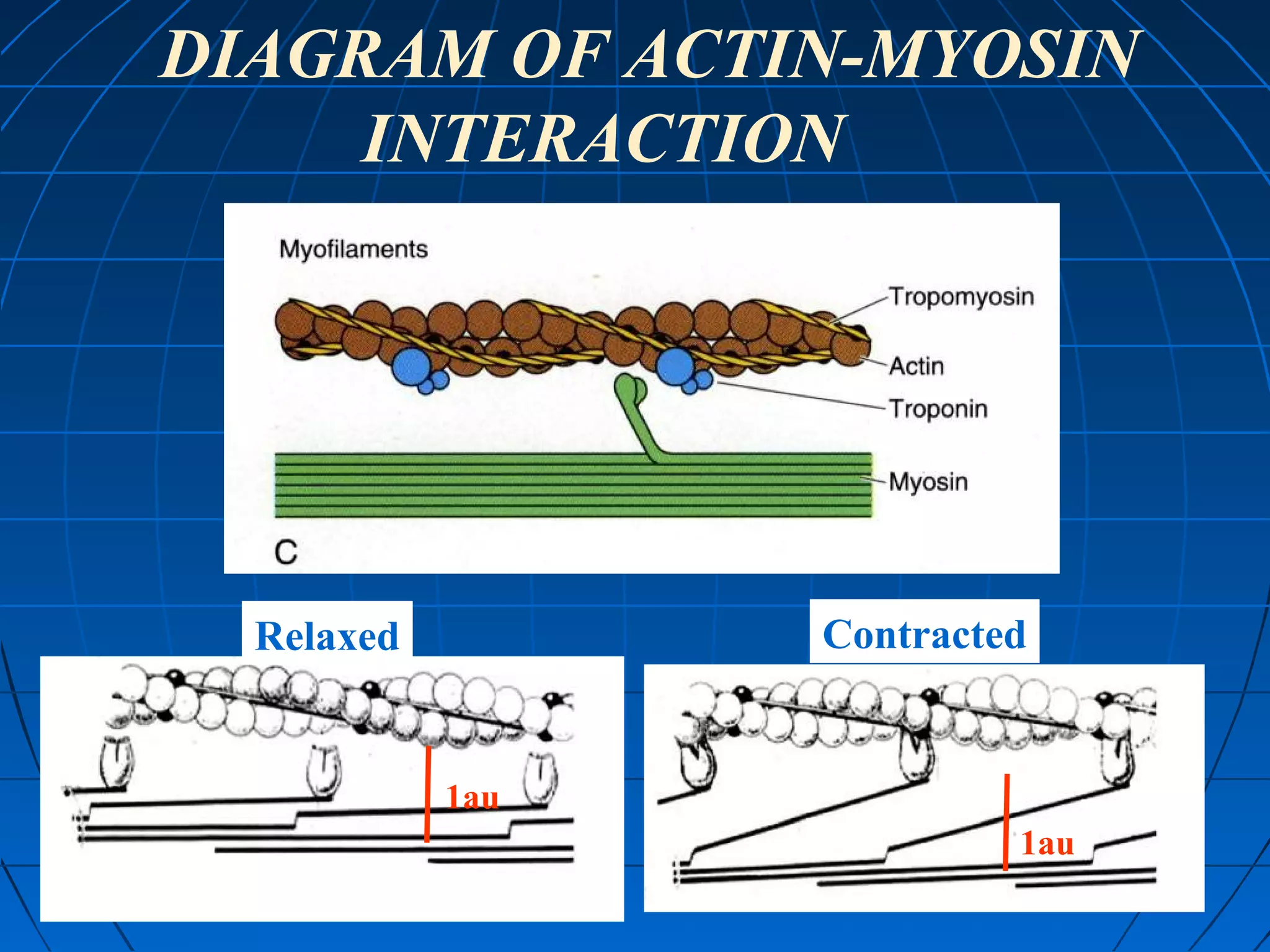
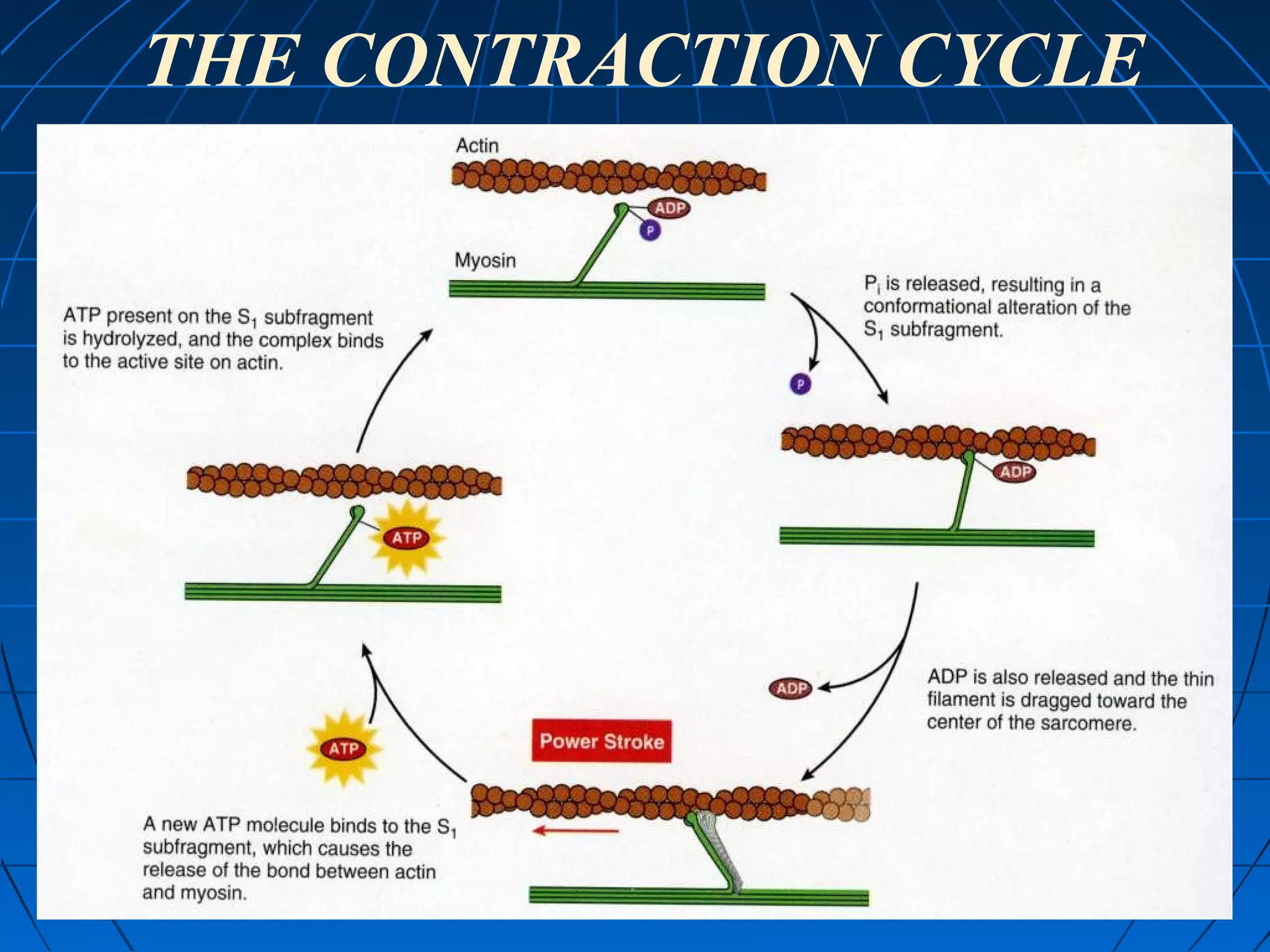
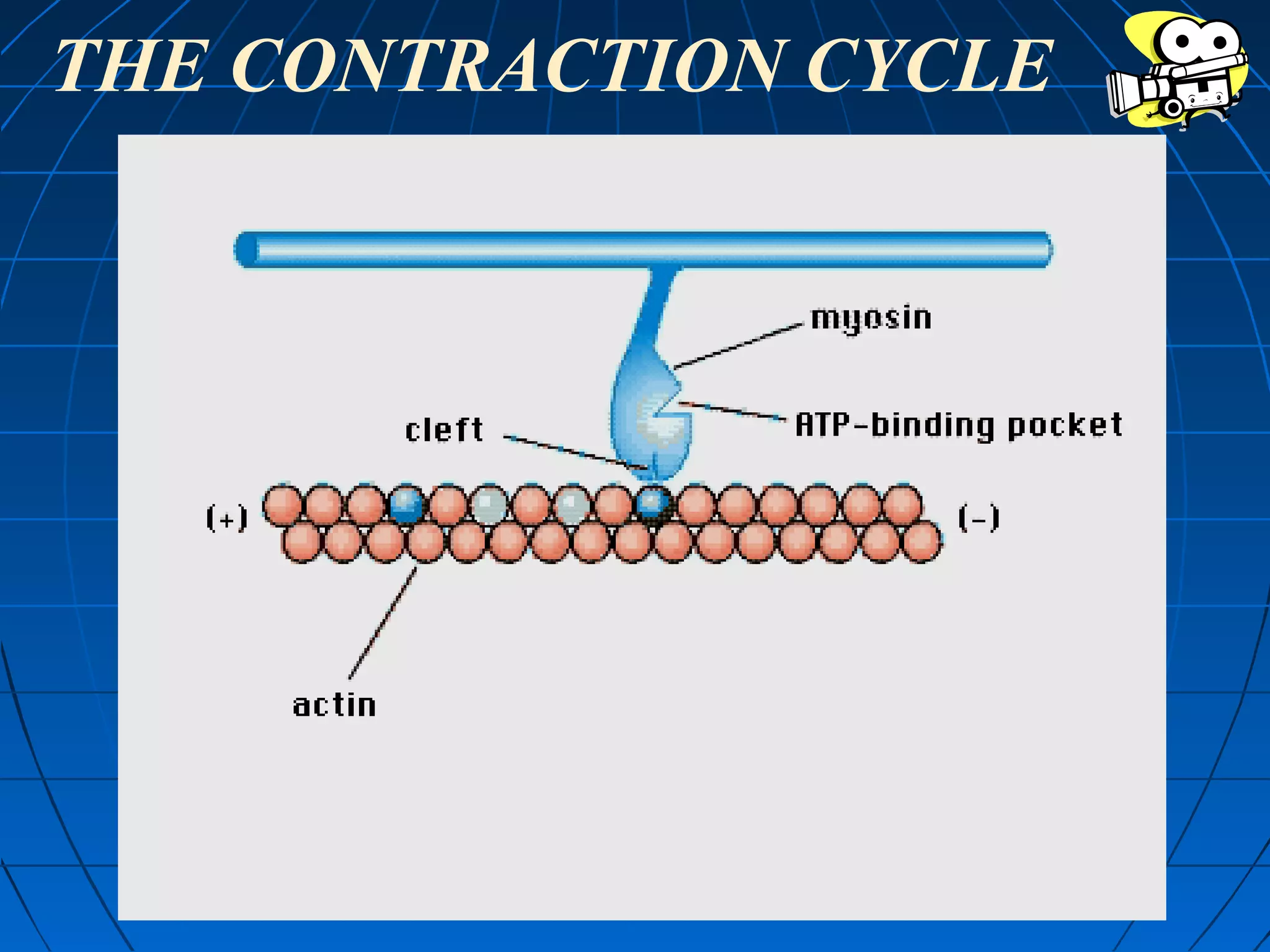
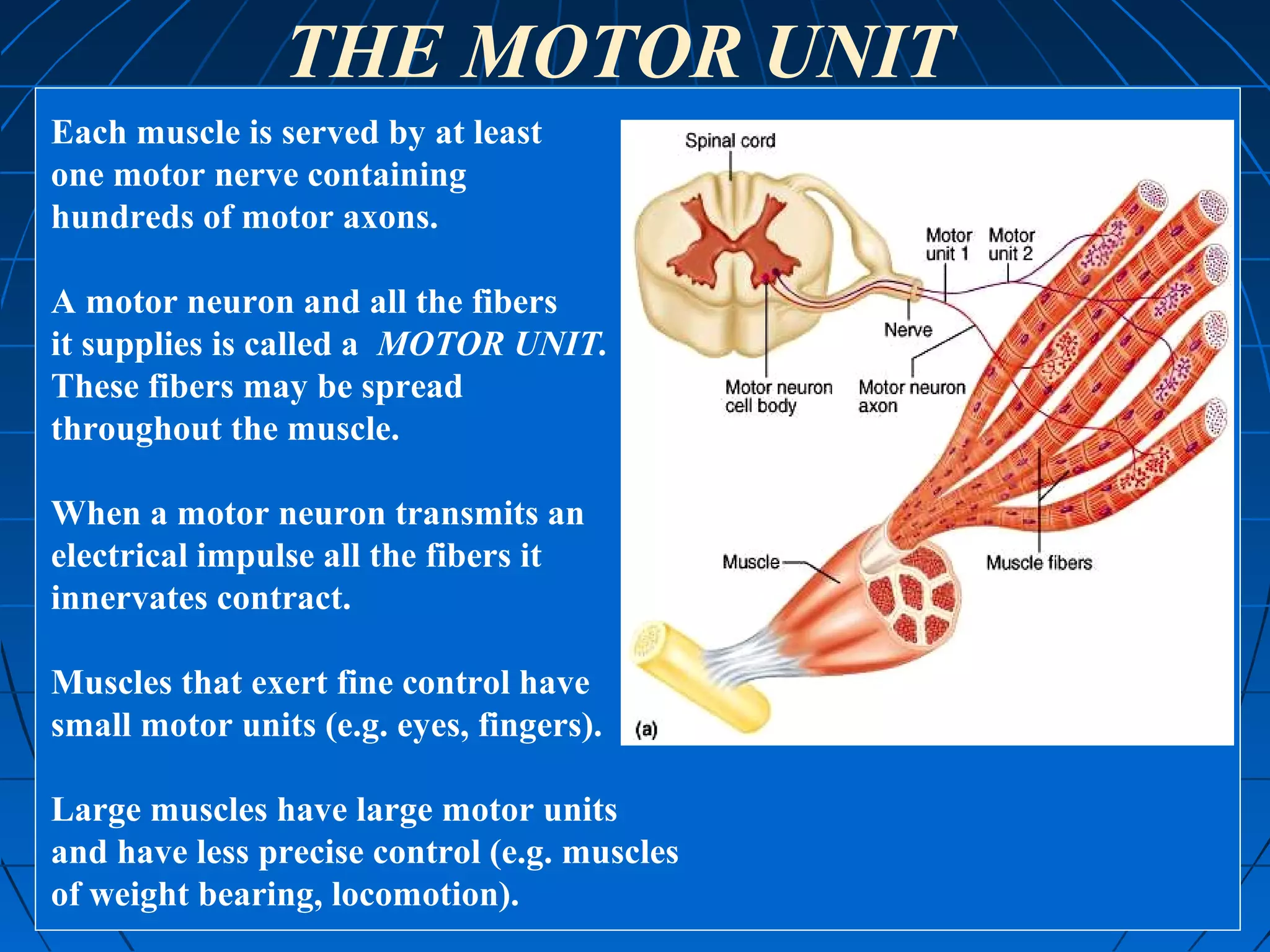
