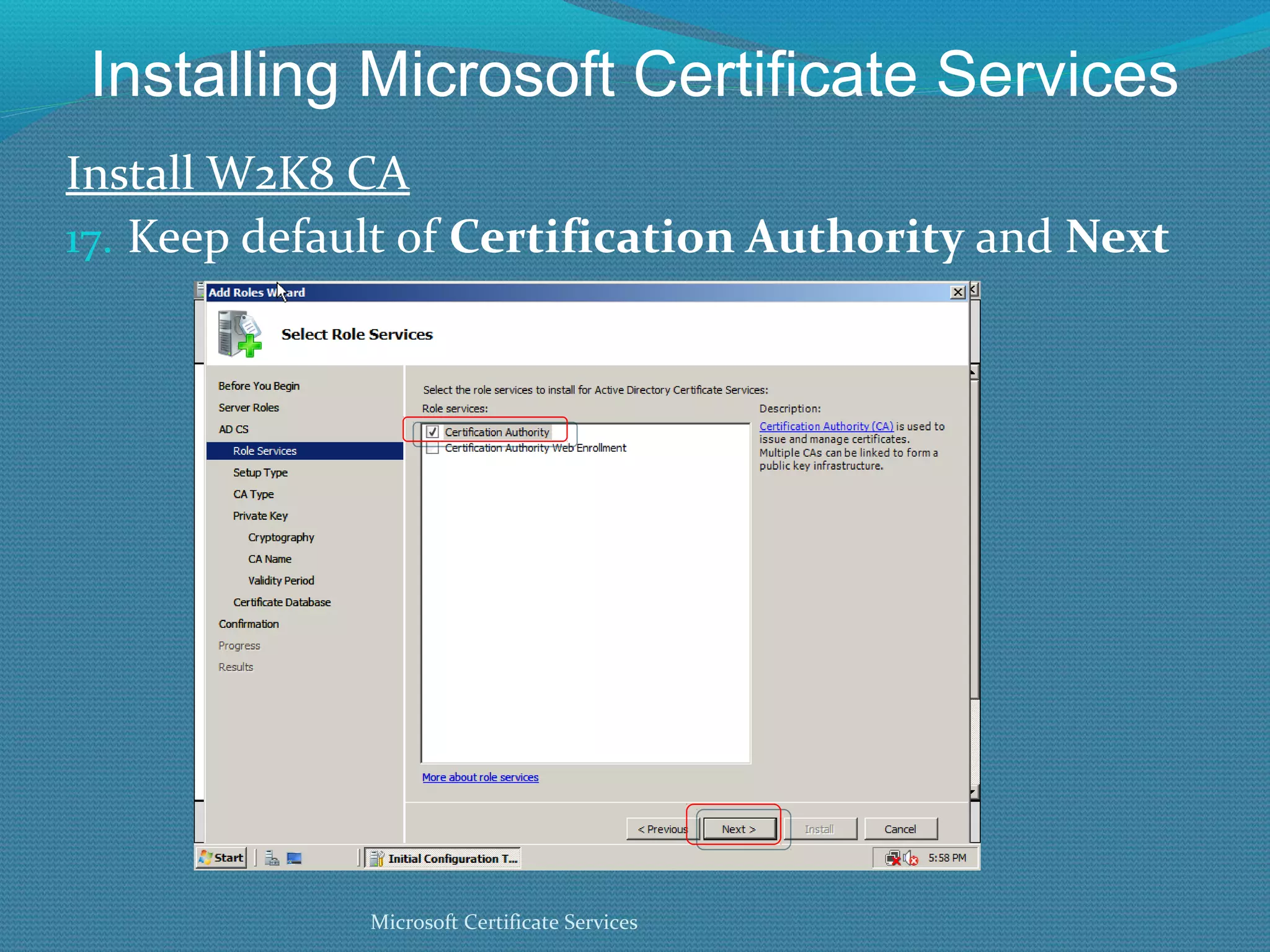
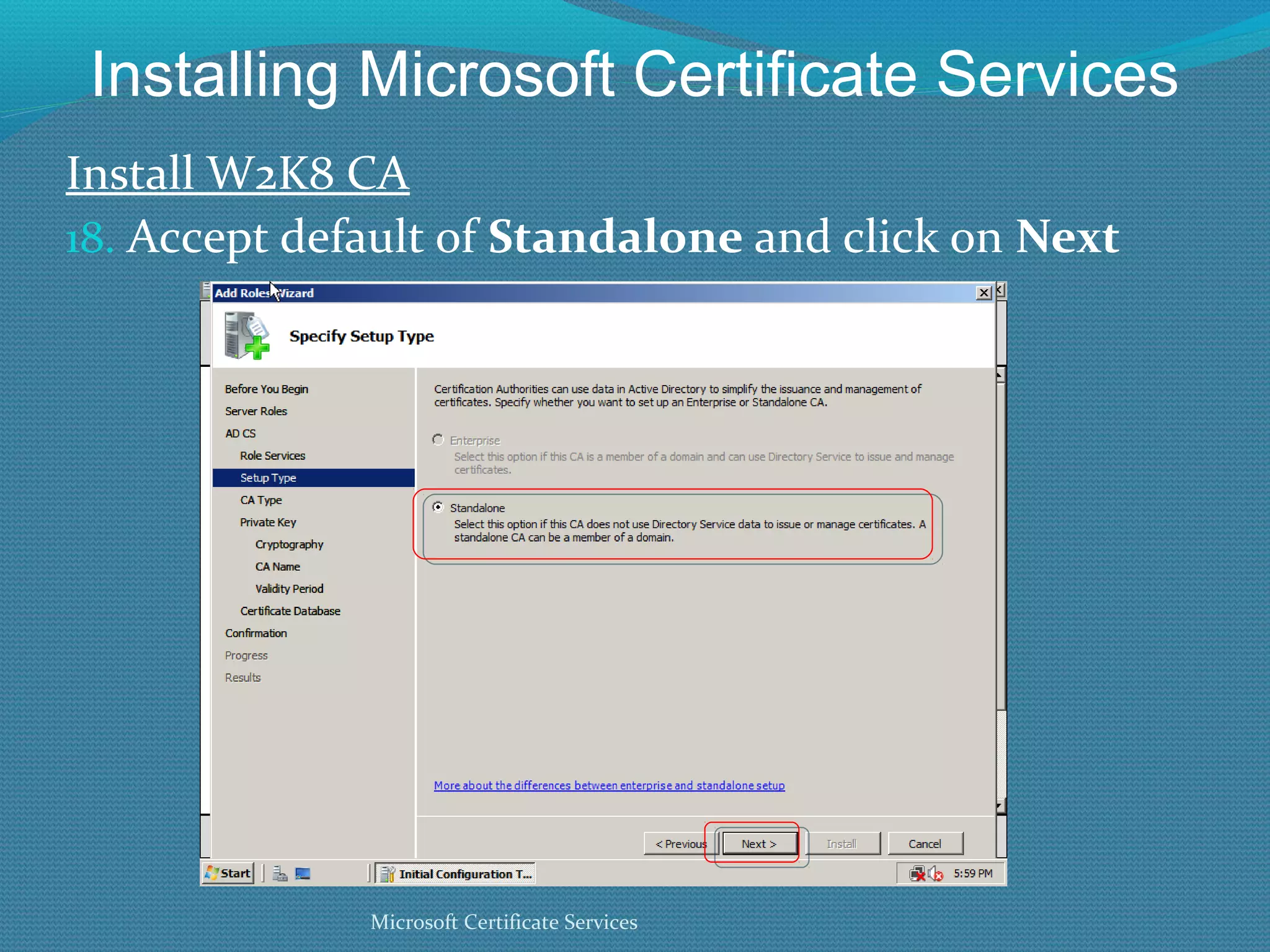
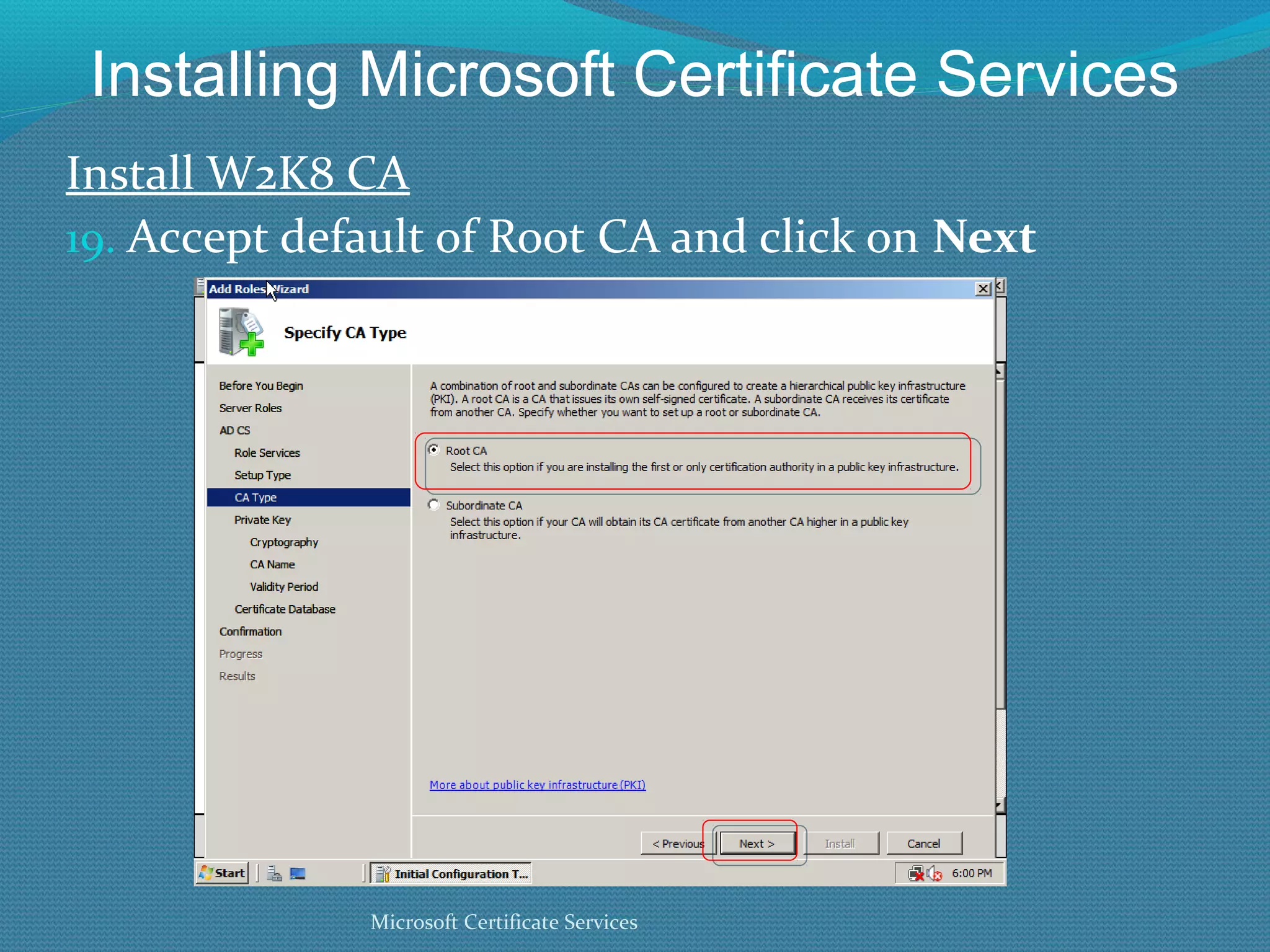
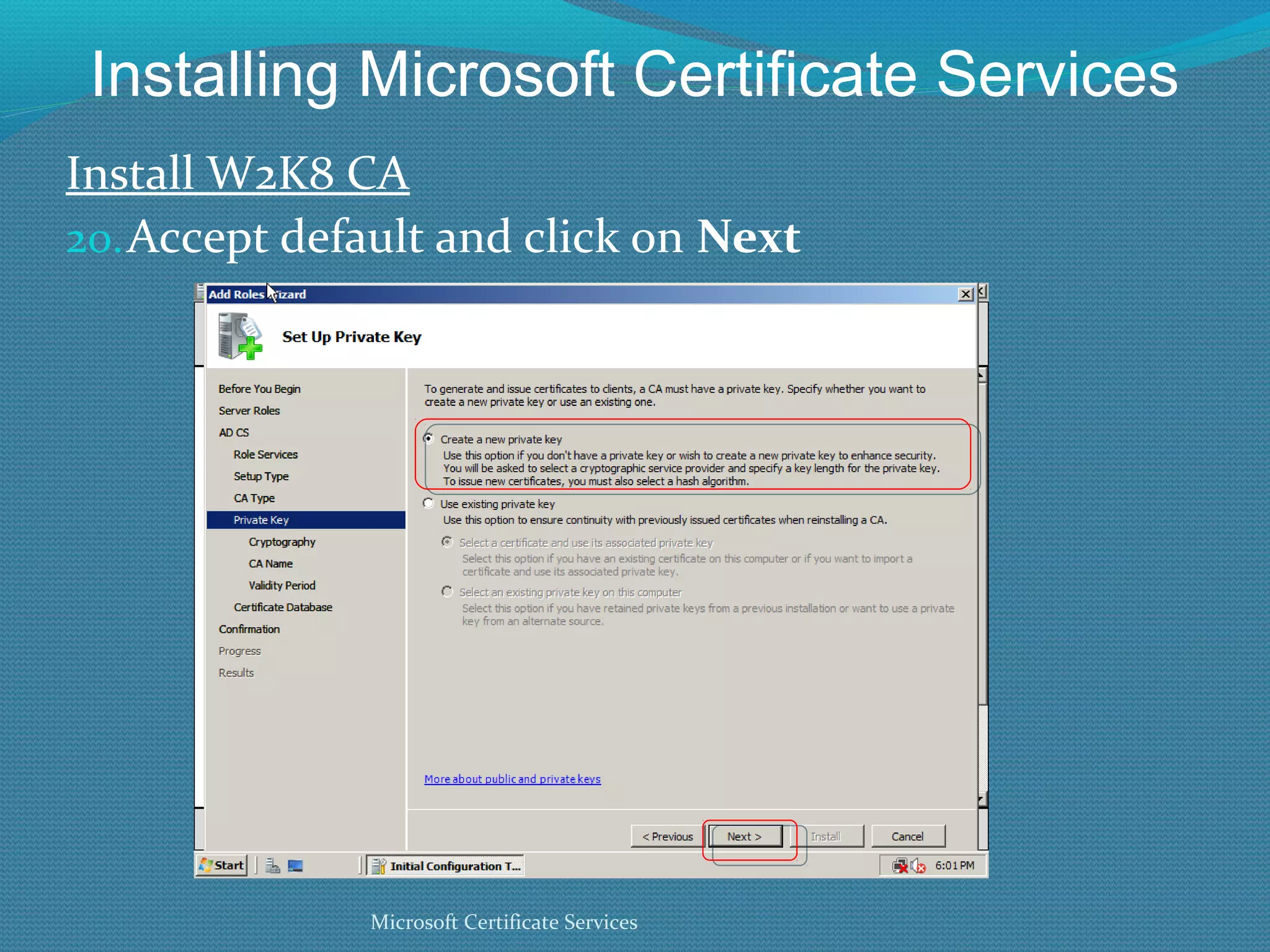
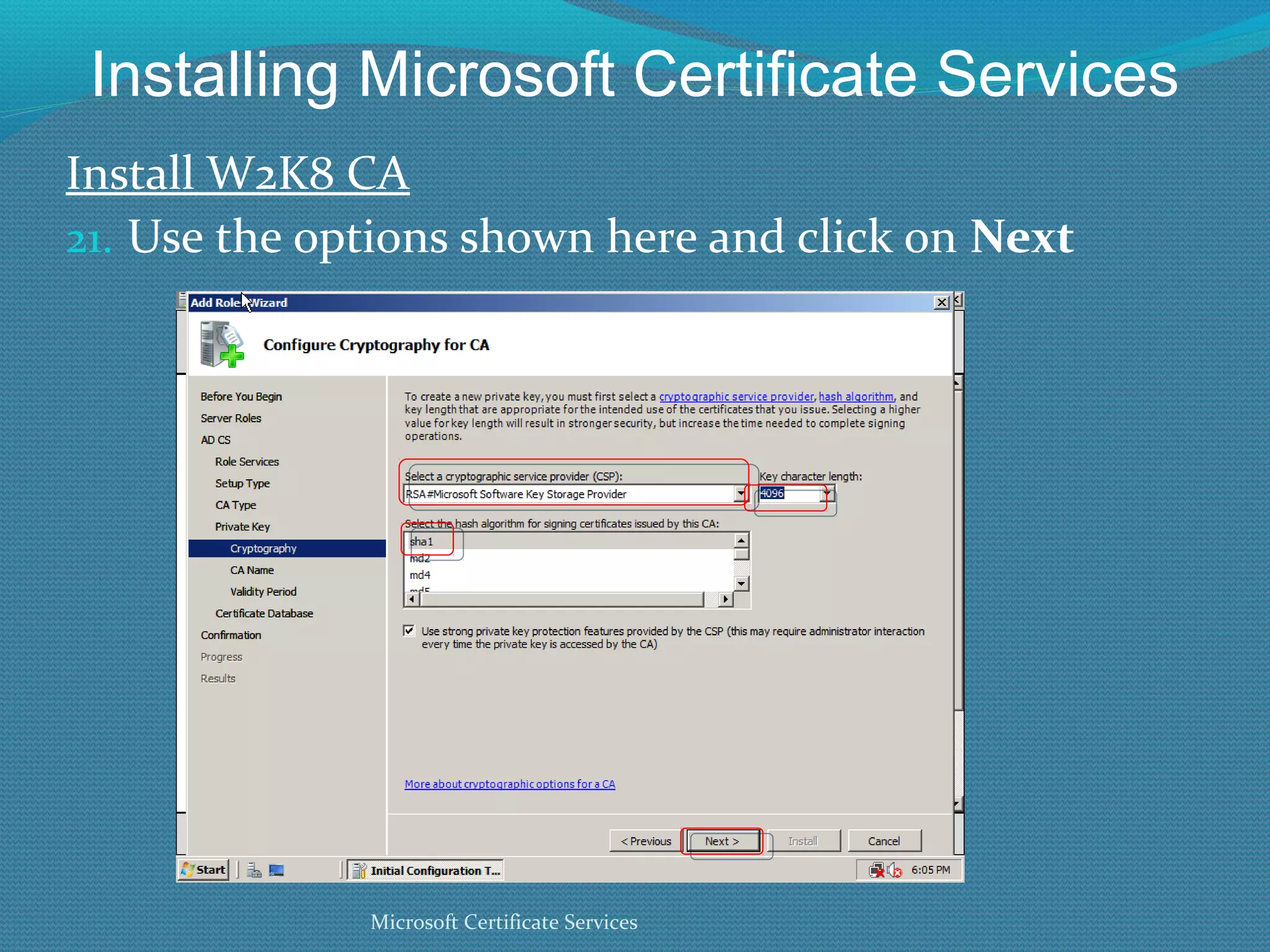
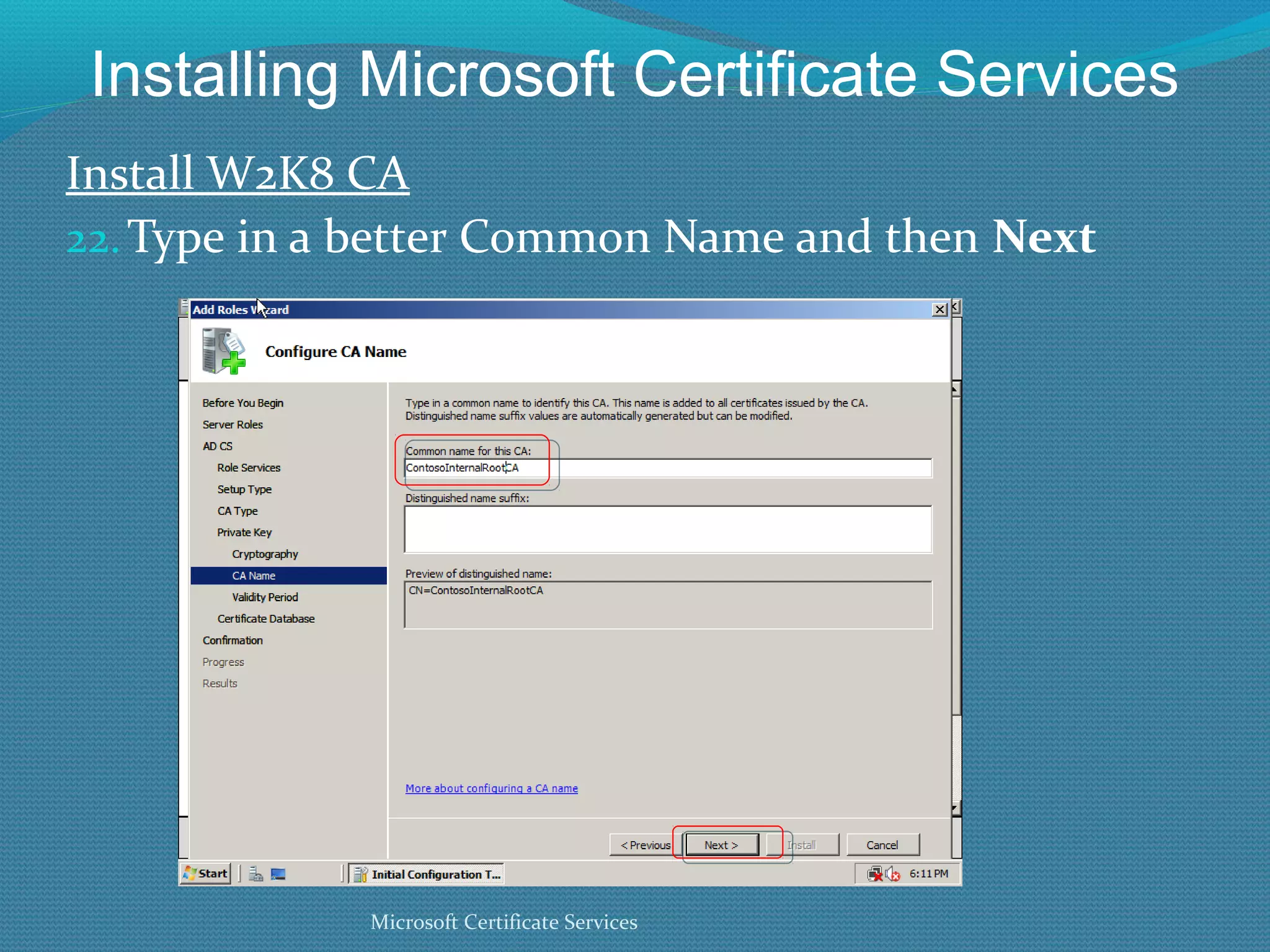
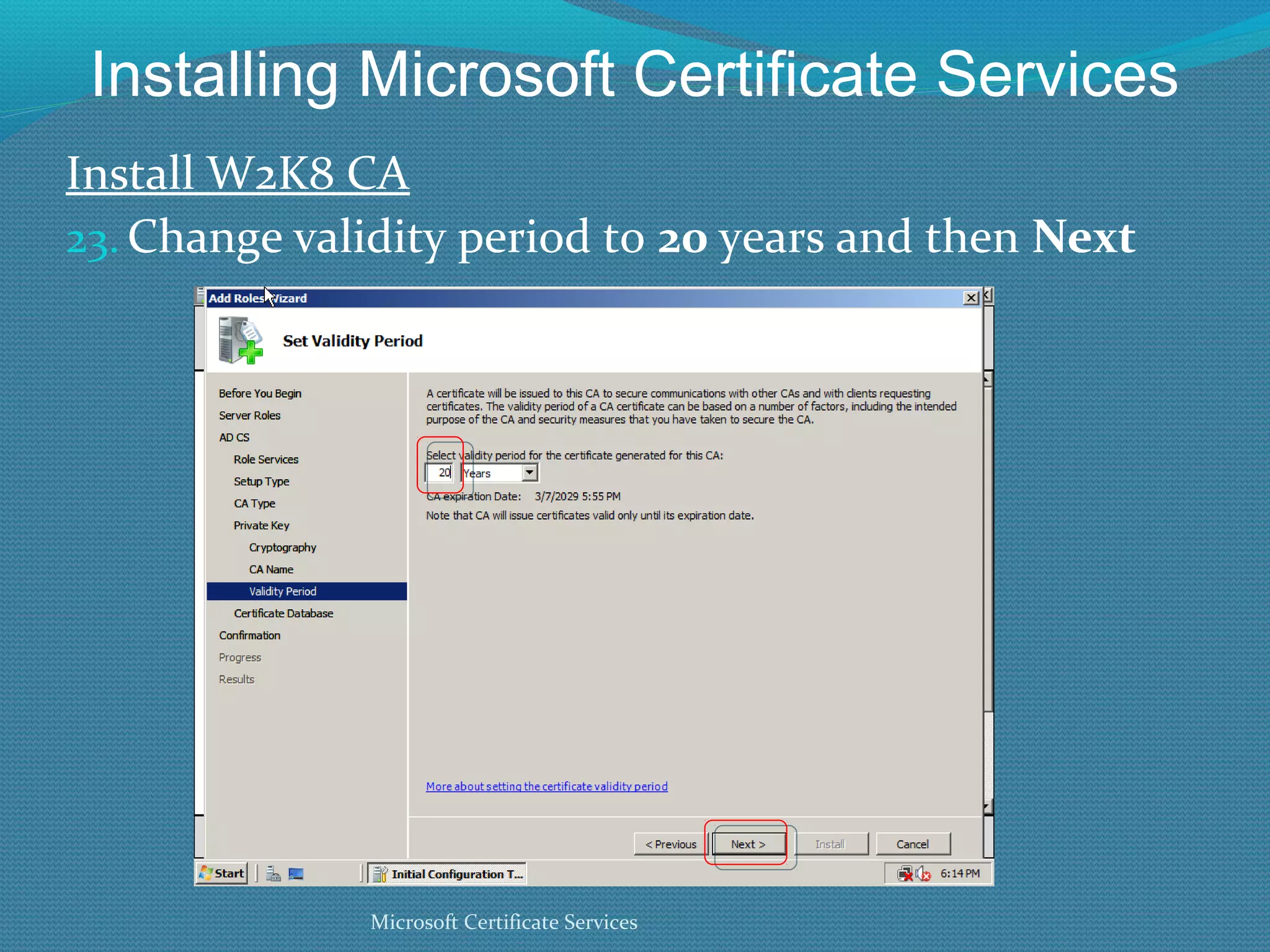
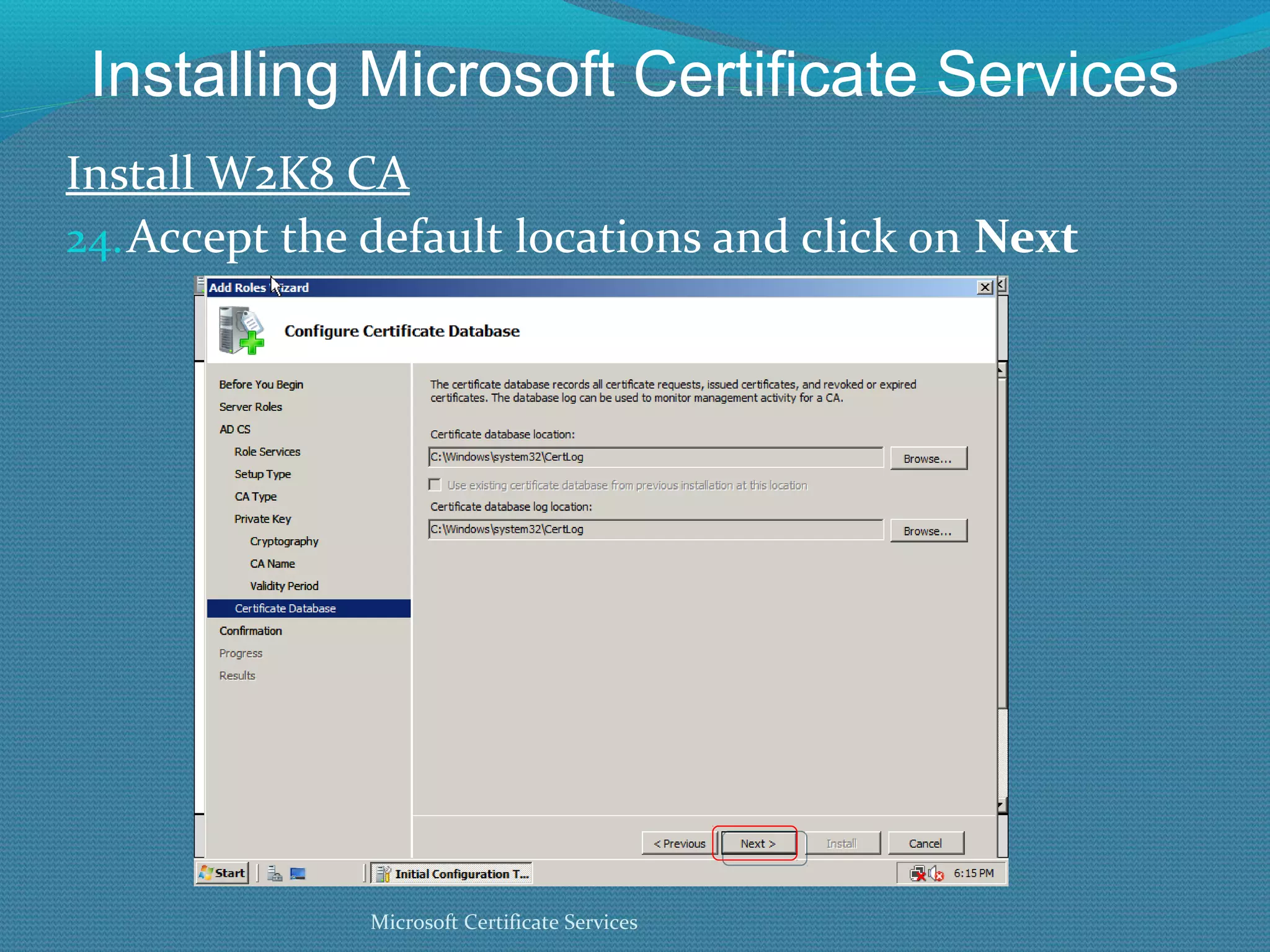
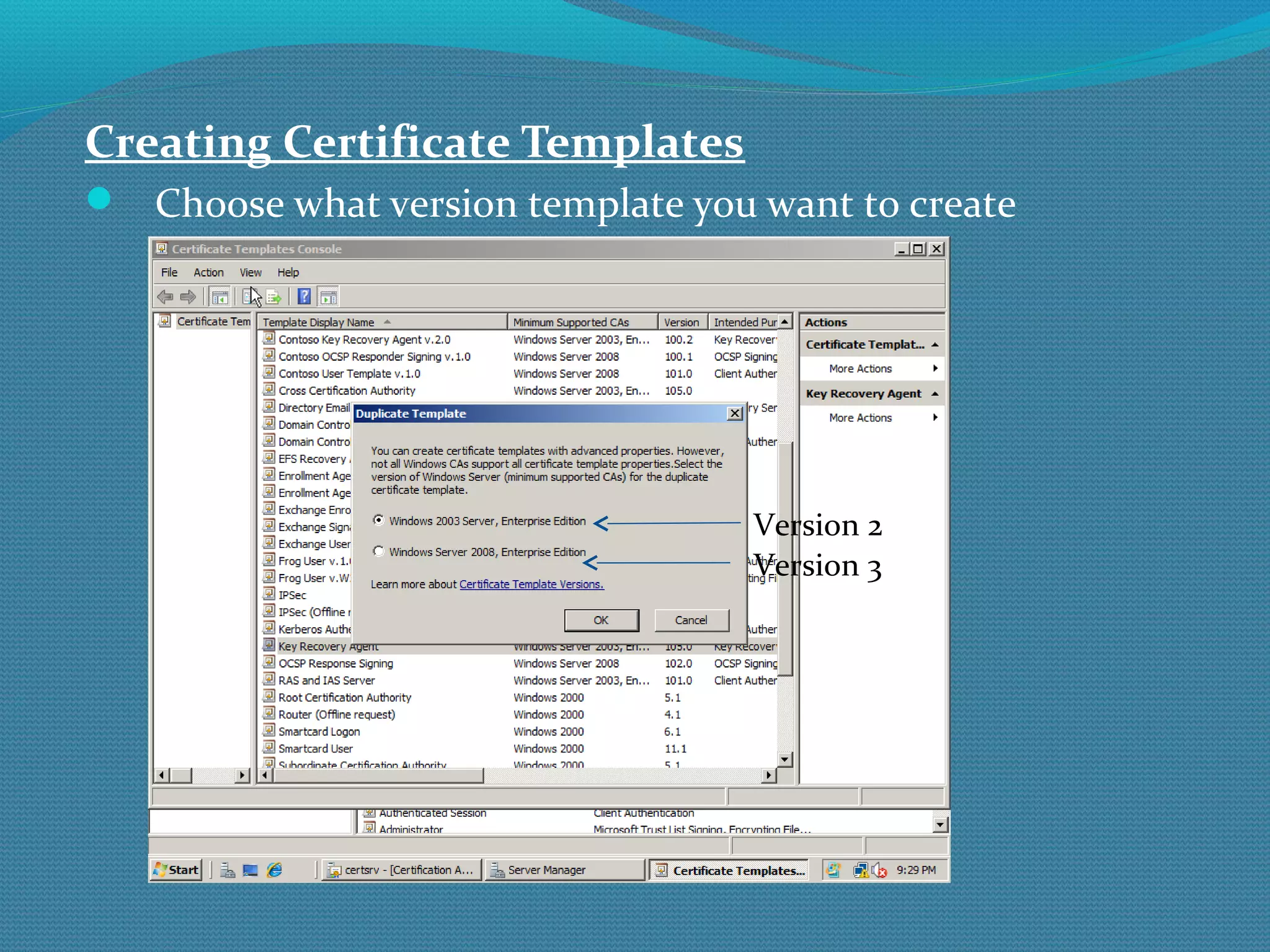
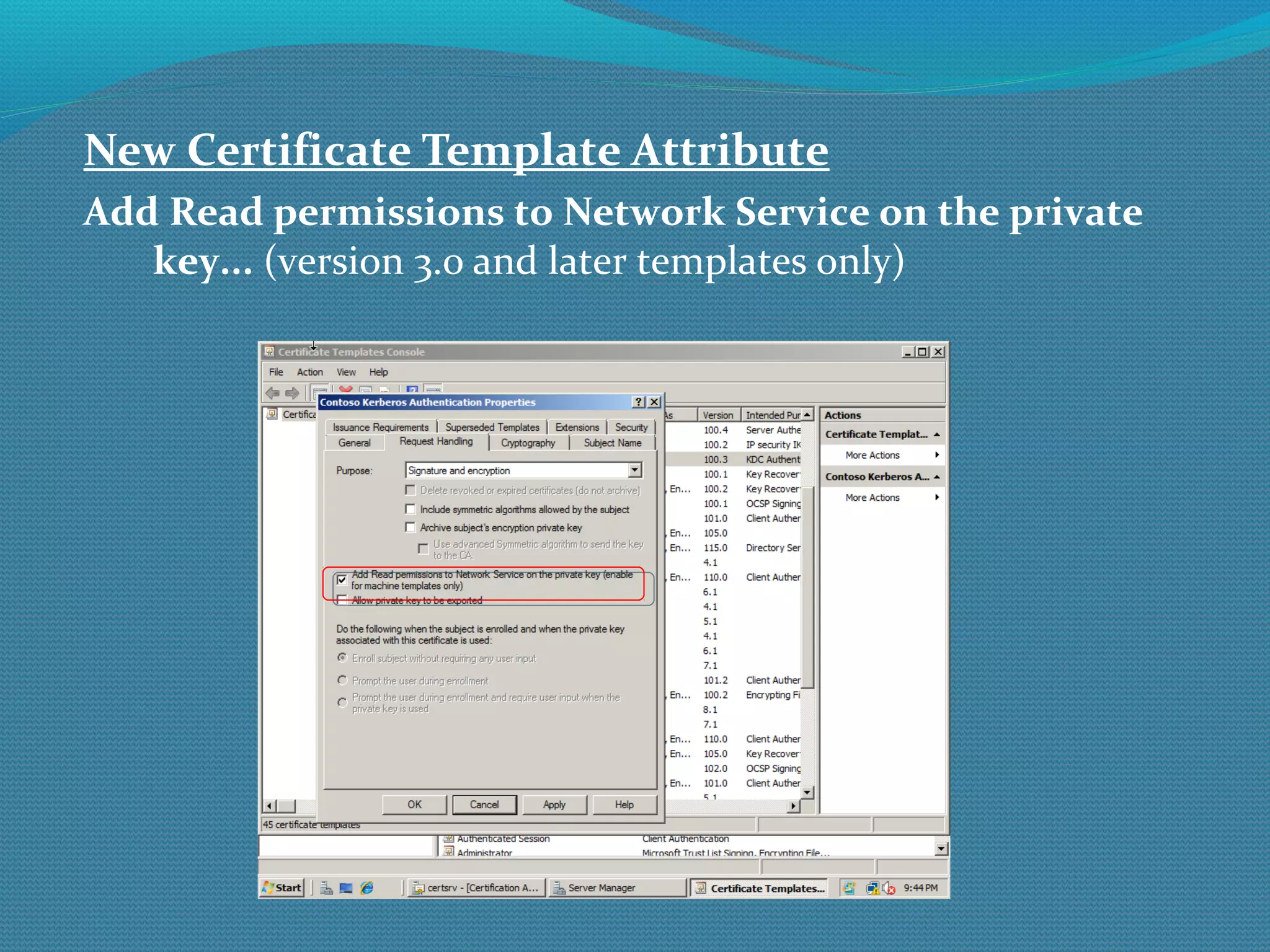
