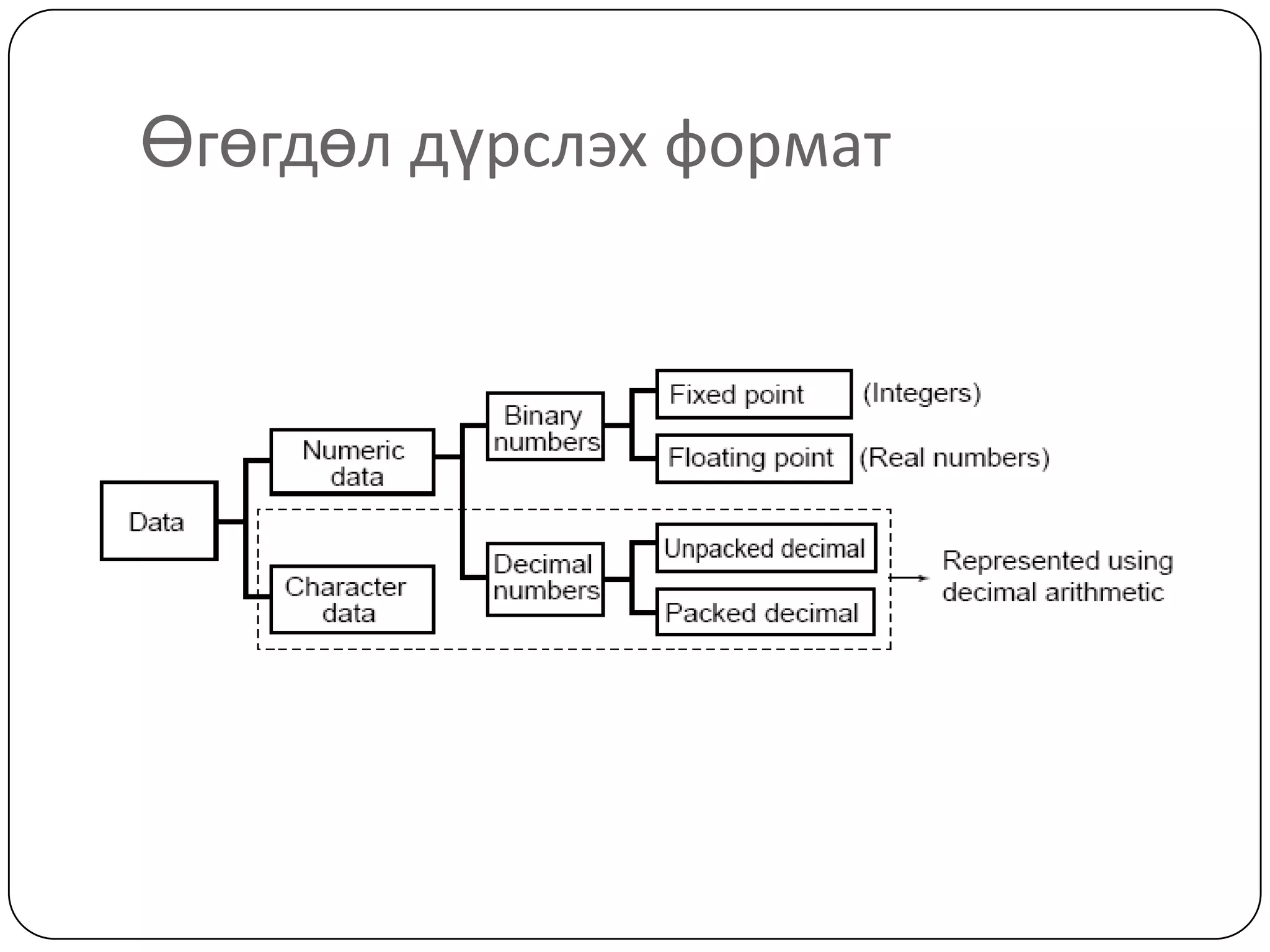
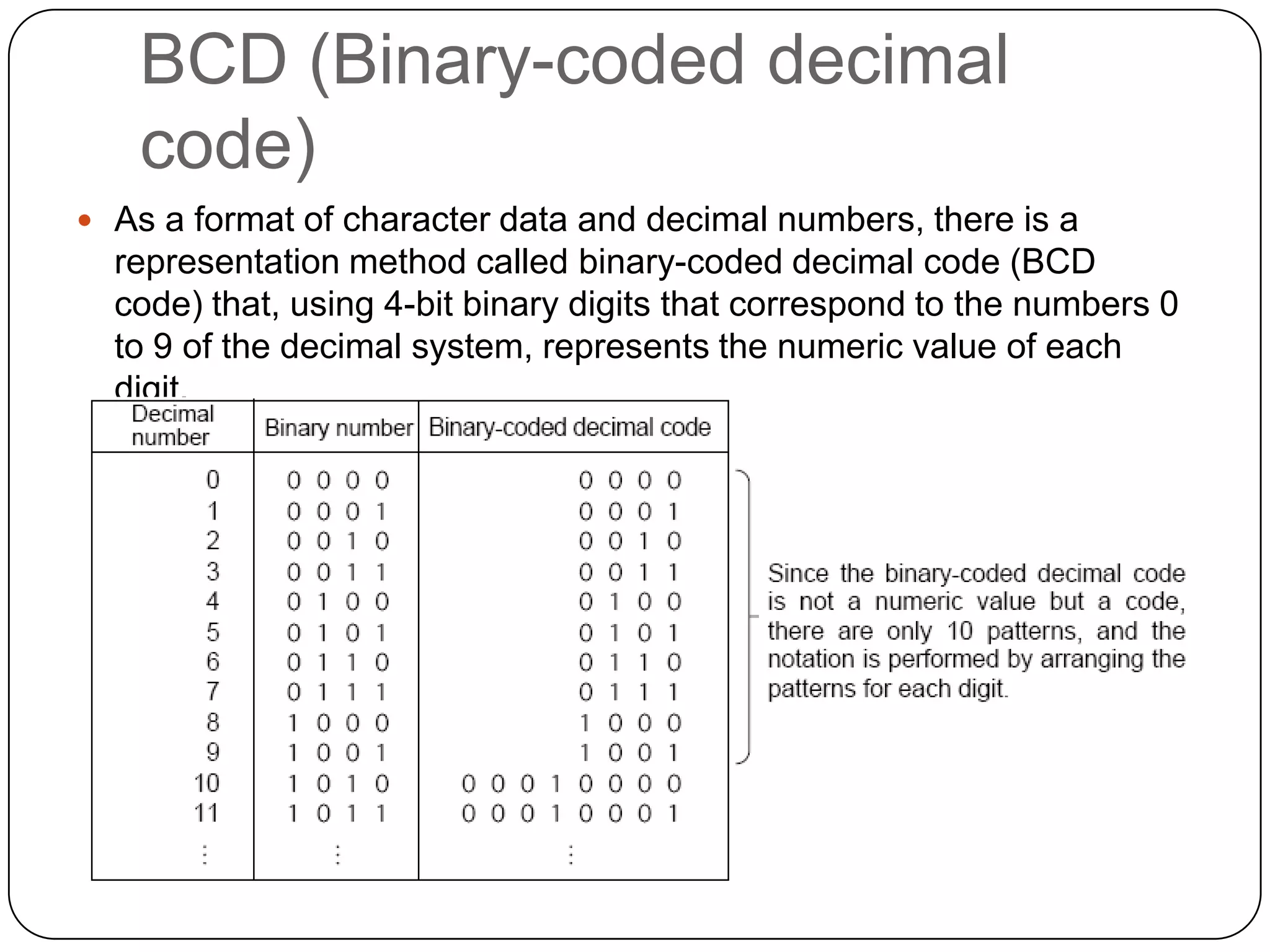
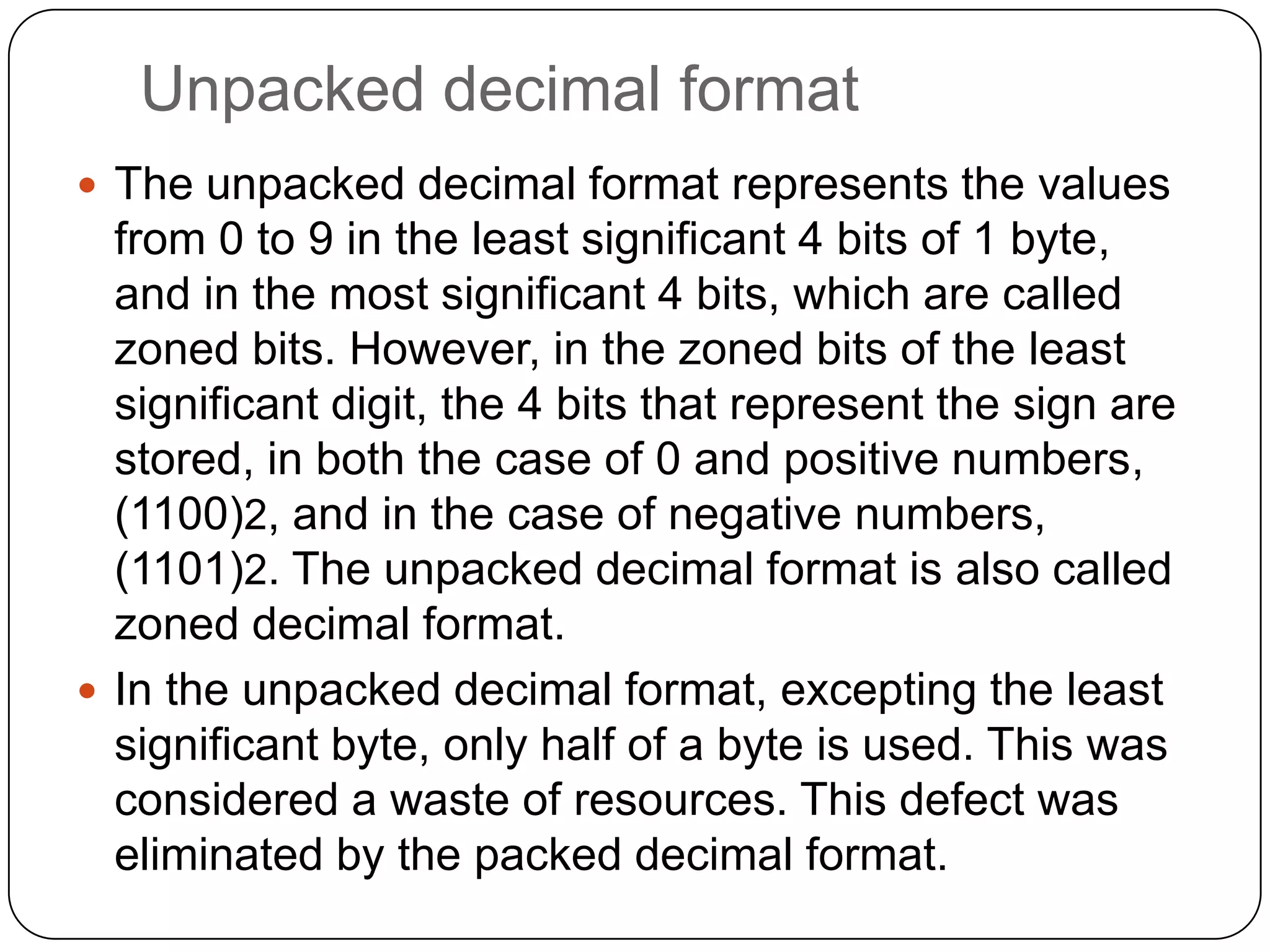