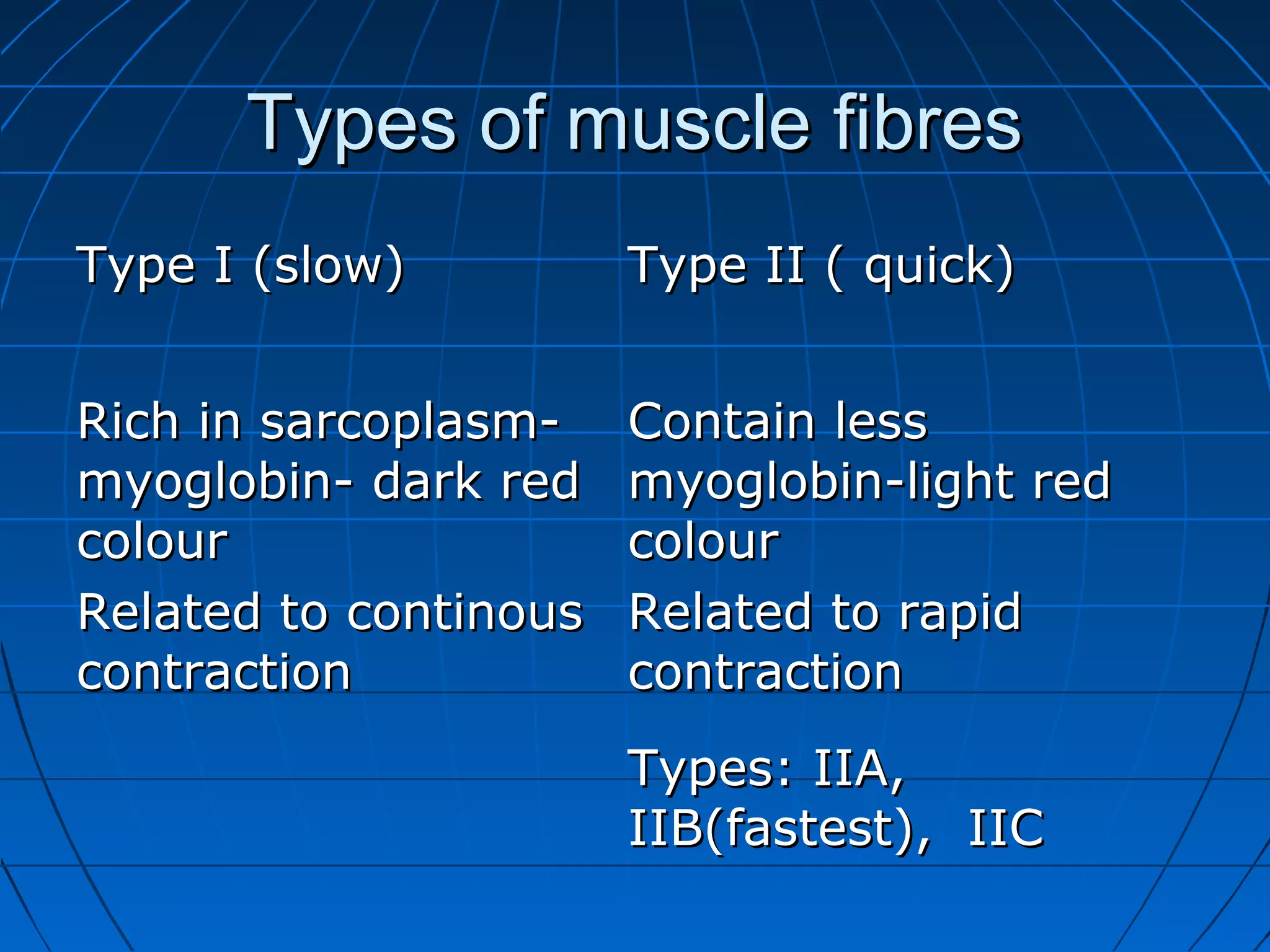
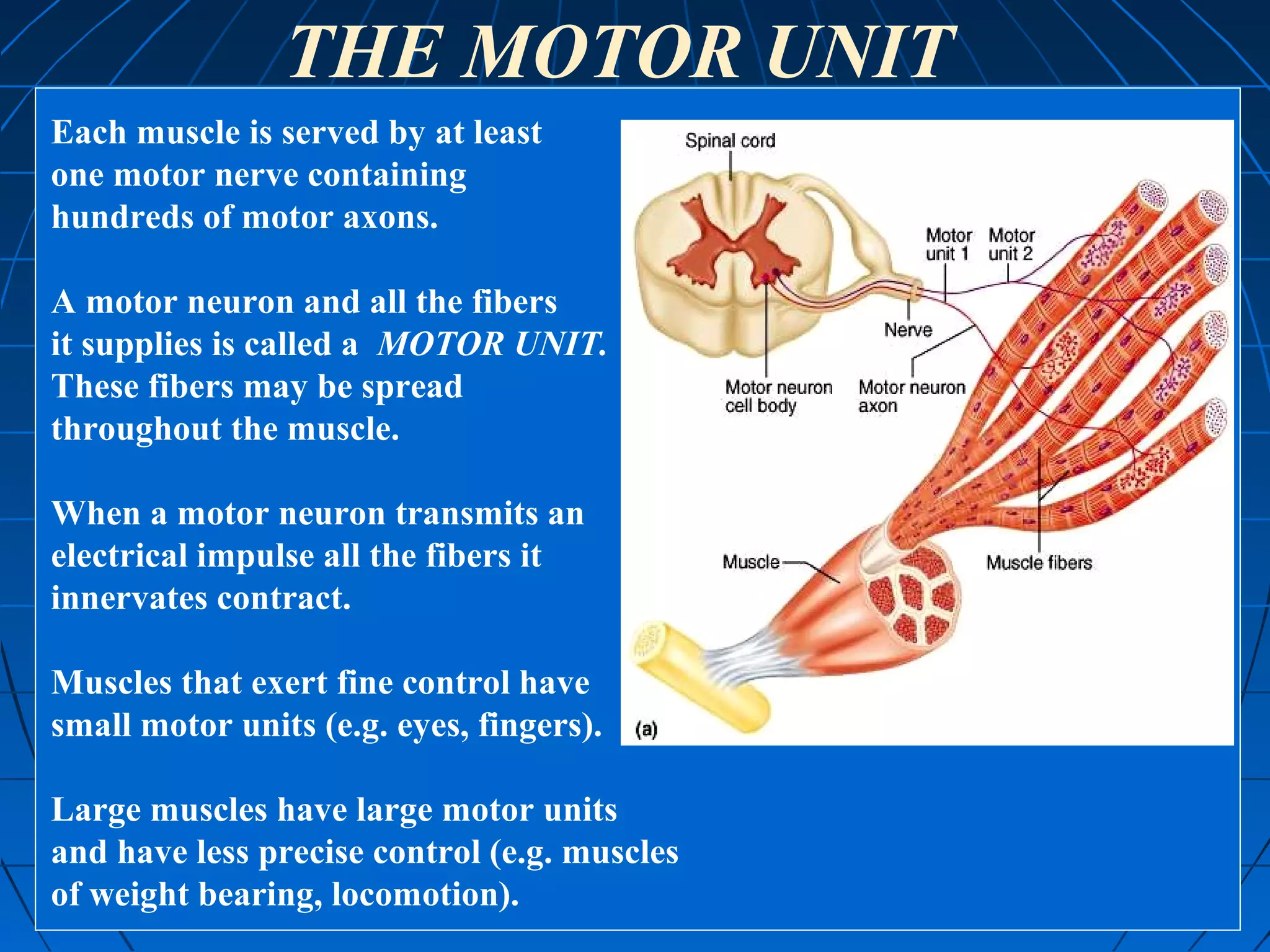
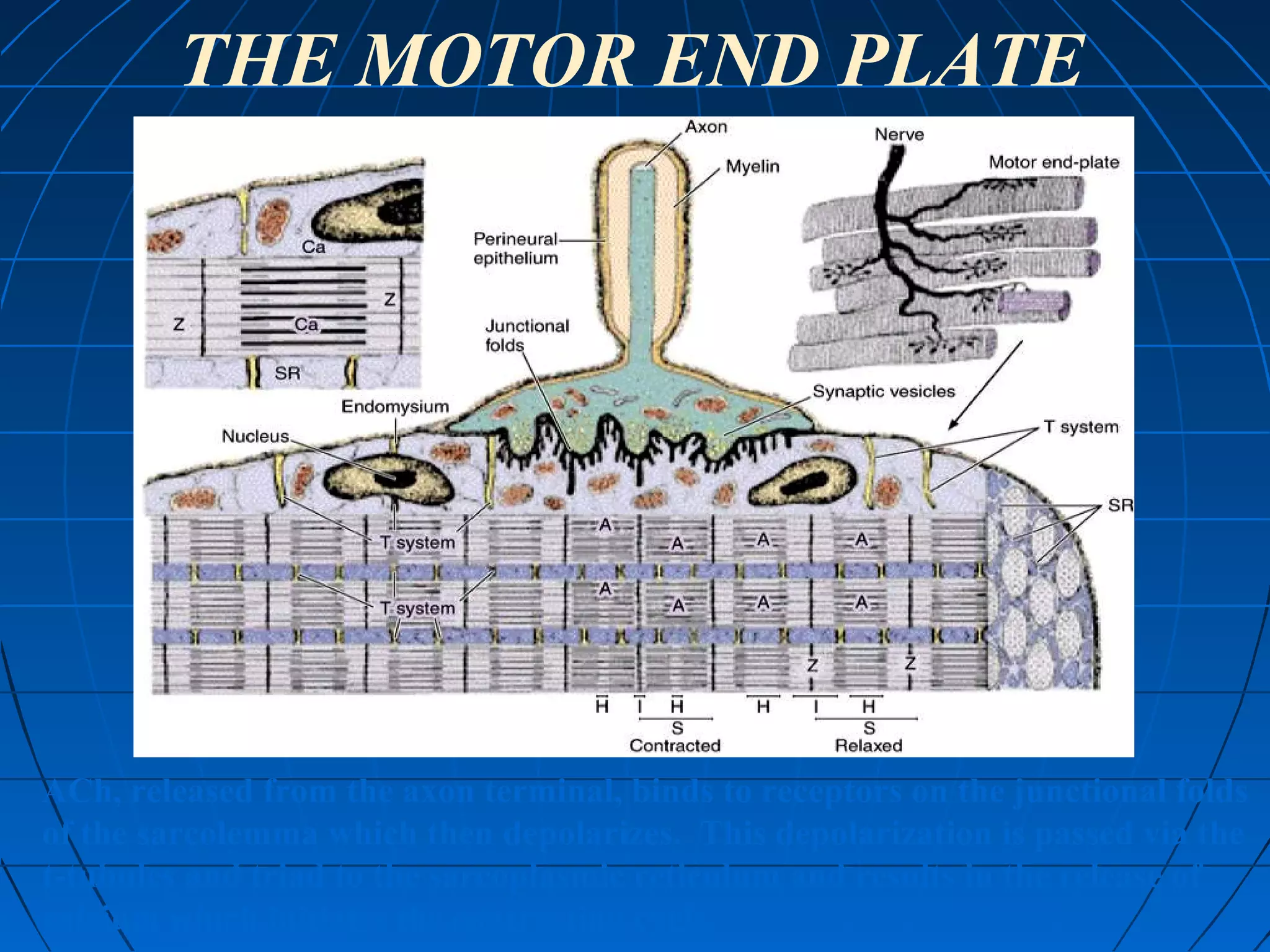
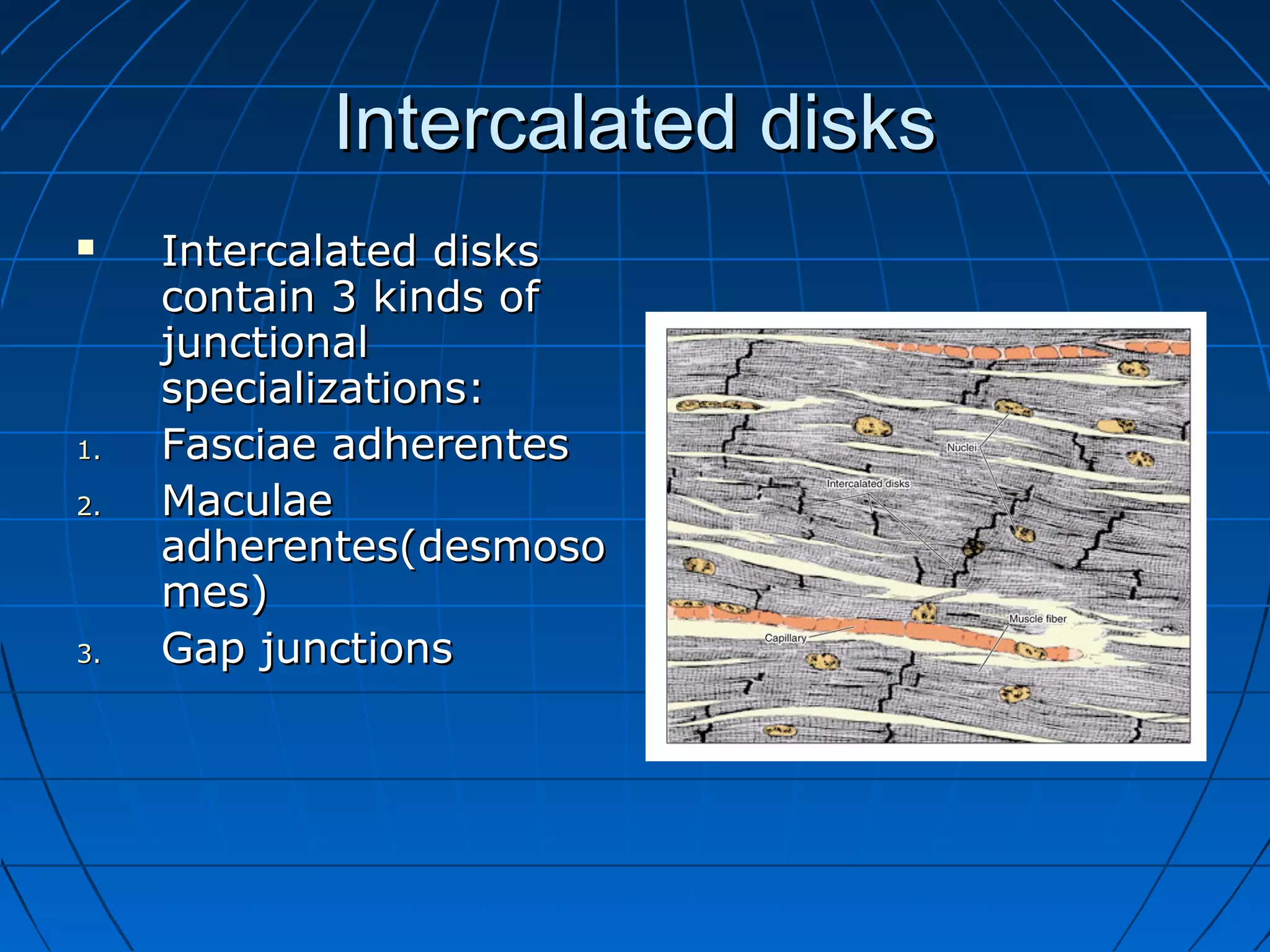
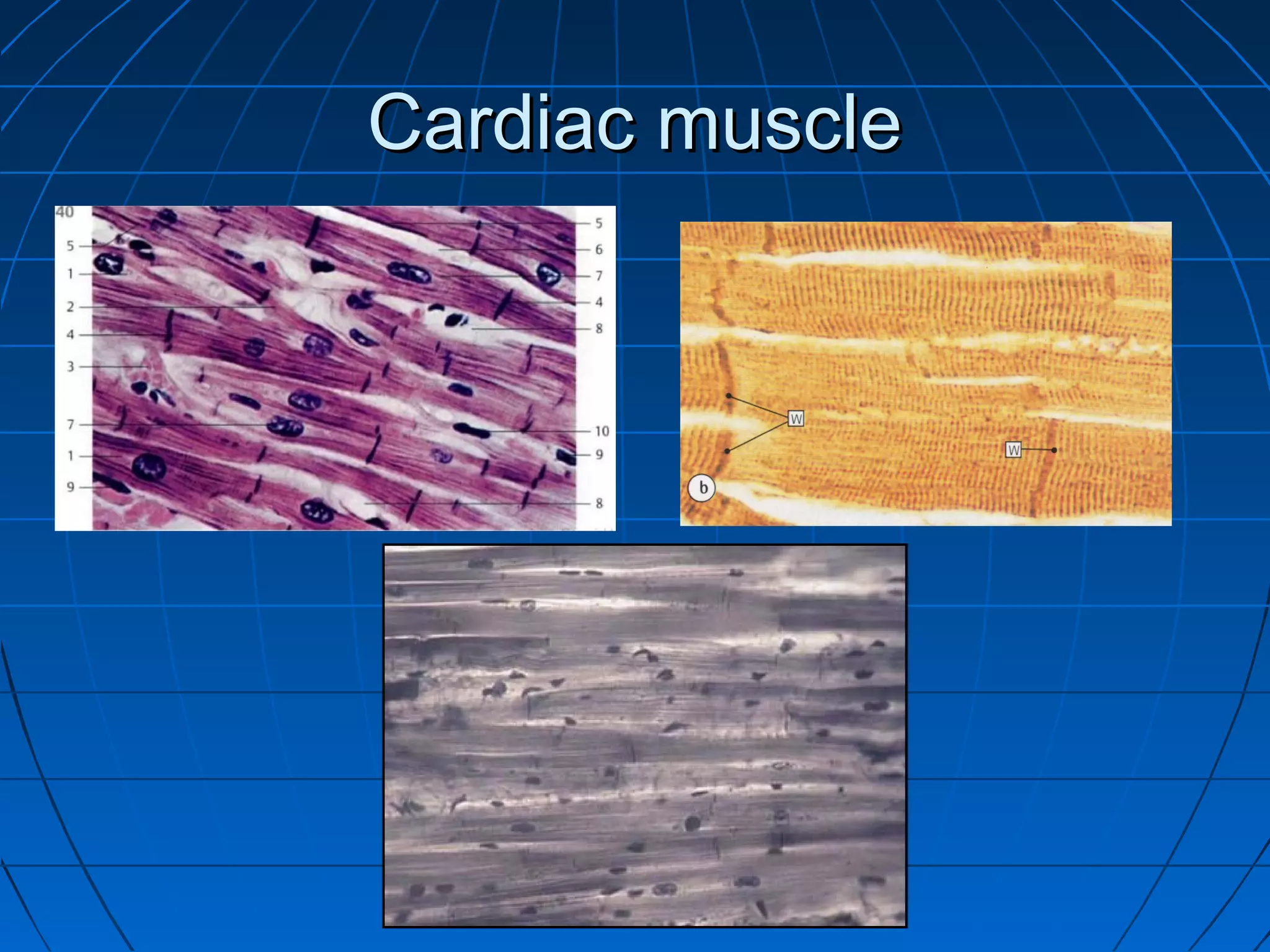