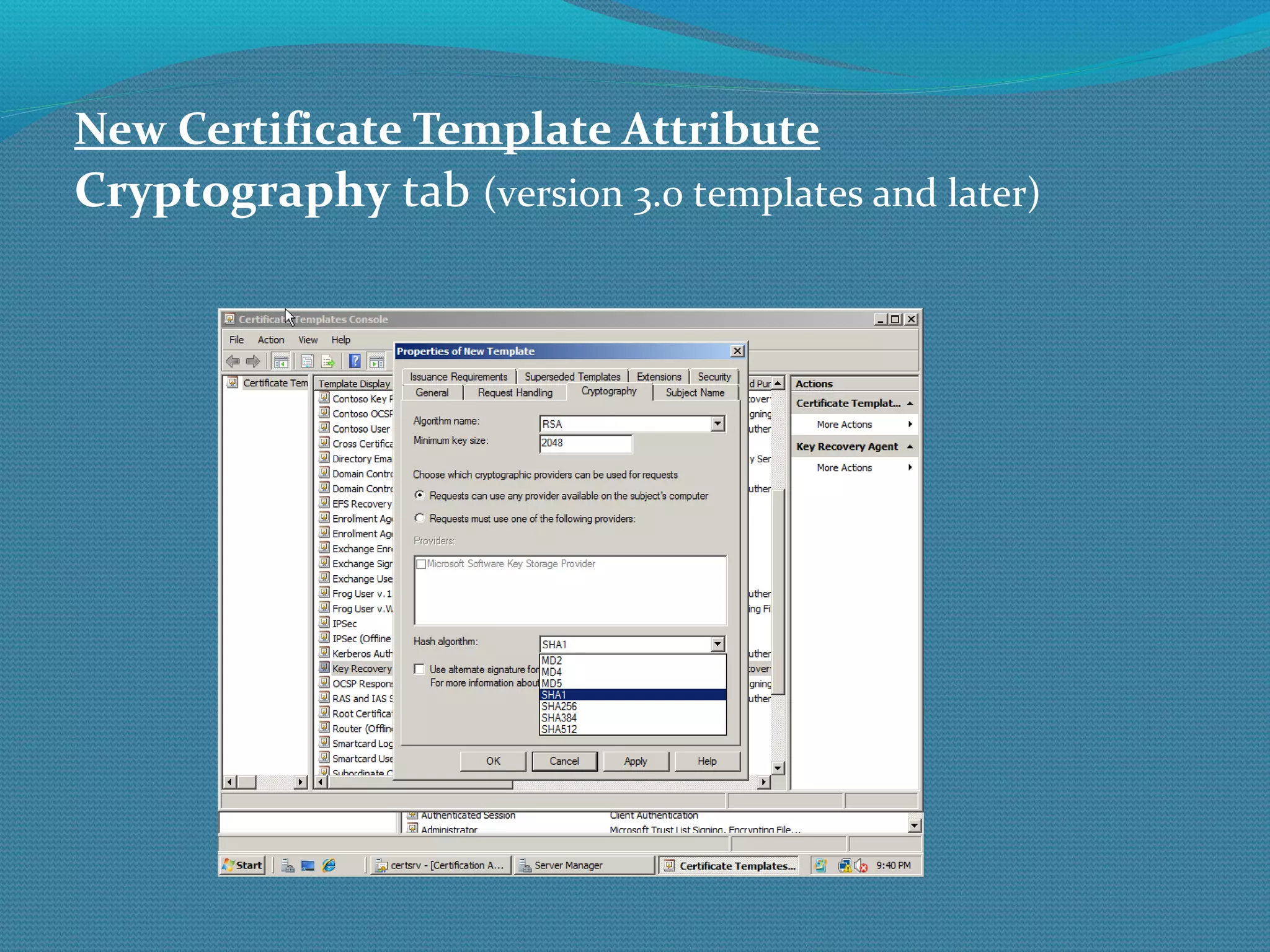
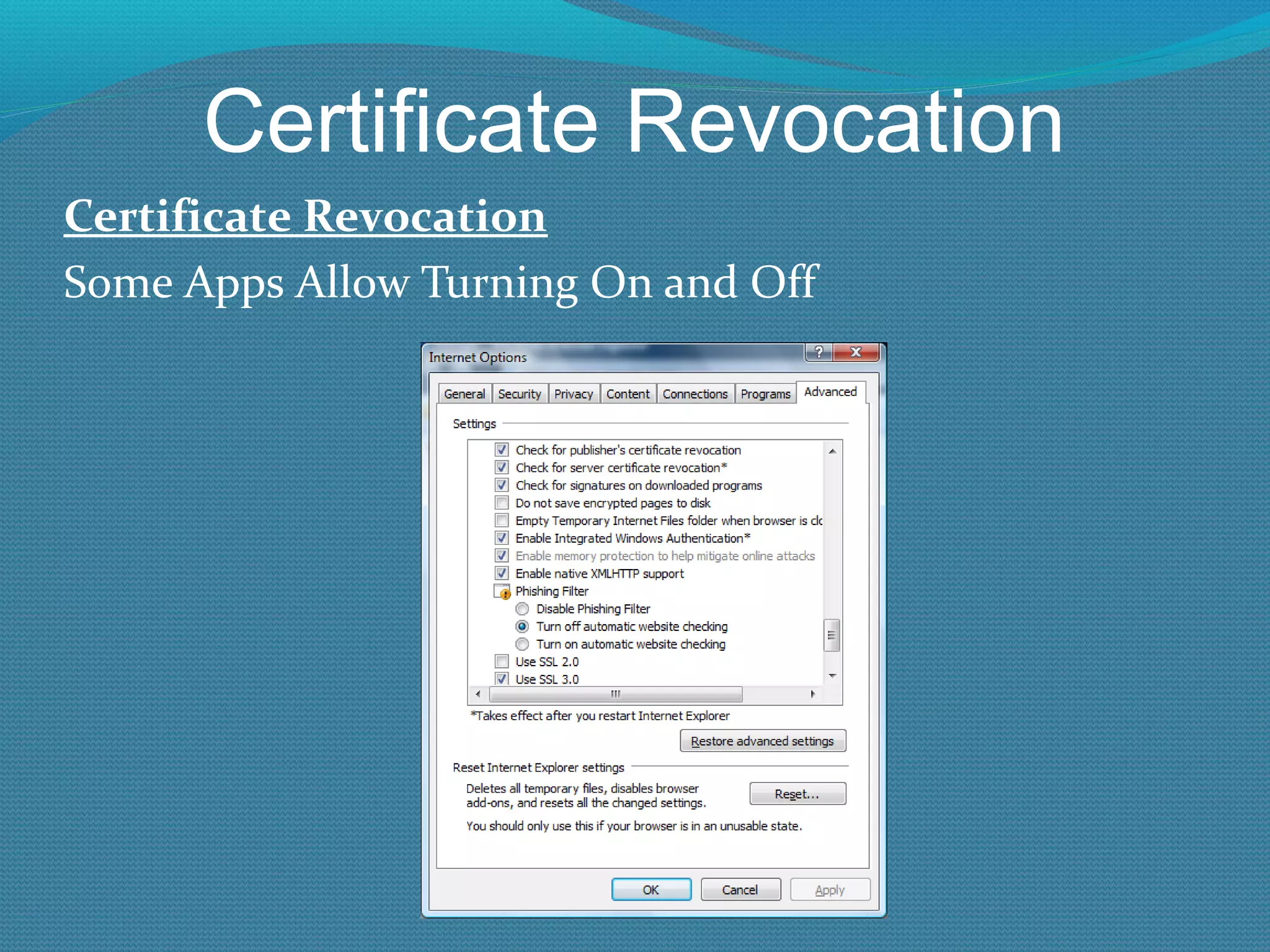
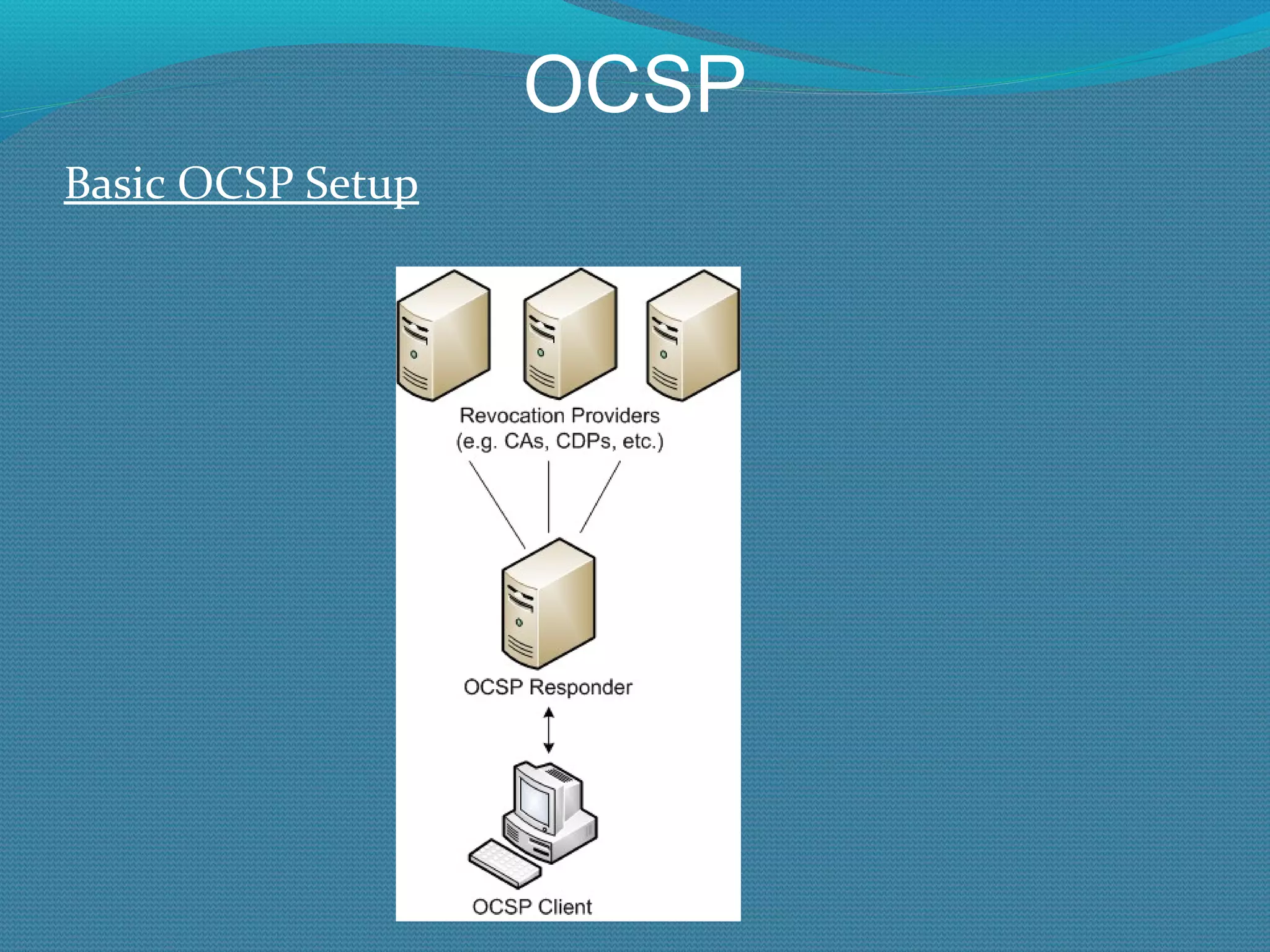
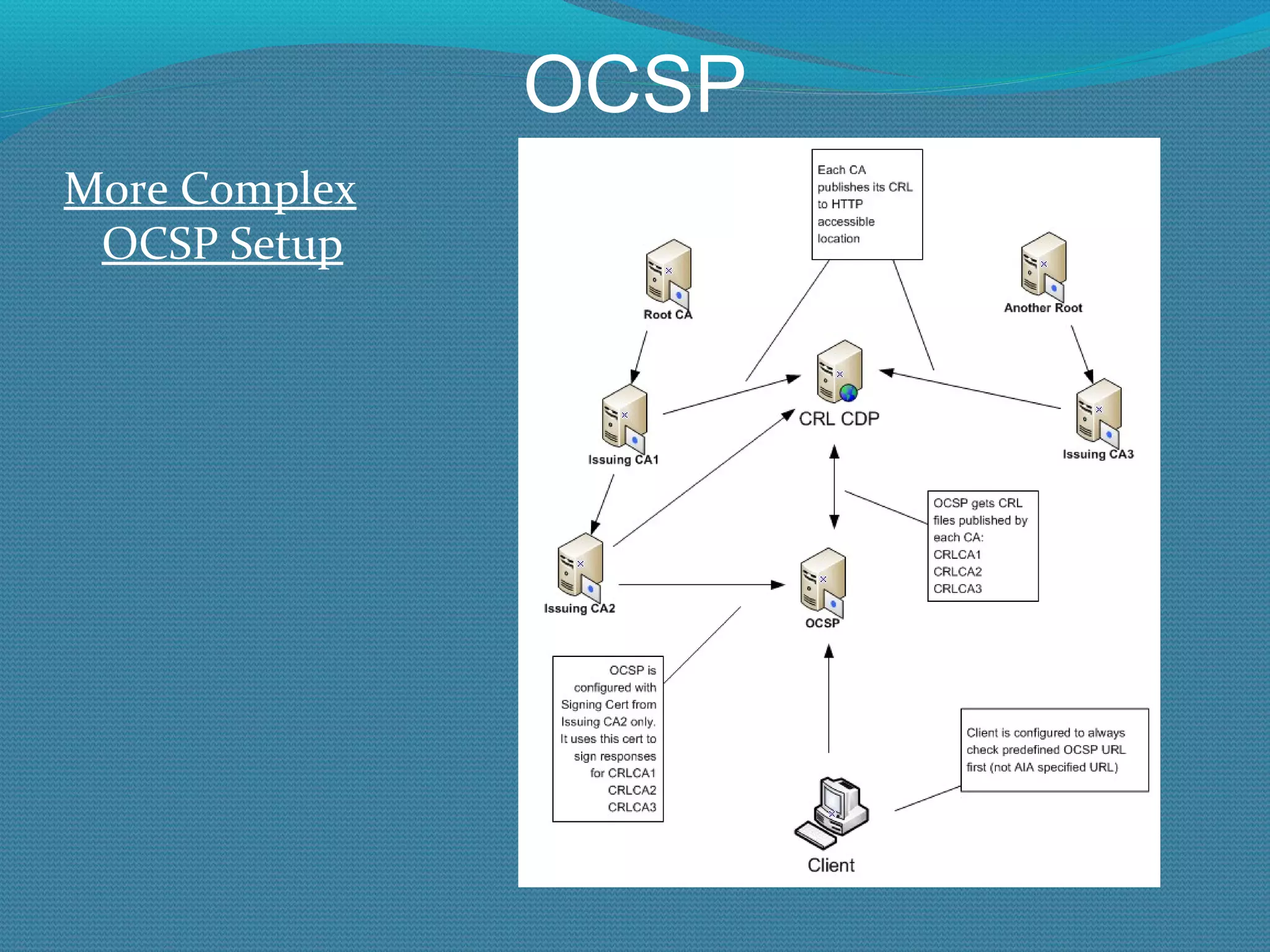
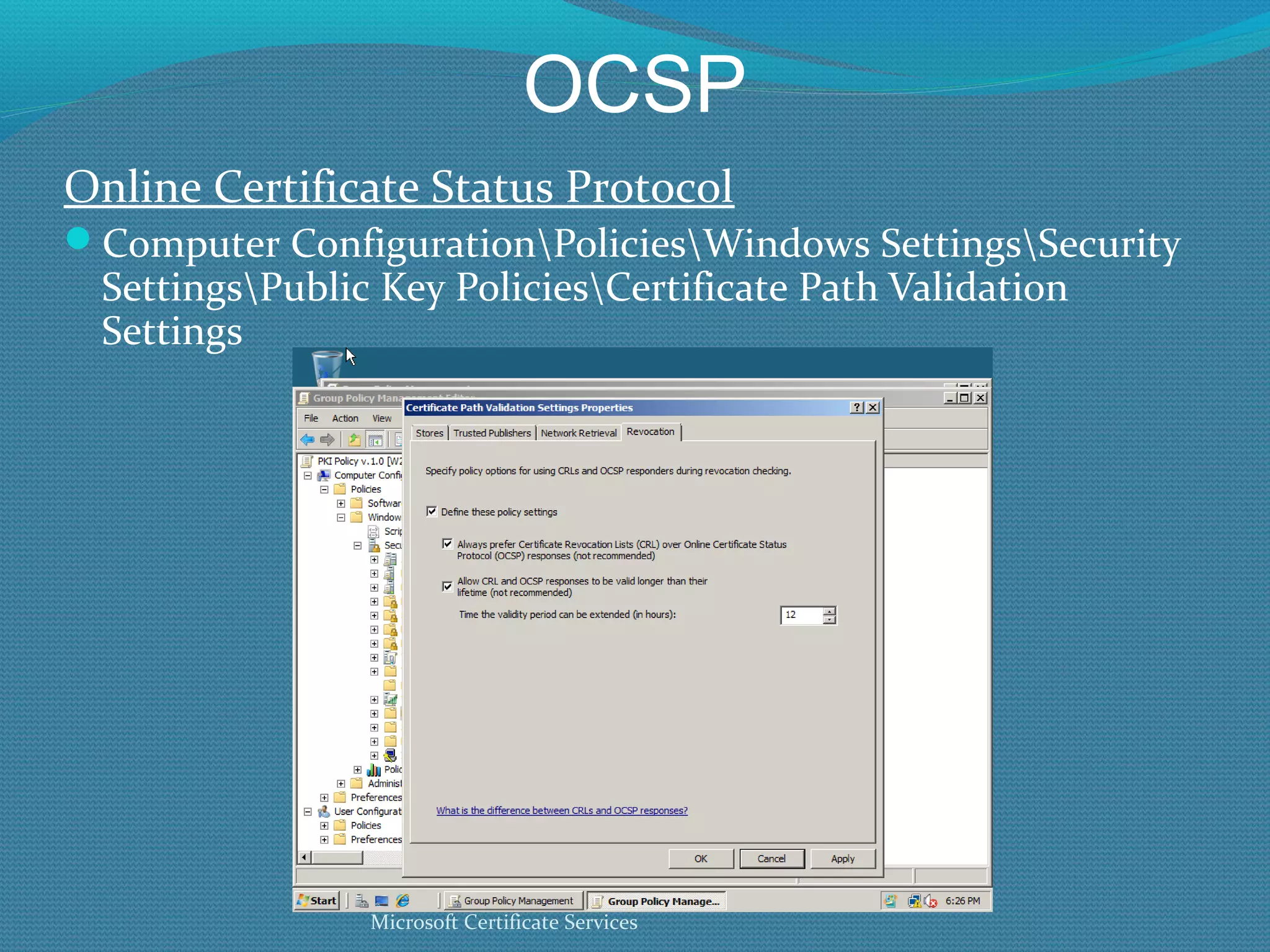
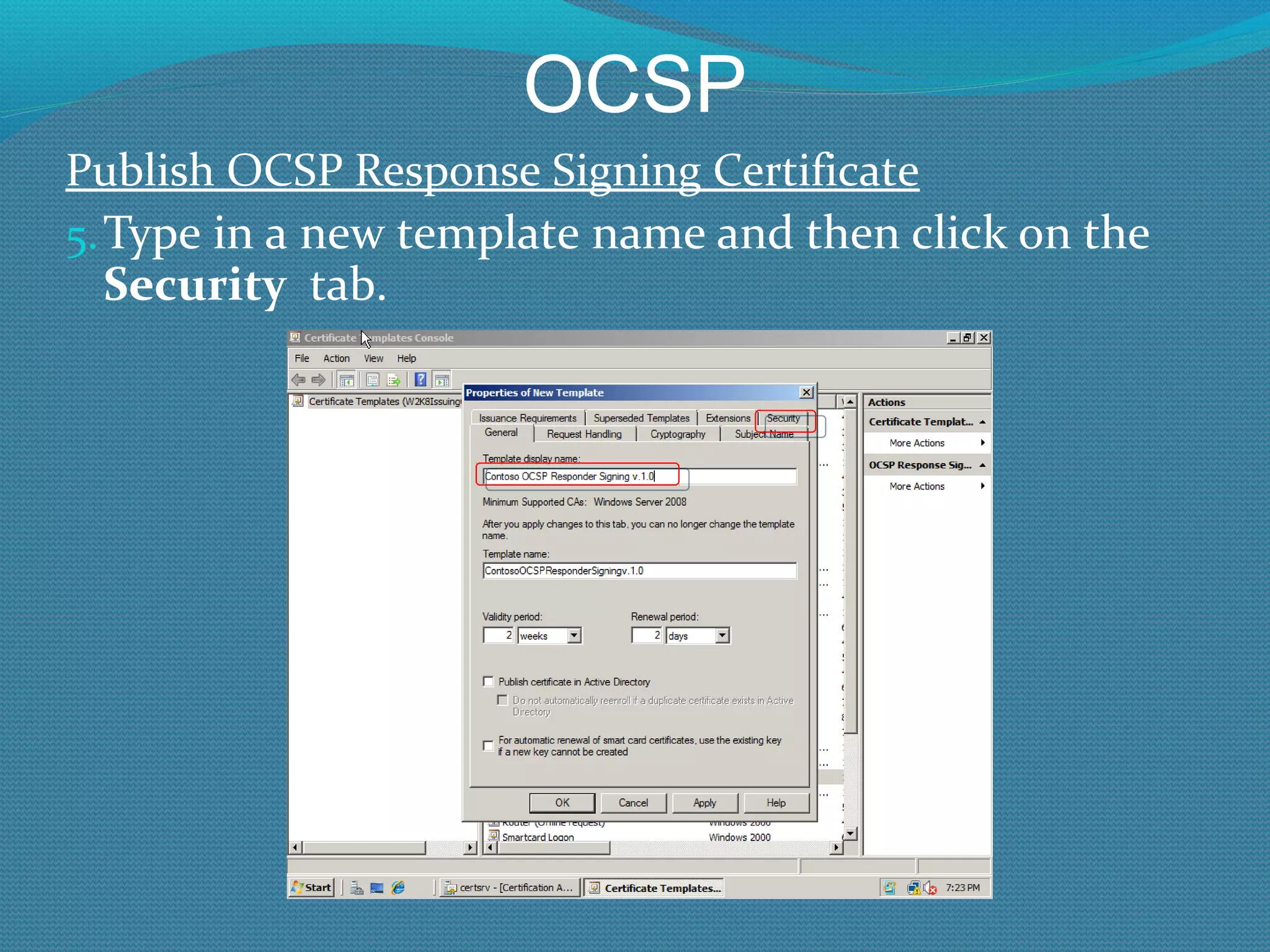
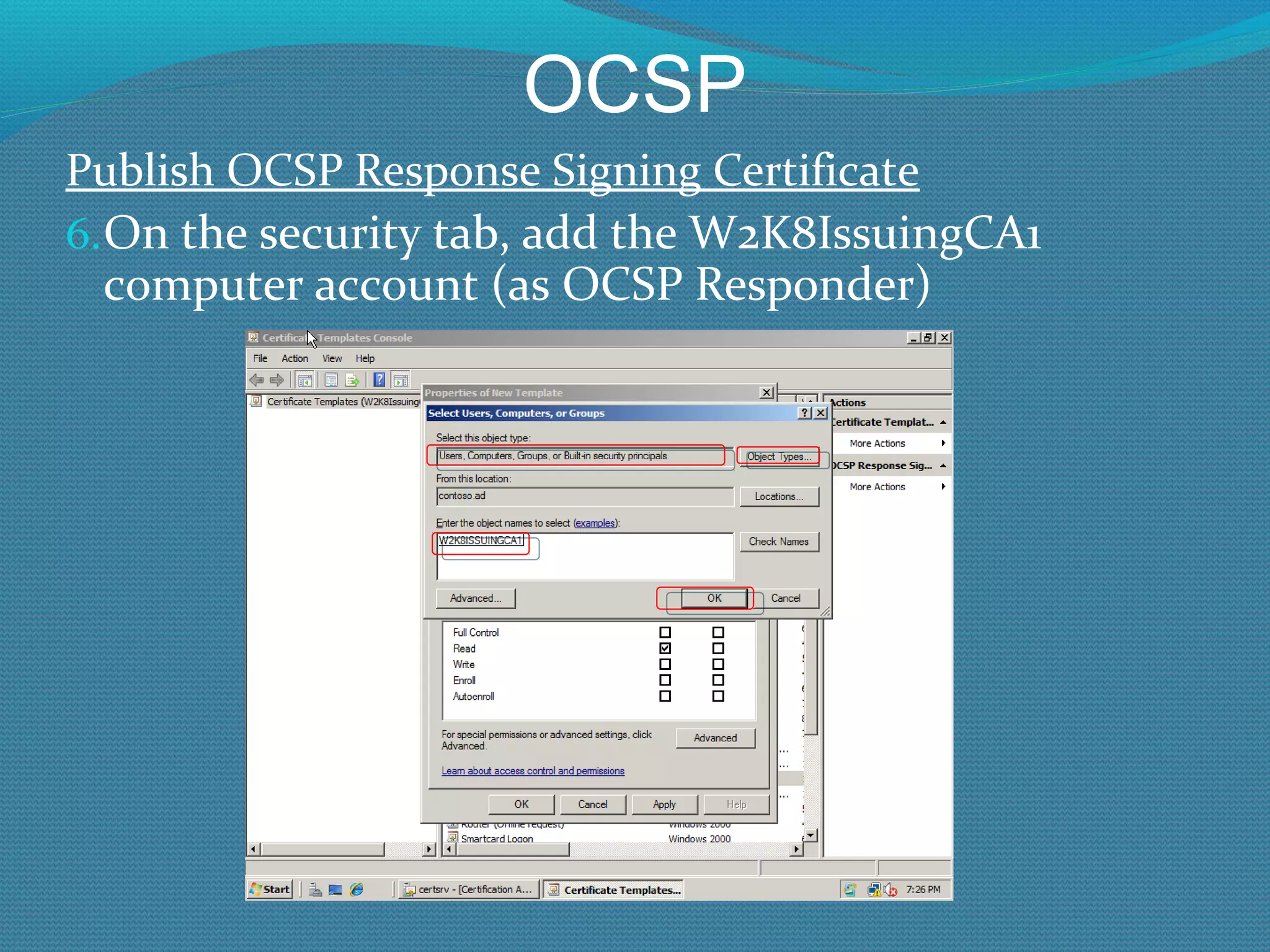
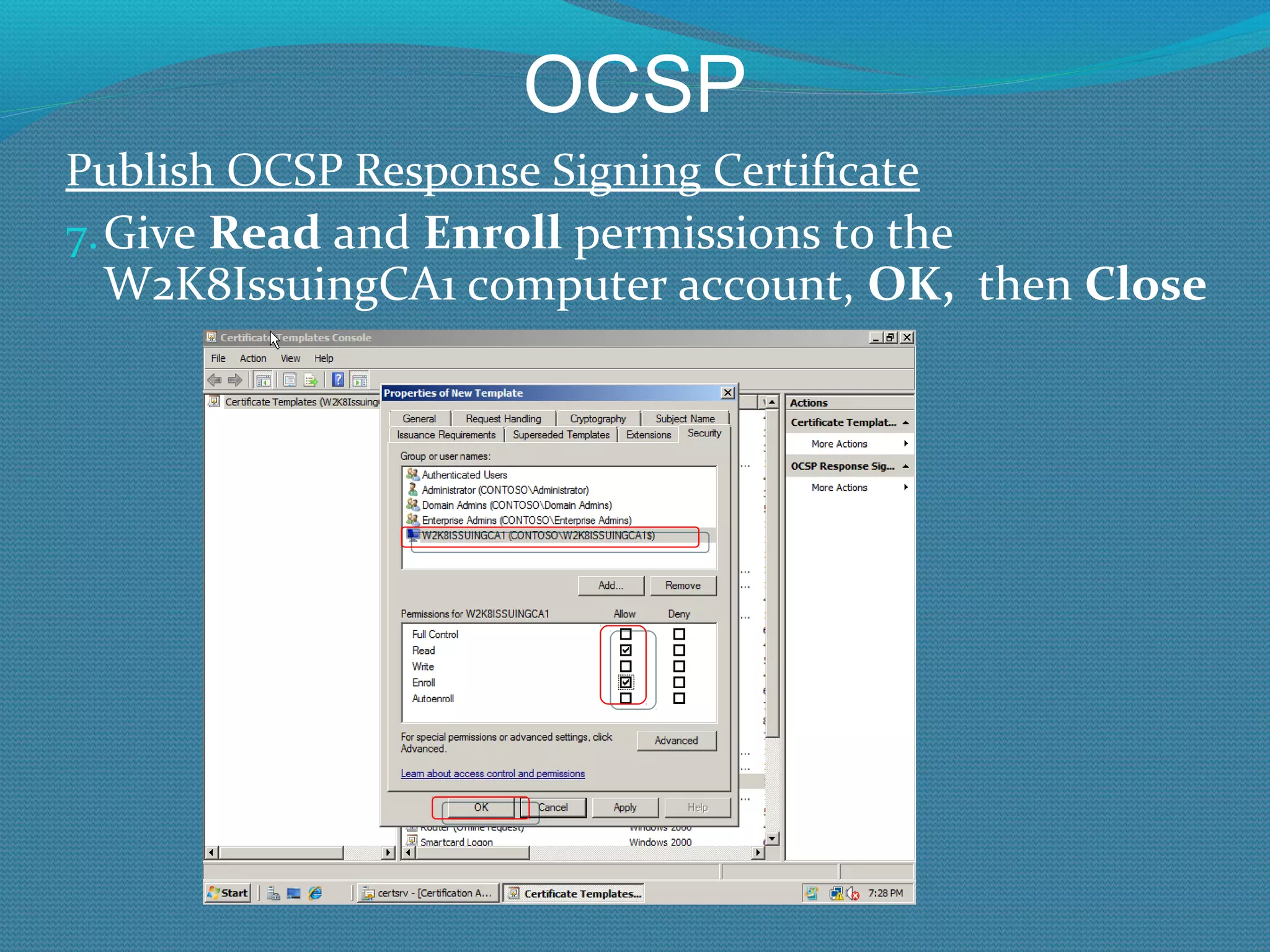
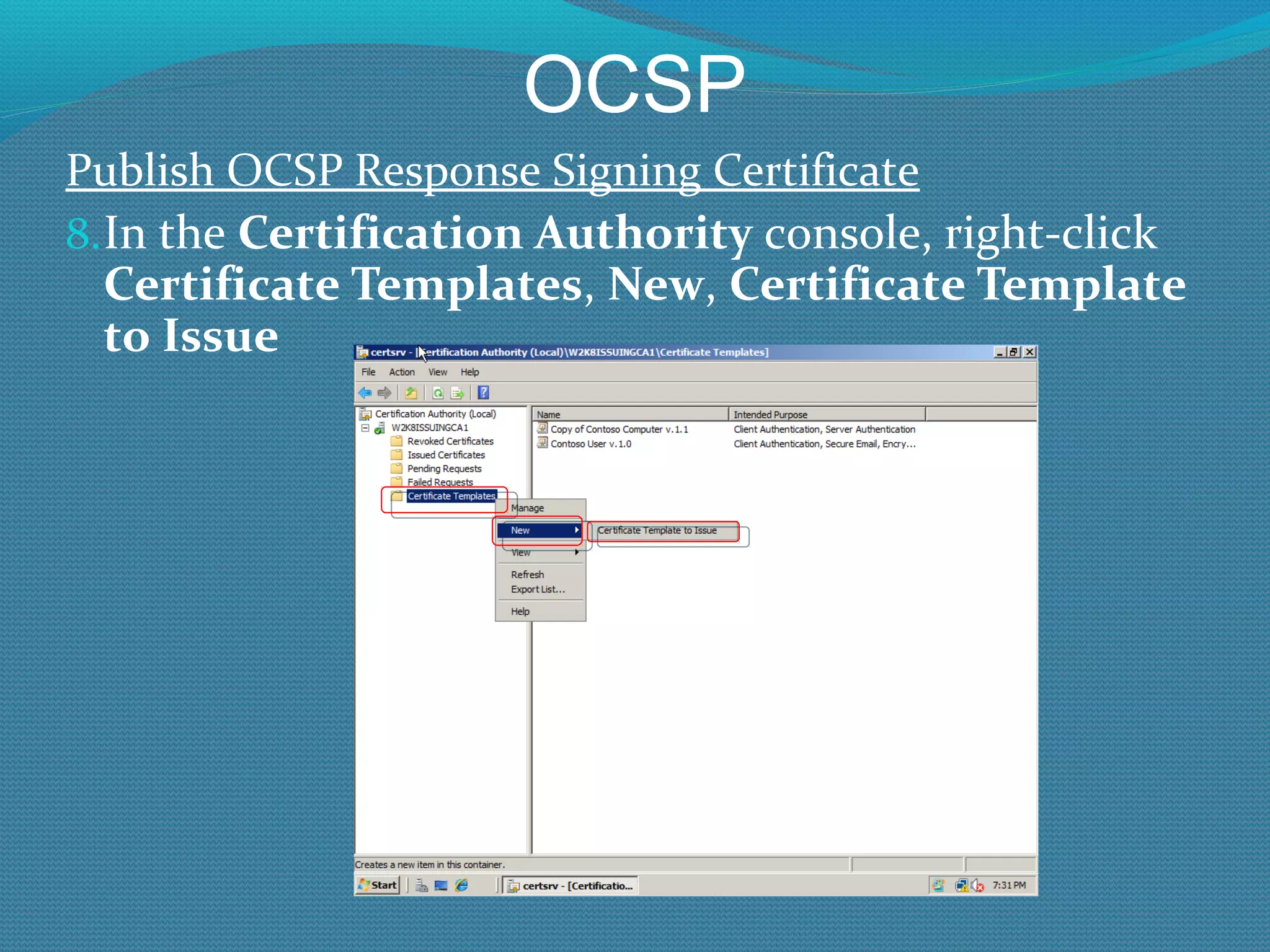