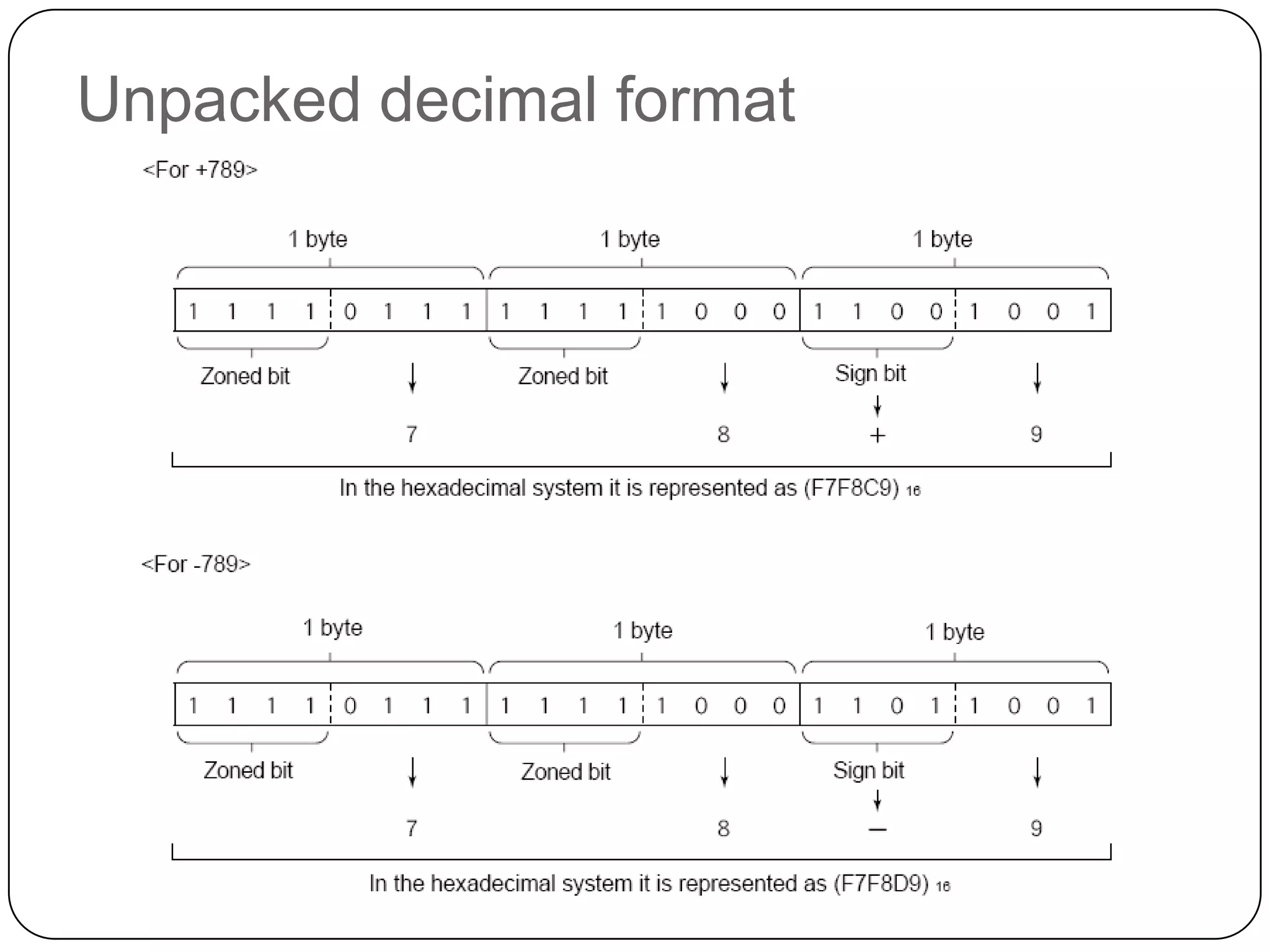
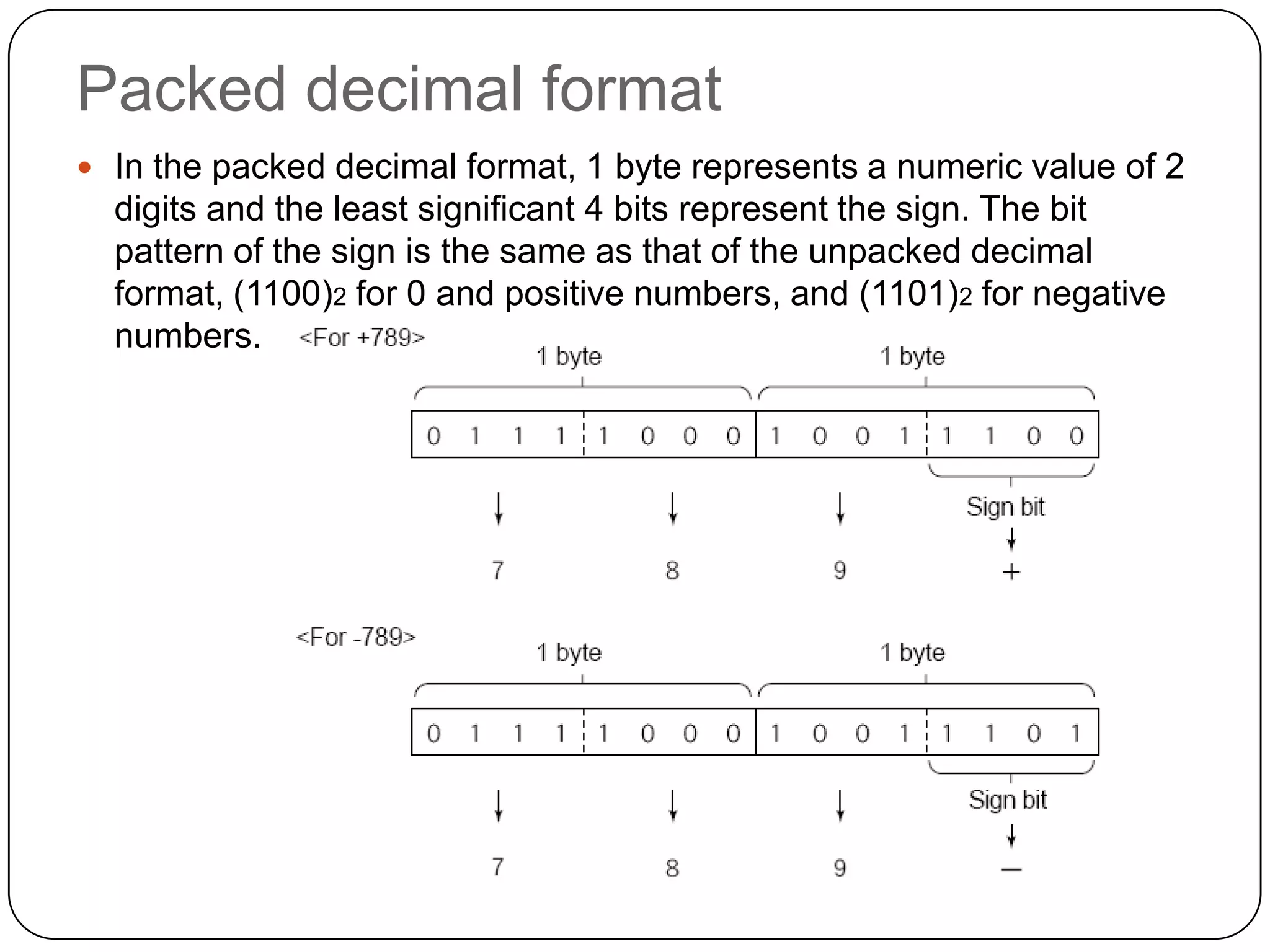
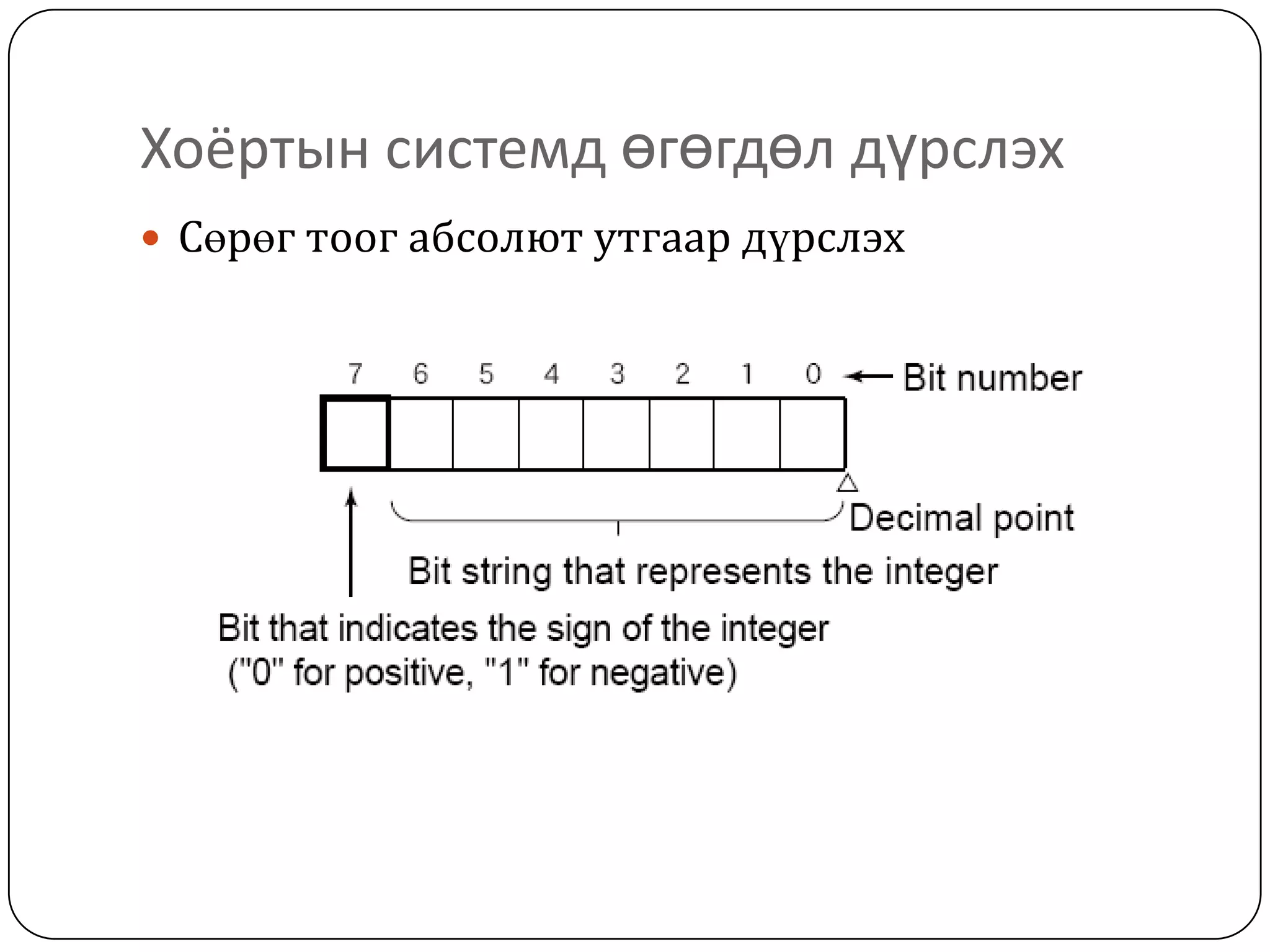
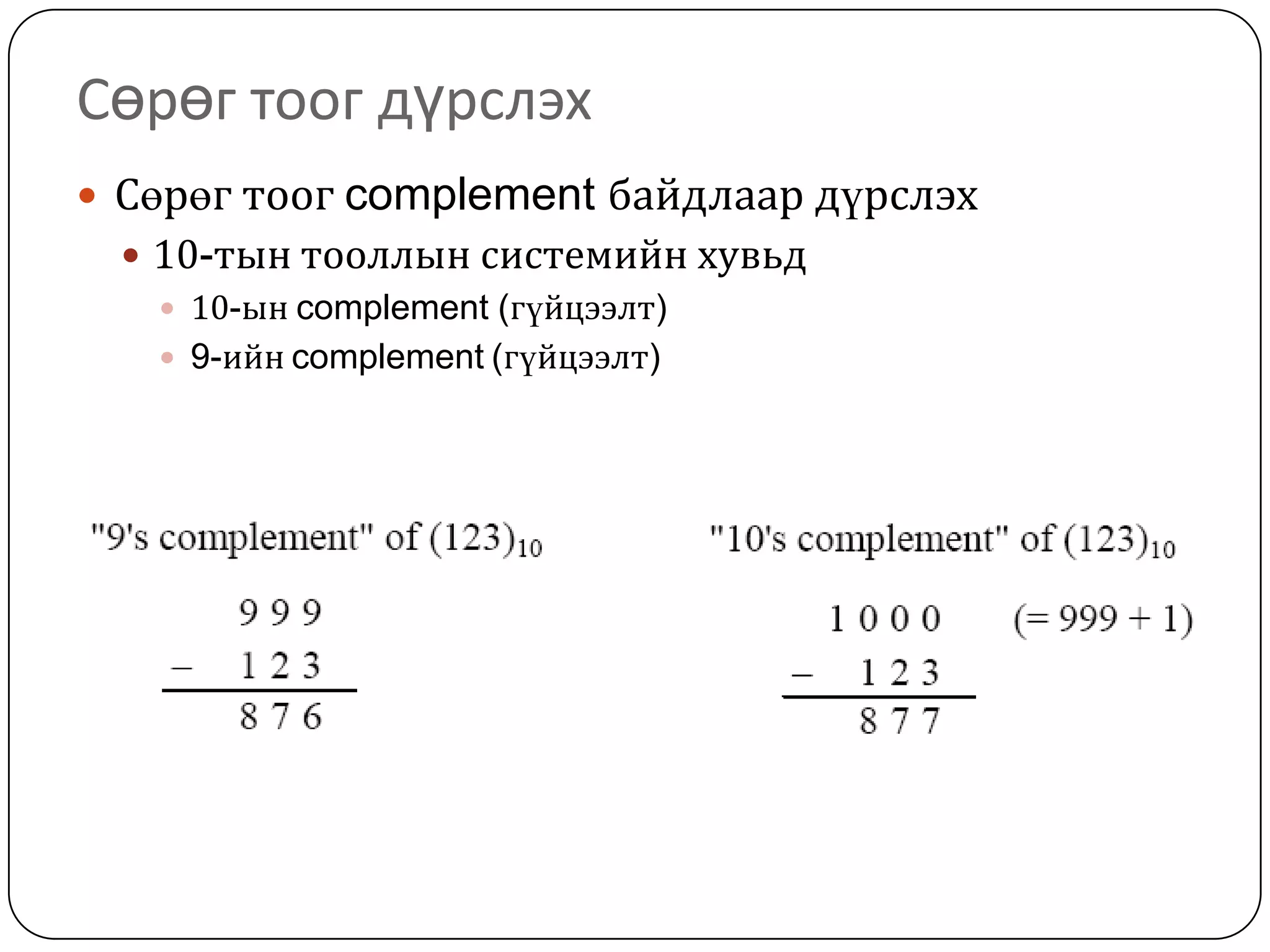