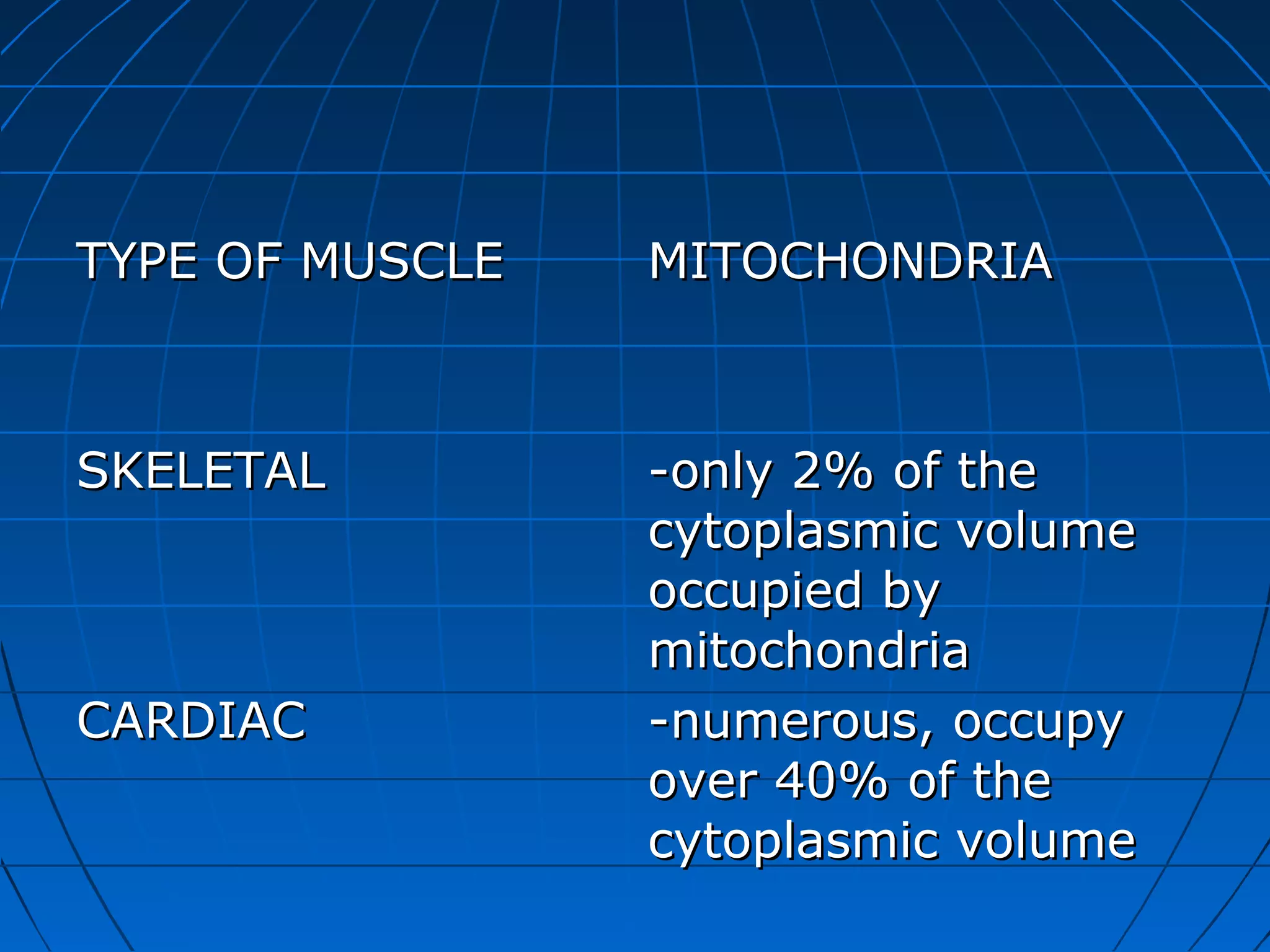
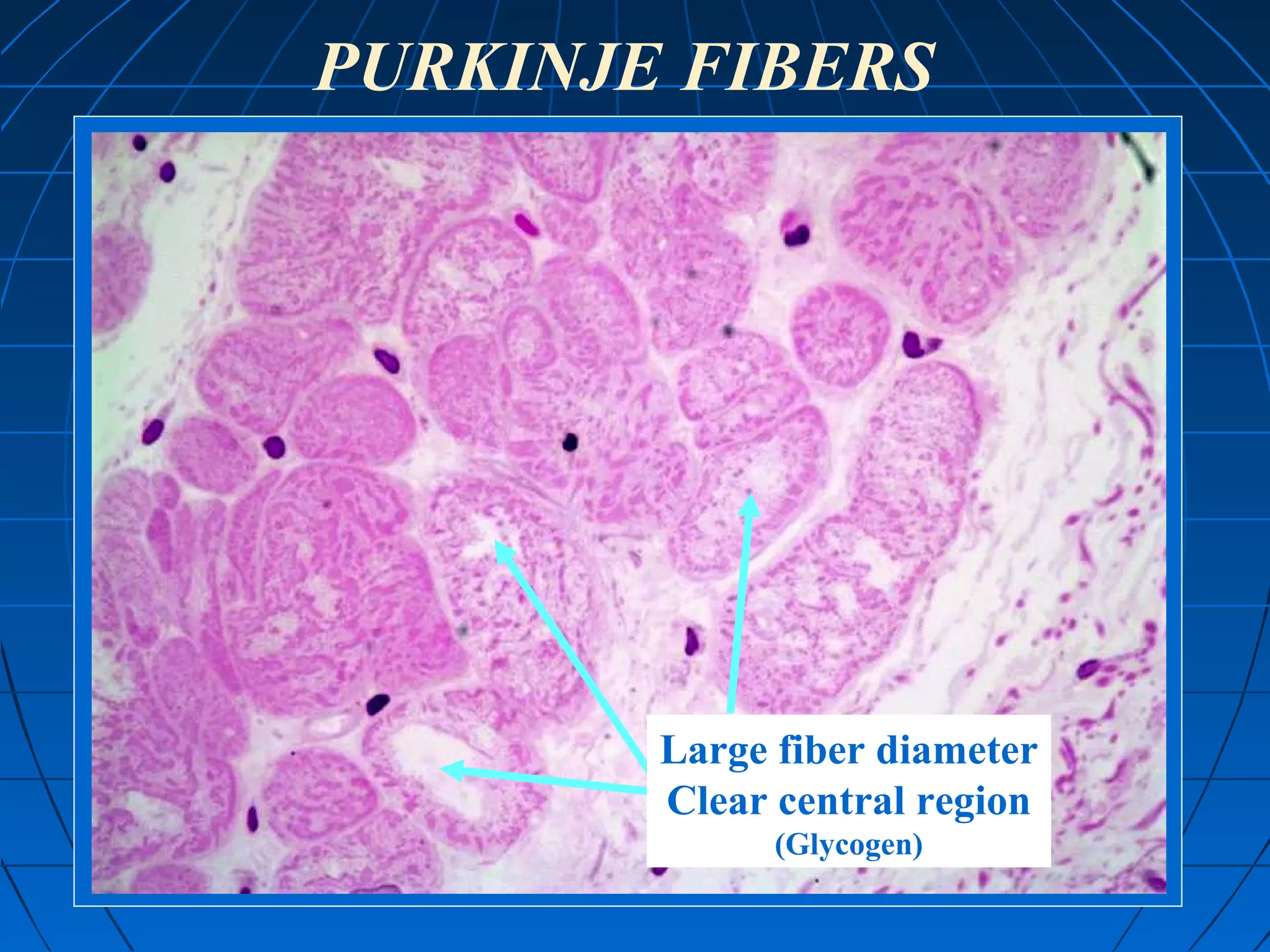
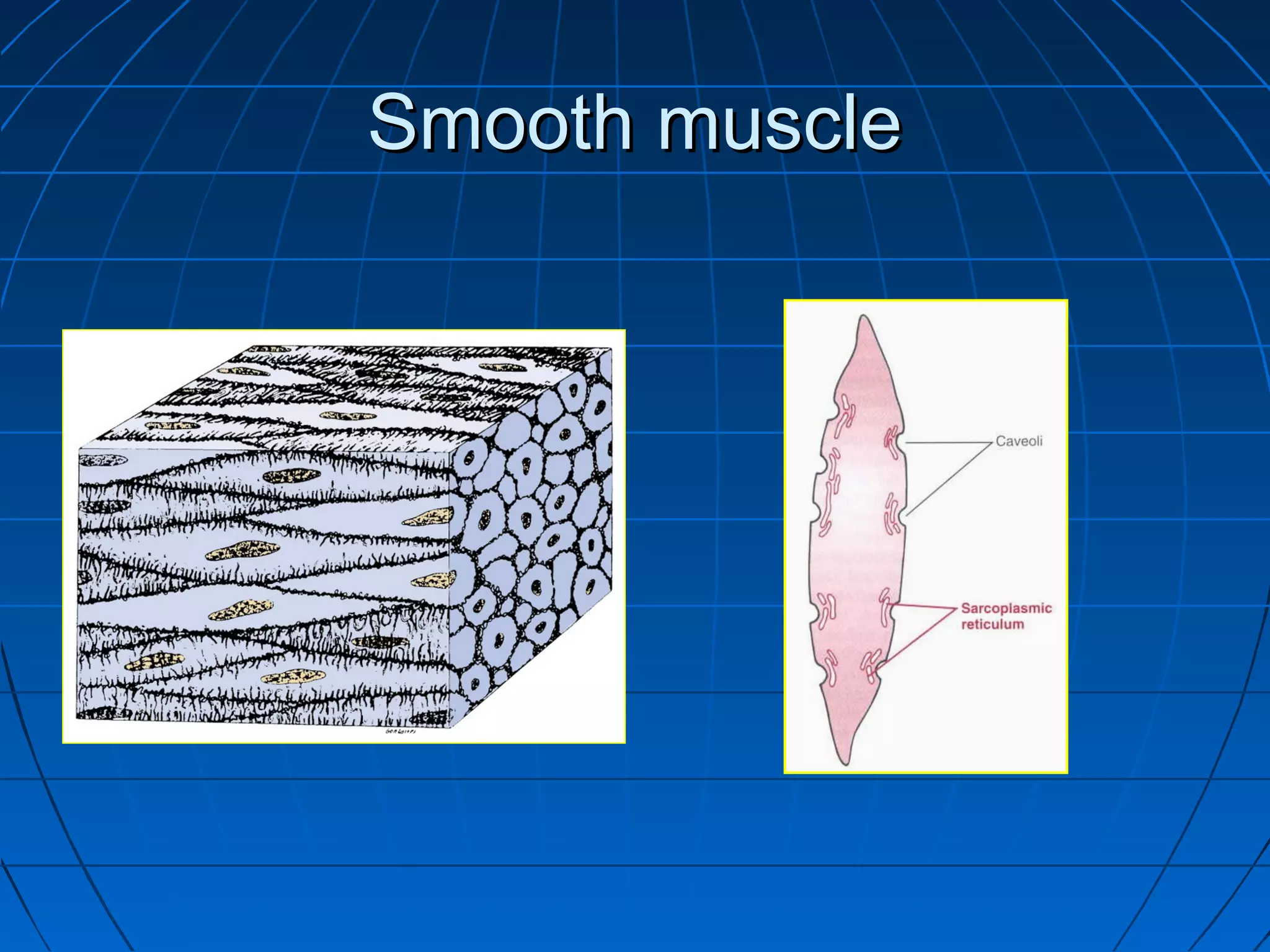
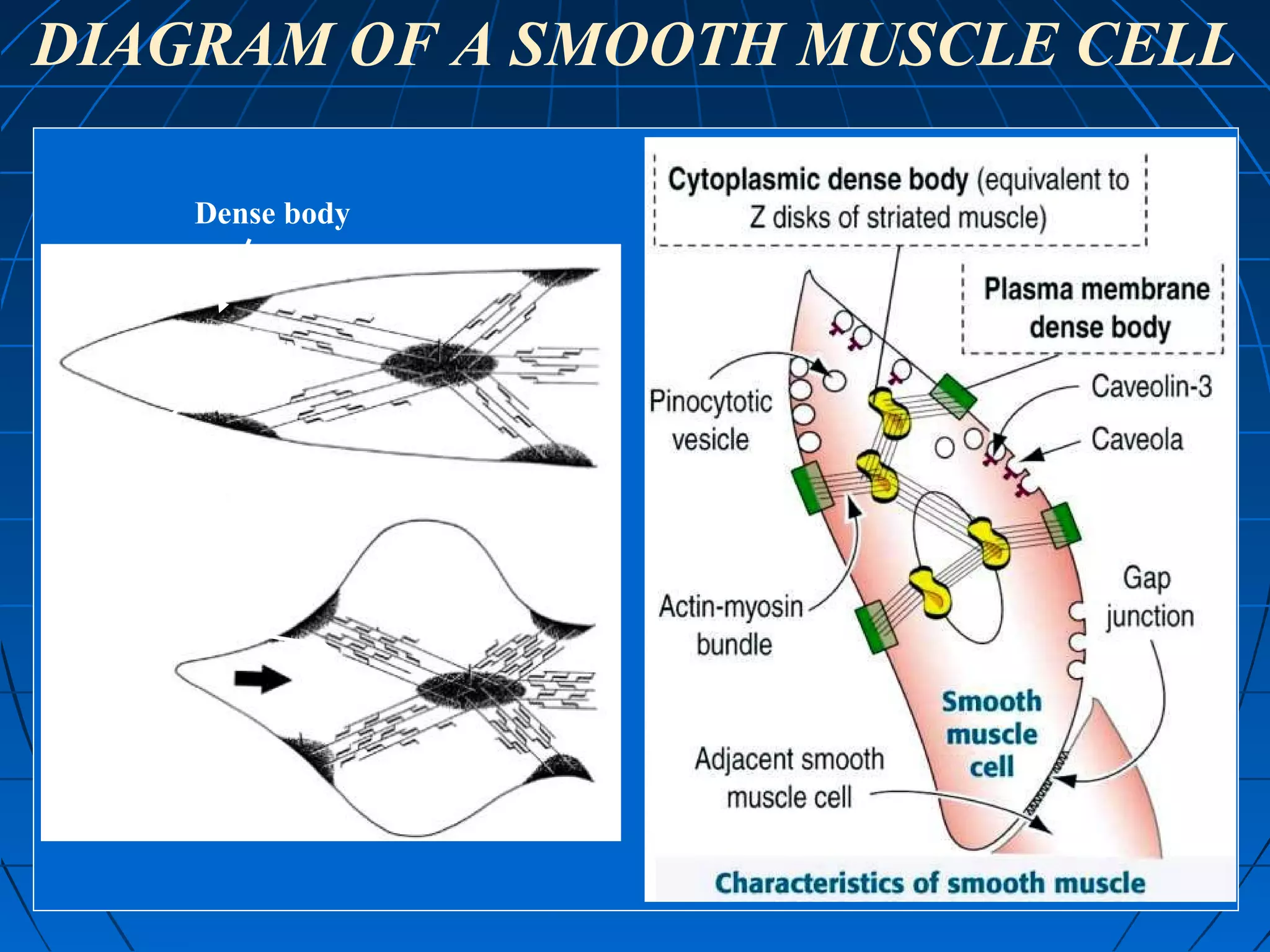