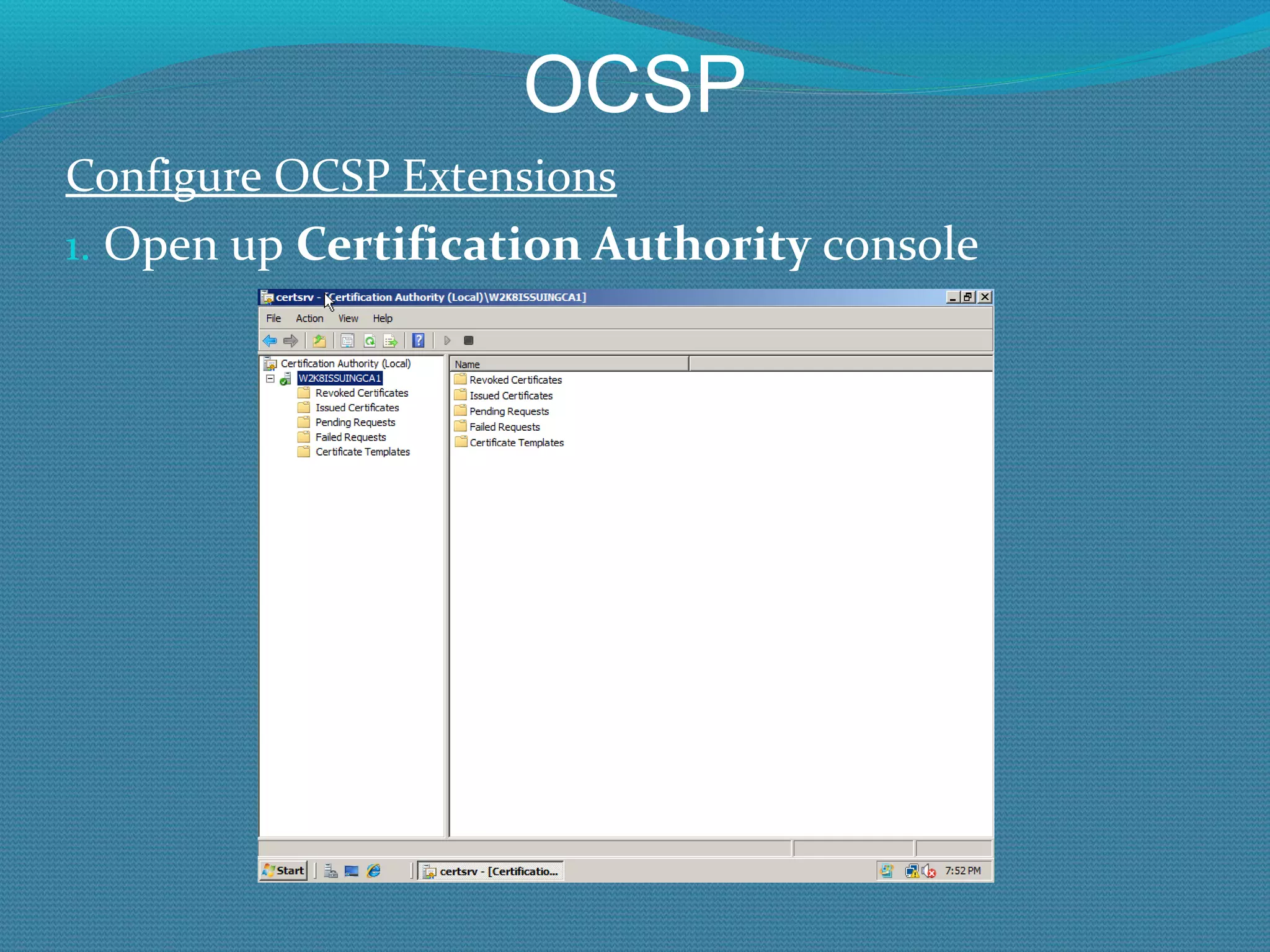
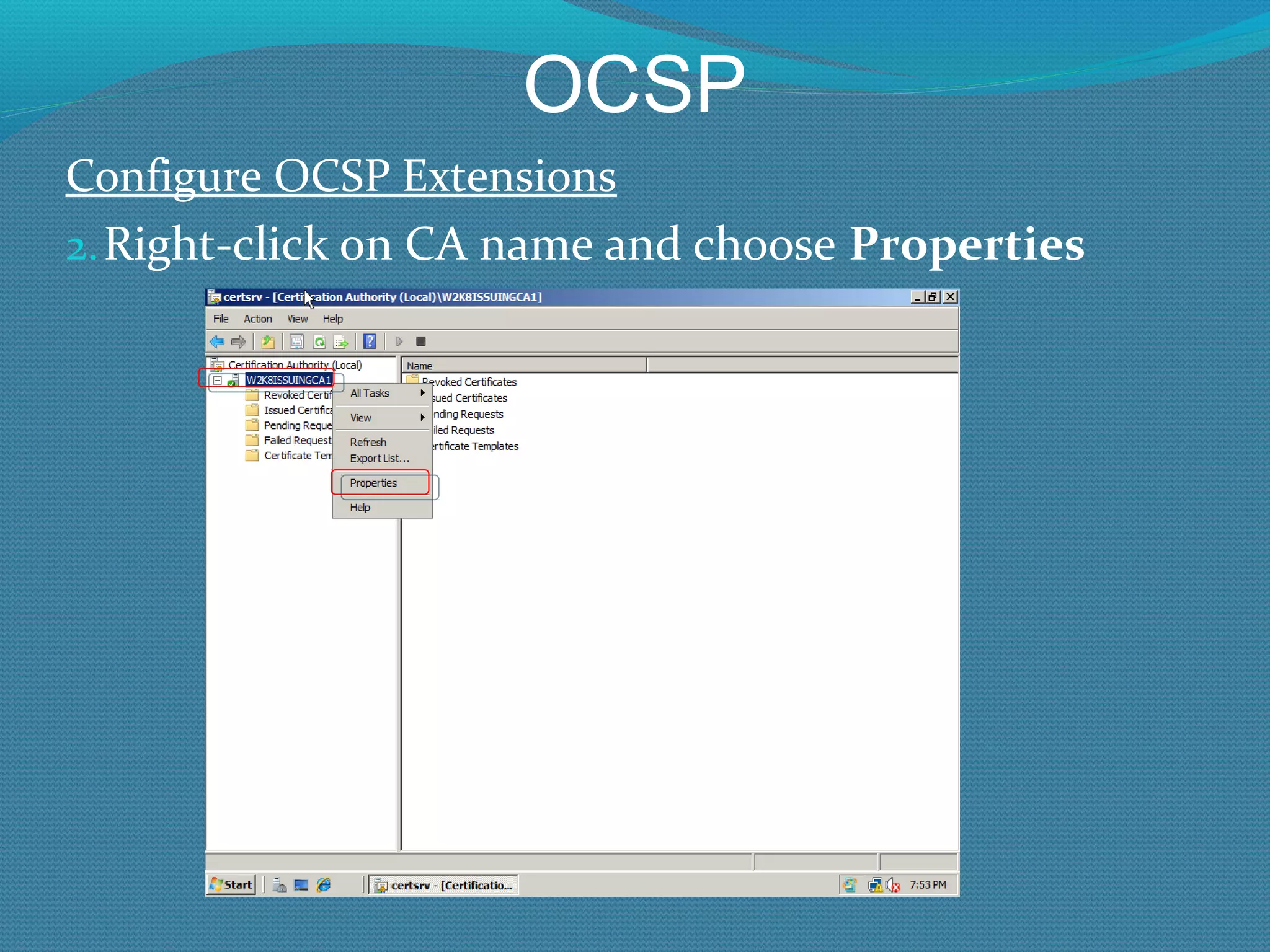
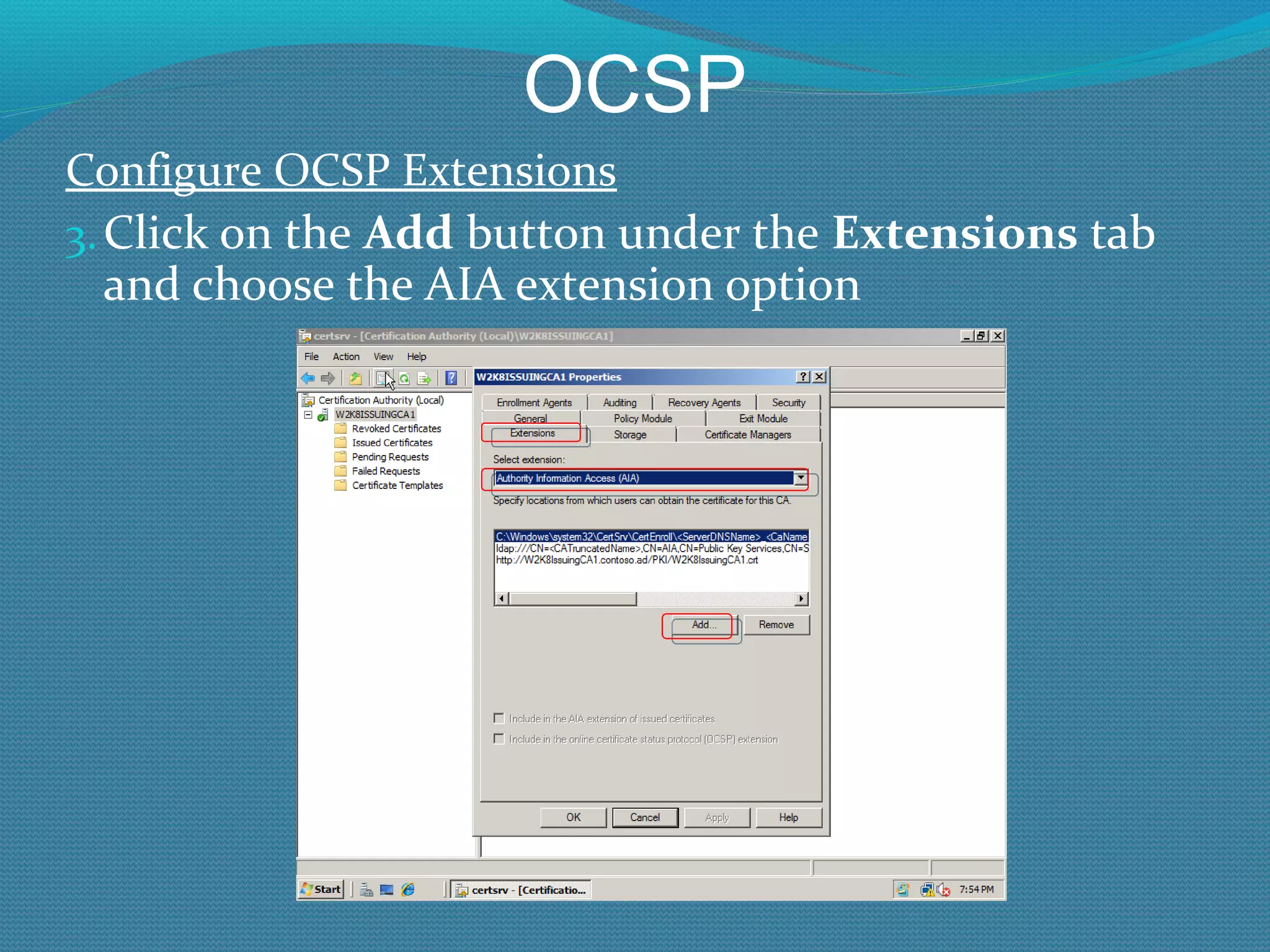
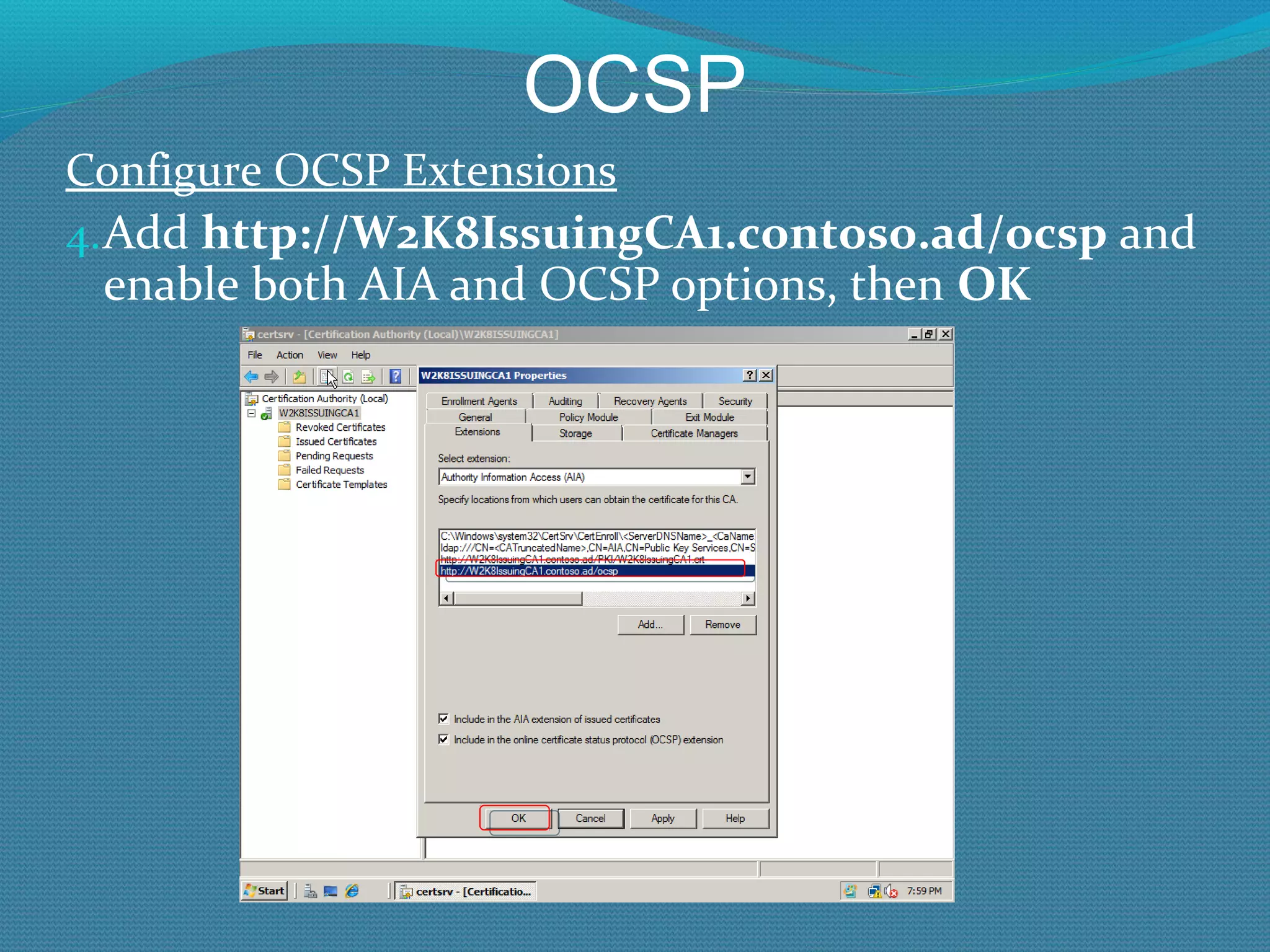
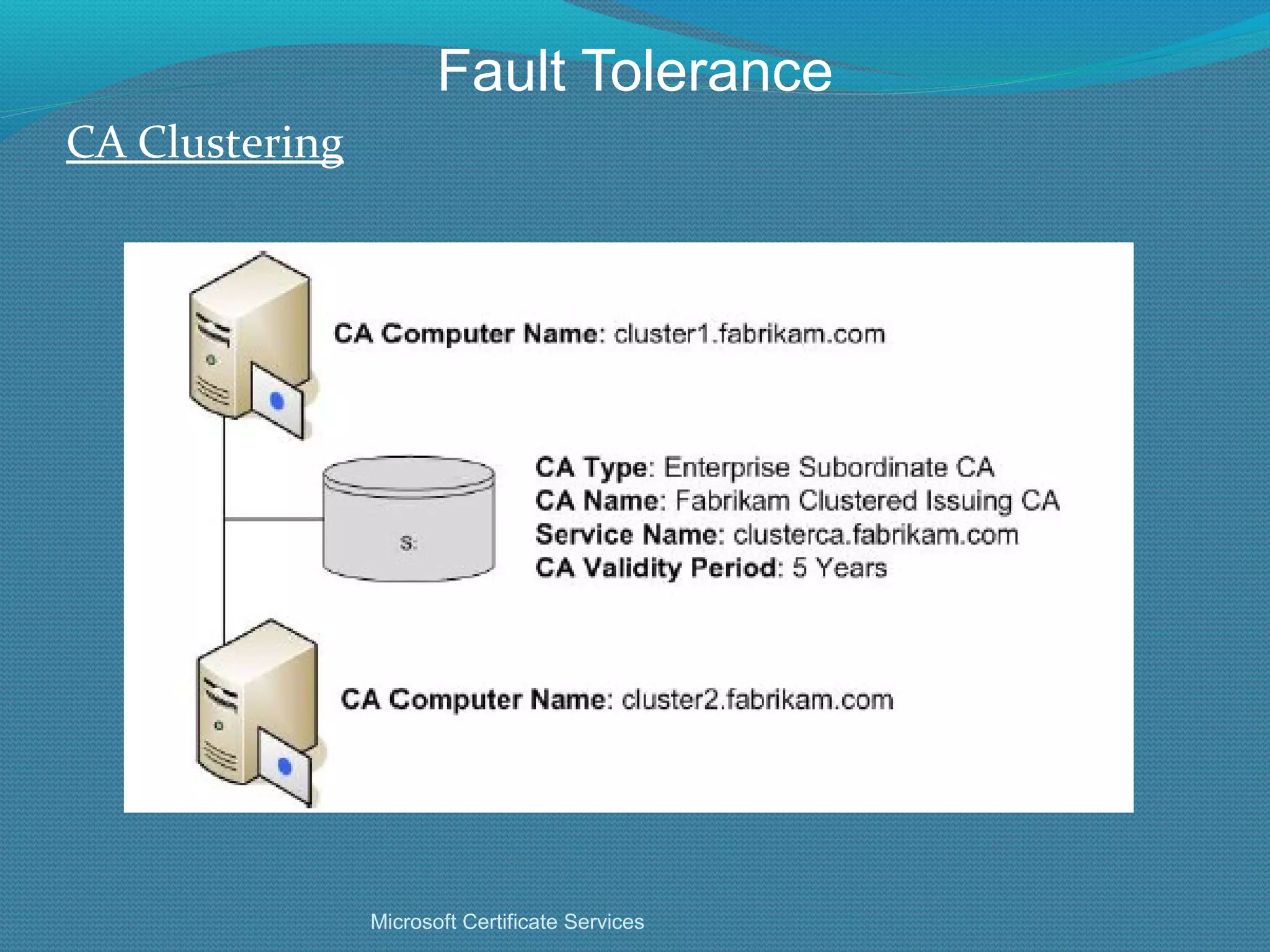
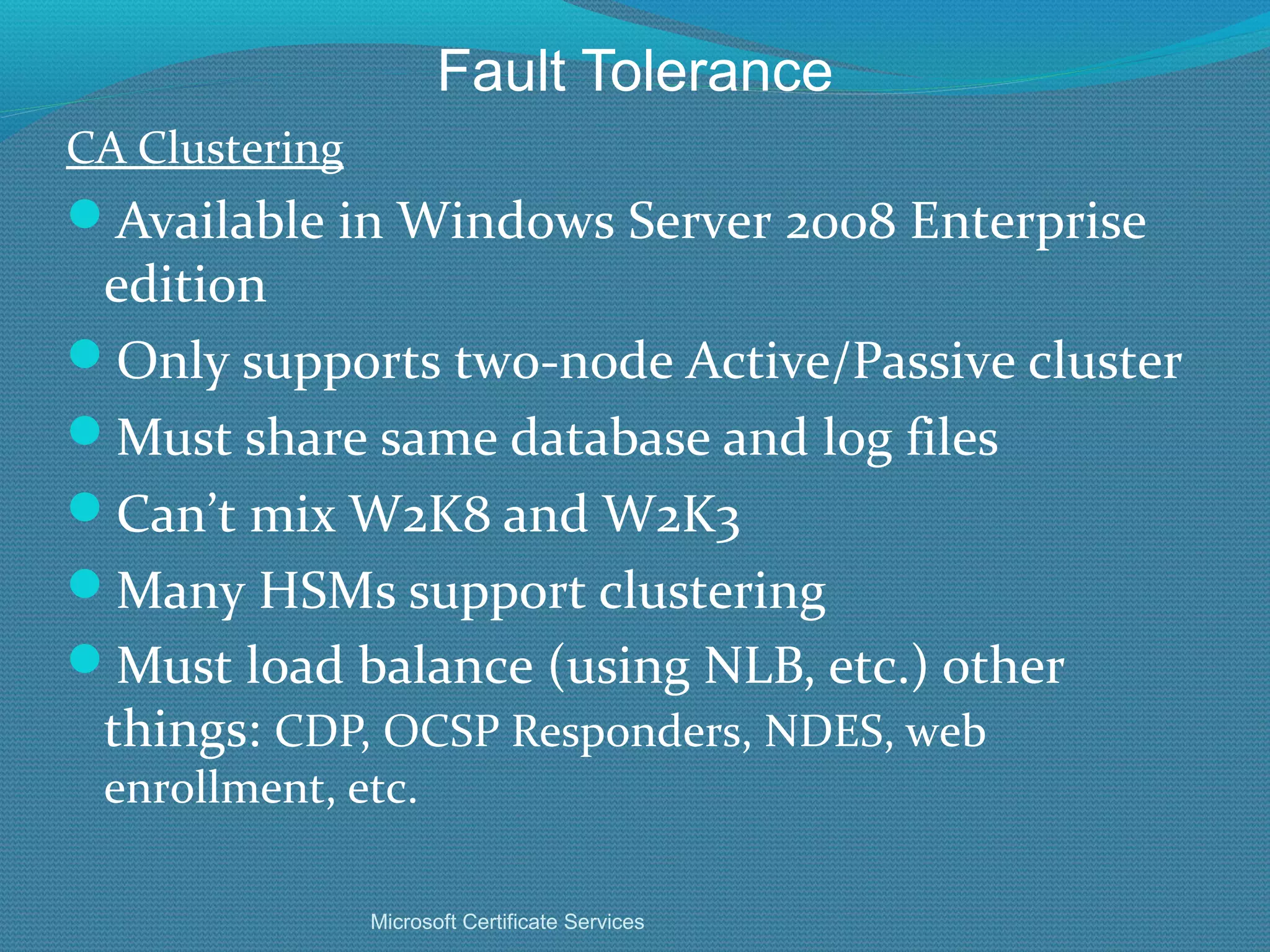
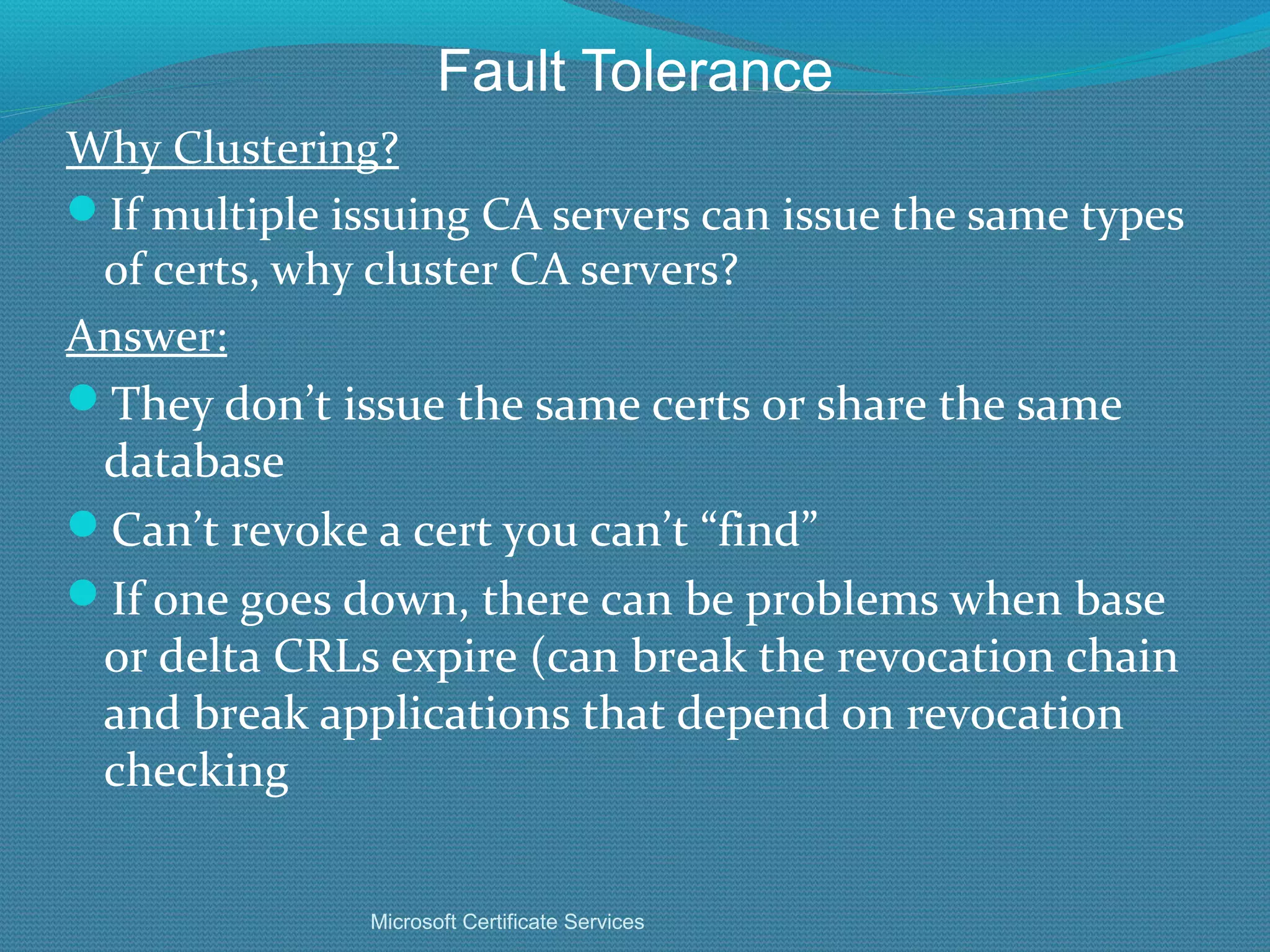
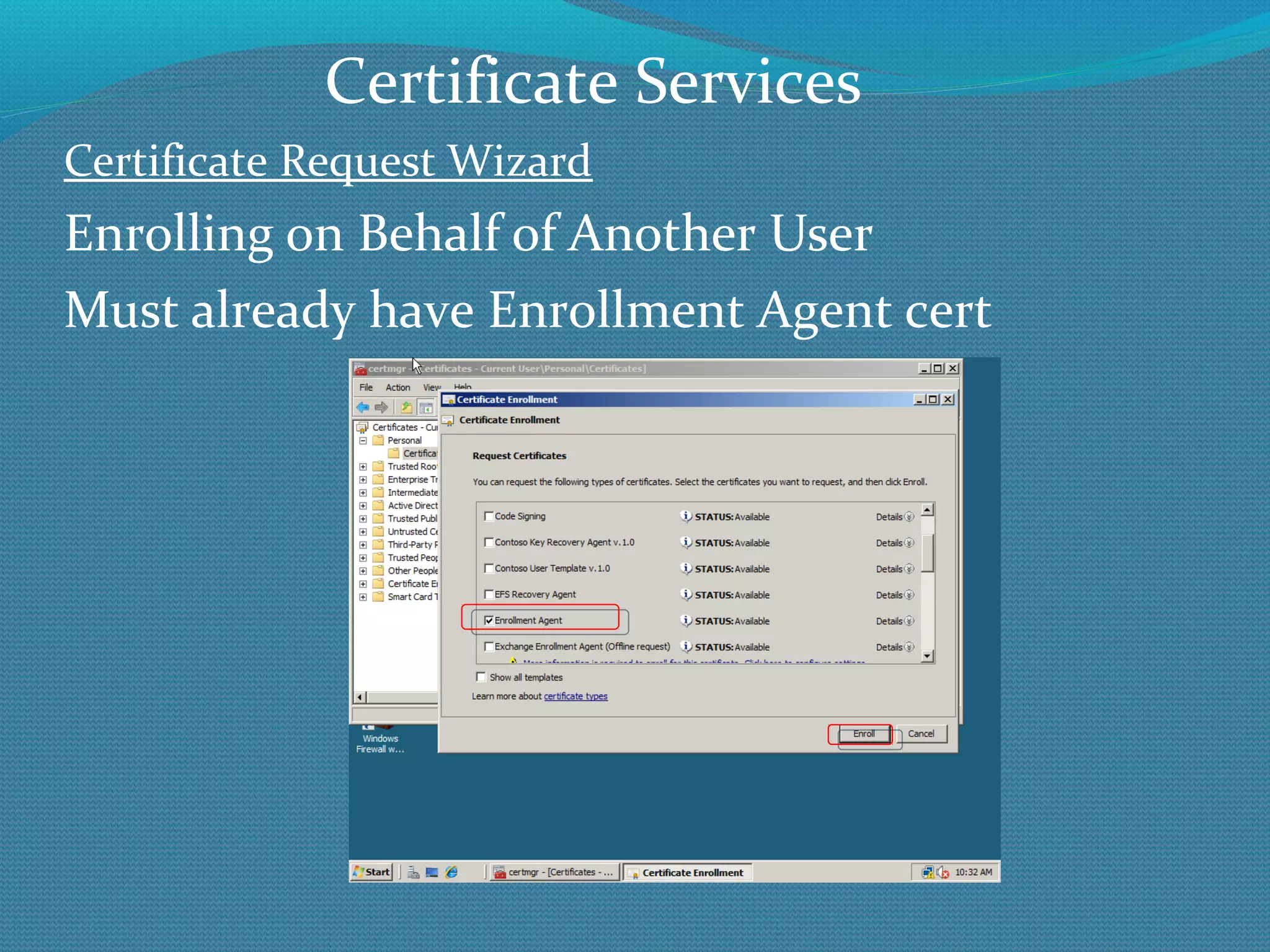
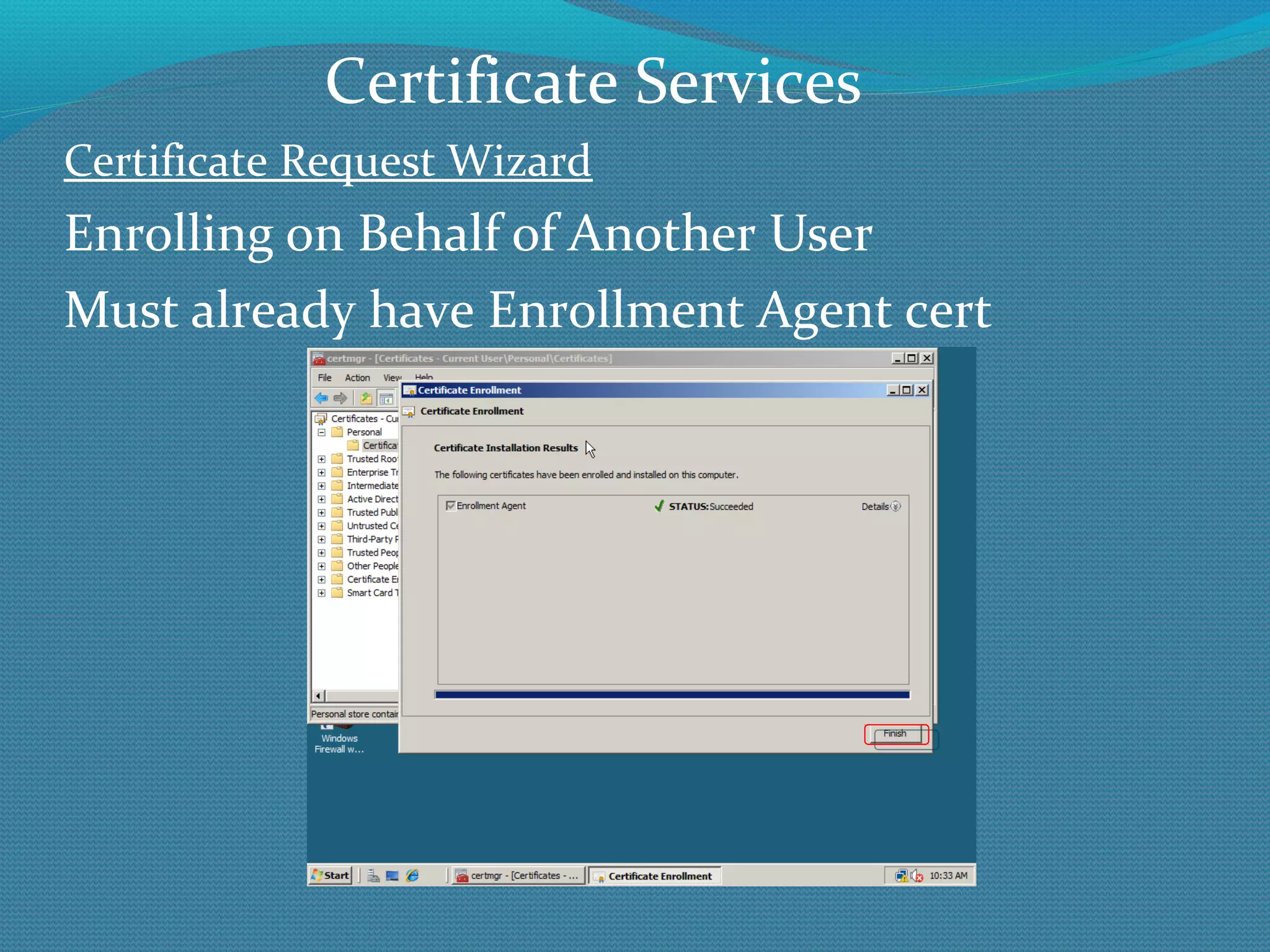
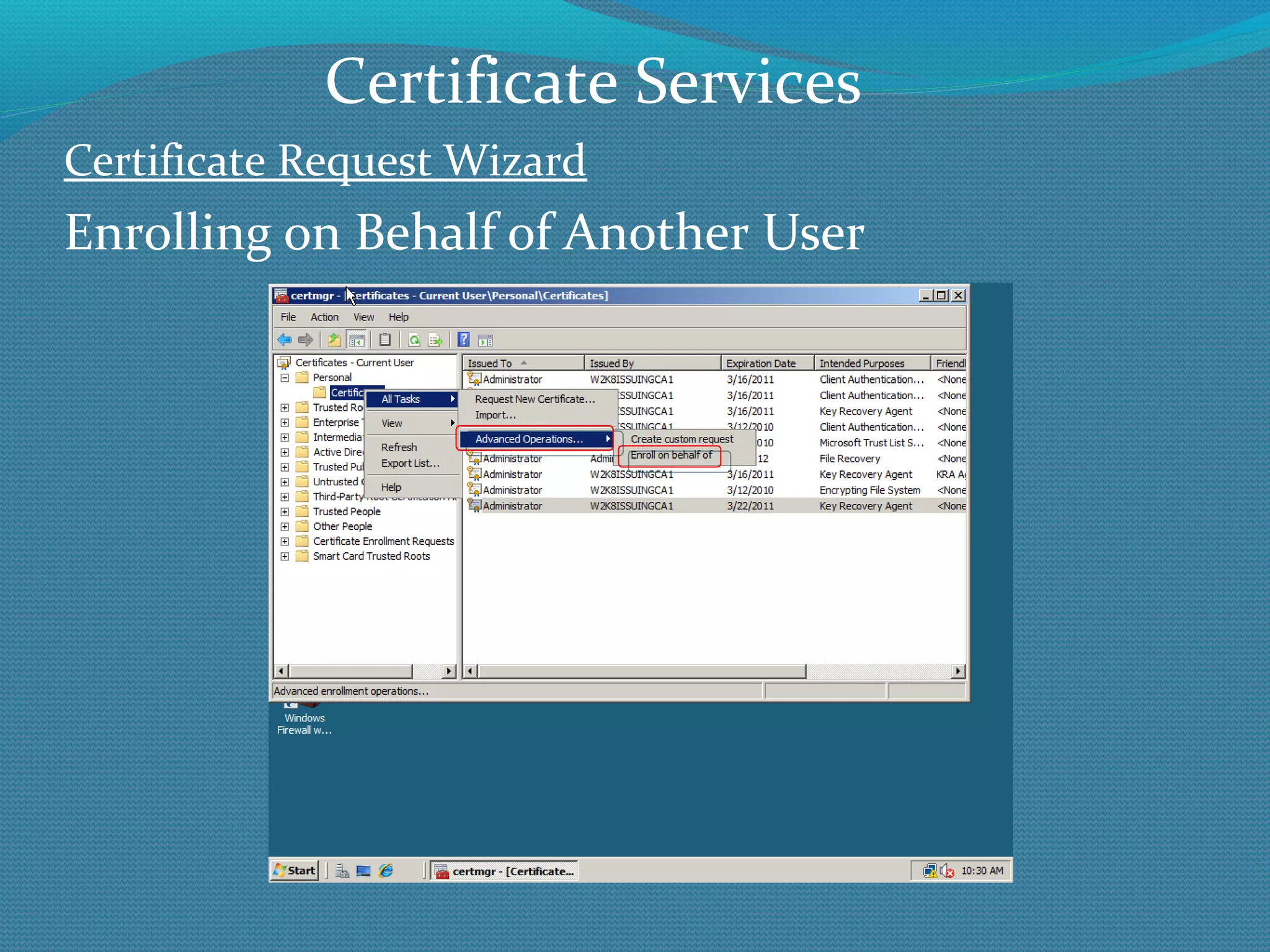