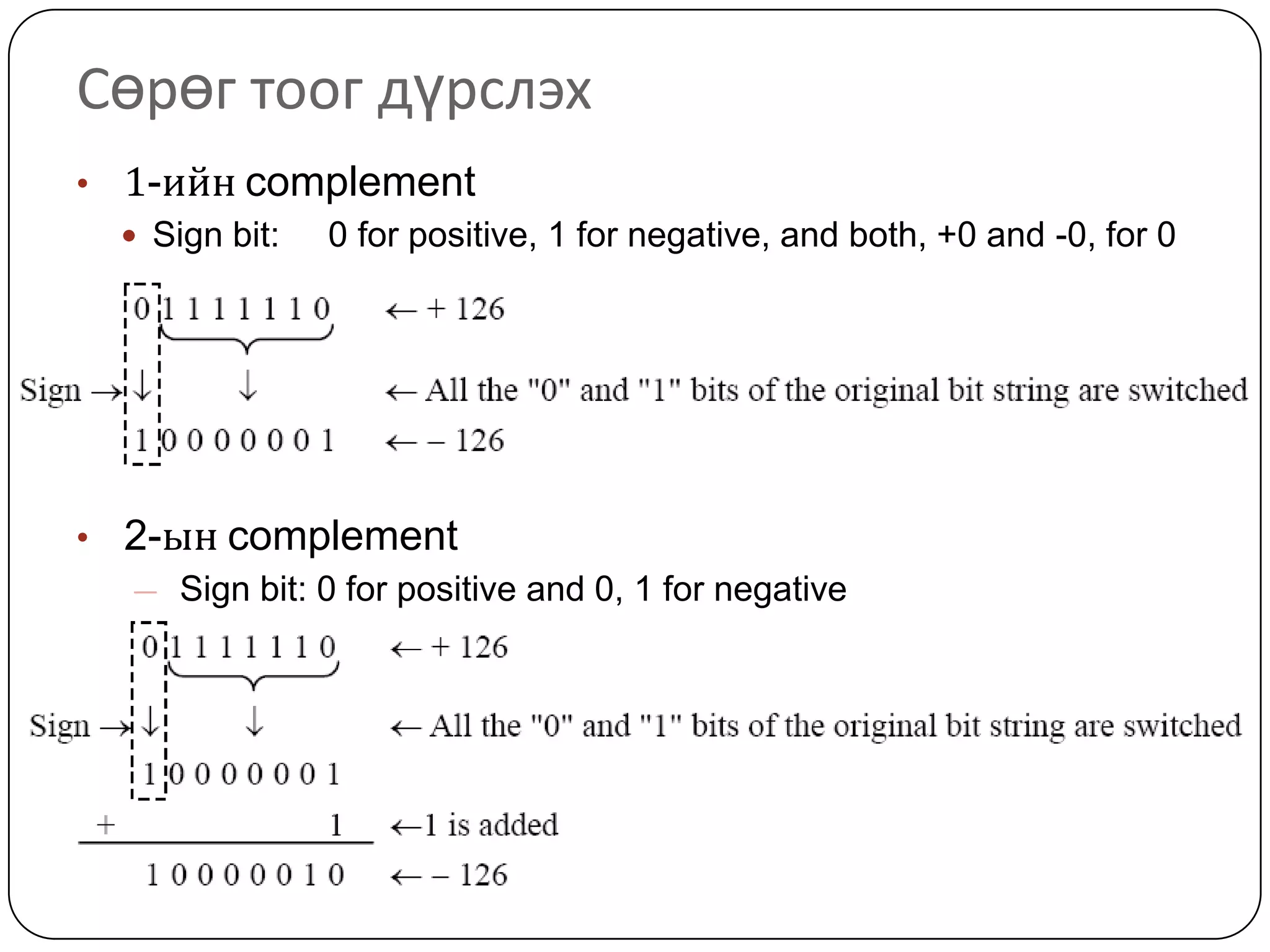
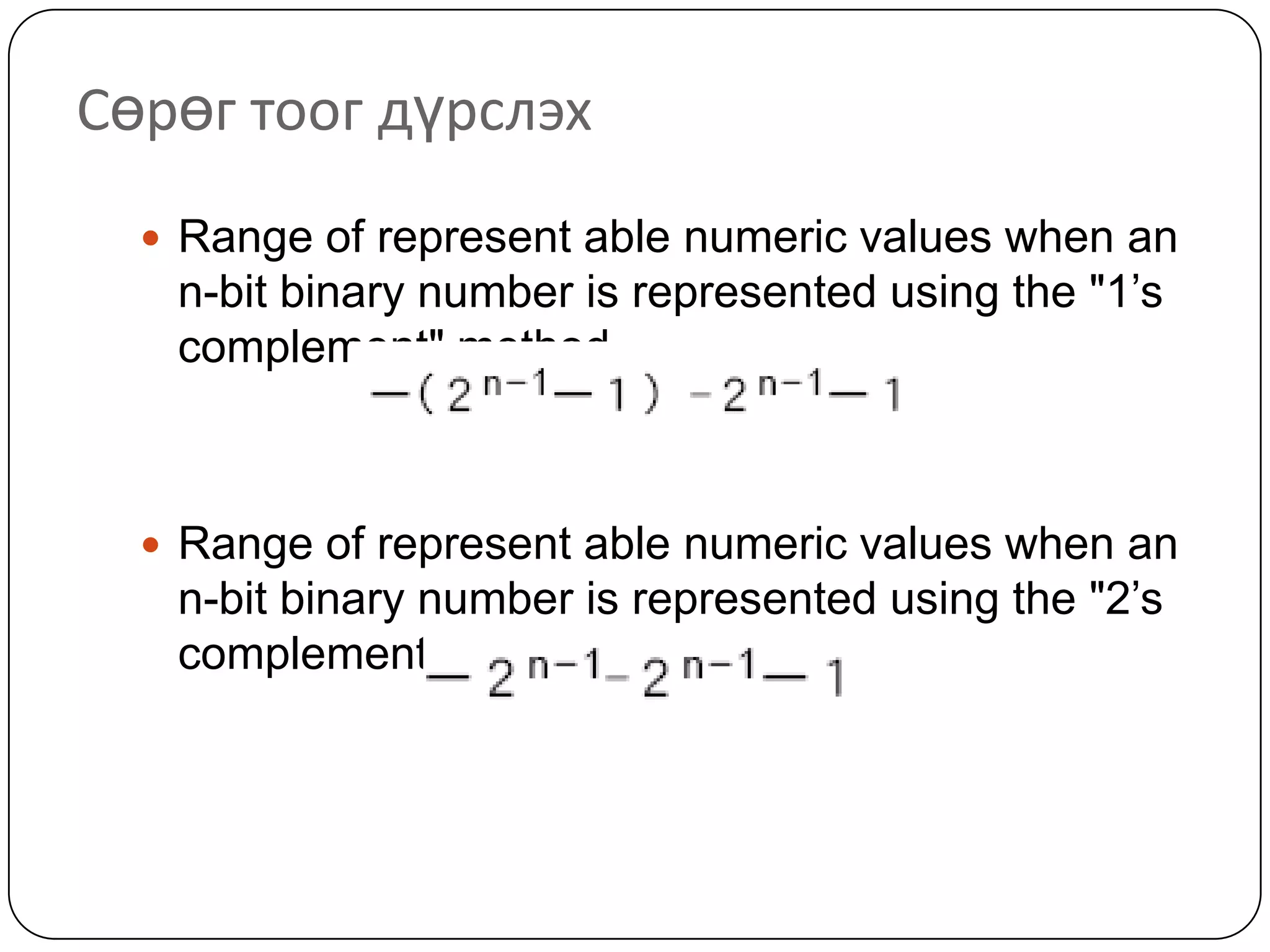
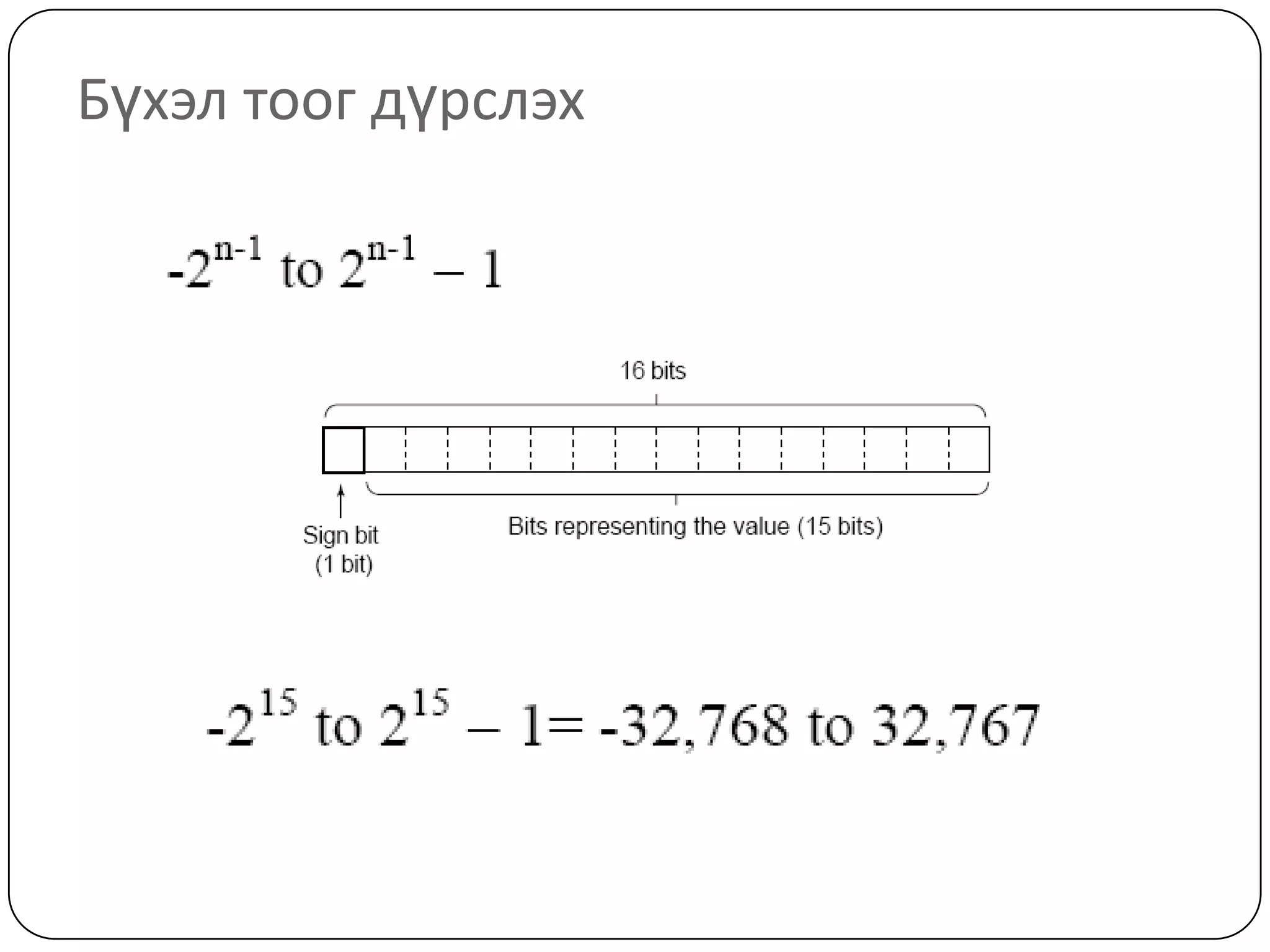
