This document discusses several key concepts in urban geography including:
1) The growth of urban areas and how cities, suburbs, and metropolitan areas are defined. Urbanization has led to both advantages and disadvantages for areas, societies, and cultures.
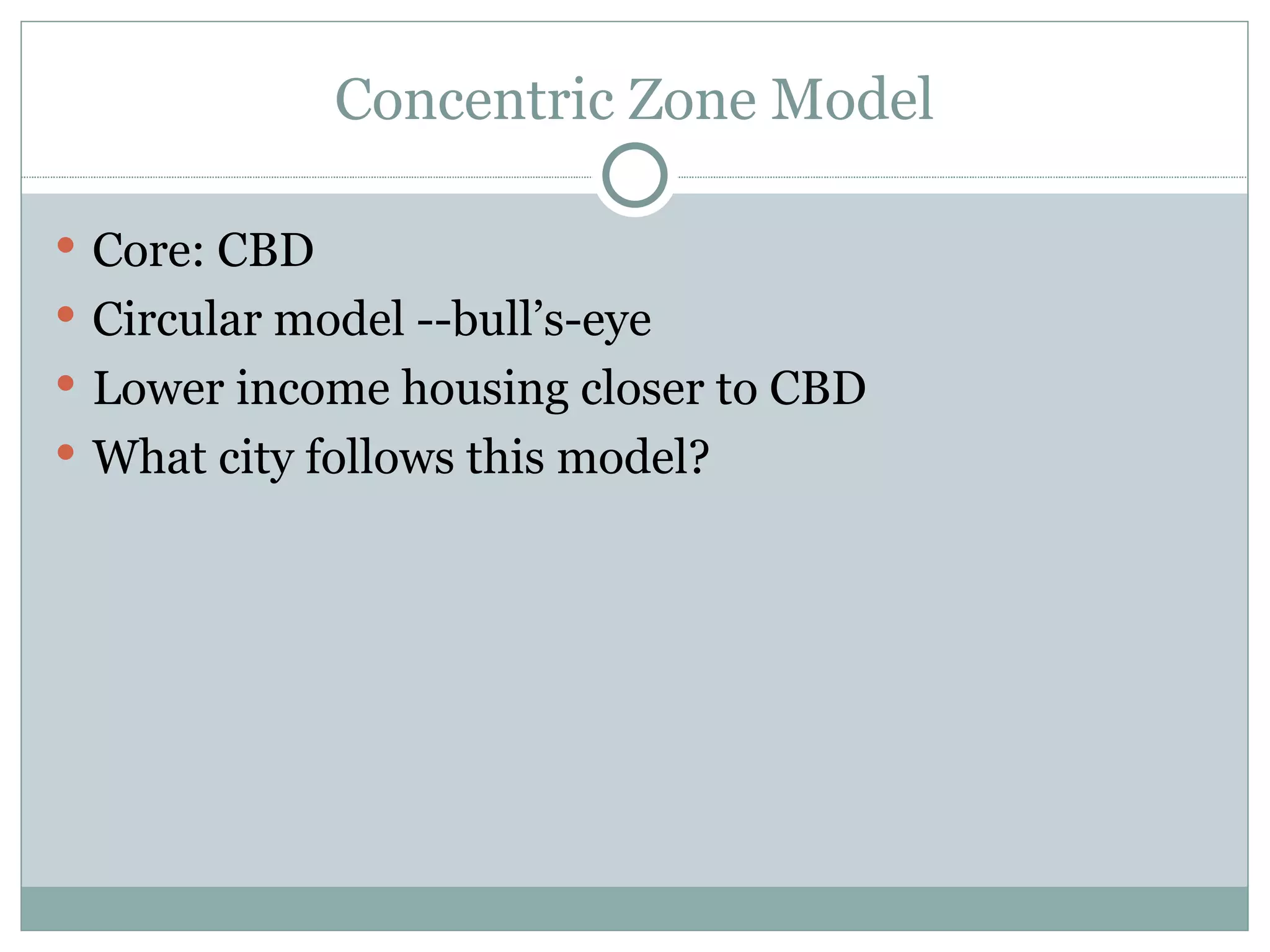
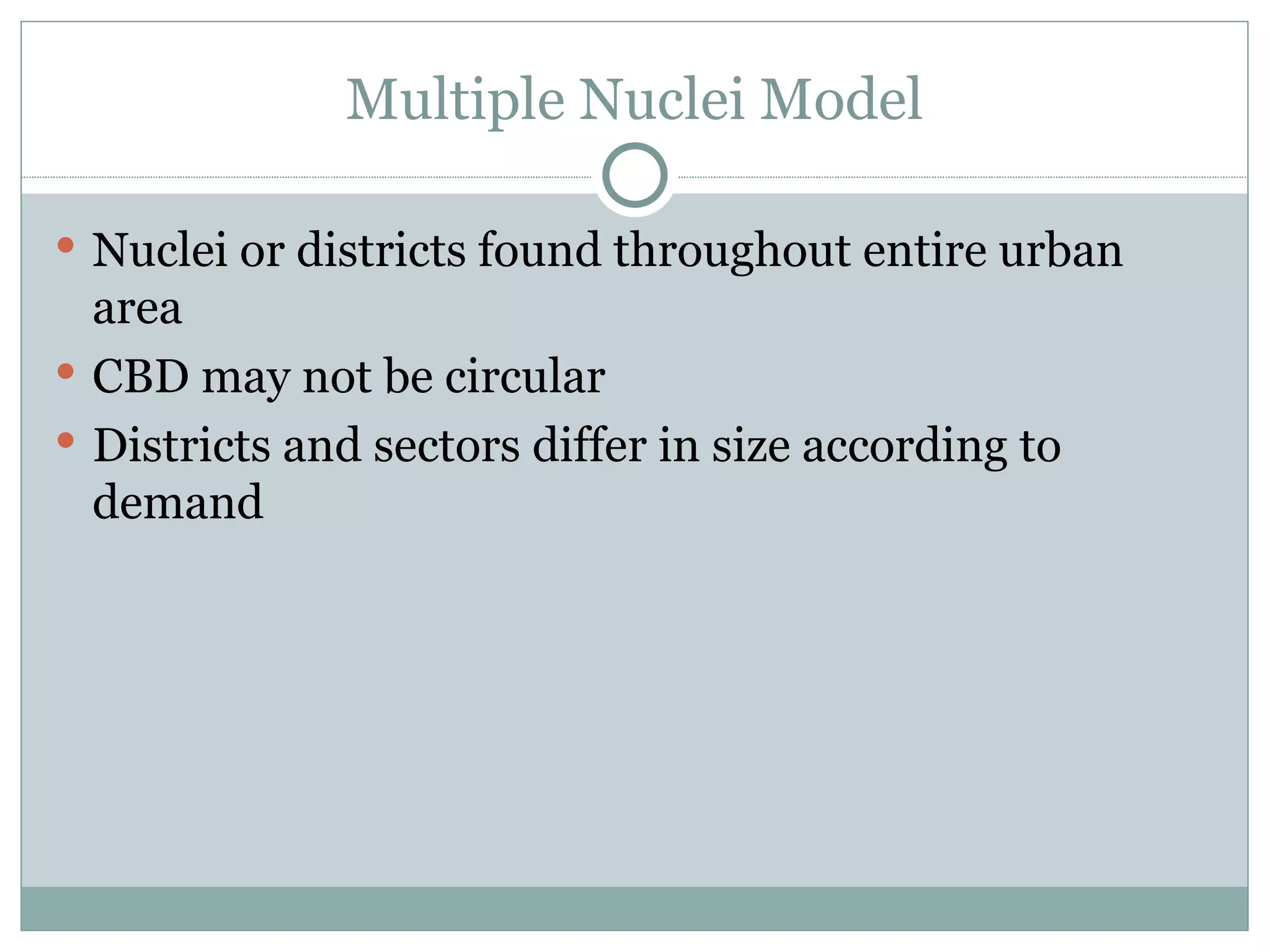
2) Models of urban land use including the concentric zone model, sector model, and multiple nuclei model which describe how different functions are arranged within a city.
3) The functions of cities which provide essential services to residents like retail, transportation, business, education, and more. Cities concentrate these functions making them efficient.