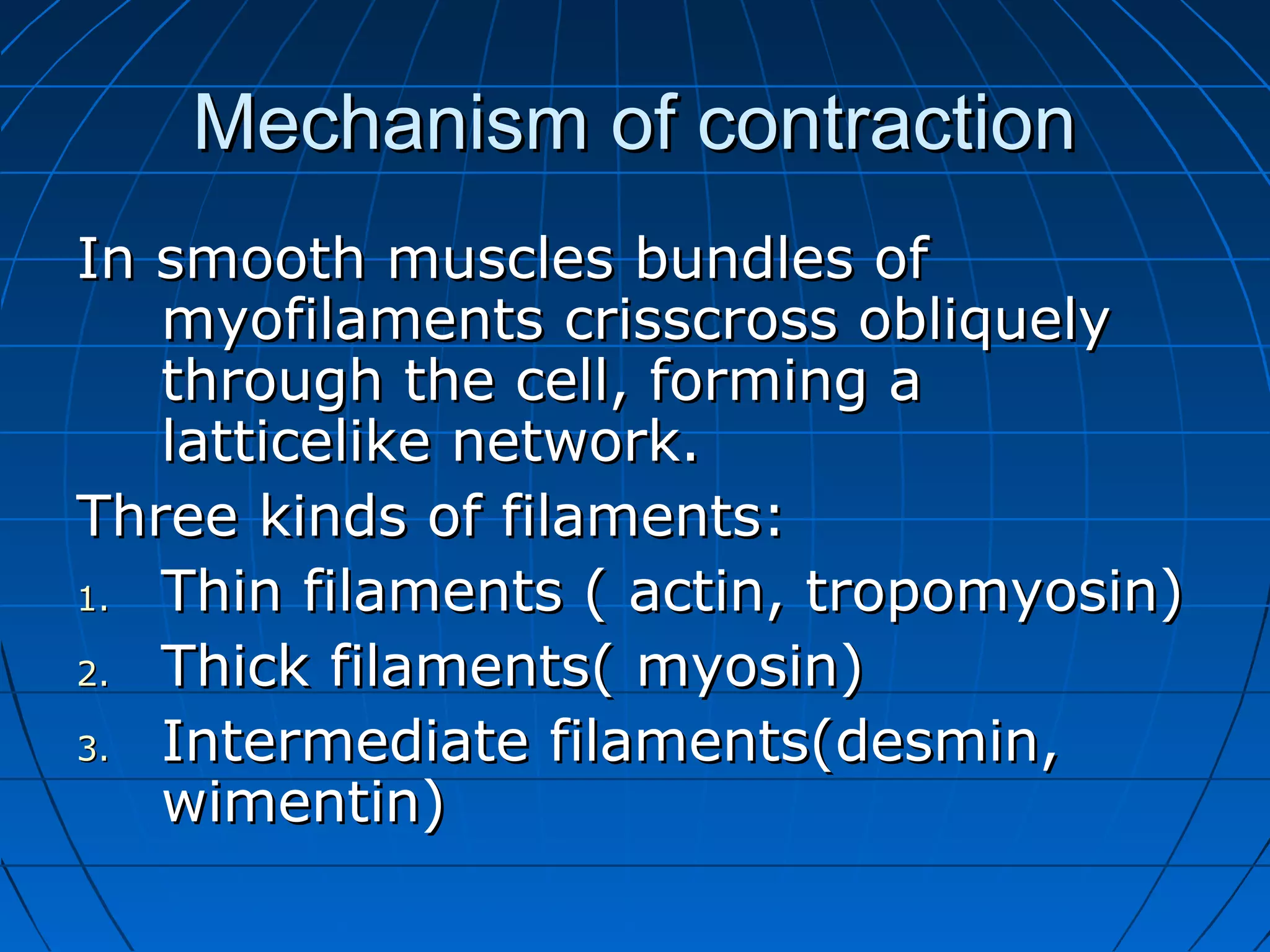
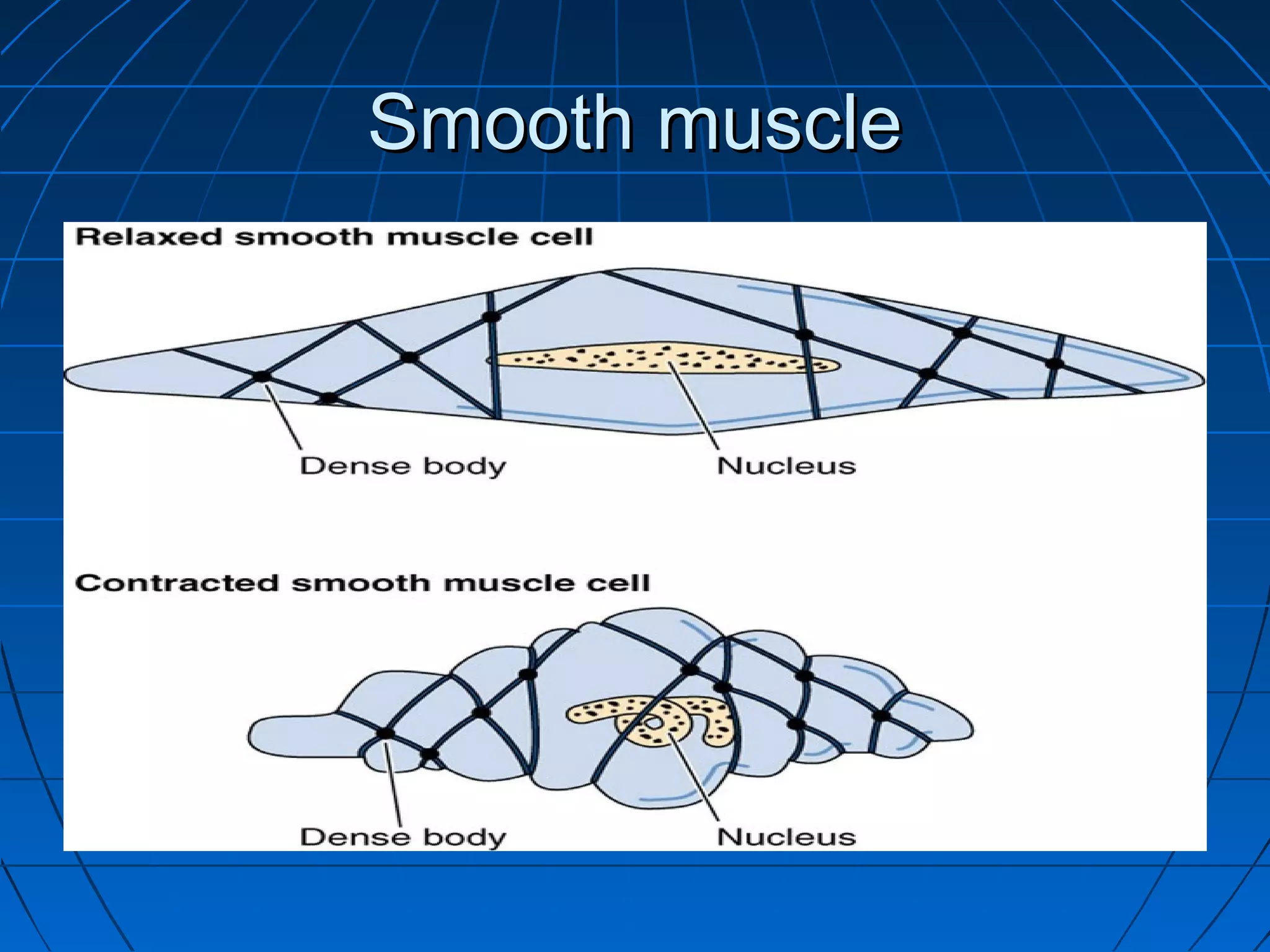
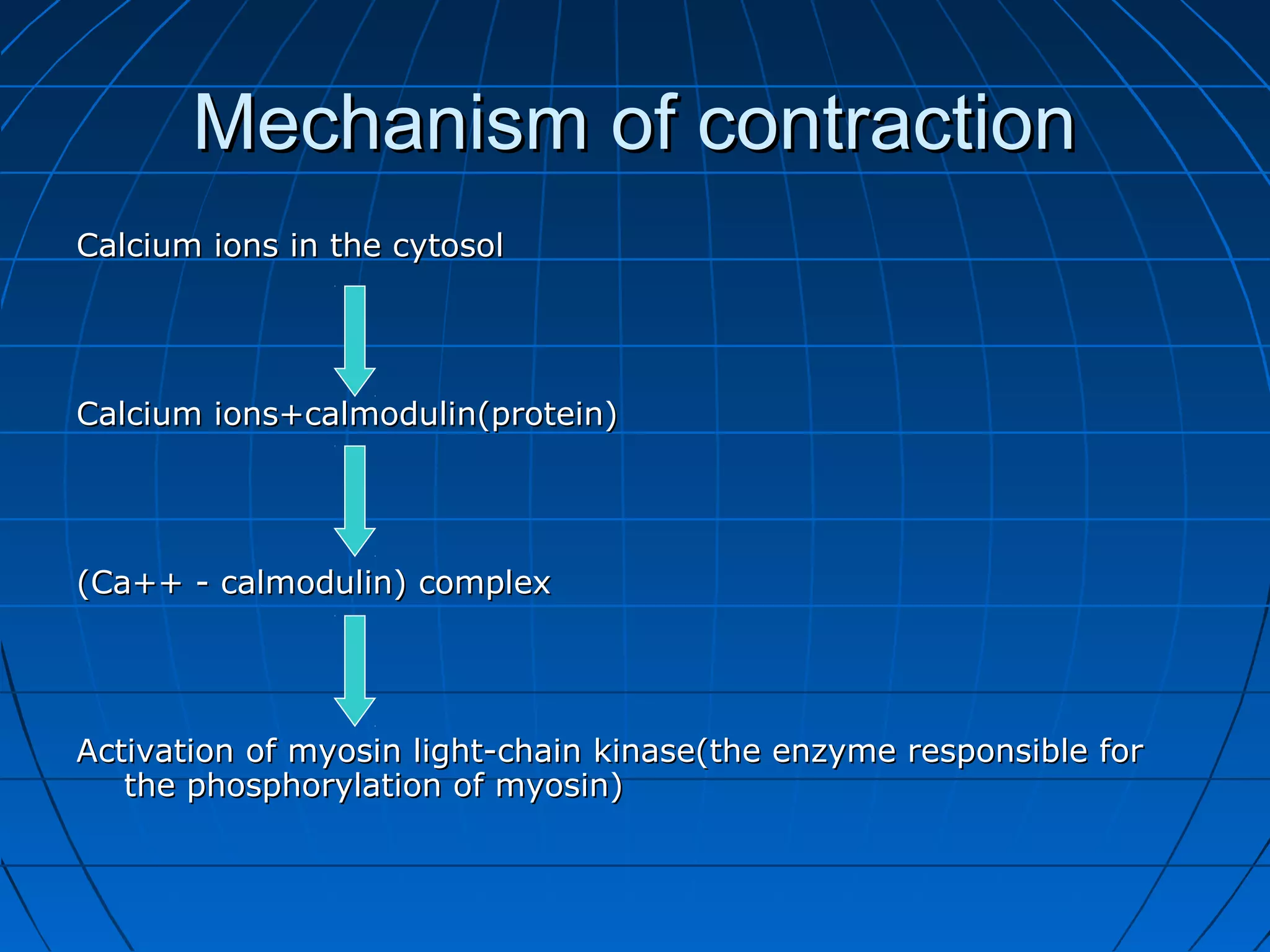
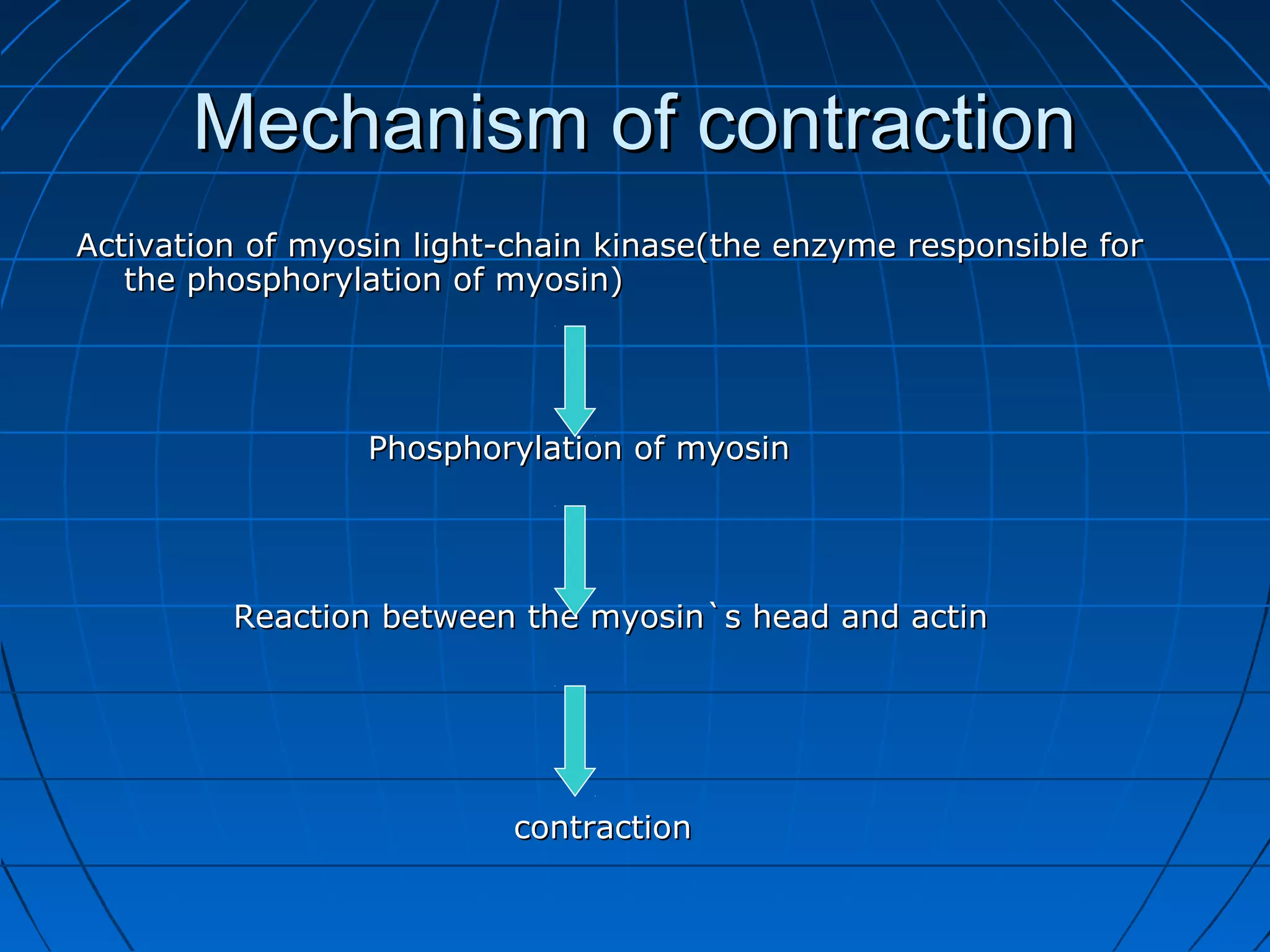