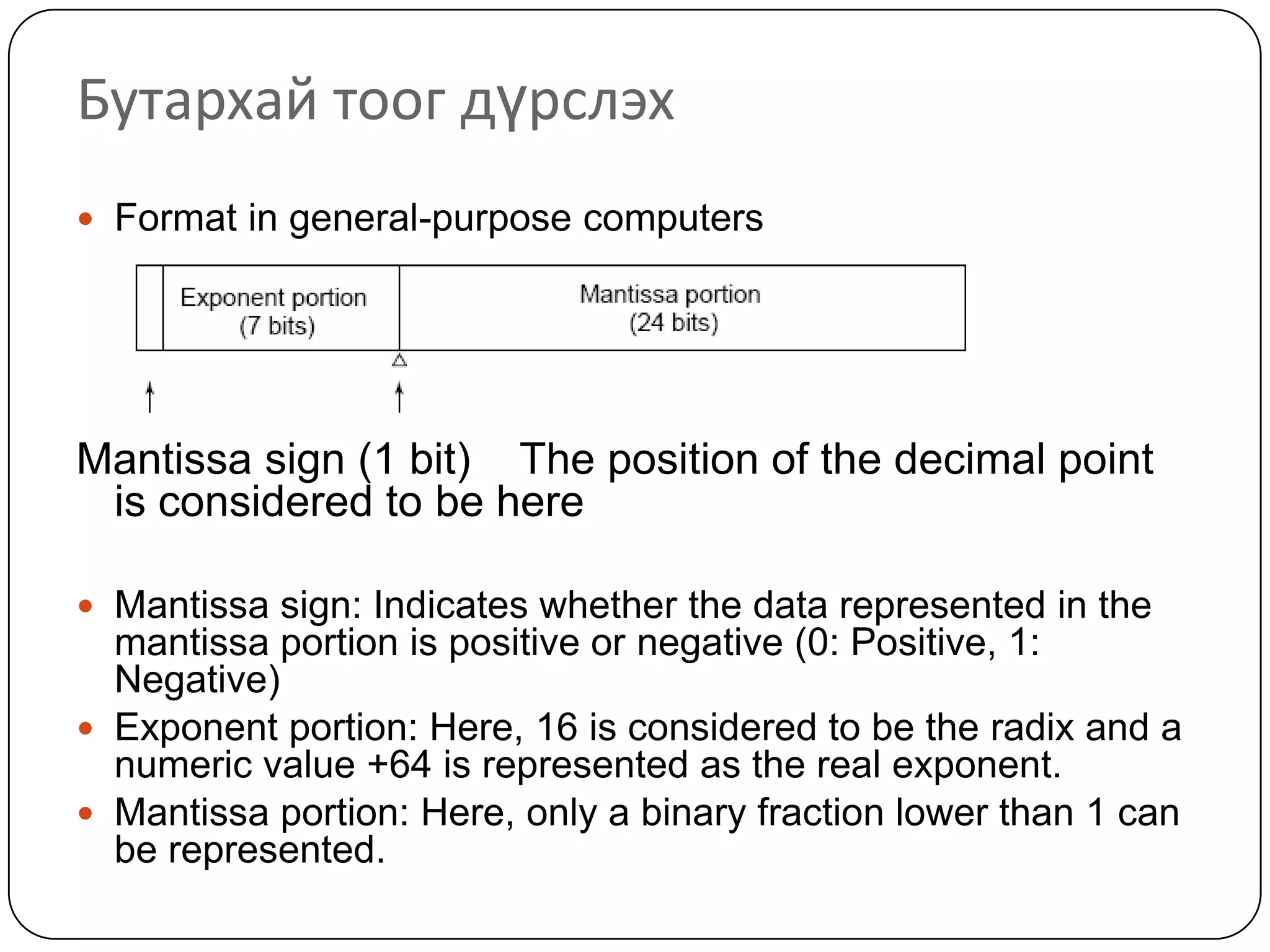
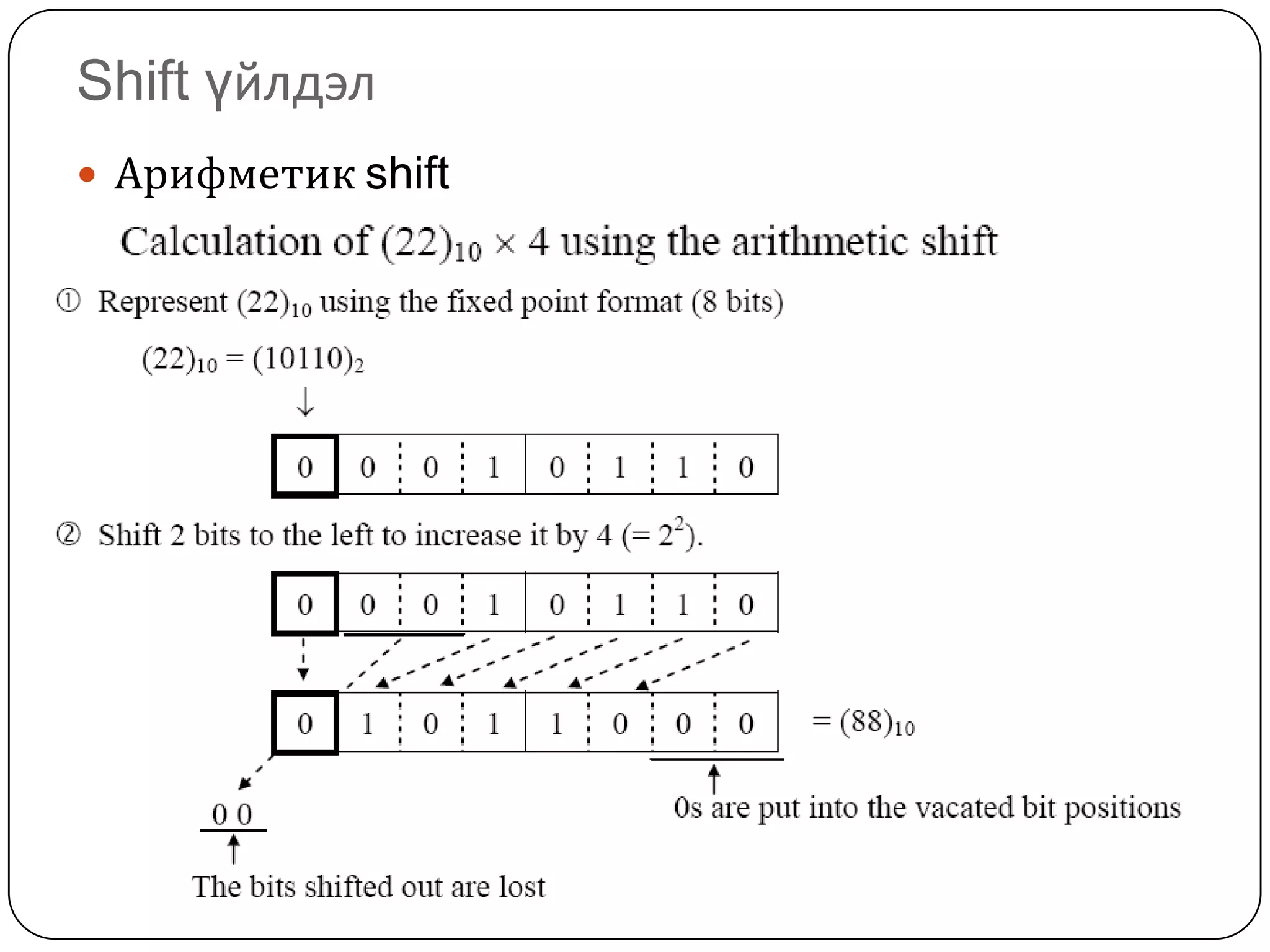
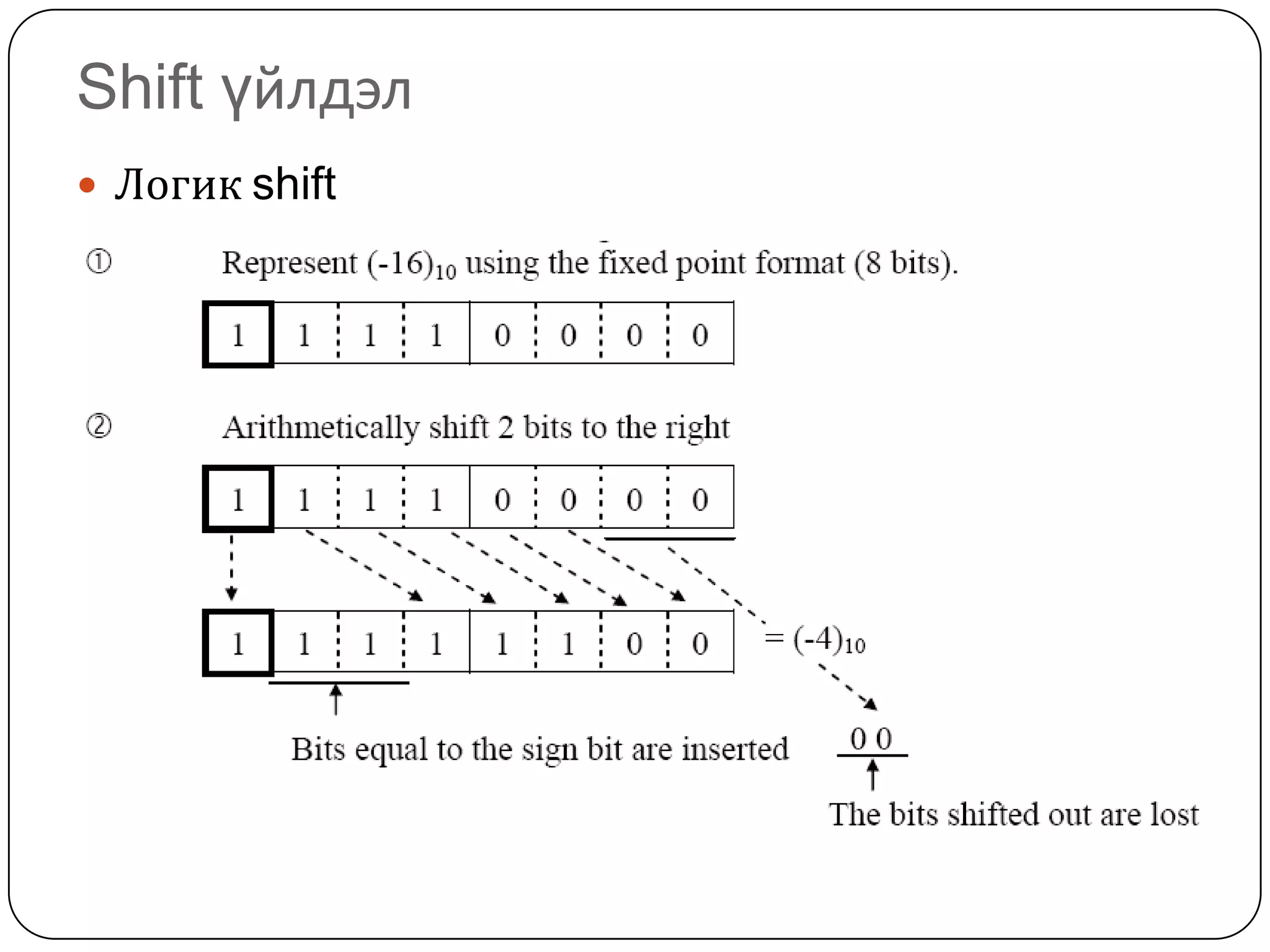
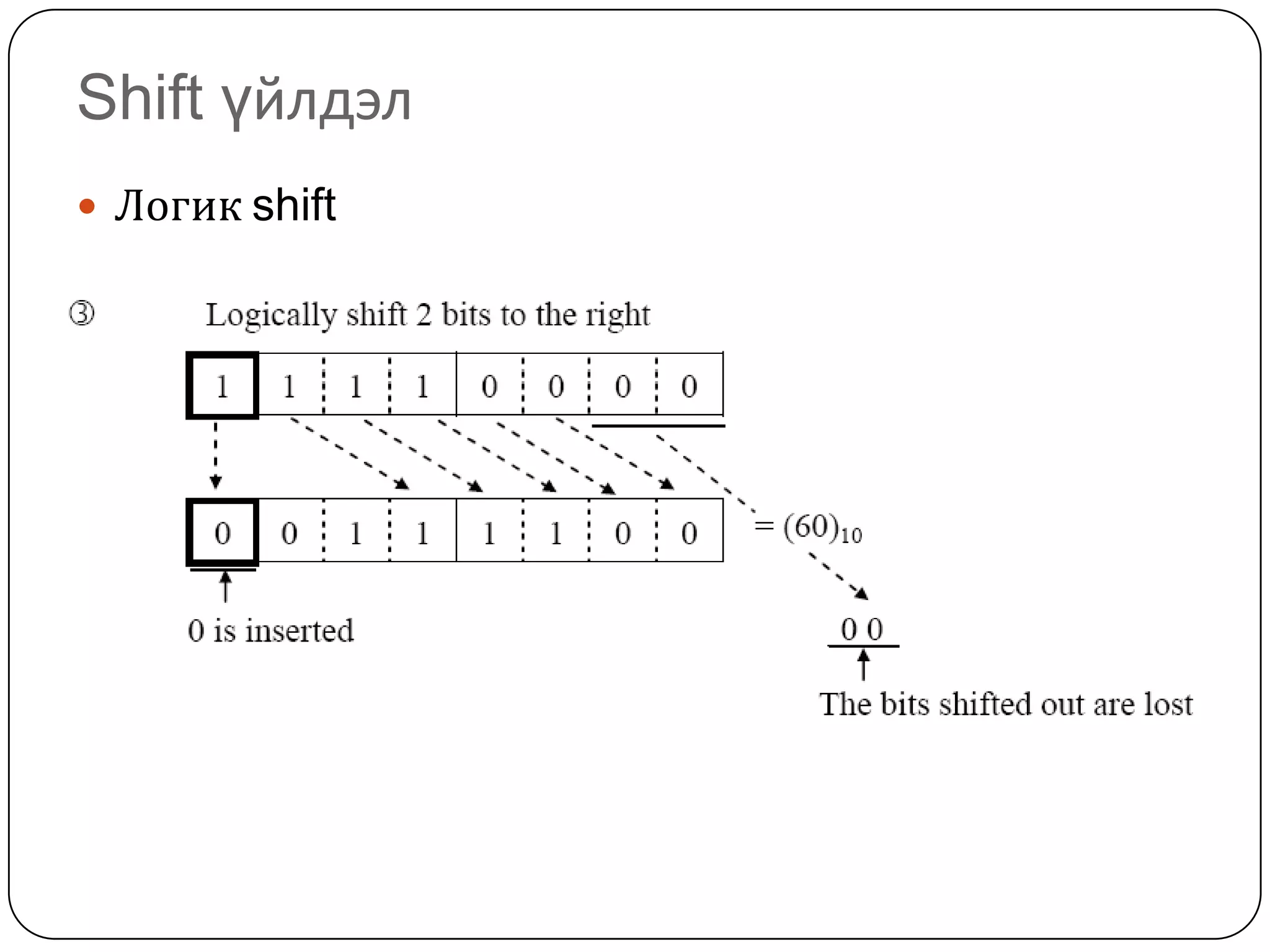