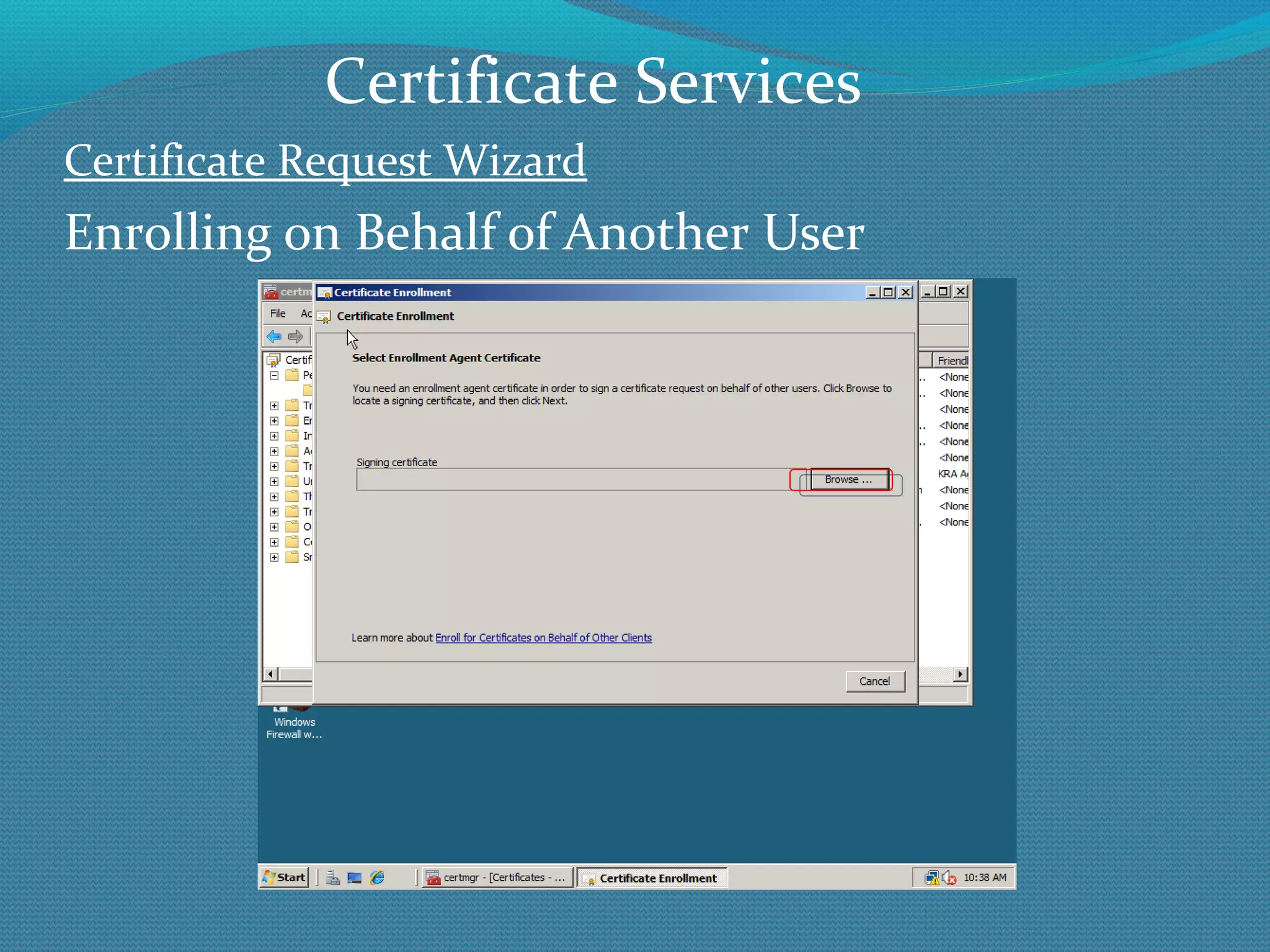
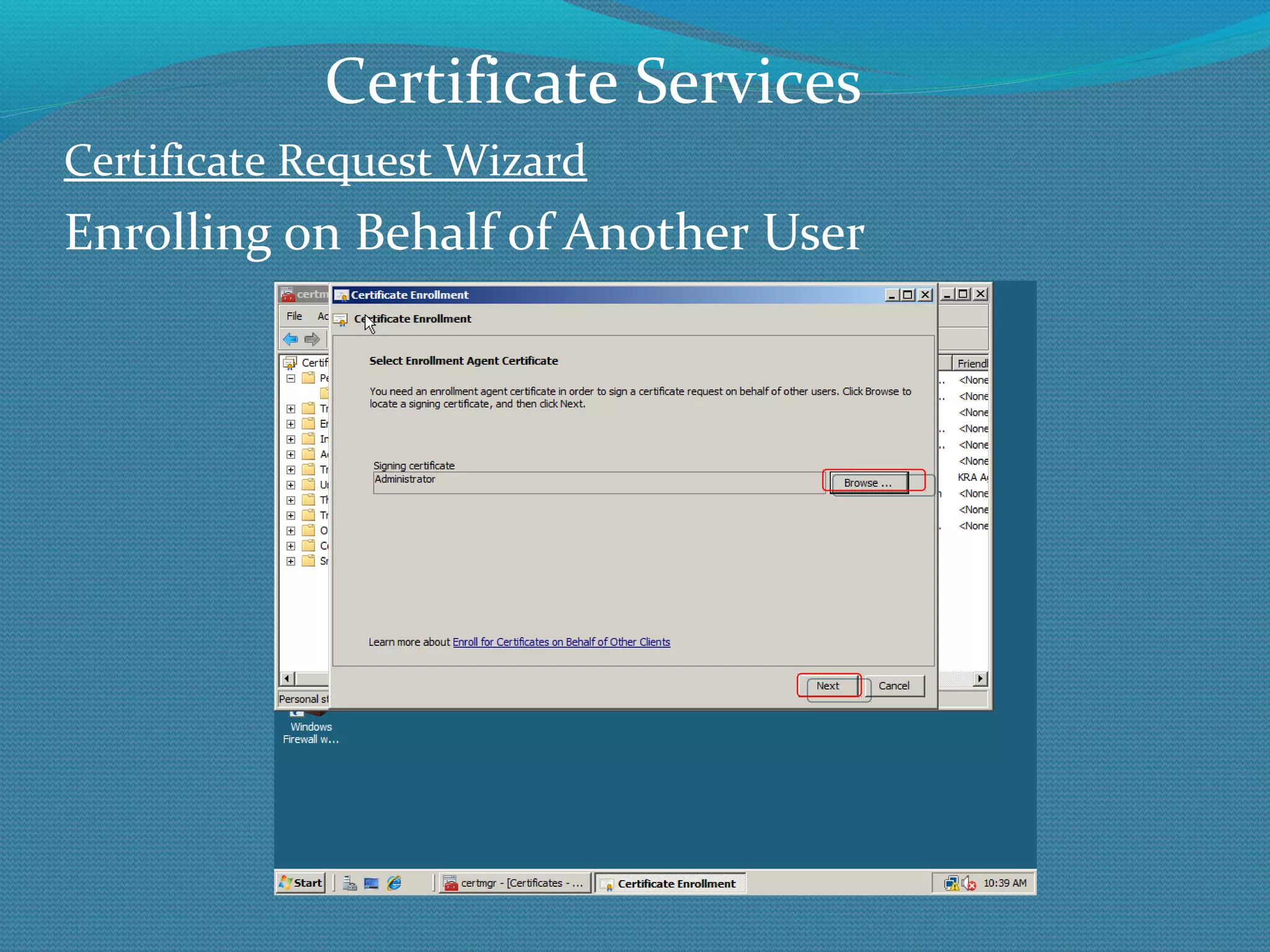
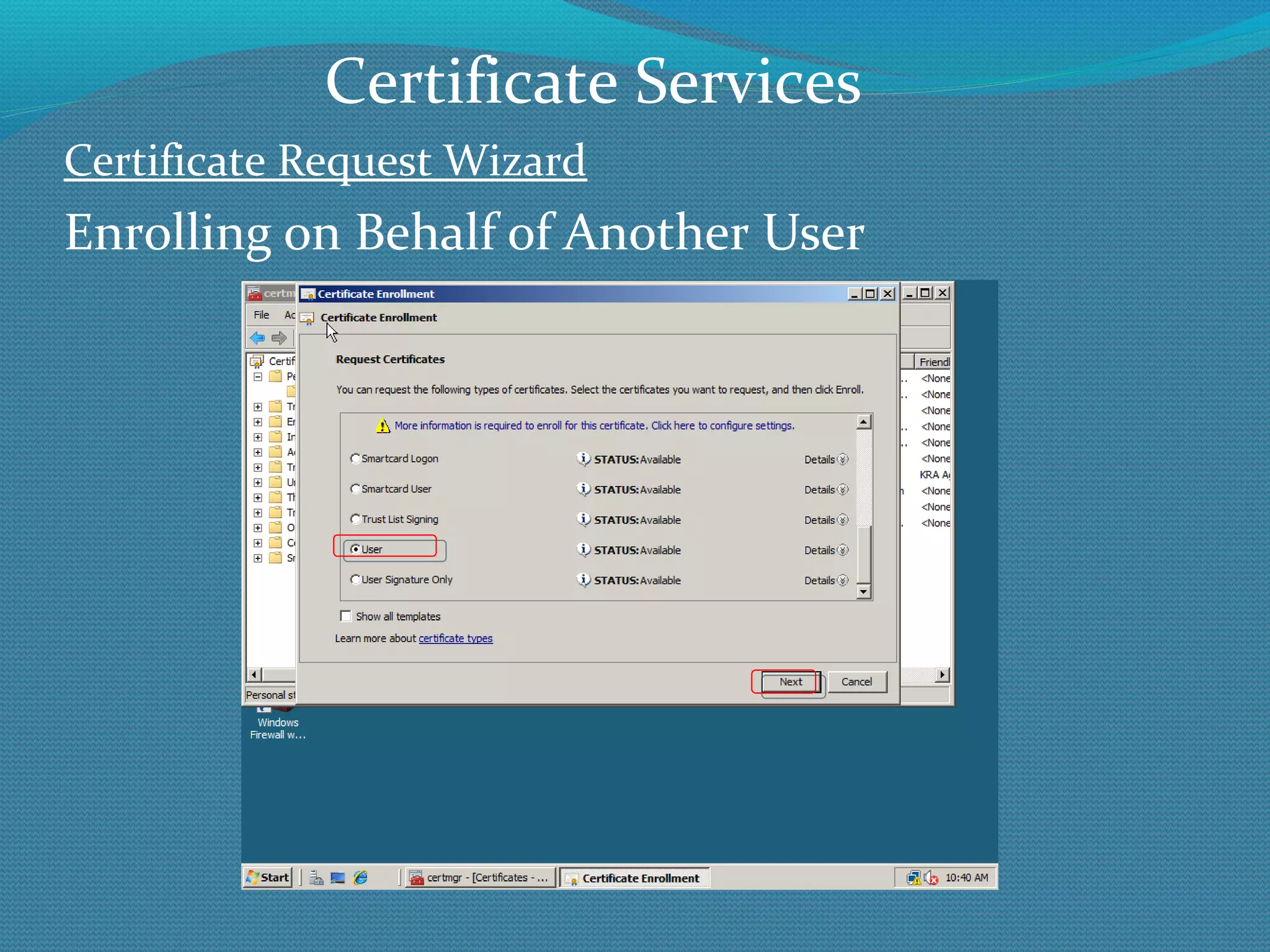
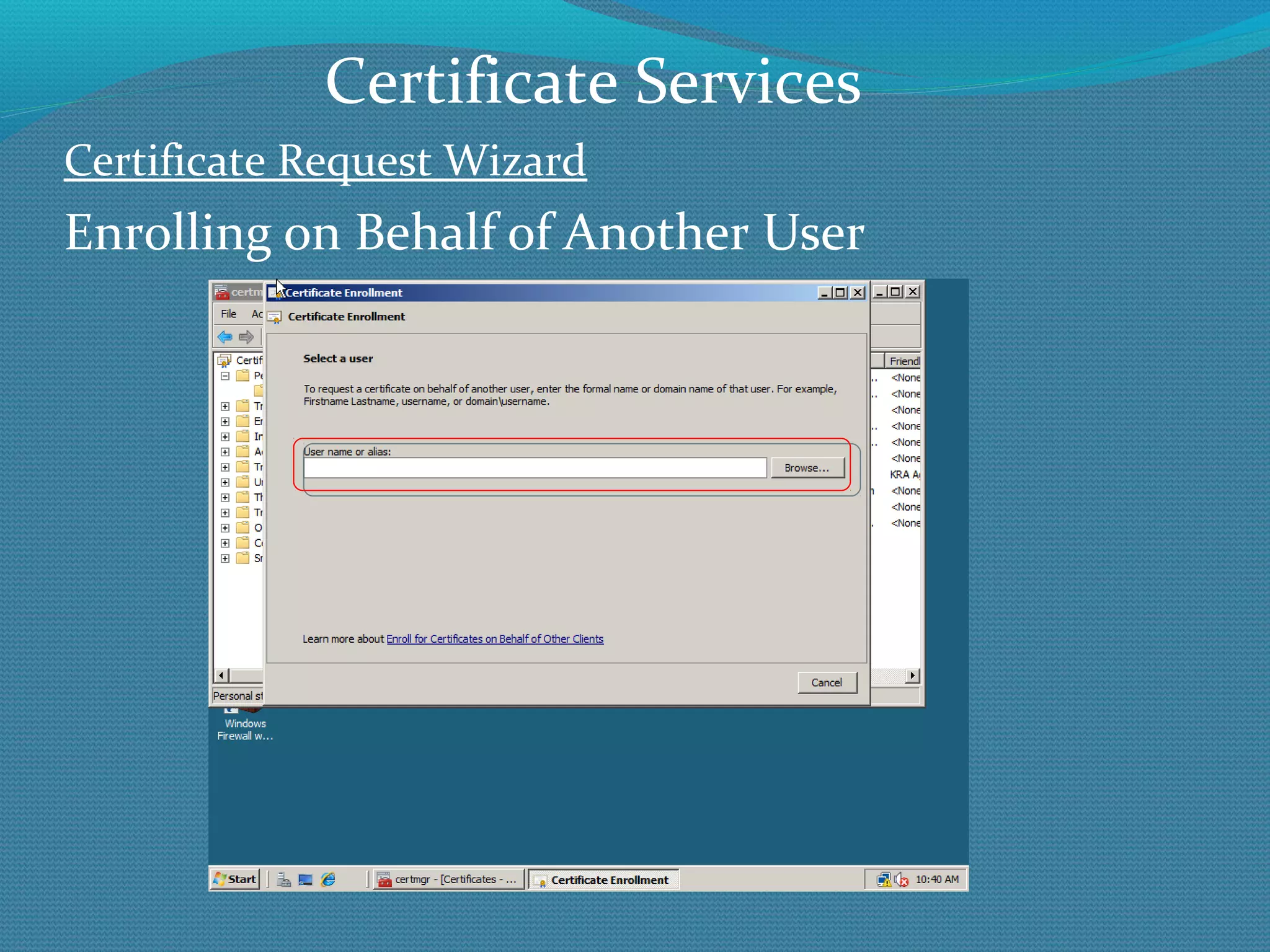
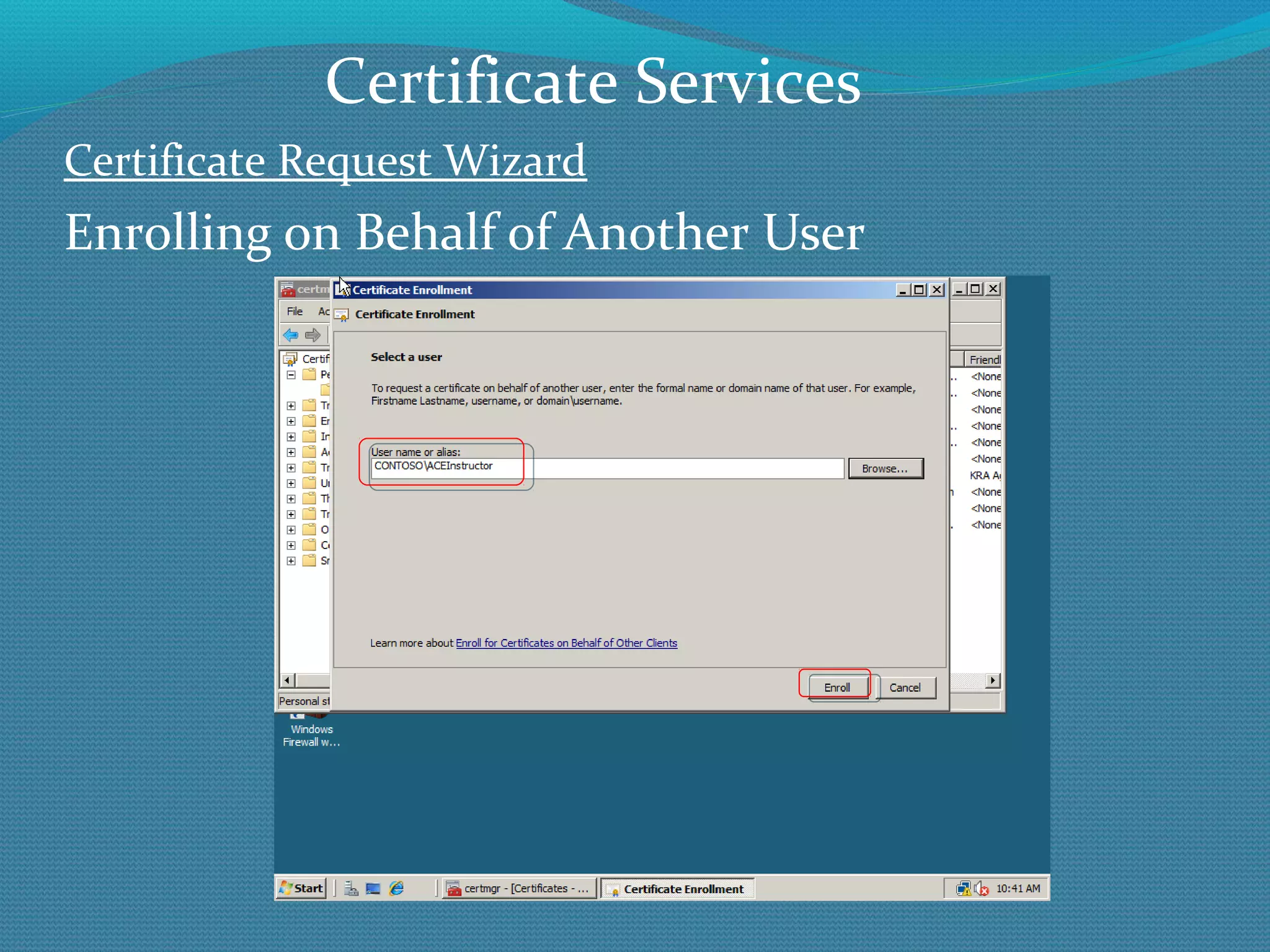
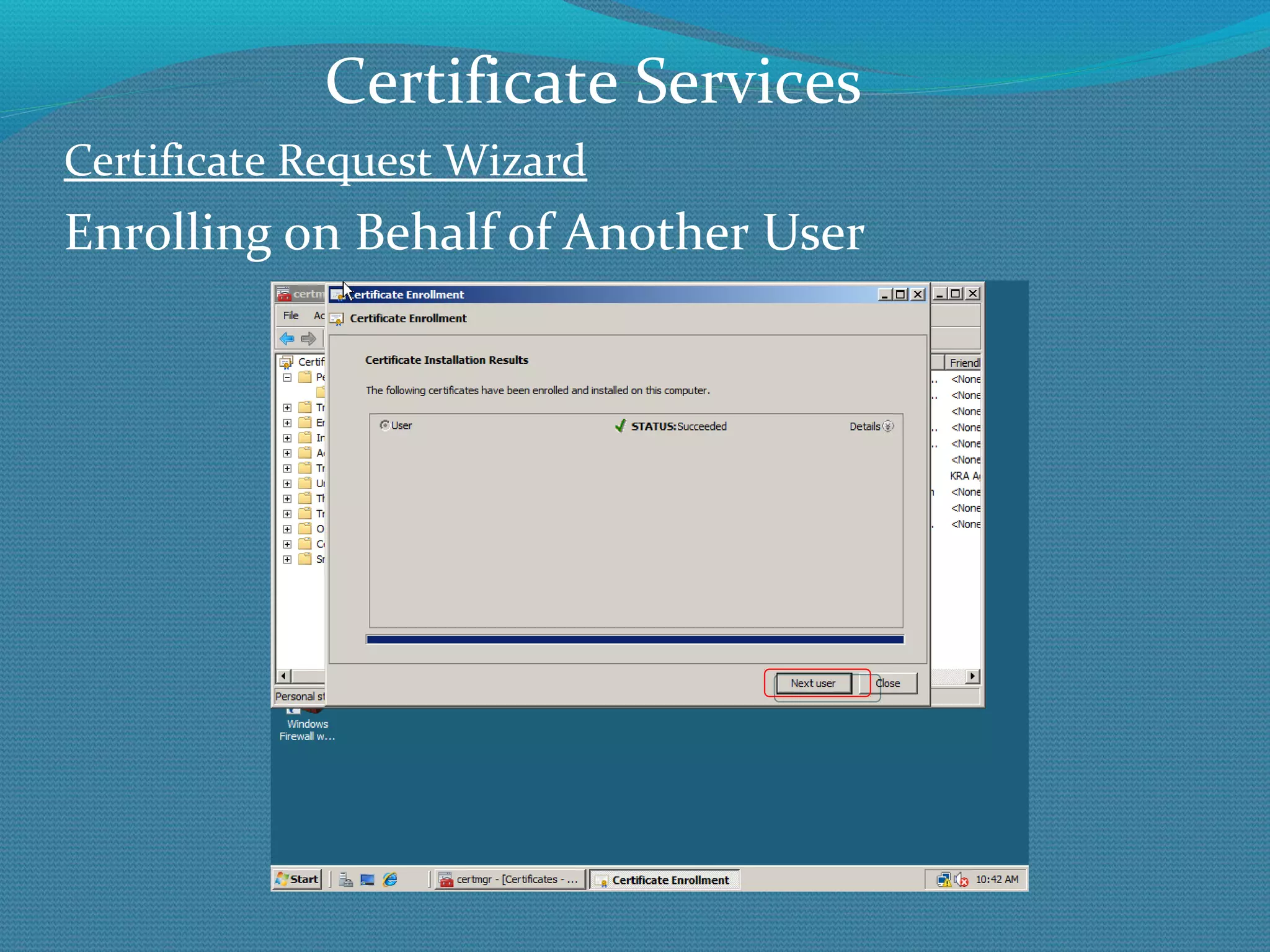
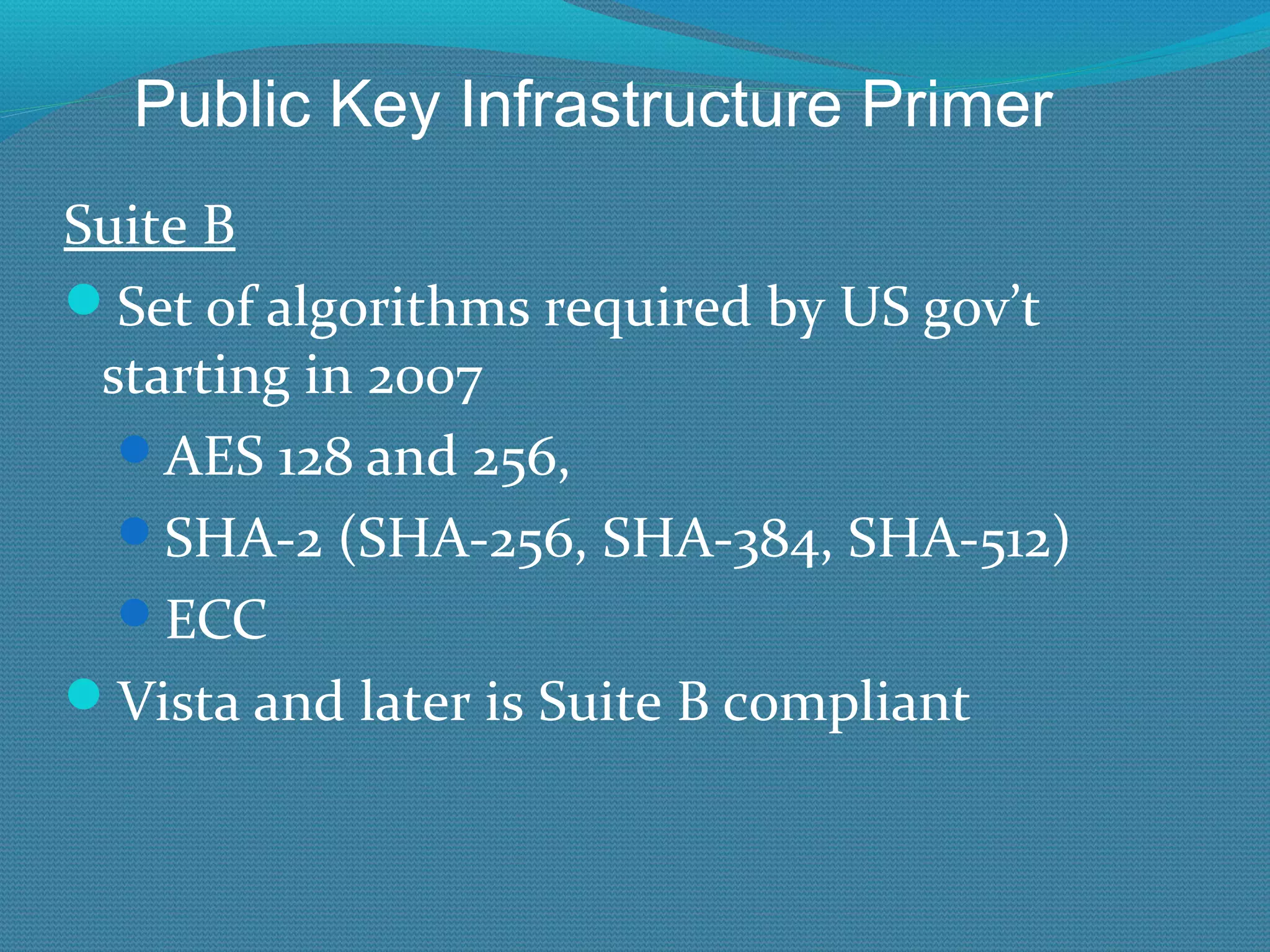
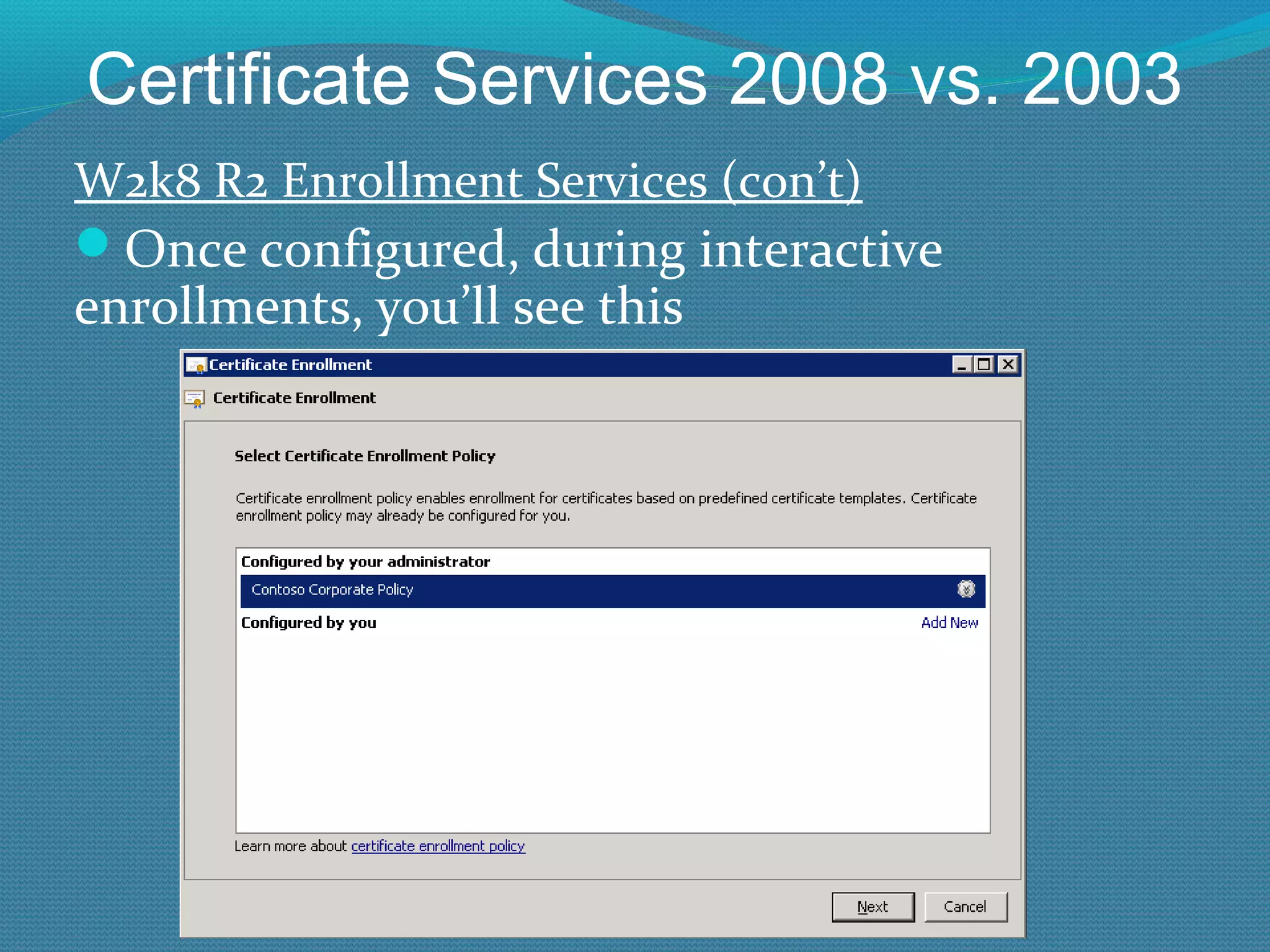
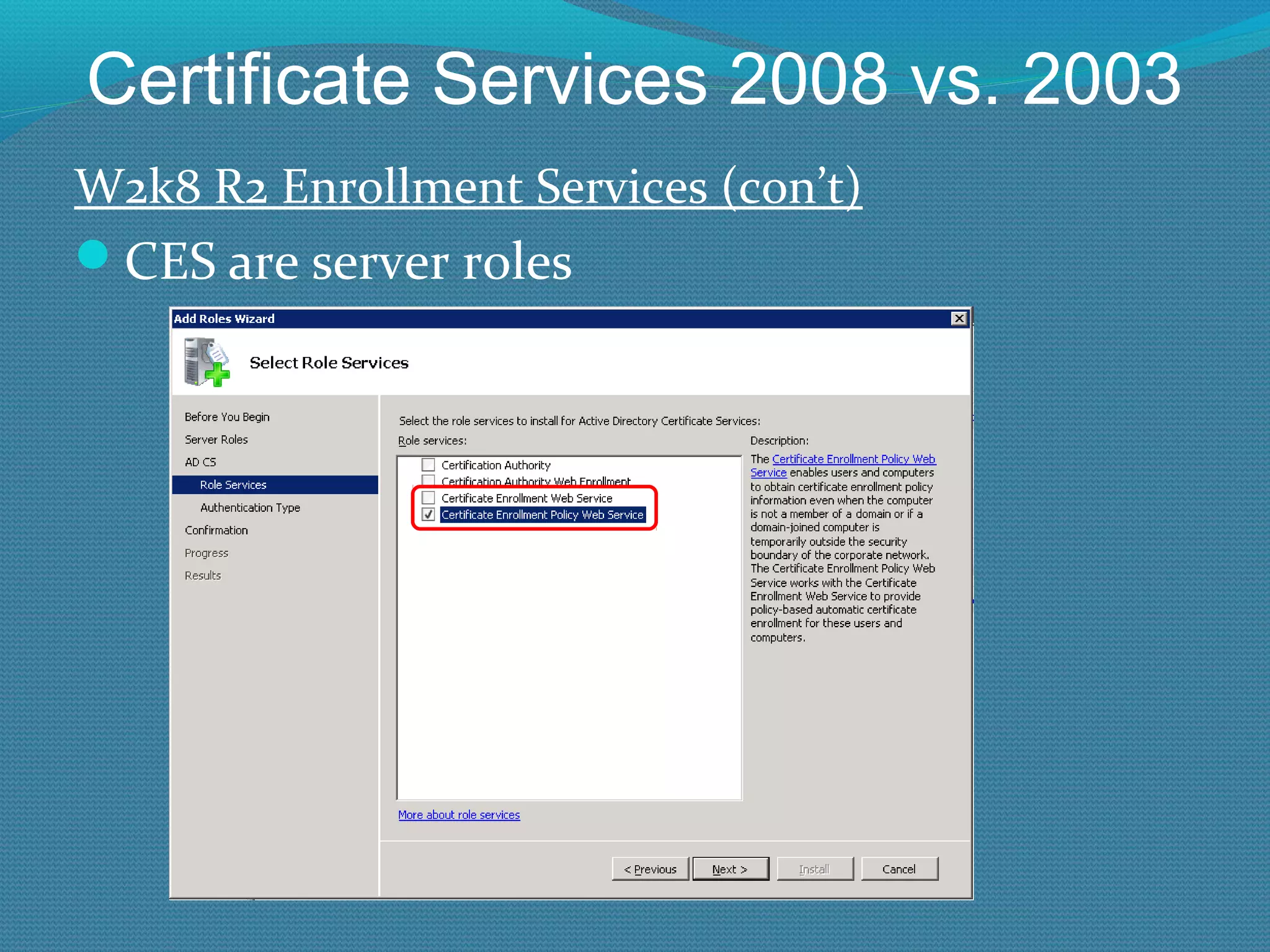
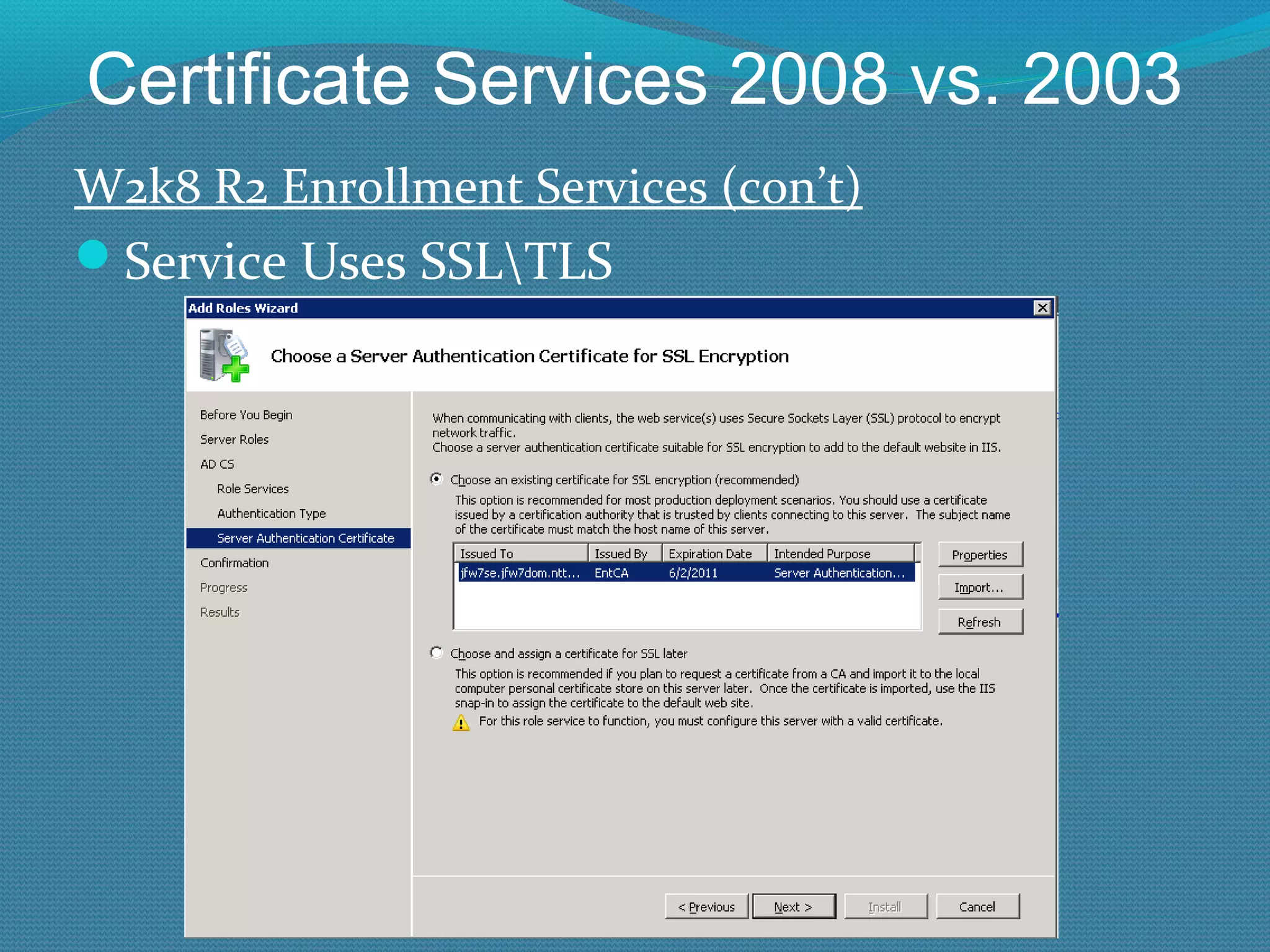