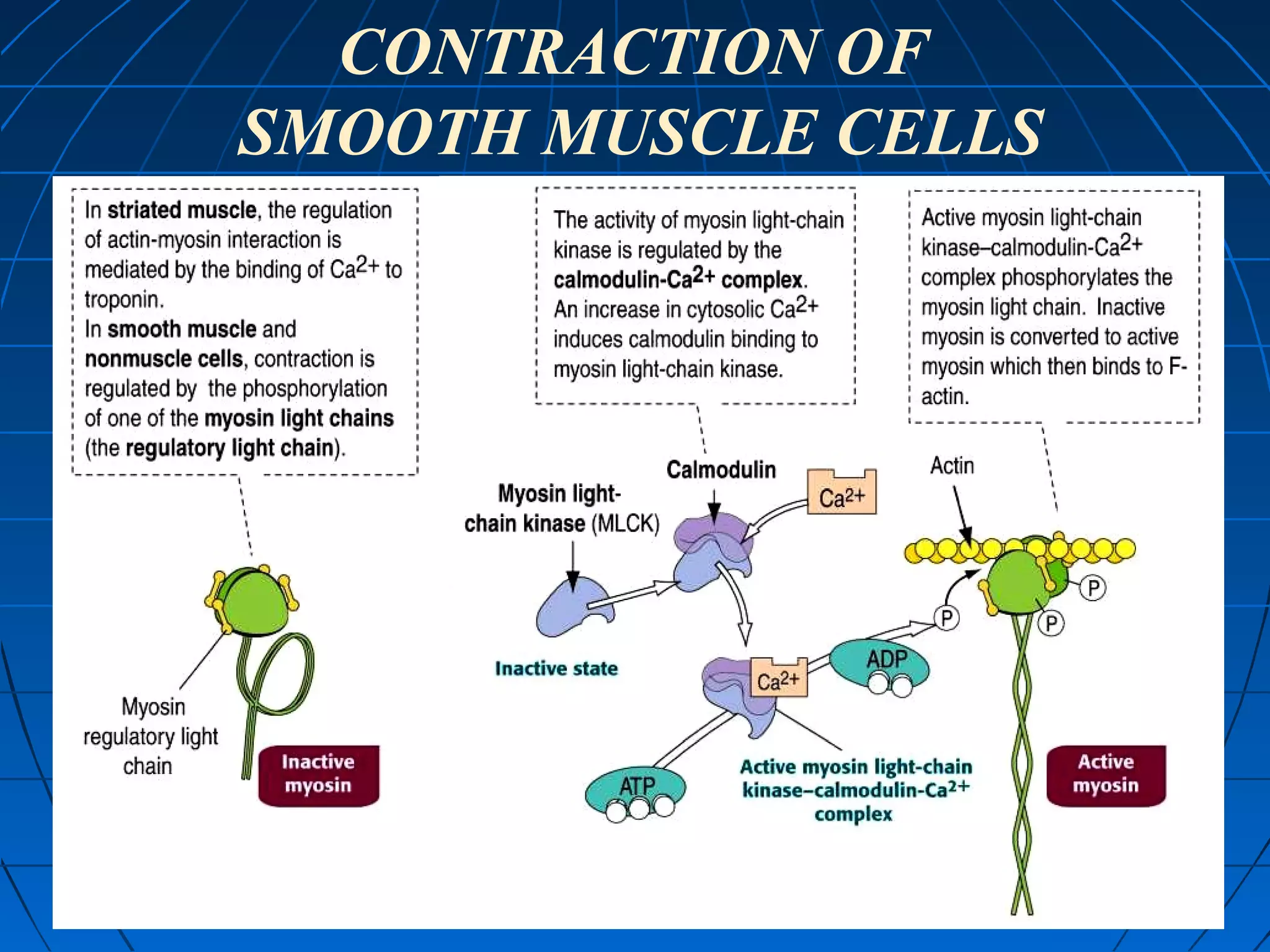
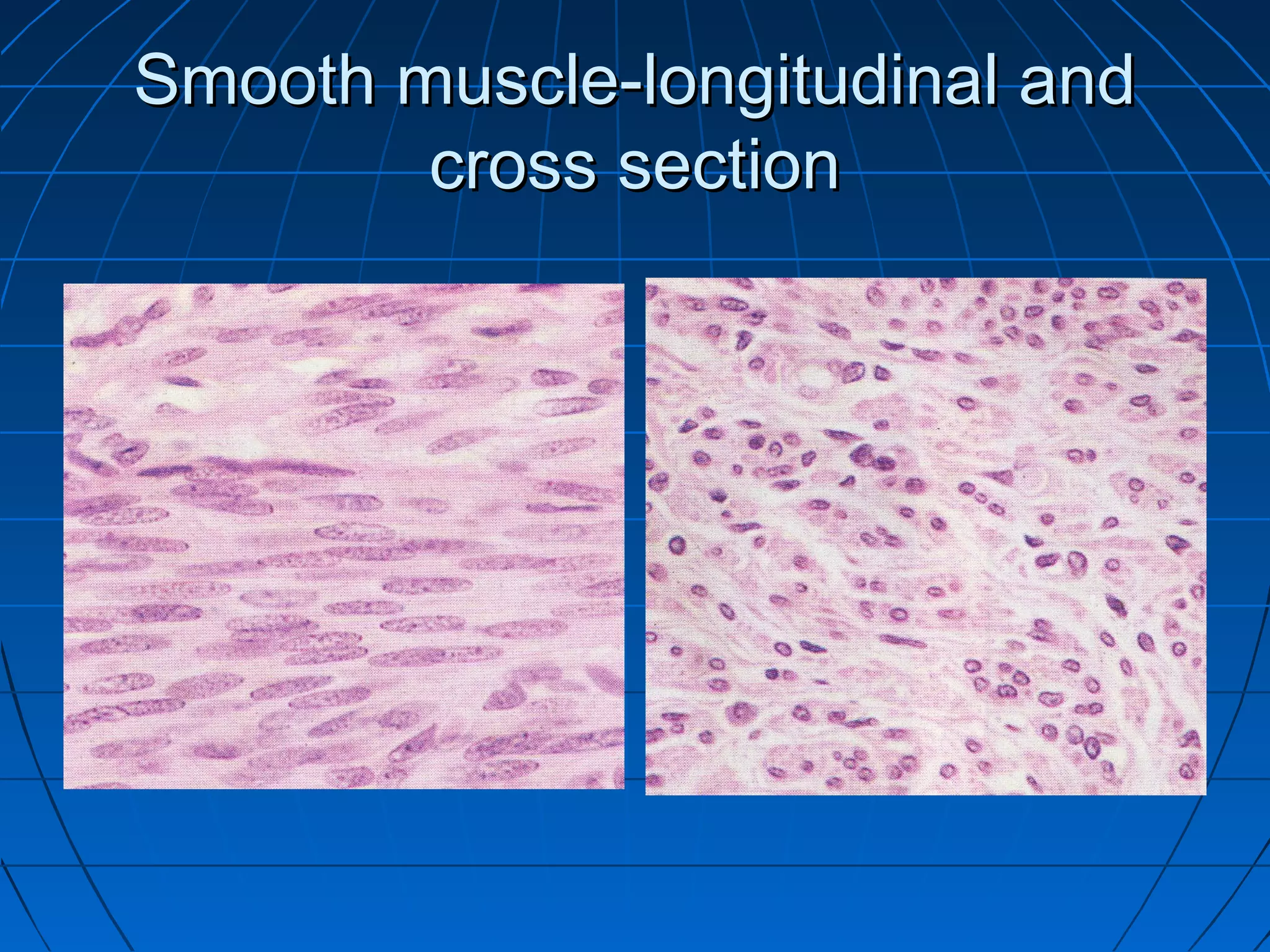
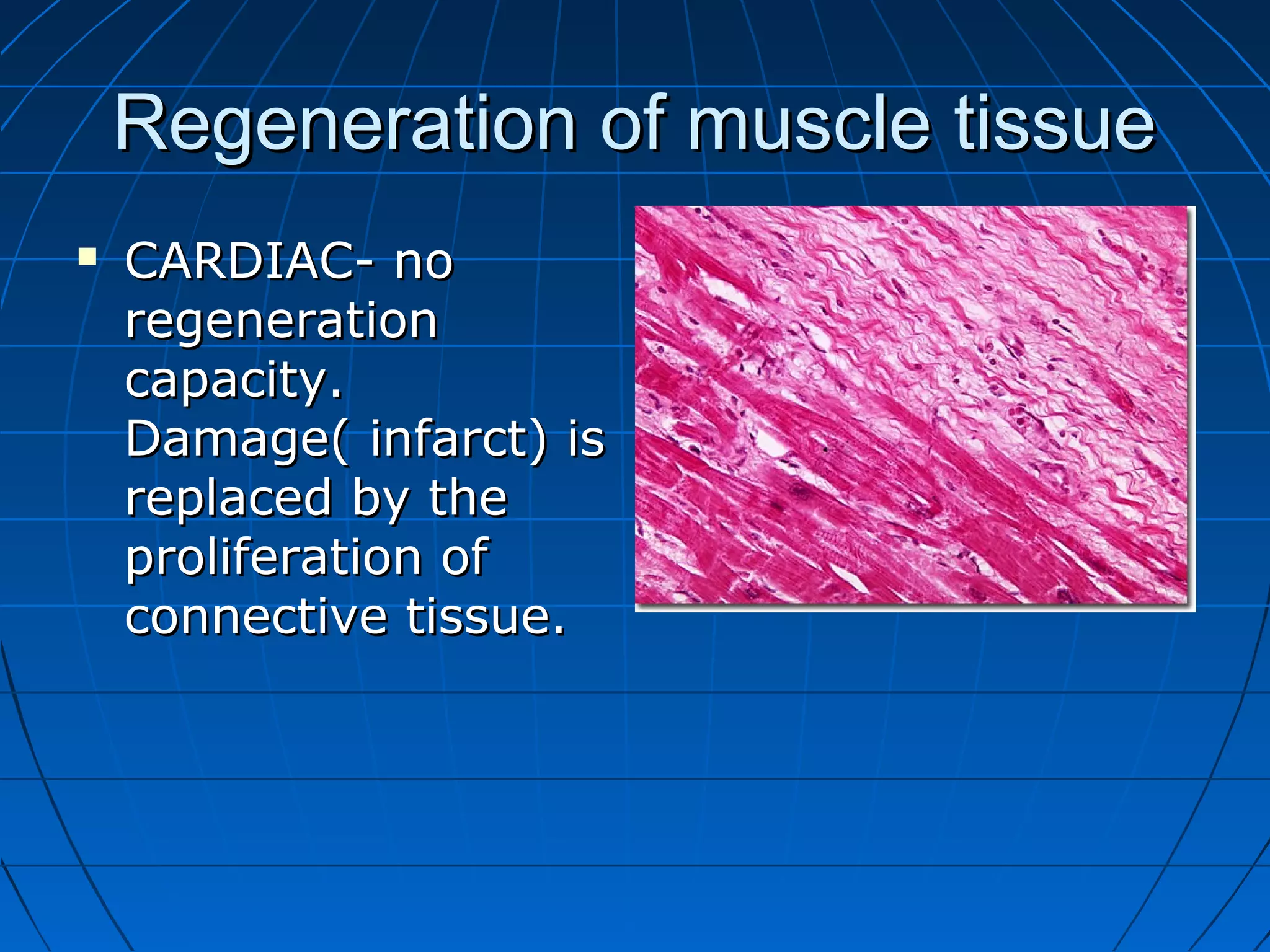
There are three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle consists of cylindrical muscle fibers that contain multiple nuclei. The fibers contain filaments called myofibrils which are made up of thick and thin filaments that give the striated appearance to skeletal muscle. Contraction occurs via the sliding filament model where the overlapping thick and thin filaments slide past each other, shortening the muscle. Calcium released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to troponin, exposing actin binding sites for myosin cross-bridging and contraction.