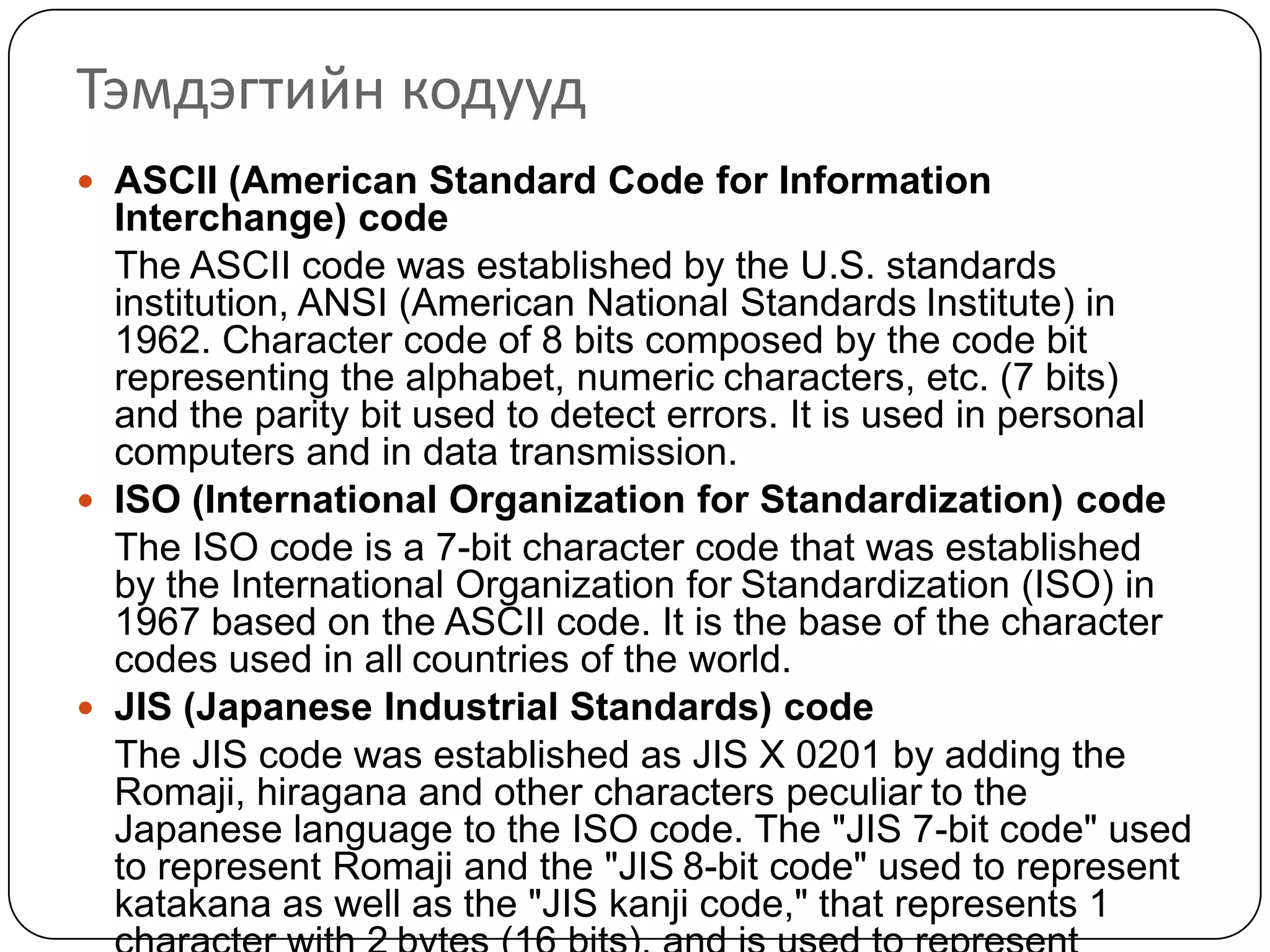
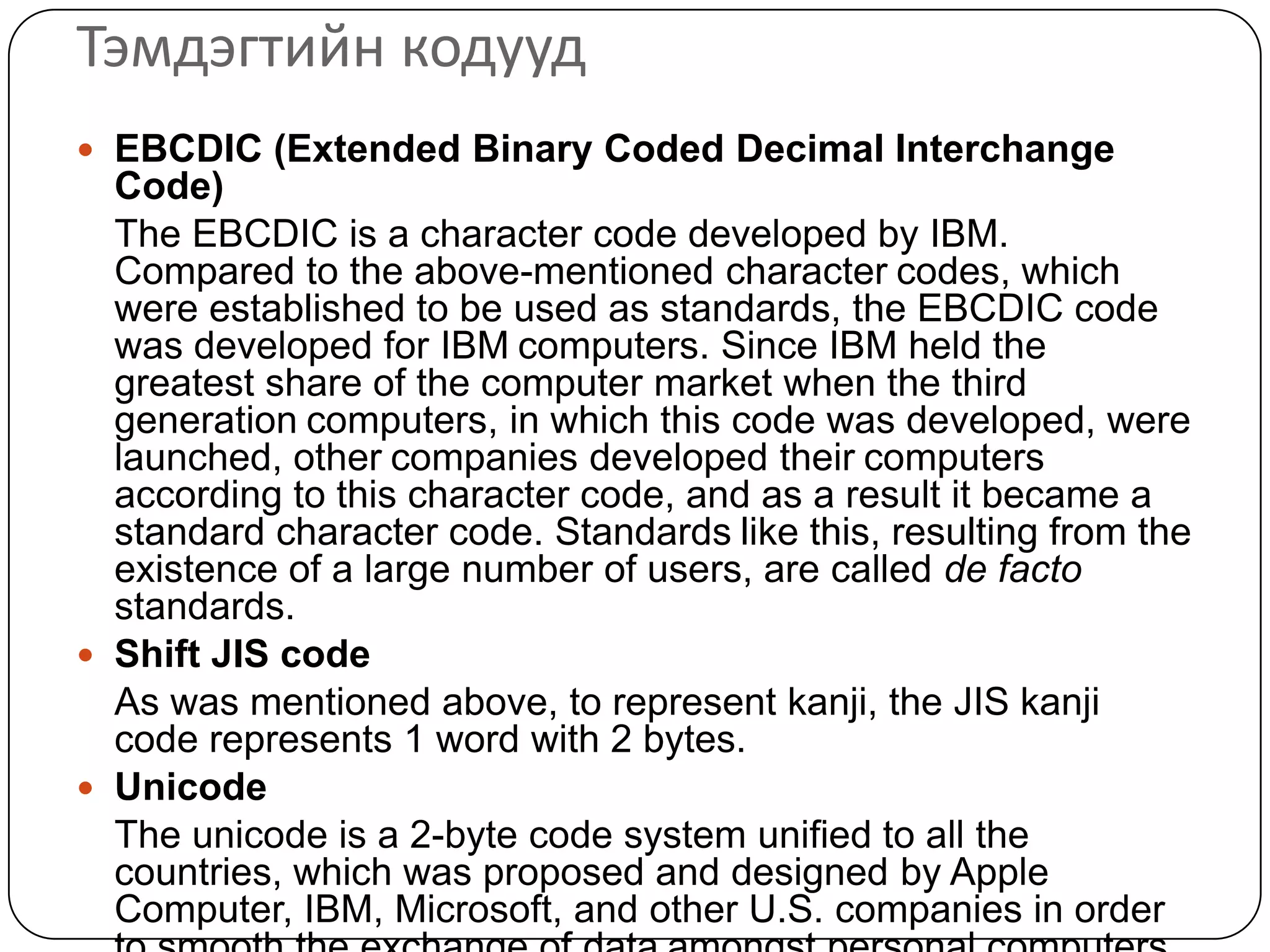
The document discusses various formats for representing numeric and character data in computers, including binary-coded decimal (BCD), unpacked decimal format, packed decimal format, signed number representation methods like 1's complement and 2's complement, floating point number representation, and character encoding standards like ASCII, ISO, JIS, EBCDIC, and Unicode. It also covers bit shifting operations and methods for representing audio and image data digitally.