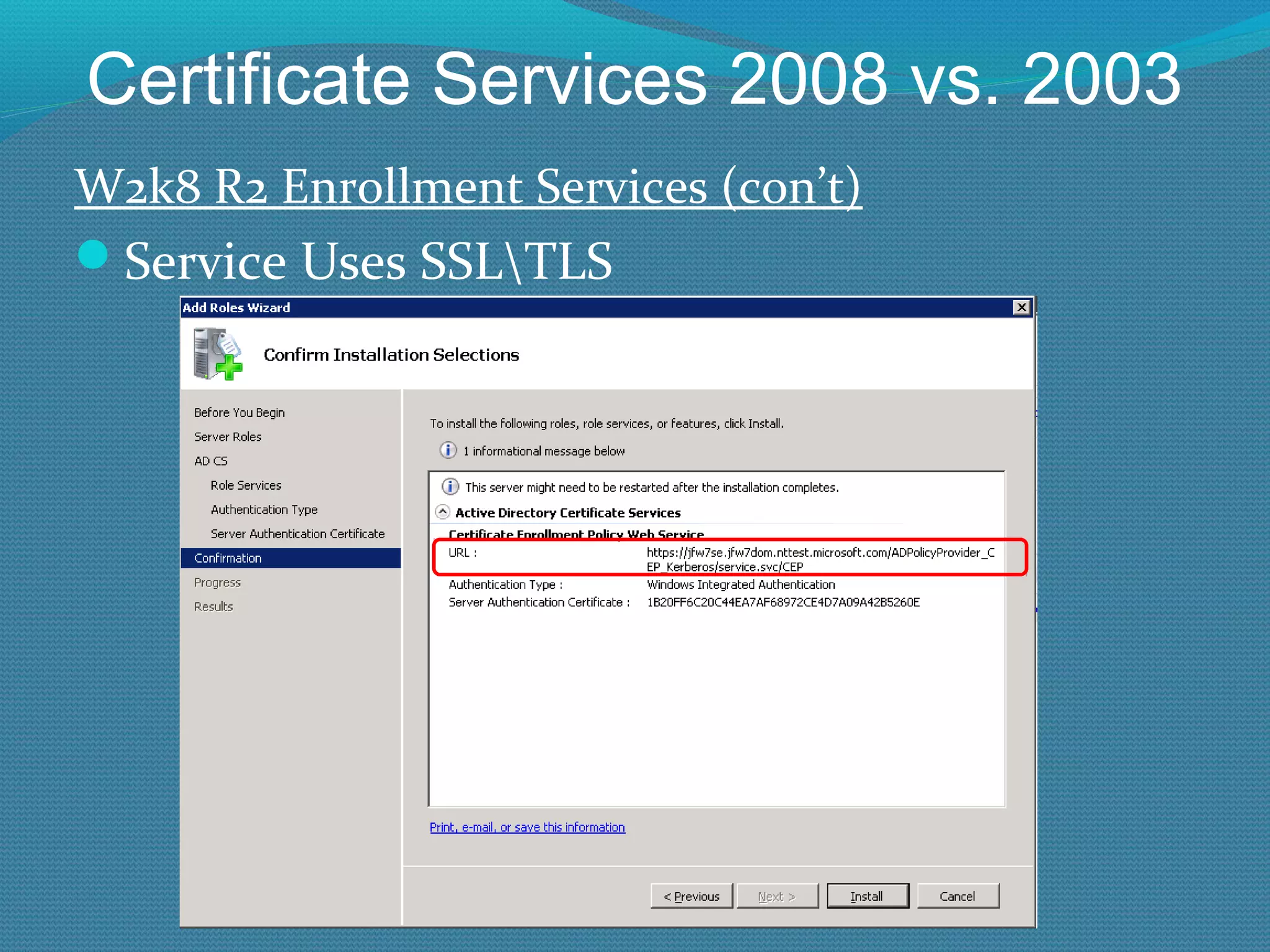
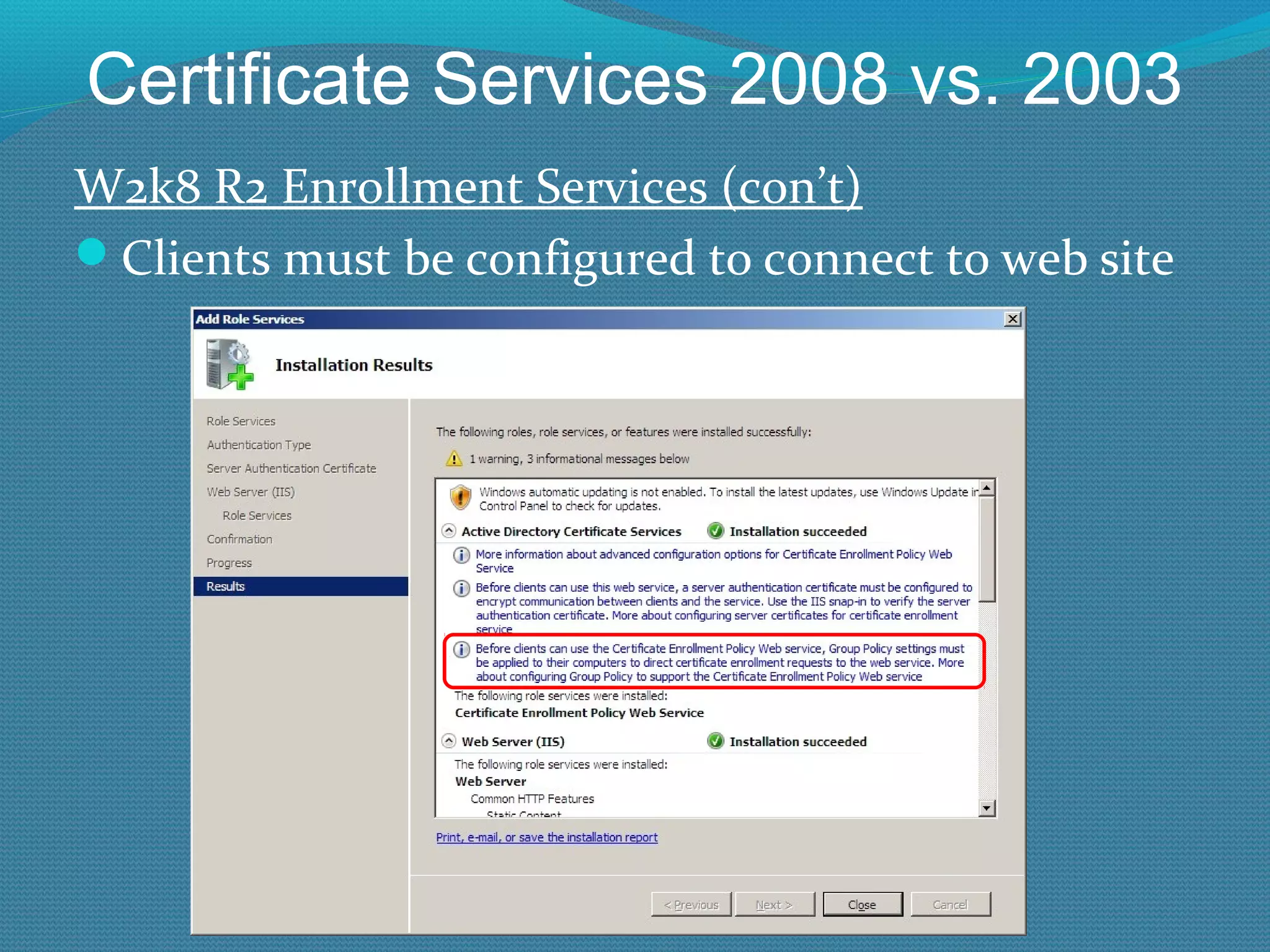
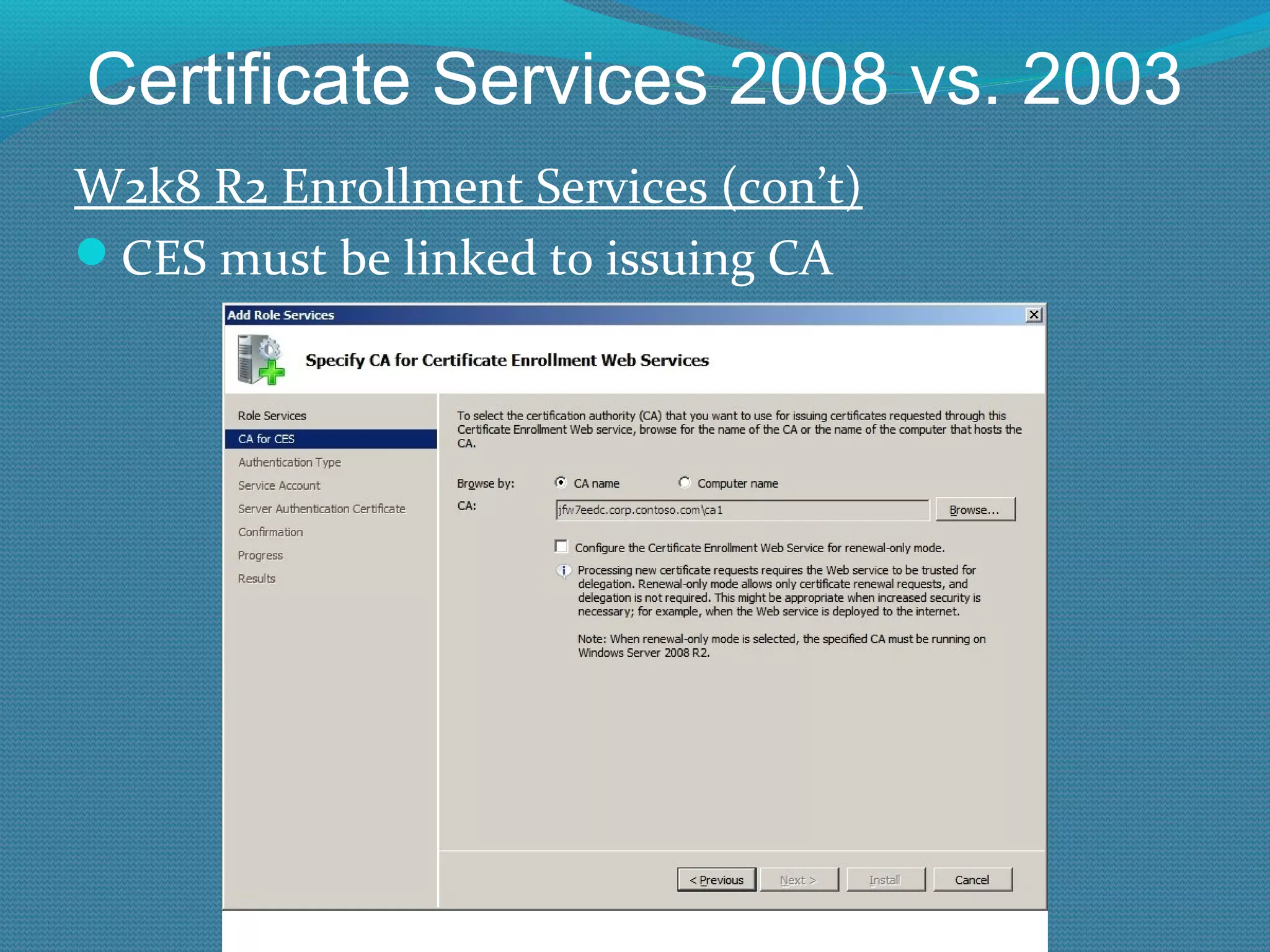
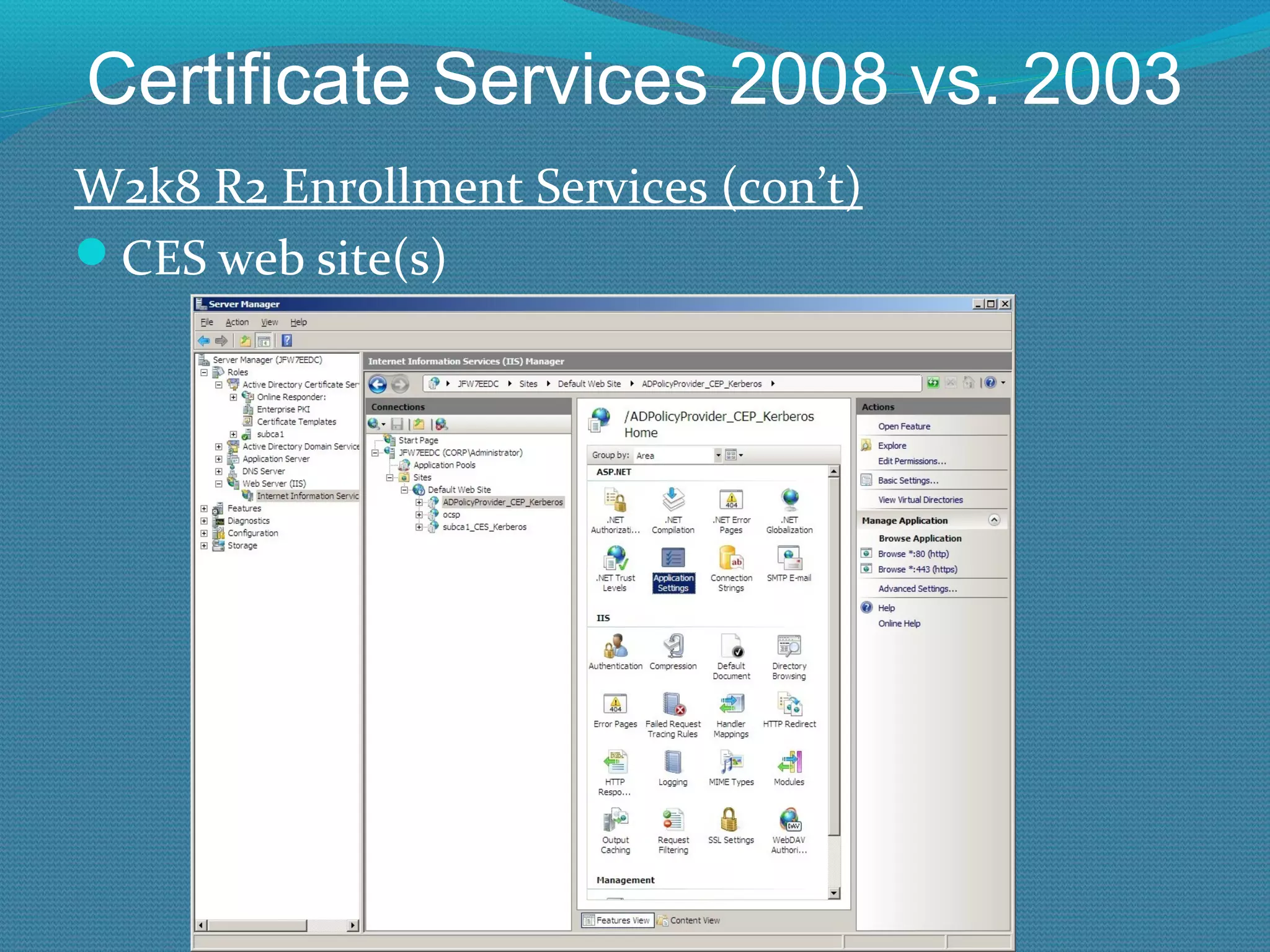
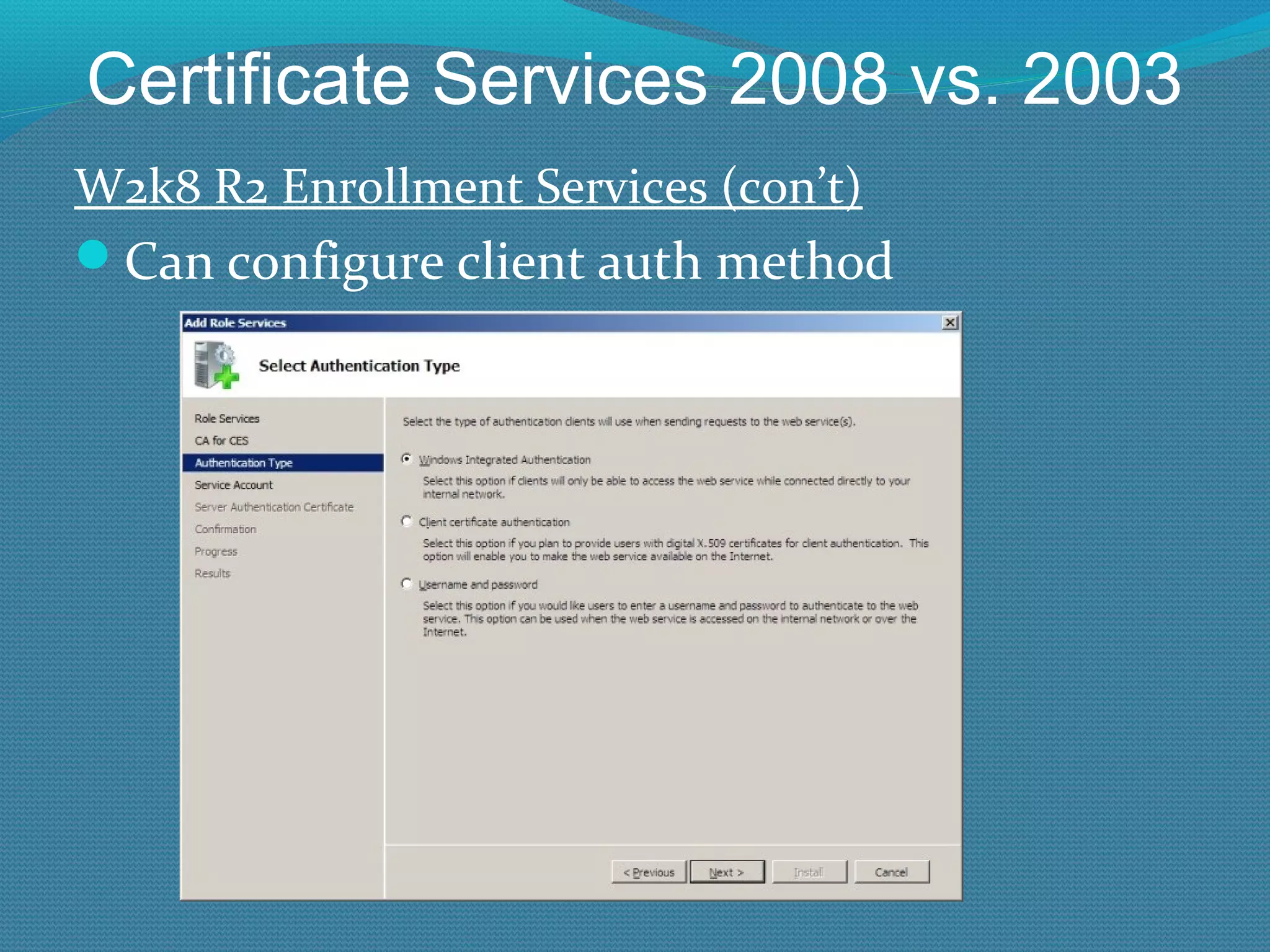
The document provides an overview of new features in Windows Server 2008 Certificate Services compared to Windows Server 2003 Certificate Services. Key changes include Certificate Services now being called Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS), support for newer cryptographic standards like Suite B, improved revocation checking with OCSP, and the ability to restrict key recovery agents and enrollment agents by template or security group. Overall, Certificate Services is largely the same between versions but Windows Server 2008 and ADCS have additional security improvements and features.







































![CAPolicy.inf File Example - Bare Minimum for Issuing CA [Version] Signature= "$Windows NT$" [Certsrv_Server] RenewalKeyLength=4096 RenewalValidityPeriod=Years RenewalValidityPeriodUnits=10 [CRLDistributionPoint] URL = “LDAP:///CN=%7,CN=CDP,CN=Public Key Services, CN=Services,%6,%10” URL = http://W2K8IssuingCA1.contoso.ad/PKI/IssuingCA1.crl URL = “http://www.contoso.com/PKI/IssuingCA1.crl” [AuthorityInformationAccess] URL = “LDAP:///CN=%7,CN=AIA,CN=Public Key Services, CN=Services,%6,%11” URL = “http://www.contoso.ad/PKI/ContosoCA.cer”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thenewrocketsciencestuffinmicrosoftpki-100518155734-phpapp02/75/The-new-rocket-science-stuff-in-microsoft-pki-66-2048.jpg)